| Citation: |
Gong Zhang, Honglin Chen, Wei Liu, Hanbing Yang, Lijuan Zhang, Xiangwei Wang, Lei Shi, Sijing Hu, Mingzhao Wang, Zhuojian Fu. An RF frontend circuit design of a Compass and GPS dual-mode dual-channel image rejection radio receiver[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2013, 34(8): 085009. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/8/085009
****
G Zhang, H L Chen, W Liu, H B Yang, L J Zhang, X W Wang, L Shi, S J Hu, M Z Wang, Z J Fu. An RF frontend circuit design of a Compass and GPS dual-mode dual-channel image rejection radio receiver[J]. J. Semicond., 2013, 34(8): 085009. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/8/085009.
|
An RF frontend circuit design of a Compass and GPS dual-mode dual-channel image rejection radio receiver
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/8/085009
More Information
-
Abstract
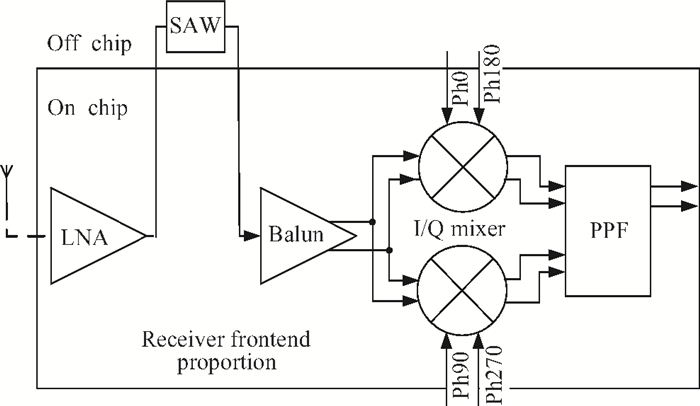
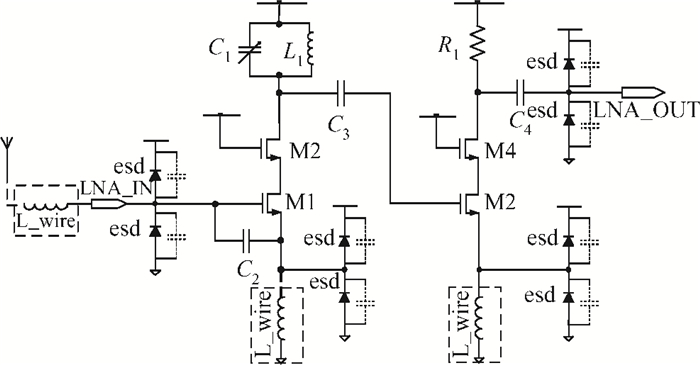
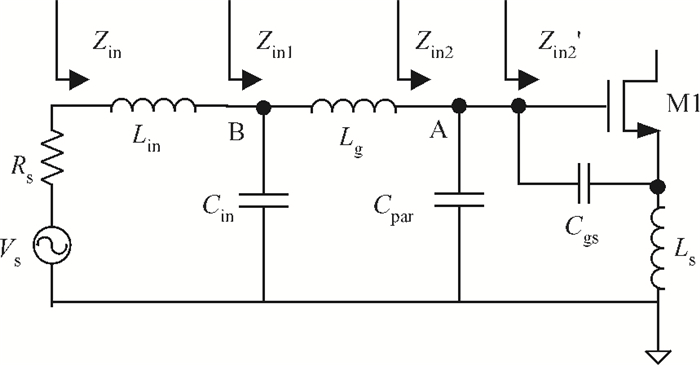
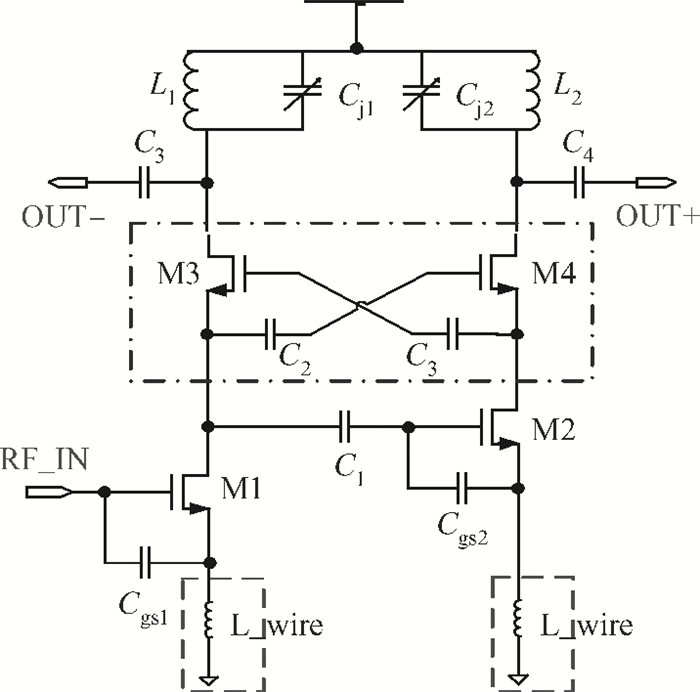
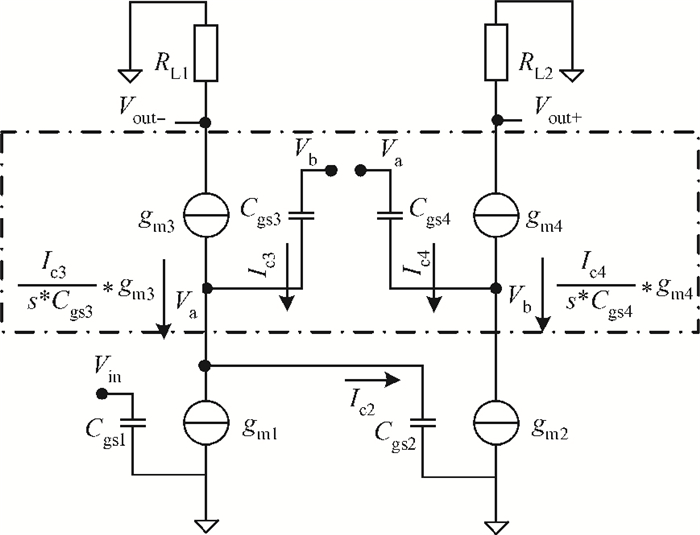
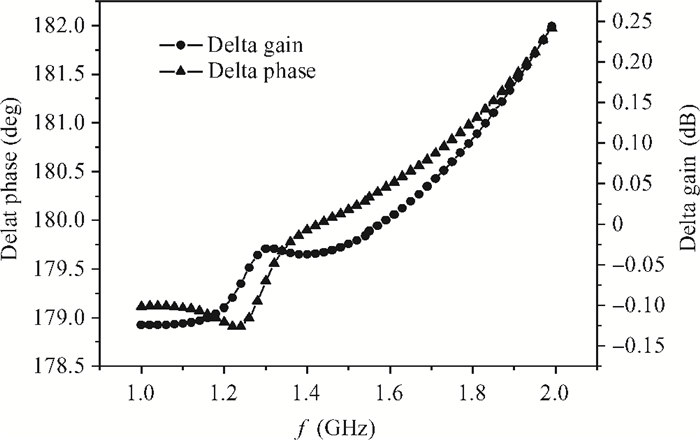
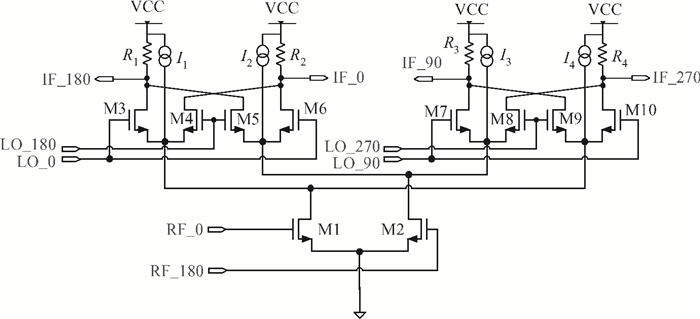
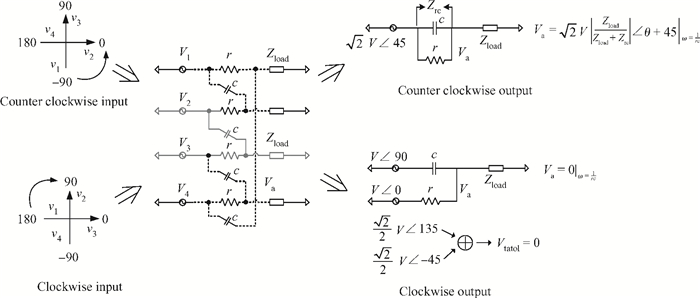
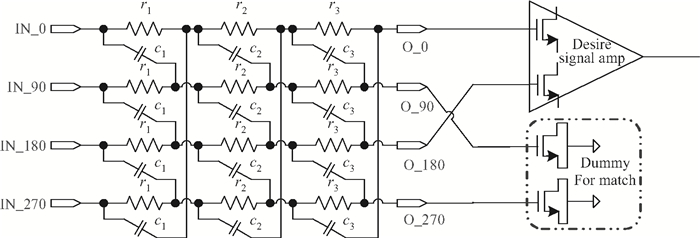
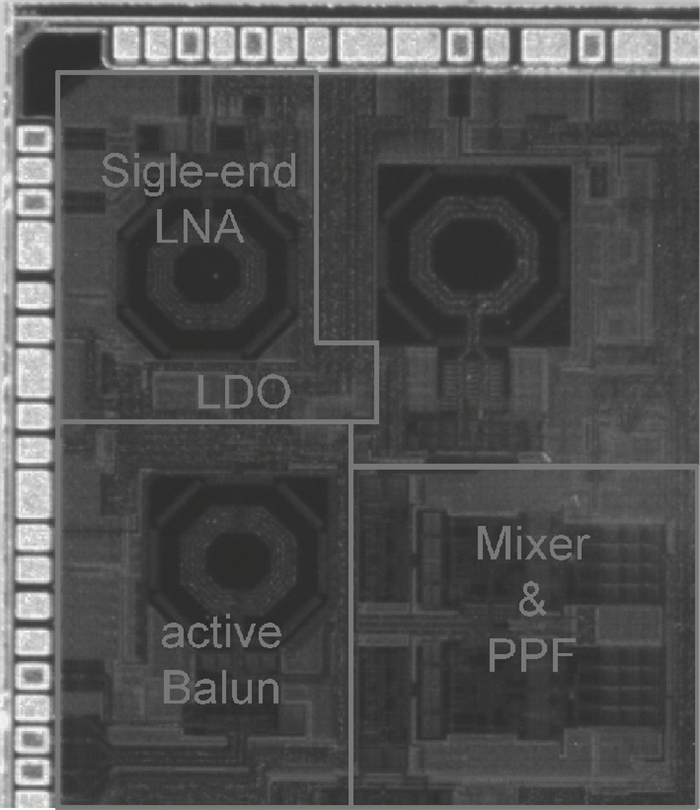
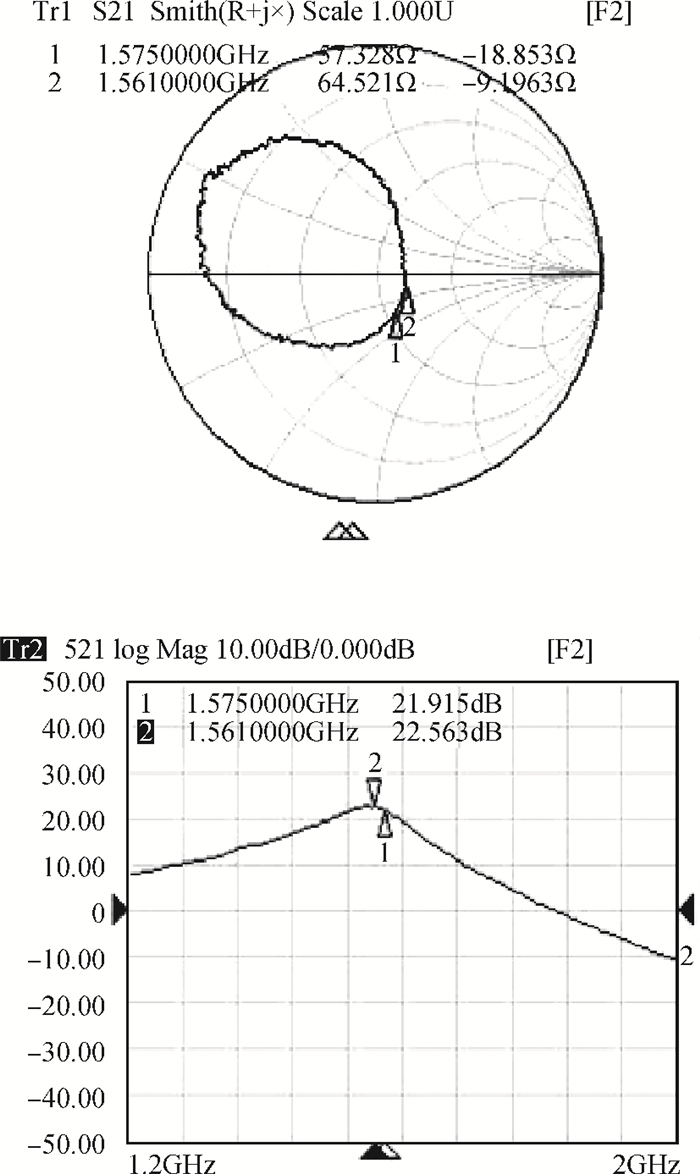
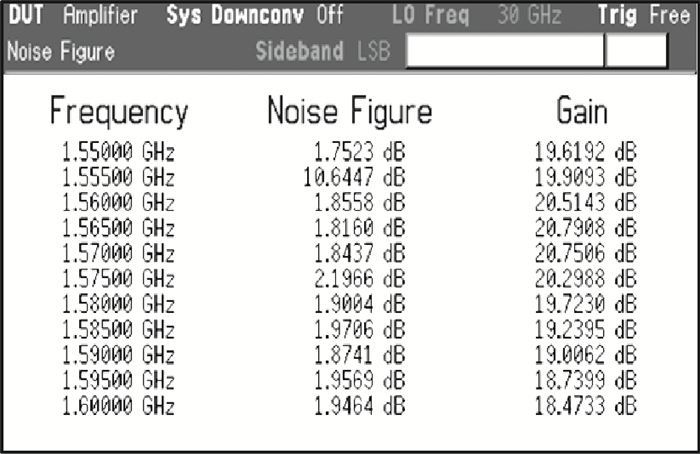
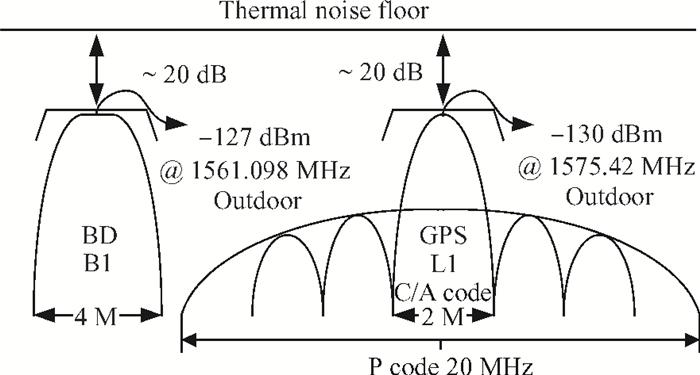
This paper introduces a fully integrated low power consumption radio receiver frontend circuit for a Compass (Beidou) and GPS dual mode dual channel system with 2.5 dB NF, 1.02 mm2 areas, and 8 mA of current in 0.18 μm TSMC CMOS process. Except for a few passive components for input matching, other components such as an off-chip low noise amplifier or a balun are not required. With a non-tunable passive image rejection filter, the receiver frontend can achieve around 60 dB gain and 34 dB image rejection.-
Keywords:
- compass (BeiDou),
- GPS,
- CMOS receiver frontend,
- active balun,
- image rejection
-
References
[1] Beidou Navigation Satellite System Signal in Space Interface Control Document Open Service Signal B1I (V1. 0). Dec 28, 2012: 4[2] Zhuang Haixiao, Ma Chenyan, Ye Tianchun. A mis-matching tolerant zero-IF mixer for GPS application. Research & Progress of SSE, 2010, 30(4):528(in Chinese)[3] Chi Baoyong, Wang Ziqiang. Analysis and design of CMOS RF integrated circuits. Beijing:Tsinghua University Press, 2006:159[4] Behbahani F. A fully integrated low-IF CMOS GPS radio with on-chip analog image rejection. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2002, 37(12):1721 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2002.804355[5] Leroux P, Steyaert M. A 1.3 dB NF CMOS LNA for GPS with 3 kV HBM ESD-protection. ESSCIRC, 2002:335[6] Rajashekharaiah M, Chen E. A new gain controllable on-chip active balun for 5 GHz direct conversion receiver. IEEE ISCAS, 2005:5115 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/1465785/[7] Lerstaveesin S. A complex image rejection circuit with sign detection only. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2006, 41(12):2693 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2006.884183[8] N Qi, Xu Y, Chi B, et al. A dual-channel GPS/compass/Galileo/GLONASS reconfigurable GNSS receiver in 65 nm CMOS. IEEE 33rd Custom Integrated Circuits Conference, 2011 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6239622/[9] Ko J, Kim J, Cho S, et al. A 19-mW 2.6-mm2 L1/L2 dual-band CMOS GPS receiver. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2005, 40(7):1414 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2005.847326[10] Jo J, Lee J, Park D J, et al. An L1-band dual-mode RF receiver for GPS and Galileo in 0.18-μm CMOS. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech, 2009, 57(4):919 doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2009.2014432[11] Yanduru N K, Low K M. A highly integrated GPS front-end for cellular applications in 90 nm CMOS. IEEE Dallas Circuits and Systems Workshop:SOC Applications, Integration, and Software, 2008:1[12] Giuseppe G, Mattos P G, Losi M, et al. A 56-mW 23-mm2 single-chip 180-nm CMOS GPS receiver with 27.2-mW 4.1-mm2 radio. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2006, 41(3):540 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2005.864136 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: