| Citation: |
Yuping Huang, Jun Liu, Kai Lü, Jing Chen. Investigation of temperature-dependent small-signal performances of TB SOI MOSFETs[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2017, 38(4): 044006. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/38/4/044006
****
Y P Huang, J Liu, K Lü, J Chen. Investigation of temperature-dependent small-signal performances of TB SOI MOSFETs[J]. J. Semicond., 2017, 38(4): 044006. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/38/4/044006.
|
Investigation of temperature-dependent small-signal performances of TB SOI MOSFETs
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/38/4/044006
More Information
-
Abstract
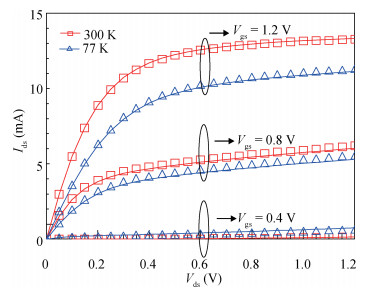
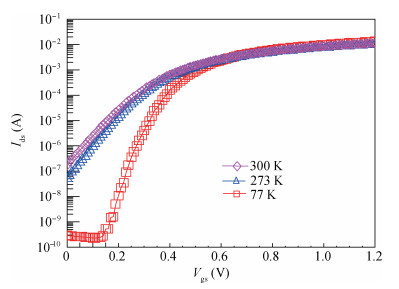
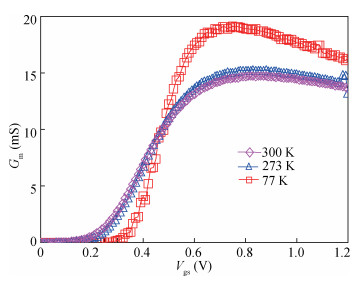
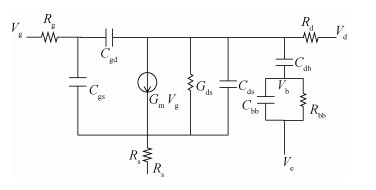
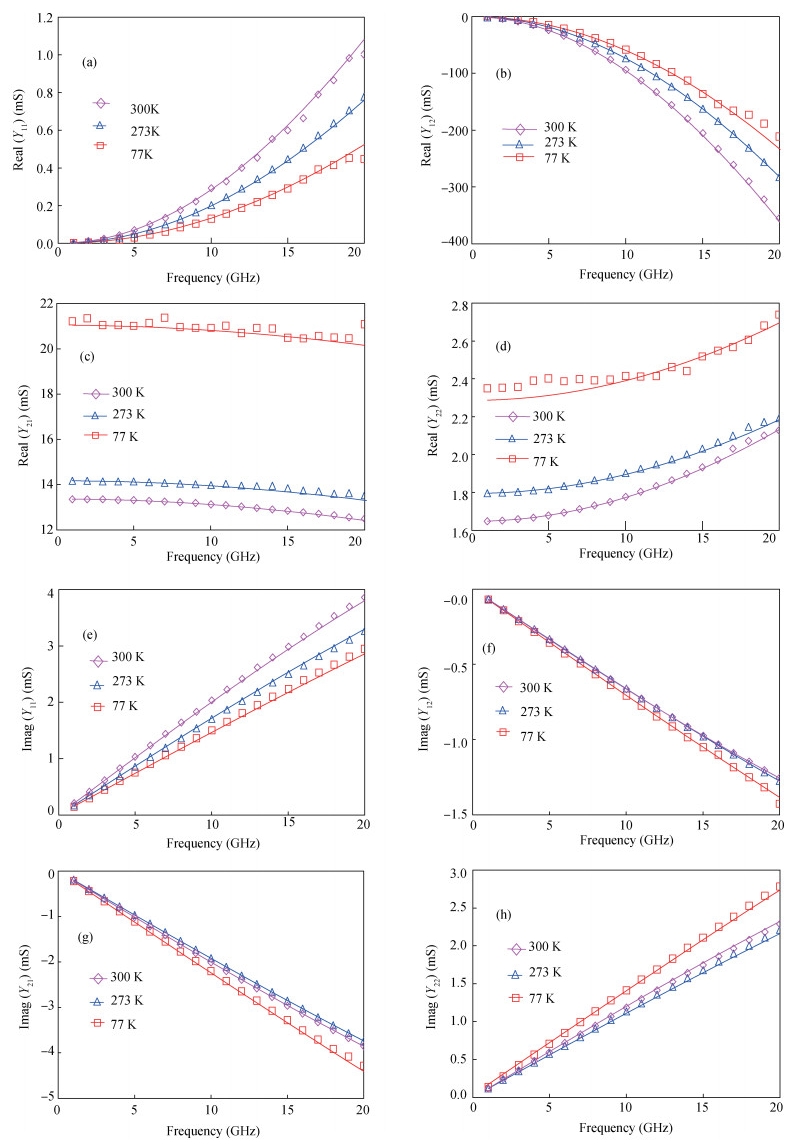
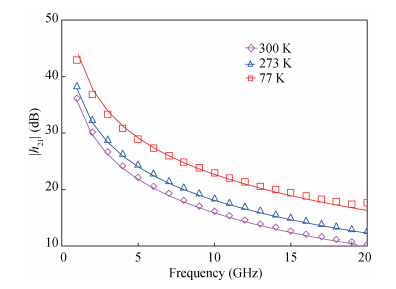
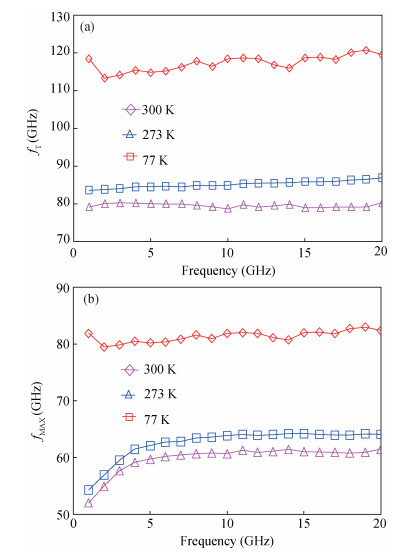
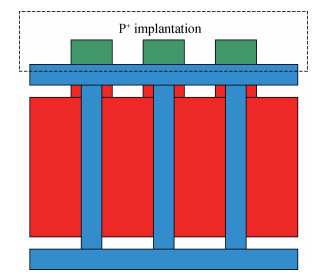
This paper investigated the temperature dependence of the cryogenic small-signal ac performances of multi-finger partially depleted (PD) silicon-on-insulator (SOI) metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors (MOSFETs), with T-gate body contact (TB) structure. The measurement results show that the cut-off frequency increases from 78 GHz at 300 K to 120 GHz at 77 K and the maximum oscillation frequency increases from 54 GHz at 300 K to 80 GHz at 77 K, and these are mainly due to the effect of negative temperature dependence of threshold voltage and transconductance. By using a simple equivalent circuit model, the temperature-dependent small-signal parameters are discussed in detail. The understanding of cryogenic small-signal performance is beneficial to develop the PD SOI MOSFETs integrated circuits for ultra-low temperature applications.-
Keywords:
- cryogenic,
- small-signal AC performance,
- PD SOI MOSFETs
-
References
[1] Lee B J, Kim K, Yu C G, et al. Effects of gate structures on the RF performance in PD SOI MOSFETs. IEEE Microwave Wireless Compon Lett, 2005, 15(4): 223 doi: 10.1109/LMWC.2005.845697[2] Rozeau O, Jomaah J, Boussey J, et al. Impact of floating body and BS-tied architectures on SOI MOSFET's radio-frequency performances. 2000 IEEE International SOI Conference, 2000: 124 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/3879519_Impact_of_floating_body_and_BS-tied_architectures_on_SOI_MOSFET%27s_radio-frequency_performances[3] Tseng Y C, Huang W M, Mendicino M, et al. Minimizing body instability in deep sub-micron SOI MOSFETs for sub-1 V RF applications. 1999 Symposium on VLSI Technology, 1999: 27 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/3820787_Minimizing_body_instability_in_deep_sub-micron_SOI_MOSFETs_for_sub-1_V_RF_applications[4] Hai C H, Han Z S, Zhou X Y, et al. Study of improved performance of SOI devices and circuits. Chin J Semicond, 2006, 27(13): 322 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/286605721_Study_of_improved_performance_of_SOI_devices_and_circuits[5] Zhou J H, Gao M H, Pang S K. Body-contact self-bias effect in partially depleted SOI-CMOS and alternatives to suppress floating body effect. J Semicond, 2011, 32(2): 024003 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/32/2/024003[6] Jiang Y H, Luo X R, Li Y F, et al. Eliminating the floating-body effects in a novel CMOS-compatible thin-SOI LDMOS. J Semicond, 2013, 34(9): 094005 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/9/094005[7] Chireix H. High power outphasing modulation. Proc IRE, 1935, 23(11): 1370 doi: 10.1109/JRPROC.1935.227299[8] Gildenblat G, Colonna-Romano L, Lau D, et al. Investigation of cryogenic CMOS performance. 1985 International IEEE Electron Devices Meeting, 1985, 31: 268[9] Martin P, Bucher M, Enz C. MOSFET modeling and parameter extraction for low temperature analog circuit design. Journal De Physique Ⅳ, 2002, 12(3): 51 https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Matt_Bucher/publication/235926777_MOSFET_Modeling_and_Parameter_Extraction_for_Low_Temperature_Analog_Circuit_Design/links/00b7d51448f5a601c7000000.pdf[10] Chen S, Cai C, Wang T, et al. Cryogenic and high temperature performance of 4H-SiC power MOSFETs. IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference & Exposition, 2013: 207 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/271543910_Cryogenic_and_high_temperature_performance_of_4H-SiC_power_MOSFETs[11] Venkataraman S, Banerjee B, Lee C H, et al. Cryogenic small signal operation of 0.18 μm MOSFETs. Silicon Monolithic Integrated Circuits in RF Systems, 2007: 52[12] Hong S H, Choi G B, Baek R H, et al. Low-temperature performance of nanoscale MOSFET for deep-space RF applications. IEEE Electron Device Lett, 2008, 29(7): 775 doi: 10.1109/LED.2008.2000614[13] Reiche M, Kittler M, Uebensee H, et al. A novel SOI-based MOSFET with ultra-low subthreshold swing for cryogenic applications. IEEE Microelectron Technol Devices, 2013: 1 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/261412269_A_novel_SOI-based_MOSFET_with_ultra-low_subthreshold_swing_for_cryogenic_applications[14] Lee J K, Choi N J, Yu C G, et al. Temperature dependence of DTMOS transistor characteristics. Solid-State Electron, 2004, 48(1): 183 doi: 10.1016/S0038-1101(03)00297-1[15] Su J G, Wong S C, Chang C Y, et al. New insights on RF CMOS stability related to bias, scaling, and temperature. 2000 IEEE Hong Kong Electron Devices Meeting, 2000: 402 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/3888672_New_insights_on_RF_CMOS_stability_related_to_bias_scaling_and_temperature[16] Razavi B, Yan R H, Lee K F. Impact of distributed gate resistance on the performance of MOS devices. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I, 1994, 41(11): 750 doi: 10.1109/81.331530[17] Jia K, Sun W F, Shi L X. A sub-circuit MOSFET model with a wide temperature range including cryogenic temperature. J Semicond, 2011, 32(6): 064002 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/32/6/064002[18] Kilchytska V, Neve A, Vancaillie L, et al. Influence of device engineering on the analog and RF performances of SOI MOSFETs. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2003, 50(3): 577 doi: 10.1109/TED.2003.810471[19] Kwon I, Je M, Lee K, et al. A simple and analytical parameter-extraction method of a microwave MOSFET. IEEE Trans Microwave Theory Tech, 2002, 50(6): 1503 doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2002.1006411 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: