| Citation: |
Xingyi Tan, Qiang Li, Yongdan Zhu. First-principles study of p-type ZnO by S-Na co-doping[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2017, 38(8): 083001. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/38/8/083001
****
X Y Tan, Q Li, Y D Zhu. First-principles study of p-type ZnO by S-Na co-doping[J]. J. Semicond., 2017, 38(8): 083001. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/38/8/083001.
|
First-principles study of p-type ZnO by S-Na co-doping
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/38/8/083001
More Information
-
Abstract
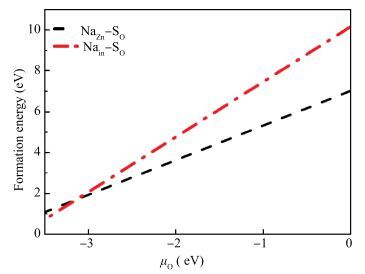
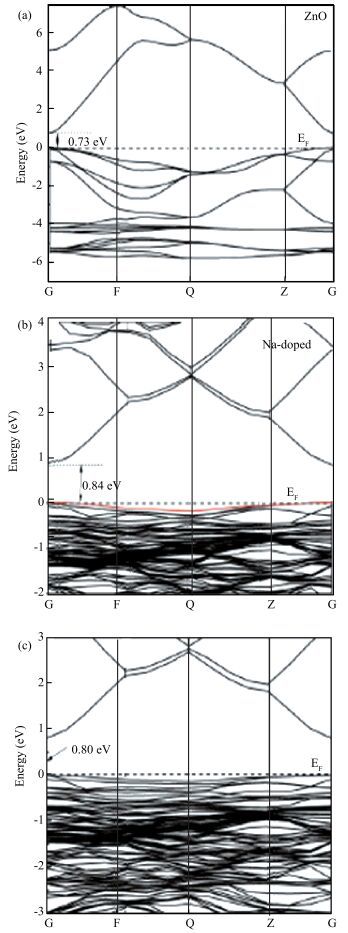
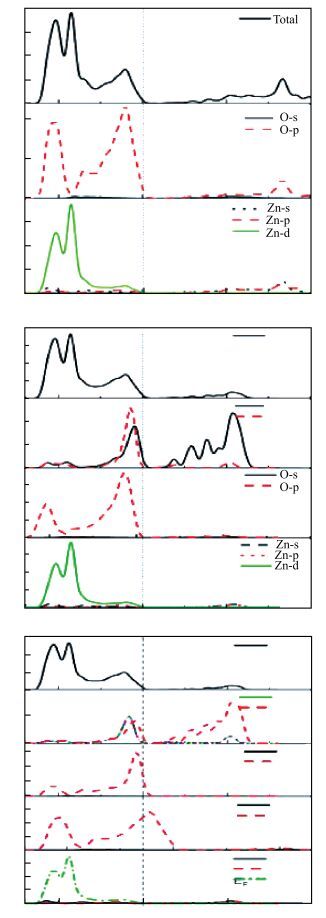
Using the first-principles method based on the density functional theory, the formation energy, electronic structures of S-Na co-doping in ZnO were calculated. The calculated results show that NaZn-SO have smaller formation energy than Nain-SO in energy ranges from -3.10 to 0 eV of μO, indicating that it opens up a new opportunity for growth the p-type ZnO. The band structure shows that the NaZn system is a p-type direct-band-gap semiconductor material and the calculated band gap (0.84 eV) is larger than pure ZnO (0.74 eV). The NaZn-SO system is also a p-type semiconductor material with a direct band gap (0.80 eV). The influence of S-Na co-doping in ZnO on p-type conductivity is also discussed. The effective masses of NaZn-SO are larger than effective masses of NaZn and the NaZn-SO have more hole carriers than NaZn, meaning the hole in the NaZn-SO system may have a better carrier transfer character. So we inferred that NaZn-SO should be a candidate of p-type conduction.-
Keywords:
- p-type ZnO,
- electronic structures,
- conductive property
-
References
[1] Özgür Ü, Alivov Y I, Liu C, et al. A comprehensive review of ZnO materials and devices. J Appl Phys, 2005, 98:0413011 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/276379347_A_Comprehensive_Review_of_ZnO_Materials_and_Devices[2] Sara K G, Ramin Y, Farid J S, et al. Optical and electrical properties of p-type Ag-doped ZnO nanostructures. Ceram Int, 2014, 40:7957 doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2013.12.145[3] Li W J, Kong C Y, Qin G P, et al. p-type conductivity and stability of Ag-N codoped ZnO thin films. J. Alloys Compd, 2014, 609:173 doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2014.04.051[4] Alivov Y I, Kalinina E V, Cherenkov A E, et al. Fabrication and characterization of n-ZnO/p-AlGaN heterojunction light-emitting diodes on 6H-SiC substrates. Appl Phys Lett, 2003, 83:4719 doi: 10.1063/1.1632537[5] Huang Y B, Zhou W, Wu P. Room-temperature ferromagnetism in epitaxial p-type K-doped ZnO films. Solid State Commun, 2014, 183:31 doi: 10.1016/j.ssc.2013.12.024[6] Makino T, Chia C H, Tuan N T, et al. Radiative and nonradiative recombination processes in lattice-matched (Cd, Zn)O/(Mg, Zn)O multiquantum wells. Appl Phys Lett, 2000, 77:1632 doi: 10.1063/1.1308540[7] Sáaedi A, Yousefi R, Jamali-Sheini F, et al. Optical and electrical properties of p-type Li-doped ZnO nanowires. Superlattices Microstruct, 2013, 61:91 doi: 10.1016/j.spmi.2013.06.014[8] Zhang S B, Wei S H, Zunger A. Intrinsic n-type versus p-type doping asymmetry and the defect physics of ZnO. Phys Rev B, 2001, 63:075205 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.63.075205[9] Dhara S, Giri P K. Stable p-type conductivity and enhanced photoconductivity from nitrogen-doped annealed ZnO thin film. Thin Solid Films, 2012, 520:5000 doi: 10.1016/j.tsf.2012.02.081[10] Liu J S, Shan C X, Shen H, et al. ZnO light-emitting devices with a lifetime of 6.8 hours. Appl Phys Lett, 2012, 101:011106 doi: 10.1063/1.4733298[11] Shen H, Shan C X, Liu J S, et al. Stable p-type ZnO films obtained by lithium-nitrogen codoping method. Phys Status Solidi B, 2013, 250:2102 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/264251371_Stable_p-type_ZnO_films_obtained_by_lithium-nitrogen_codoping_method[12] Park C H, Zhang S B, Wei S H. Origin of p-type doping difficulty in ZnO:the impurity perspective. Phys Rev B, 2002, 66:073202 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.66.073202[13] Yang X P, Lu J G, Zhang H H, et al. Preparation and XRD analyses of Na-doped ZnO nanorod arrays based on experiment and theory. Chem Phys Lett, 2012, 528(3):16 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/256683125_Preparation_and_XRD_Analyses_of_Na-Doped_ZnO_Nanorod_Arrays_Based_on_Experiment_and_Theory[14] Lin S S, Lu J G, Ye Z Z, et al. p-type behavior in Na-doped ZnO films and ZnO homojunction light-emitting diodes. Solid State Commun, 2008, 148:25 doi: 10.1016/j.ssc.2008.07.028[15] Pandey S K, Awasthi V, Sengar B S, et al. Band alignment and photon extraction studies of Na-doped MgZnO/Ga-doped ZnO heterojunction for light-emitter applications. J Appl Phys, 2015, 118:165301 doi: 10.1063/1.4934560[16] Persson C, Platzer-Björkman C, Malmström J, et al. Strong valence-band offset bowing of ZnO1-xSx enhances p-type nitrogen doping of ZnO-like alloys. Phys Rev Lett, 2006, 97:146403 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.97.146403[17] Xu T N, Li X, Lu Z, et al. Realization of Ag-S codoped p-type ZnO thin films. Appl Sur Sci, 2014, 316:62 doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.07.156[18] Xu Y, Yang T, Yao B, et al. Influence of Ag-S codoping on silver chemical states and stable p-type conduction behavior of the ZnO films. Ceram Int, 2014, 40:2161 doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2013.07.133[19] Niu W Z, Xu H B, Guo Y M, et al. The effect of sulfur on the electrical properties of S and N co-doped ZnO thin films:experiment and first-principles calculations. Phys Chem Chem Phys, 2015, 17:16705 doi: 10.1039/C5CP02434J[20] Perdew J P, Burke S, Ernzerhof M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys Rev Lett, 1996, 77:3865 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.77.3865[21] Van de Walle C G, Neugebauer J. First-principles calculations for defects and impurities:applications to Ⅲ-nitrides. J Appl Phys, 2004, 95:3851 doi: 10.1063/1.1682673[22] Oba F, Togo A, Tanaka I, et al. Defect energetics in ZnO:a hybrid Hartree-Fock density functional study. Phys Rev B, 2008, 77:245202 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.77.245202[23] Yan Y F, Zhang S B, Pantelides S T. Control of doping by impurity chemical potentials:predictions for p-type ZnO. Phys Rev Lett, 2001, 86:5723 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.86.5723[24] Guo T T, Dong G B, Chena Q, et al. First-principles calculation on p-type conduction of (Sb, N) codoping in ZnO. J Phys Chem Solid, 2014, 75:42 doi: 10.1016/j.jpcs.2013.08.006[25] Zhang J K, Deng S H, Jin H, et al. First-principle study on the electronic structure and p-type conductivity of ZnO. Acta Phys Sin, 2007, 56:5371 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/291645152_First-principle_study_on_the_electronic_structure_and_p-type_conductivity_of_ZnO[26] Limpijumnong S, Zhang S B, Wei S H, et al. Doping by large-size-mismatched impurities:the microscopic origin of arsenic-or antimony-doped p-type zinc oxide. Phys Rev Lett, 2004, 92:155504 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.92.155504 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: