| Citation: |
Shubin Liu, Zhangming Zhu, Yintang Yang, Lianxi Liu. A high speed low power low offset dynamic comparator used in SHA-less pipelined ADC[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2014, 35(5): 055008. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/5/055008
****
S B Liu, Z M Zhu, Y T Yang, L X Liu. A high speed low power low offset dynamic comparator used in SHA-less pipelined ADC[J]. J. Semicond., 2014, 35(5): 055008. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/5/055008.
|
A high speed low power low offset dynamic comparator used in SHA-less pipelined ADC
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/5/055008
More Information
-
Abstract
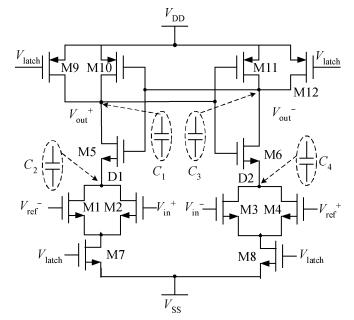
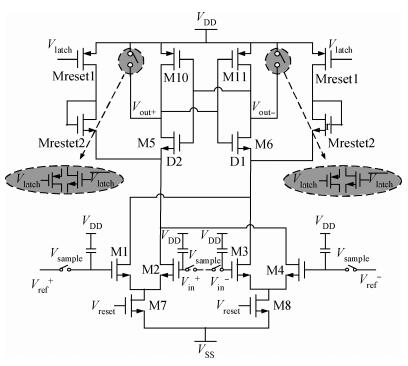
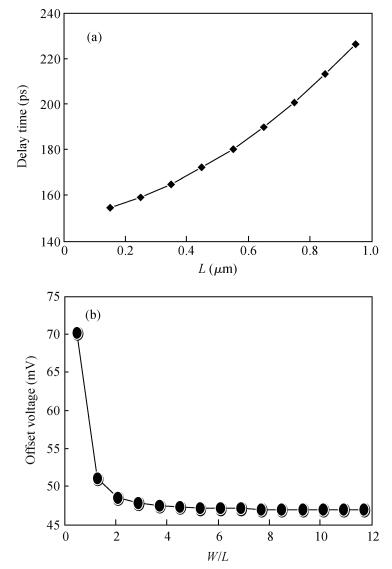
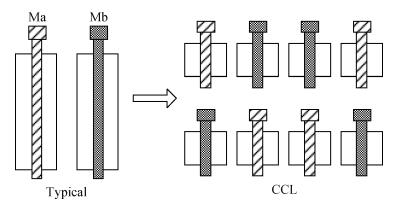
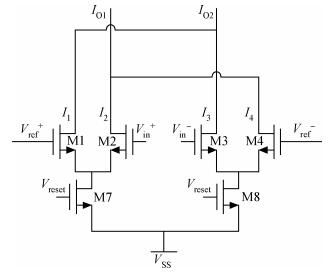
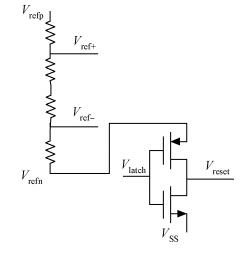
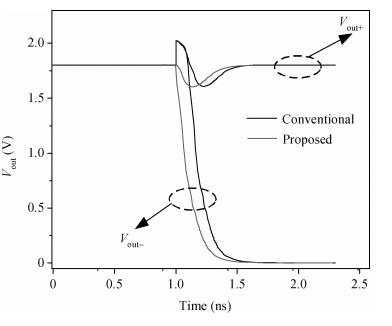
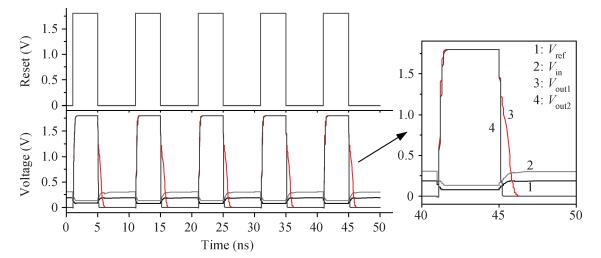
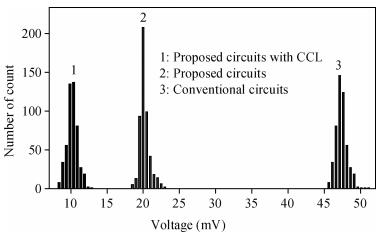
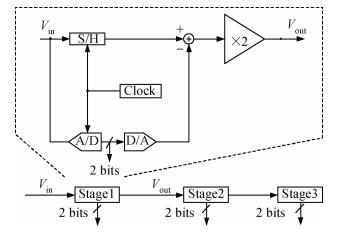
A novel fully differential high speed high resolution low offset CMOS dynamic comparator has been implemented in the SMIC 0.18 μm process used for a sample-and-hold amplifier (SHA)-less pipelined analog-to-digital converters (ADC). Based on the analysis and optimization between delay time and offset, an enhanced reset architecture with transmission gate was introduced to speed up the comparison and reset procedure. Four inputs with two cross coupled differential pairs, reconstituted bias circuit for tail current transistor and common centroid layouts make the comparator more robust against mismatch and process variations. The simulation results demonstrate that the proposed design achieves 1 mV sensitivity at 2.2 GHz sampling rate with a power consumption of 510 μW, while the mean offset voltage is equal to 10.244 mV.-
Keywords:
- SHA-less ADC,
- dynamic comparator,
- high speed,
- low offset,
- low power,
- transmission gate
-
References
[1] Li Z. A high-speed comparator for a 12-bit 100 MS/s pipelined ADC. International Conference on Intelligent Computation Technology and Automation (ICICTA), Huhehaote, China, 2011:27[2] Khosrov D S. A new offset cancelled latch comparator for high-speed, low-power ADCs, APCCAS. IEEE Asia Pacific Conference on Circuits and Systems, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2010[3] Ye X, Ytterdal T. A low-offset dynamic comparator using bulk biasing technique in digital 65 nm CMOS technology. 10th IEEE International Conference on Solid-State and Integrated Circuit, ICSICT, Shanghai, China, 2010[4] Solis C J, Ducoudray G O. High resolution low power 0.6μm CMOS 40 MHz dynamic latch comparator. 53rd IEEE International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems (MWSCAS), Washington, USA, 2010:1045 https://www.mendeley.com/research-papers/high-resolution-low-power-06m-cmos-40mhz-dynamic-latch-comparator/[5] Yu L, Doris K, Hegt H, et al. A dynamic latched comparator for low supply voltages down to 0.45 V in 65-nm COMS. IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), 2012:2737 https://www.narcis.nl/publication/RecordID/oai%3Alibrary.tue.nl%3A732087[6] Moni D J, Jisha P. High-speed and low-power dynamic latch comparator. International Conference on Devices, Circuits and Systems (ICDCS), 2012:259 http://www.ijera.com/papers/Vol2_issue3/HS2313011312.pdf[7] Jeon H J, Kim Y B. A novel low-power, low-offset, and highspeed CMOS dynamic latched comparator. Analog Integr Circ Sig Process, 2011, 70:337 doi: 10.1007/s10470-011-9687-5[8] Murmann B, Nikaeen P, Connelly D J, et al. Impact of scaling on analog performance and associated modeling needs. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2006, 53:2160 doi: 10.1109/TED.2006.880372[9] Lin T, Wang M S, Gu W R, et al. A wide-range and high-precision real-time calibration for dynamic comparator. IEEE 11th International Conference on Solid-State and Integrated Circuit Technology (ICSICT), 2012:1 https://www.date-conference.com/date16/_create_app_xml[10] Sumanen L, Waltari M, Halonen K. A mismatch insensitive CMOS dynamic comparator for pipeline A/D converters. IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Circuits and Systems (IECS), 2000, 1:32 http://www.ijritcc.org/IJRITCC%20Vol_2%20Issue_5/Design%20of%20a%20CMOS%20Comparator.pdf[11] Cho T B, Gray P R. A 10 b, 20 Msample/s, 35 mW pipeline A/D converter. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 1995, SC-30:166 http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/showciting?cid=2631868[12] Johns D, Martin K. Analog integrated circuit design. New York: Wiley, 2000[13] Wicht B, Nirschl T, Schmitt-Landsiedel D. Yield and speed optimization of a latch-type voltage sense amplifier. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2004, 39:1148 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2004.829399[14] He J, Zhan S, Chen D, et al. Analyses of static and dynamic random offset voltages in dynamic comparators. IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, 2009, 56:911 http://class.ece.iastate.edu/vlsi2/docs/Papers%20Done/2009-05-TCAS1-JH.pdf[15] Nikoozadeh A, Murmann B. An analysis of latch comparator offset due to load capacitor mismatch. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Ⅱ:Express Briefs, 2006, 53:1398 doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2006.883204[16] Bichan M, Carusone A C. The effect of redundancy on mismatch-induced offset and random noise in a dynamic comparator. Research in Microelectronics and Electronics, 2009:180 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/5201314/[17] Kinget P R. Device mismatch and tradeoffs in the design of analog circuits. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2005, 40:1212 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2005.848021[18] Savengsveksa V, Heedley P L, Matthews T, et al. An 8-b 20 Msample/s pipelined A/D converter in 0.5μm CMOS with 7.8 ENOB. IEEE MWSCAS, 2005:409 https://es.scribd.com/document/90619371/Digital-and-Analogue-Instrumentation-Testing-and-Measurement-Electrical-Measurement[19] Kim J, Leibowitz B, Ren J, et al. Simulation and analysis of random decision errors in clocked comparators. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I, Reg Papers, 2009, 56:1844 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2009.2028449 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: