| Citation: |
Xin Wang, Cuiluan Wang, Xia Wu, Lingni Zhu, Hongqi Jing, Xiaoyu Ma, Suping Liu. Researching the 915 nm high-power and high-brightness semiconductor laser single chip coupling module[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2017, 38(2): 024006. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/38/2/024006
****
X Wang, C L Wang, X Wu, L N Zhu, H Q Jing, X Y Ma, S P Liu. Researching the 915 nm high-power and high-brightness semiconductor laser single chip coupling module[J]. J. Semicond., 2017, 38(2): 024006. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/38/2/024006.
|
Researching the 915 nm high-power and high-brightness semiconductor laser single chip coupling module
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/38/2/024006
More Information
-
Abstract
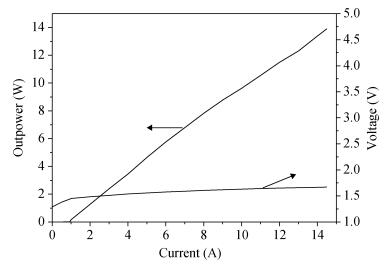
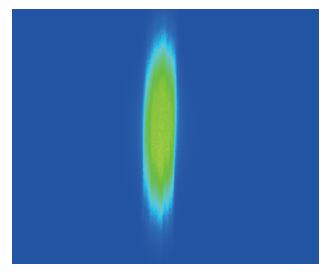
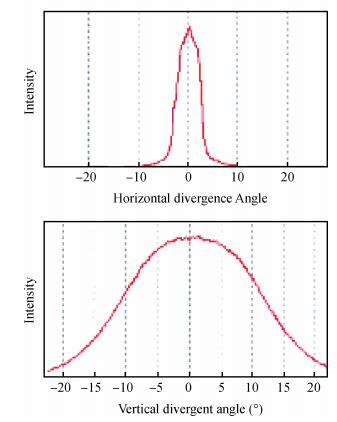
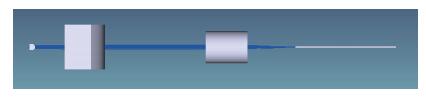
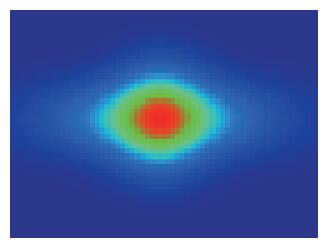
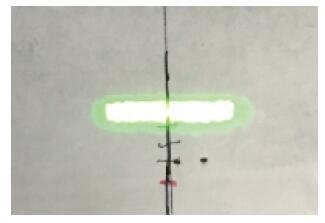
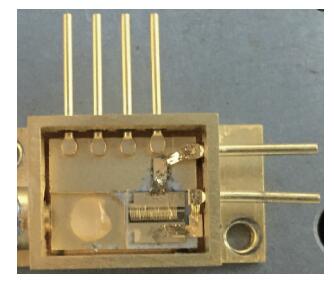
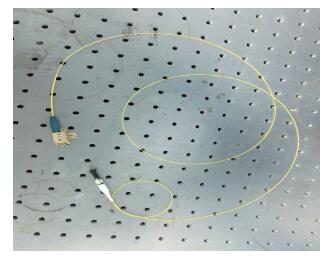
Based on the high-speed development of the fiber laser in recent years, the development of researching 915 nm semiconductor laser as main pumping sources of the fiber laser is at a high speed. Because the beam quality of the laser diode is very poor, the 915 nm laser diode is generally based on optical fiber coupling module to output the laser. Using the beam-shaping and fiber-coupling technology to improve the quality of output beam light, we present a kind of high-power and high-brightness semiconductor laser module, which can output 13.22 W through the optical fiber. Based on 915 nm GaAs semiconductor laser diode which has output power of 13.91 W, we describe a thoroughly detailed procedure for reshaping the beam output from the semiconductor laser diode and coupling the beam into the optical fiber of which the core diameter is 105 μm and the numerical aperture is 0.18. We get 13.22 W from the output fiber of the module at 14.5 A, the coupling efficiency of the whole module is 95.03% and the brightness is 1.5 MW/cm2-str. The output power of the single chip semiconductor laser module achieves the advanced level in the domestic use.-
Keywords:
- semiconductor laser,
- fiber coupling,
- high power,
- high brightness,
- module
-
References
[1] Dong Z, Zhao Y H, Zhang Q, et al. High power 980 nm broad area distributed feedback laser with first-order gratings. J Semicond, 2016, 37(2):024010 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/37/2/024010[2] Li X, Zhao D G, Jiang D S, et al. Suppression of electron leakage in 808 nm laser diodes with asymmetric waveguide layer. J Semicond, 2016, 37(1):014007 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/37/1/014007[3] Zhu Z, Zhang X, Li P X, et al. Voltage reduction of 808 nm GaAsP/(Al) GaInP laser diodes with GaInAsP intermediate layer. J Semicond, 2015, 36(1):014011 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/36/1/014011[4] Feng P, Zhang Y J, Wang Y F, et al. A novel hybrid Ⅲ-V/silicon deformed micro-disk single-mode laser. J Semicond, 2015, 36(2):024012 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/36/2/024012[5] Liao Y P, Zhang Y, Xing J L, et al. High power laser diodes of 2μm AlGaAsSb/InGaSb type I quantum-wells. J Semicond, 2015, 36(5):054007 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/36/5/054007[6] Ke Q, Tan S Y, Liu S T, et al. Fabrication and optimization of 1.55-μm InGaAsP/InP high-power semiconductor diode laser. J Semicond, 2015, 36(9):094010 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/36/9/094010[7] Gong X Q, Feng S W, Yue Y, et al. Thermal analysis in high power GaAs-based laser diodes. J Semicond, 2016, 37(4):044011 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/37/4/044011[8] Zhu Z, Zhang X, Li P X, et al. Voltage reduction of 808 nm GaAsP/(Al) GaInP laser diodes with GaInAsP intermediate layer. J Semicond, 2015, 36(10):1014011[9] Dong Z, Wang C L, Jing H Q, et al. High power single mode 980 nm AlGaInAs/AlGaAs quantum well lasers with a very low threshold current. J Semicond, 2013, 34(11):114011 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/11/114011[10] Liu Y Q, Cao Y H, Li J. 5 kW fiber coupling diode laser forlaser processing. Opt Precision Eng, 2015, 23(5):1279 doi: 10.3788/OPE.[11] Liu R C, Liu Y Y, Chen X, et al. Beam multiplexing of diode laser array. J Semicond, 2015, 36(4):004008[12] Bo B X, Gao X, Wang L, et al. 808 nm wavelength high power fibre coupling LD. Chin J Lasers, 1999, 269(3):193[13] Faircloth B. High-brightness high-power fiber coupled diode laser system for material processing and laser pumping. Proc SPIE, 2003, 4973:34 doi: 10.1117/12.478365[14] Chen H N, Zou Y G, Xu L, et al. Fiber coupling technology of high power semiconductor laser. Journal of Changchun University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2014, 37(1):6[15] Zhou Z P. Fiber coupling design of hundred-watt high brightness semiconductor lasers. Changchun University Science and Techonlogy, 2014[16] Gao X, Bo B X, Zhang J, et al. High brightness operation of fiber coupling multiplex diode lasers. Chin J Lasers, 2007, 34(11):1472 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/287883325_High_brightness_operation_of_fiber_coupling_multiplex_diode_lasers[17] Zhu H B, Hao M M, Peng H Y, et al. Module of fiber coupled diode laser based on 808 nm single emitters combination. Chin J Lasers, 2012, 39(5):0502001 doi: 10.3788/CJL[18] Zhu H B, Hao M M, et al. 808 nm high brightness module of fiber coupled diode laser. Opt Precision Eng, 2012, 8:20 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/270171400_808_nm_high_brightness_module_of_fiber_coupled_diode_laser -
Proportional views






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: