| Citation: |
Yanzhou Sun, Xiaoqian Liu, Dati Su, Huibin Yang. Memory characteristics of microcavity dielectric barrier discharge[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2018, 39(11): 114008. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/39/11/114008
****
Y Z Sun, X Q Liu, D T Su, H B Yang, Memory characteristics of microcavity dielectric barrier discharge[J]. J. Semicond., 2018, 39(11): 114008. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/39/11/114008.
|
Memory characteristics of microcavity dielectric barrier discharge
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/39/11/114008
More Information
-
Abstract
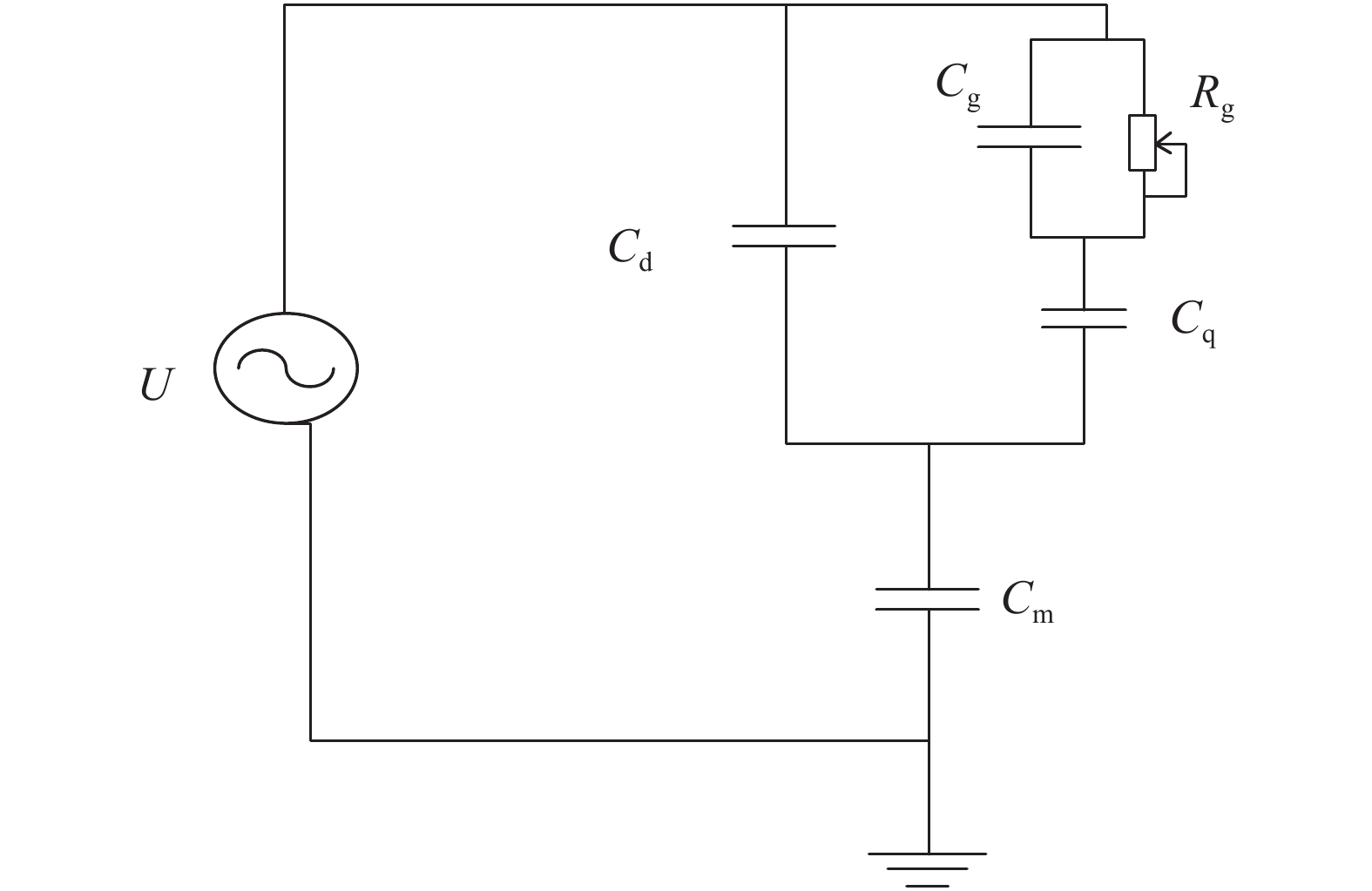
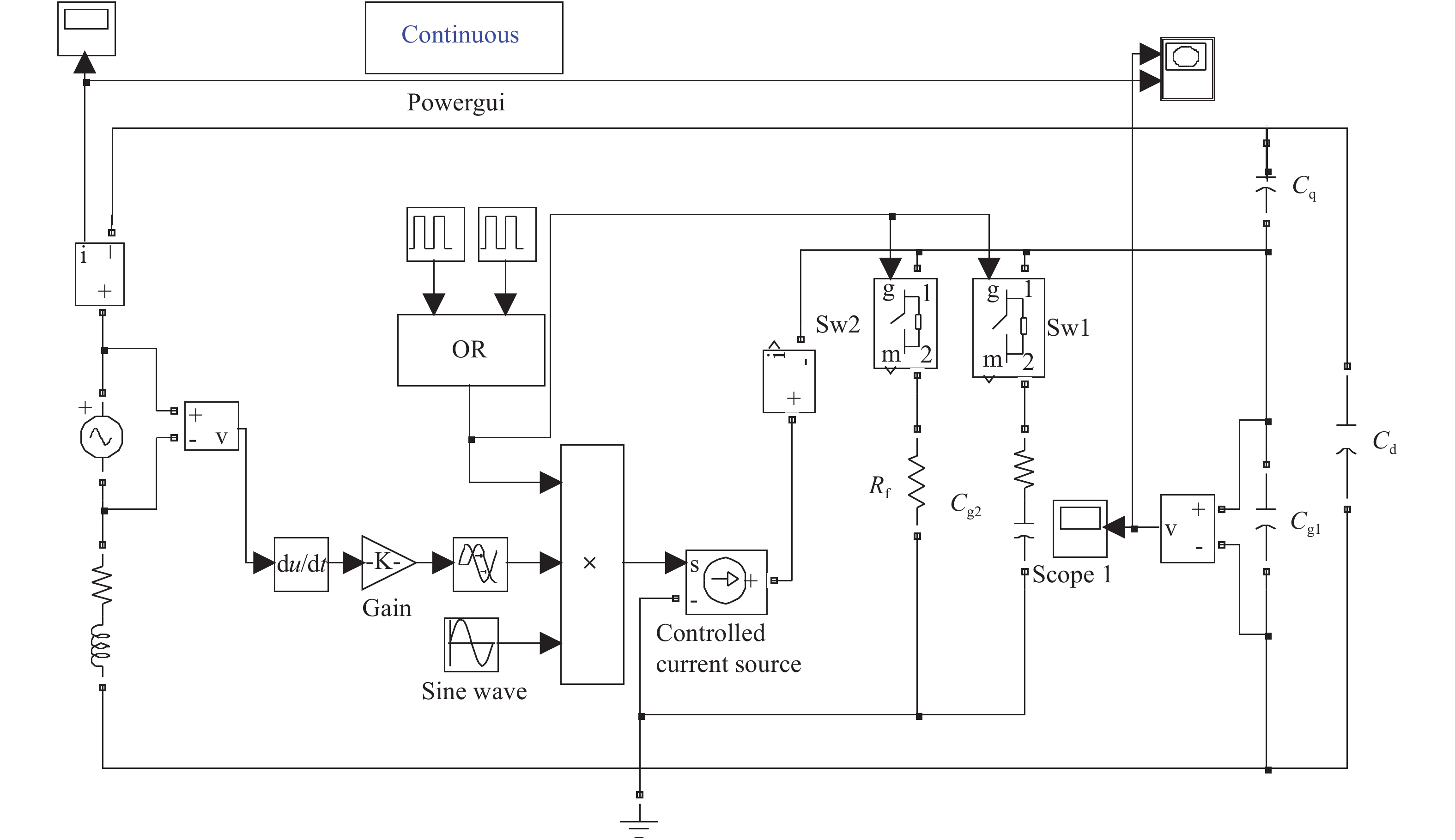
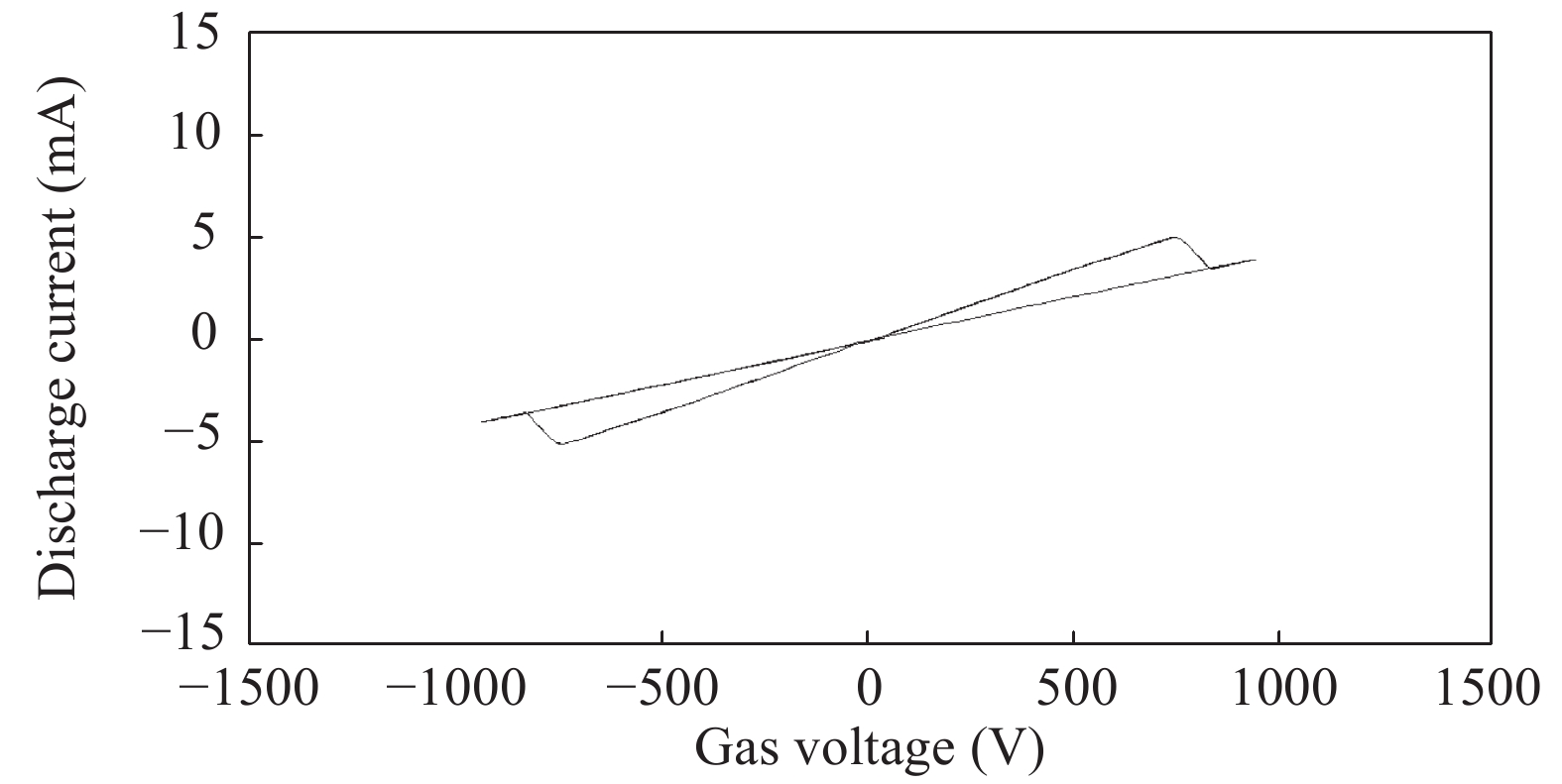
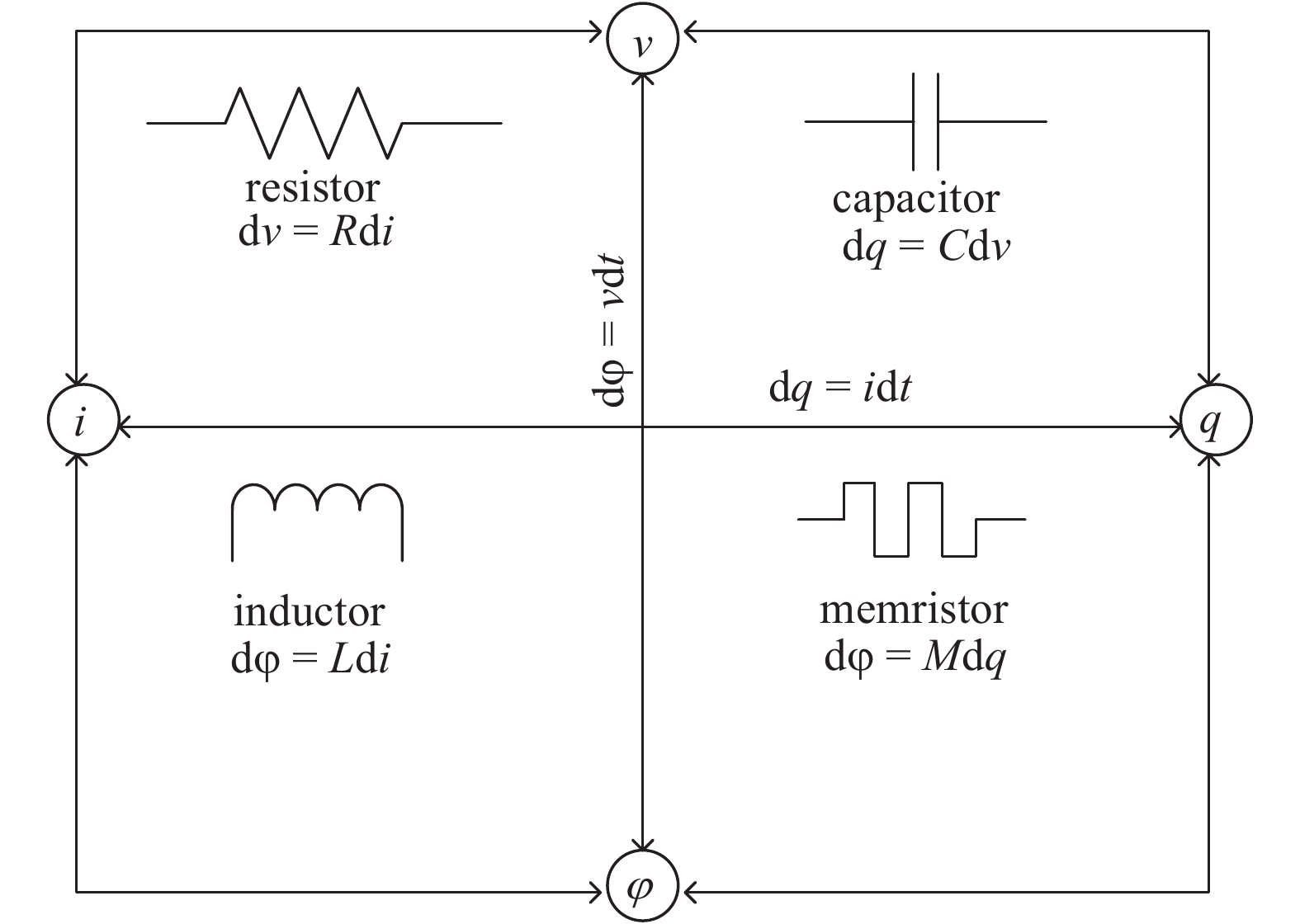
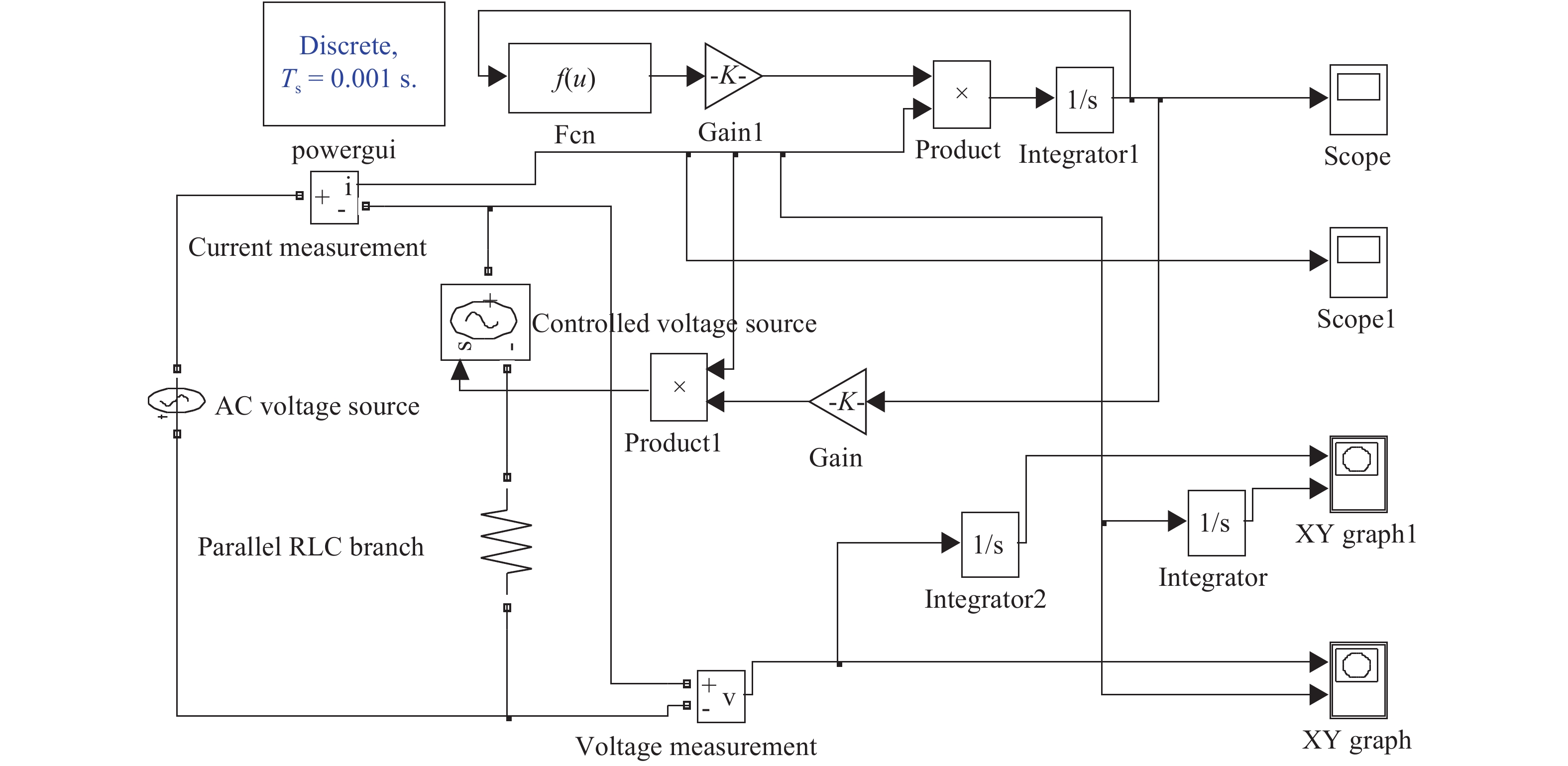
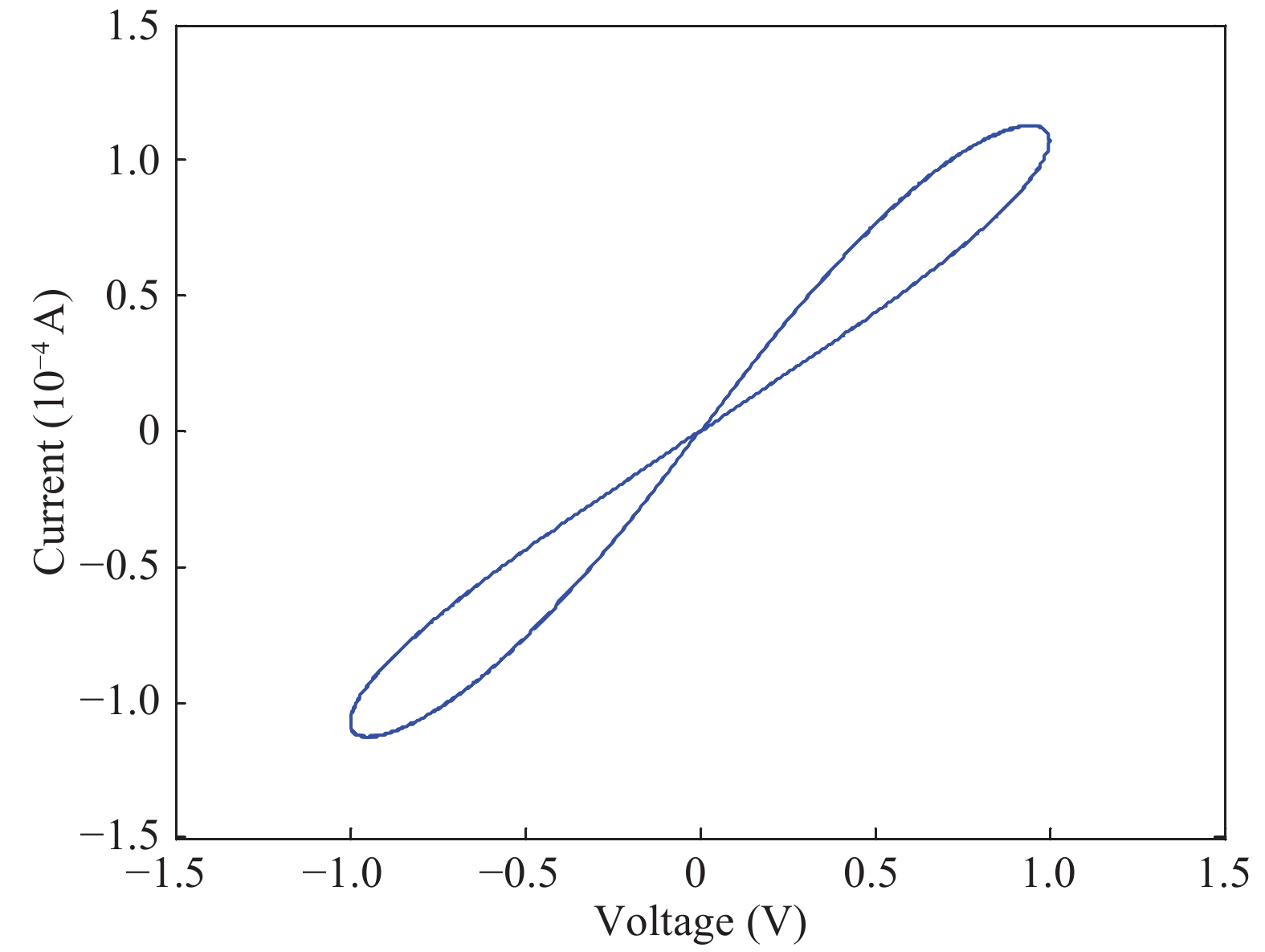
The nonlinear resistance characteristics of microcavity dielectric barrier discharge are mainly studied in the paper. A simulation model of microcavity dielectric barrier discharge is herein built to study the relationship between voltage and current in the process of discharge, and thus its I–V characteristic curve can be obtained. The I–V characteristics of the memristor are analyzed and compared with the I–V characteristics of the dielectric barrier discharge; it can be found that the I–V characteristics of the microcavity dielectric barrier discharge are similar to the characteristics of the memristor by analyzing them. The memory characteristics of microcavity dielectric barrier discharge are further analyzed. -
References
[1] Chua L O. Memristor—the missing circuit element. IEEE Trans Circuit Theory, 1971, 18(5): 507 doi: 10.1109/TCT.1971.1083337[2] Chua L O, Kang S M. Memristive devices and systems. Proc IEEE, 1976, 64(2): 209 doi: 10.1109/PROC.1976.10092[3] Chua L O. Nonlinear circuit foundations for nanodevices. Part I. The four-element torus. Proc IEEE, 2003, 91(11): 1830[4] Wu J, Mccreery R L. Solid-state electrochemistry in molecule/TiO2 molecular heterojunction as the basis of the TiO2 "memristor". Electrochem Soc, 2009, 156(1): 29 doi: 10.1149/1.3021033[5] Yang L X, Wang L C, Qi K J. Gas discharge lamp voltage current function. Journal of Zhengzhou Institute of Technology, 1995, 16(1): 79[6] Shinde S S, Dongle T D. Modelling of nanostructured TiO2-based memristors. J Semicond, 2015, 36(3): 034001 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/36/3/034001[7] Liang Y, Yu D S, Chen H. A novel meminductor emulator based on analog circuits. Acta Phys Sin, 2013, 62(15): 158501[8] Ho P W C, Almurib H A F, Kumar T N. Memristive SRAM cell of seven transistors and one memristor. J Semicond, 2016, 37(10): 104002 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/37/10/104002[9] Wang X Y, Andrew L F, Herbert H C I, et al. Implementation of an analogue model of a memristor based on a light-dependent resistor. Chin Phys B, 2012, 21(10): 108501 doi: 10.1088/1674-1056/21/10/108501[10] Wang X X. Dielectric barrier discharge and its applications. High Volt Eng, 2009, 35(1): 1[11] Sun Y Z, Sun N N, Gong Y M. Electrical characteristics of microcavity structure dielectric barrier dischargec. High Volt Eng, 2015, 41(12): 4008[12] Zhang C, Fang Z, Zhao L Z, et al. Simulation of dielectric barrier discharge using SIMULINK. High Volt Appar, 2007, 43(3): 218[13] Strukov D B, Snider G S, Stewart D R, et al. The missing memristor found. Nature, 2008, 453(7191): 80 doi: 10.1038/nature06932[14] Zhu Z M, Wang Y H. Device modeling and parameter analysis of passive electronic component of the memristor. Electron Compon Mater, 2014, 33(8): 62[15] Song W P, Ding S S, Ning S P. Memory resistor is based on Simulink model. Journal of Taiyuan University of Science and Technology, 2014, 35(01): 23[16] Liu D Q, Cheng H F, Zhu X, et al. Research progress of memristors and memristive mechanism. Acta Phys Sin, 2014, 63(18): 187301 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: