| Citation: |
Pengpeng Sun, Hui Liu, Miao Geng, Rong Zhang, Qi Wang, Weijun Luo. An X-band 22.5°/45° digital phase shifter based on switched filter networks[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2017, 38(6): 065001. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/38/6/065001
****
P P Sun, H Liu, M Geng, R Zhang, Q Wang, W J Luo. An X-band 22.5°/45° digital phase shifter based on switched filter networks[J]. J. Semicond., 2017, 38(6): 065001. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/38/6/065001.
|
An X-band 22.5°/45° digital phase shifter based on switched filter networks
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/38/6/065001
More Information
-
Abstract
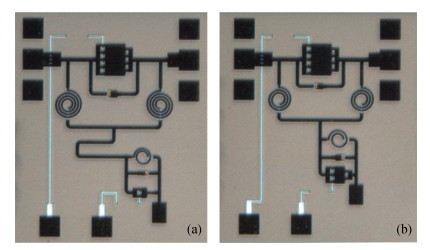
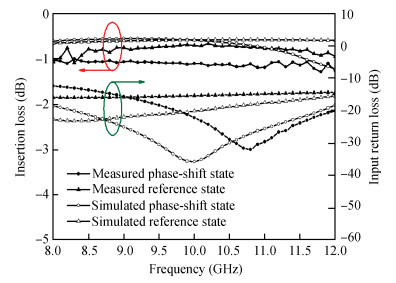
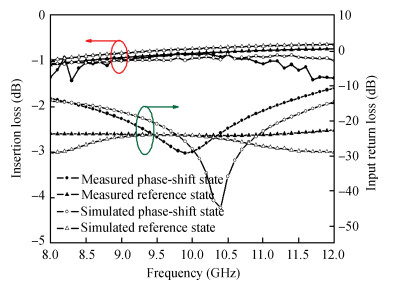
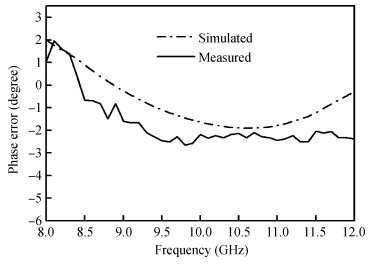
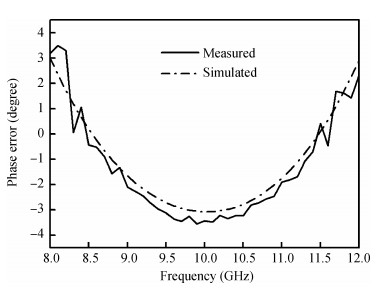
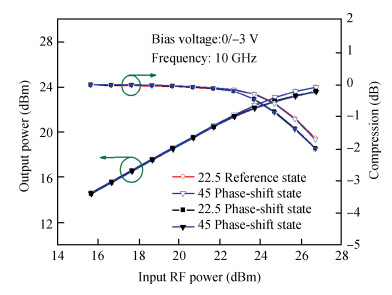
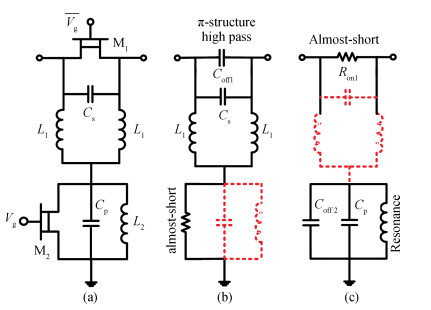
The design approach and performance of a 22.5°/45°digital phase shifter based on a switched filter network for X-band phased arrays are described. Both the MMIC phase shifters are fabricated employing a 0.25μm gate GaAs pHEMT process and share in the same chip size of 0.82×1.06 mm2. The measurement results of the proposed phase shifters over the whole operating frequency range show that the phase shift error is less than 22.5°±2.5°, 45°±3.5°, which shows an excellent agreement with the simulated performance, the insertion loss is within the range of 0.9-1.2 dB for the 22.5°phase shifter and 0.9-1.4 dB for the 45°phase shifter, and the input/output return loss is better than -12.5 and -11 dB respectively. They also achieve the similar P1dB continuous wave power handing capability of 24.8 dBm at 10 GHz. The phase shifters show a good phase shift error, insertion loss and return loss in the X-band (40%), which can be employed into the wide bandwidth multi-bit digital phase shifter.-
Keywords:
- phase shifter,
- switched filter,
- X-band,
- GaAs pHEMT
-
References
[1] Edward B J, Helms D R, Webb R S, et al. W-band active transmit and receive phased array antennas. Microwave Systems Conference Proceedings, IEEE NTC, 1995:254 https://www.researchgate.net/profile/G_Sadowy/publication/224620702_An_active_membrane_phased_array_radar/links/5419a8de0cf203f155ae0bf9.pdf?origin=publication_detail[2] Chen L, Chen X Y, Zhang Y T, et al. A high linearity X-band SOI CMOS digitally-controlled phase shifter. J Semicond, 2015, 36(6):065004 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/36/6/065004[3] Christopher D W, Derek T D, Steven A L, et al. Space radiation environment testing of liquid crystal phase shifter devices. IEEE Antennas Wireless Propag Lett, 2016, 15:1923 doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2015.2511058[4] Kiarash G, Naser M, Milad K, et al. A fully integrated 0.18-m CMOS transceiver chip for X-band phased-array systems. IEEE Trans Microwave Theory Tech, 2015, 60(7):2192 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/265672576_A_Fully_Integrated_018-m_CMOS_Transceiver_Chip_for_-Band_Phased-Array_Systems[5] Xiao Q. A compact L-band broadband 6-bit MMIC phase shifter with low phase error. Proceedings of the 6th European Microwave Integrated Circuits Conference, 2011:410 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpl/articleDetails.jsp?arnumber=6102765&[6] Tang X Y, Koen M. Design considerations for octave-band phase shifters using discrete components. IEEE Trans Microwave Theory Tech, 2010, 58(12):3459 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/224180844_Design_Considerations_for_Octave-Band_Phase_Shifters_Using_Discrete_Components[7] Tsai J H, Kuo Y T, Yu H C. A Ku-band 3-bit phase shifter MMIC using GaAs pHEMT technology for phased array system. Microwave Opt Technol Lett, 2015, 57(4):771 doi: 10.1002/mop.v57.4[8] Tang X Y, Mouthaan K. Loaded-line phase shifter with enlarged phase shift range and bandwidth. IEEE 40th European Microwave Conference, 2010:818 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpl/articleDetails.jsp?reload=true&arnumber=5616342&filter%3DAND%28p_IS_Number%3A5614756%29[9] Zheng S Y, Chan W S, Man K F. Broadband phase shifter using loaded transmission line. IEEE Microwave Wireless Compon Lett, 2010, 20(9):498 doi: 10.1109/LMWC.2010.2050868[10] Bahl I J, Dayton M. A Ku-band 4-bit compact octave bandwidth GaAs MMIC phase shifter. Microwave J, 2008, 51(6):30 http://www.microwavejournal.com/articles/6334-a-ku-band-4-bit-compact-octave-bandwidth-gaas-mmic-phase-shifter[11] Campbell C F, Brown S A. A compact 5-bit phase shifter MMIC for K-band satellite communication systems. IEEE MTT-S Int, 2000:217 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/3121393_Compact_5-bit_phase_shifter_MMIC_for_K-band_satellite_communication_systems[12] Hieda M, Miyaguchi K, Ikematsu H, et al. A compact Ku-band 5-bit MMIC phase shifter. IEICE Trans Electron, 2003, E86-C(12):2437 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/293241241_A_compact_Ku-band_5-bit_MMIC_phase_shifter[13] Hangai M, Hieda M, Yunoue N, et al. S-and C-band ultracompact phase shifters based on all-pass networks. IEEE Trans Microwave Theory Tech, 2010, 58(1):41 doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2009.2036322[14] Yang X F, Shi J Y. C-band 6-bit phase shifter for a phase array antenna. J Semicond, 2013, 34(4):045009 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/4/045009[15] Tsai J H, Liu C K, Lin J Y. A 12GHz 6-bit switch-type phase shifter MMIC. IEEE 44th European Microwave Conference, 2014:1916 https://www.deepdyve.com/lp/institute-of-electrical-and-electronics-engineers/a-12-ghz-6-bit-switch-type-phase-shifter-mmic-jZakOiTVP2 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: