| Citation: |
Xiaoyu Chen, Hao Wang, Gongchen Sun, Xiaoyu Ma, Jianguang Gao, Wengang Wu. Resistive switching characteristic of electrolyte-oxide-semiconductor structures[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2017, 38(8): 084003. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/38/8/084003
****
X Y Chen, H Wang, G C Sun, X Y Ma, J G Gao, W G Wu. Resistive switching characteristic of electrolyte-oxide-semiconductor structures[J]. J. Semicond., 2017, 38(8): 084003. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/38/8/084003.
|
Resistive switching characteristic of electrolyte-oxide-semiconductor structures
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/38/8/084003
More Information
-
Abstract
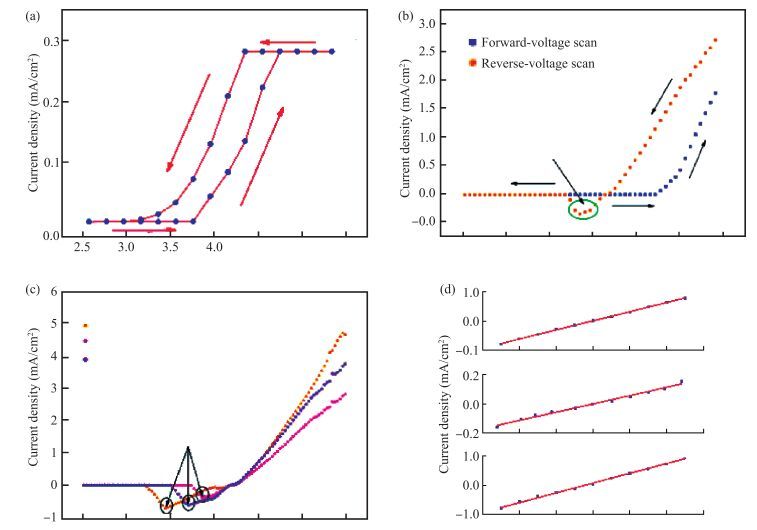
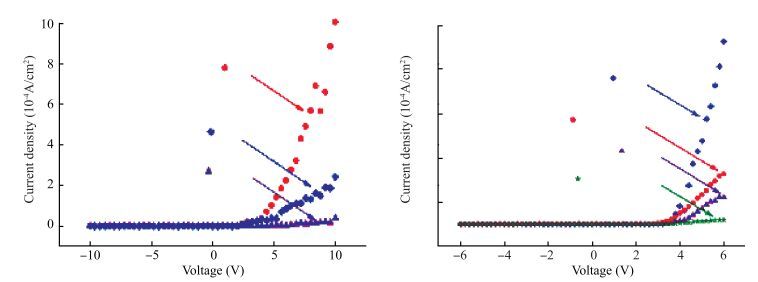
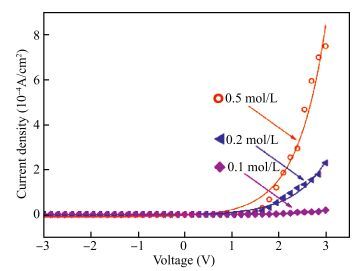
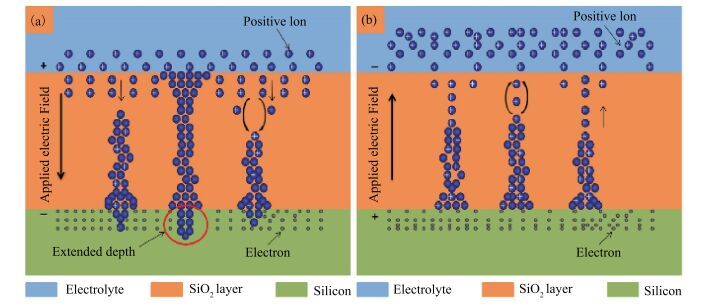
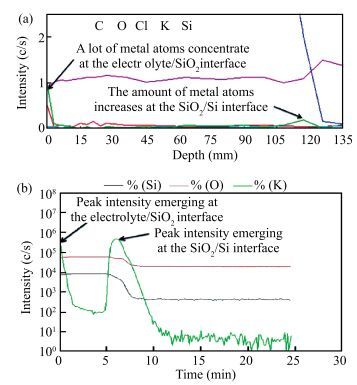
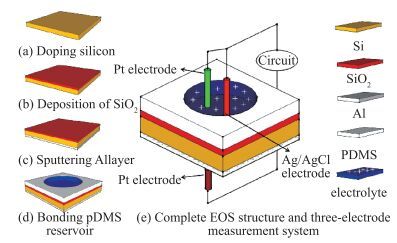
The resistive switching characteristic of SiO2 thin film in electrolyte-oxide-semiconductor (EOS) structures under certain bias voltage is reported. To analyze the mechanism of the resistive switching characteristic, a batch of EOS structures were fabricated under various conditions and their electrical properties were measured with a set of three-electrode systems. A theoretical model based on the formation and rupture of conductive filaments in the oxide layer is proposed to reveal the mechanism of the resistive switching characteristic, followed by an experimental investigation of Auger electron spectroscopy (AES) and secondary ion mass spectroscopy (SIMS) to verify the proposed theoretical model. It is found that different threshold voltage, reverse leakage current and slope value features of the switching I-V characteristic can be observed in different EOS structures with different electrolyte solutions as well as different SiO2 layers made by different fabrication processes or in different thicknesses. With a simple fabrication process and significant resistive switching characteristic, the EOS structures show great potential for chemical/biochemical applications. -
References
[1] Hudec B, Paskaleva A, Jancovic P, et al. Resistive switching in TiO2-based metal-insulator-metal structures with Al2O3 barrier layer at the metal/dielectric interface. Thin Solid Films, 2014, 563:10 doi: 10.1016/j.tsf.2014.02.030[2] Jeon H, Park J, Jang W, et al. Stabilized resistive switching behaviors of a Pt/TaOx/TiN RRAM under different oxygen contents. Phys Status Solidi A, 2014, 211(9):2189 doi: 10.1002/pssa.v211.9[3] Sawa A. Resistive switching in transition metal oxides. Mater Today, 2008, 11(6):28 doi: 10.1016/S1369-7021(08)70119-6[4] Yu S, Guan X, Wong H S P. Conduction mechanism of TiN/HfOx/Pt resistive switching memory:a trap-assisted-tunneling model. Appl Phys Lett, 2011, 99(6):063507 doi: 10.1063/1.3624472[5] Zhu X J, Shang J, Liu G, et al. Ion transport-related resistive switching in film sandwich structures. Chin Sci Bull, 2014, 59(20):2363 doi: 10.1007/s11434-014-0284-8[6] Goux L. Resistive switching:from concept to device optimization. 2015 IEEE 15th International Conference on Nanotechnology (IEEE-NANO), 2015:17 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/304297853_Resistive_switching_From_concept_to_device_optimization[7] Dearnaley G, Stoneham A, Morgan D. Electrical phenomena in amorphous oxide films. Rep Prog Phys, 1970, 33(3):1129 doi: 10.1088/0034-4885/33/3/306[8] Afanas'ev V, Stesmans A. Hydrogen related leakage currents induced in ultrathin SiO2/Si structures by vacuum ultraviolet radiation. J Electrochem Soc, 1999, 146(9):3409 doi: 10.1149/1.1392487[9] Blöhl P E, Stathis J H. Hydrogen electrochemistry and stress-induced leakage current in silica. Phys Rev Lett, 1999, 83(2):372 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.83.372[10] DiMaria D, Cartier E. Mechanism for stressinduced leakage currents in thin silicon dioxide films. J Appl Phys, 1995, 78(6):3883 doi: 10.1063/1.359905[11] Kügeler C, Rosezin R, Linn E, et al. Materials, technologies, and circuit concepts for nanocrossbar-based bipolar RRAM. Appl Phys A, 2011, 102(4):791 doi: 10.1007/s00339-011-6287-2[12] Yang Y, Gao P, Gaba S, et al. Observation of conducting filament growth in nanoscale resistive memories. Nat Commun, 2012, 3:732 doi: 10.1038/ncomms1737[13] Menzel S, Tappertzhofen S, Waser R, et al. Switching kinetics of electrochemical metallization memory cells. Phys Chem Chem Phys, 2013, 15(18):6945 doi: 10.1039/c3cp50738f[14] Schoch R B, Han J, Renaud P. Transport phenomena in nanofluidics. Rev Modern Phys, 2008, 80(3):839 doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.80.839[15] Fung C D, Cheung P W, Ko W H. A generalized theory of an electrolyte-insulator-semiconductor field-effect transistor. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 1986, 33(1):8 doi: 10.1109/T-ED.1986.22429[16] Kurtz H A, Karna S P. Proton mobility in a-SiO2. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci, 1999, 46(6):1574 doi: 10.1109/23.819123 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: