| Citation: |
Hongbing Wu, Jingyu Wang, Hongxia Liu. A 5 Gb/s CMOS adaptive equalizer for serial link[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2018, 39(4): 045003. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/39/4/045003
****
H B Wu, J Y Wang, H X Liu. A 5 Gb/s CMOS adaptive equalizer for serial link[J]. J. Semicond., 2018, 39(4): 045003. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/39/4/045003.
|
A 5 Gb/s CMOS adaptive equalizer for serial link
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/39/4/045003
More Information
-
Abstract
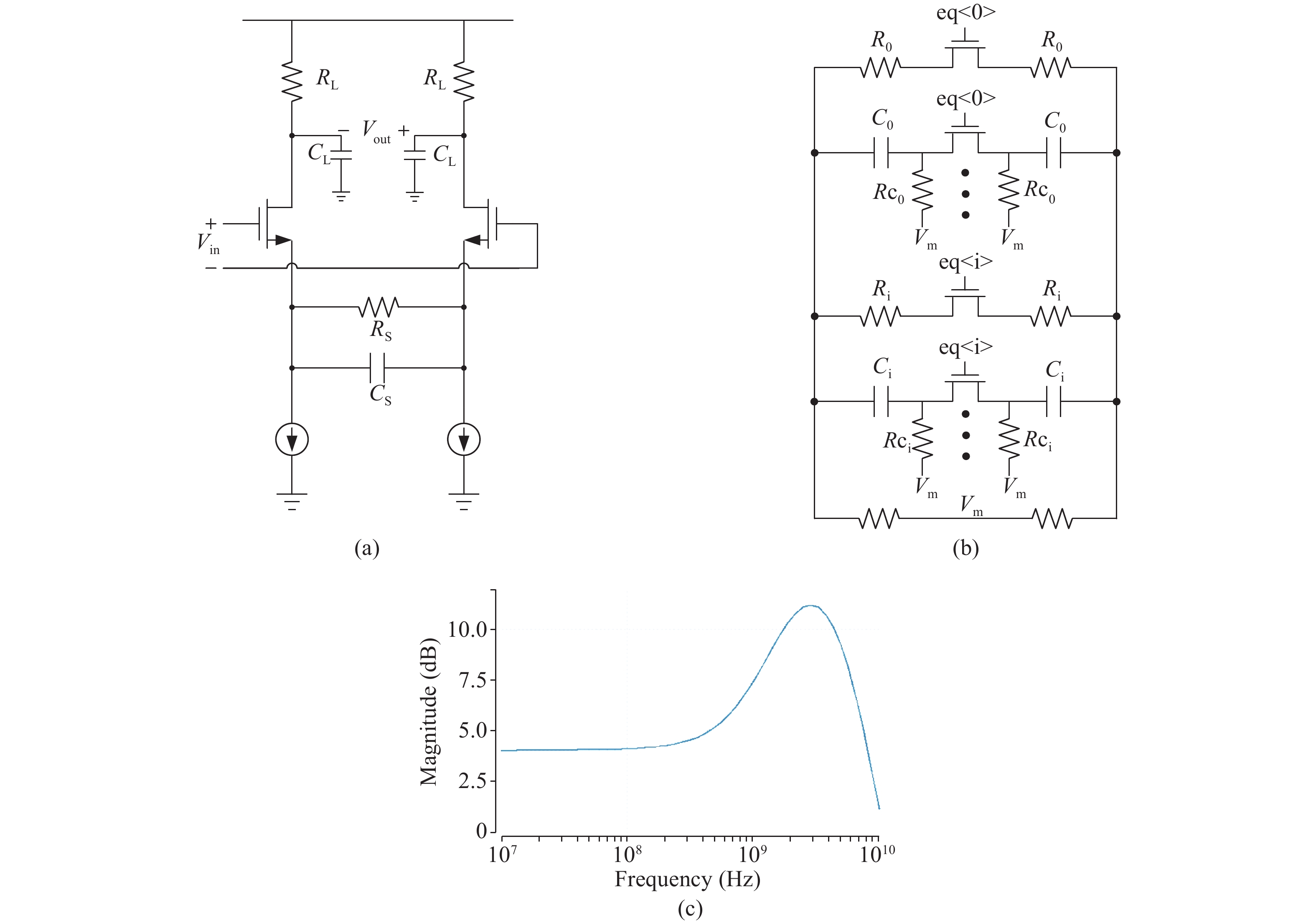
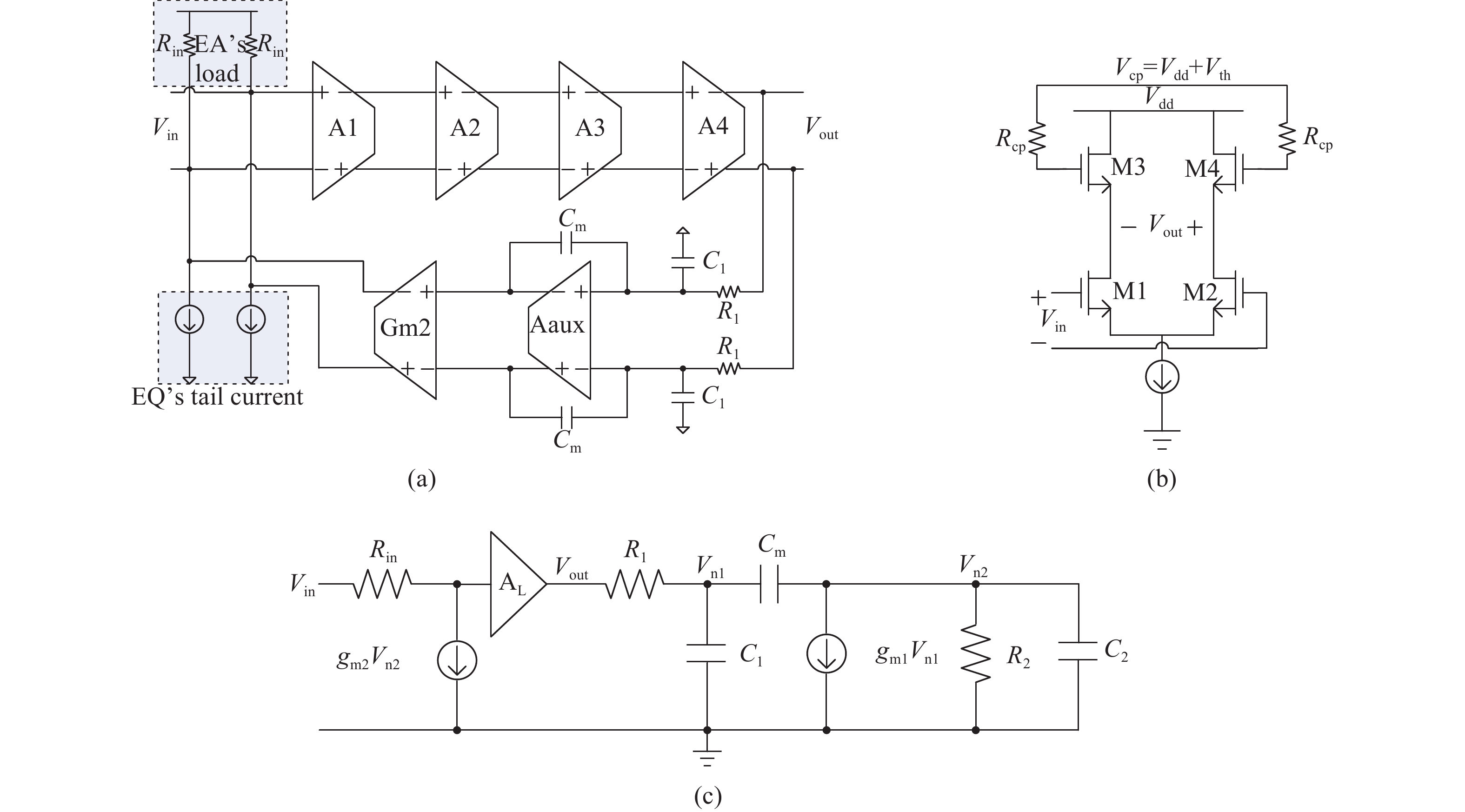
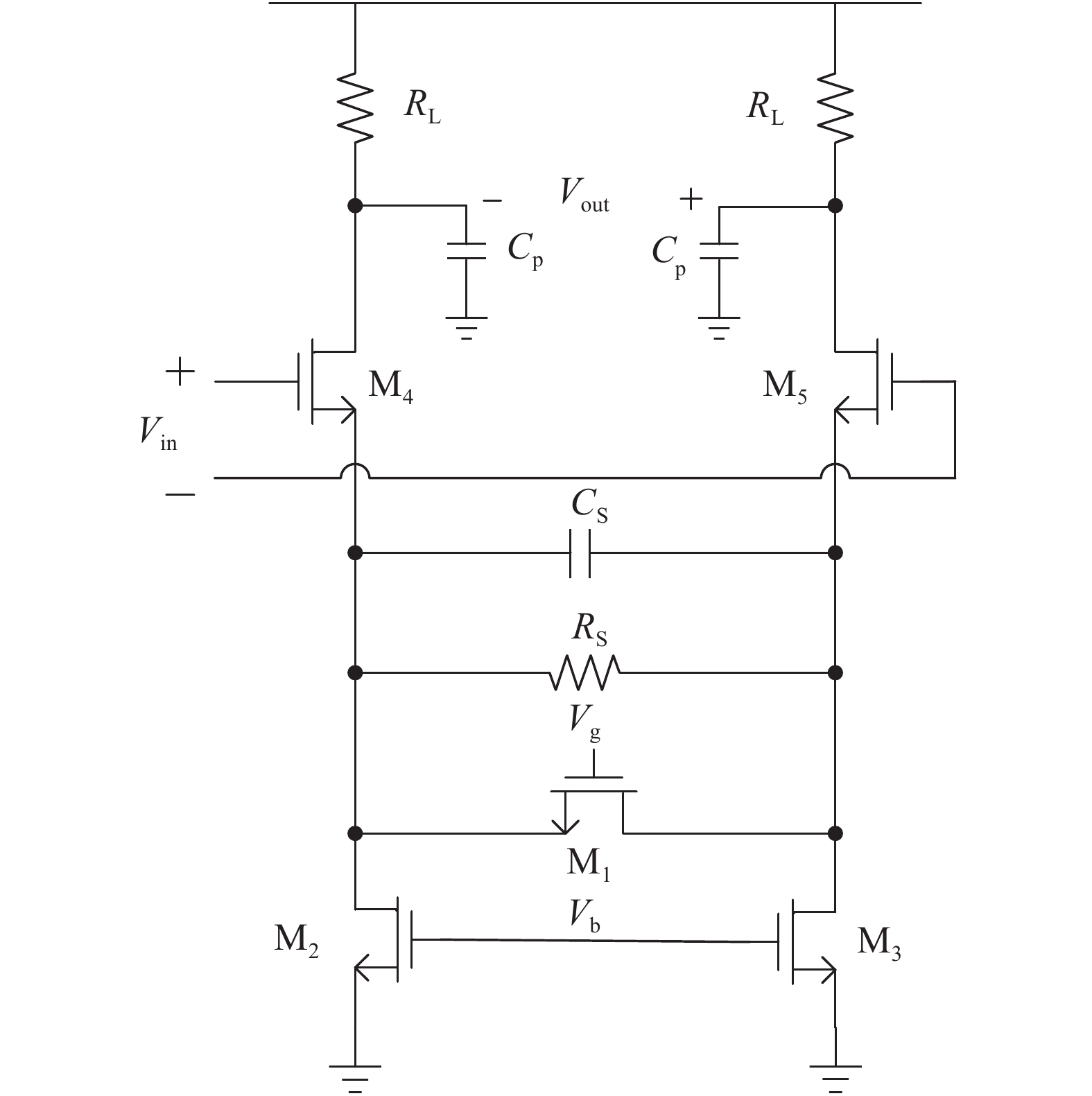
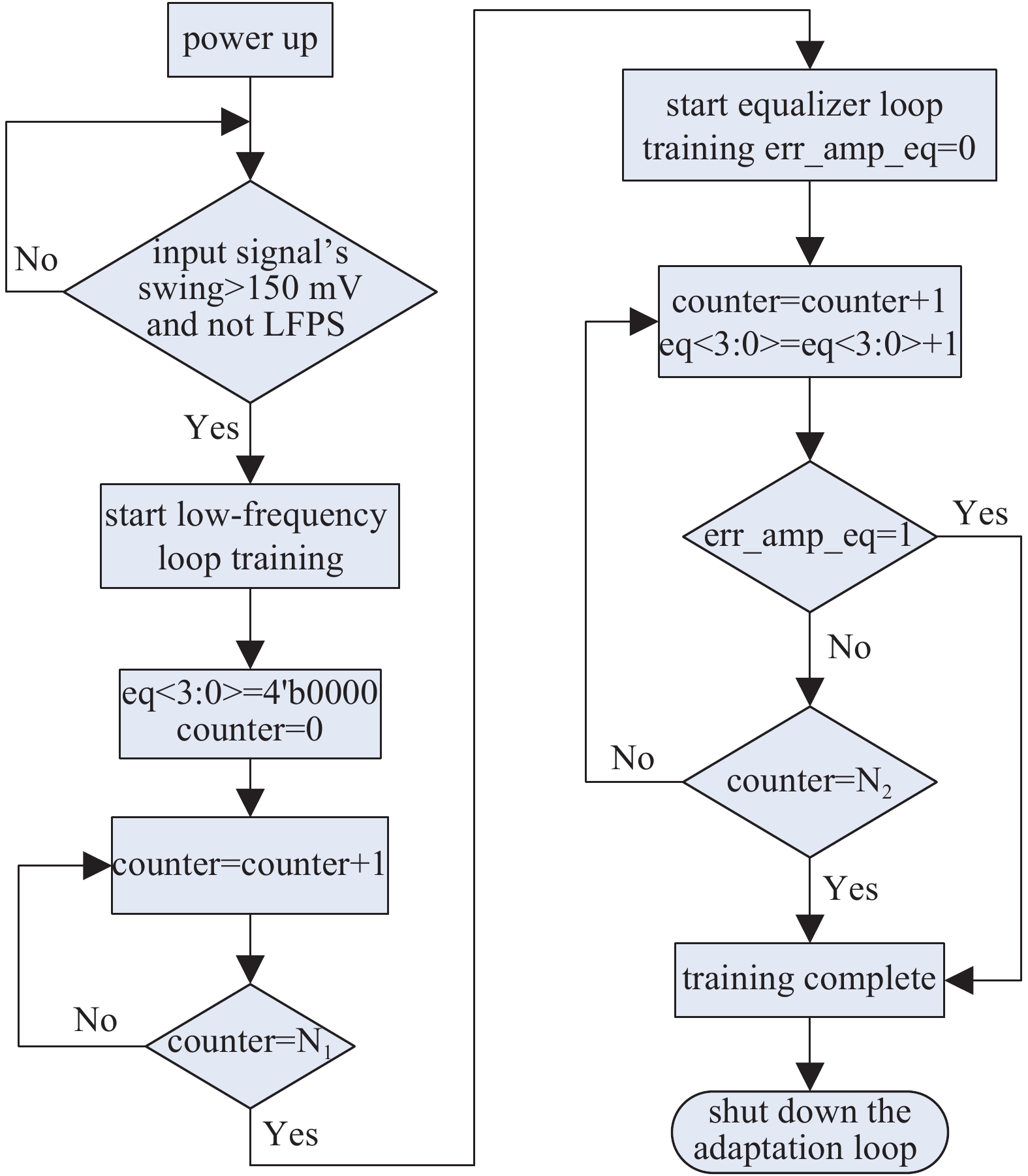
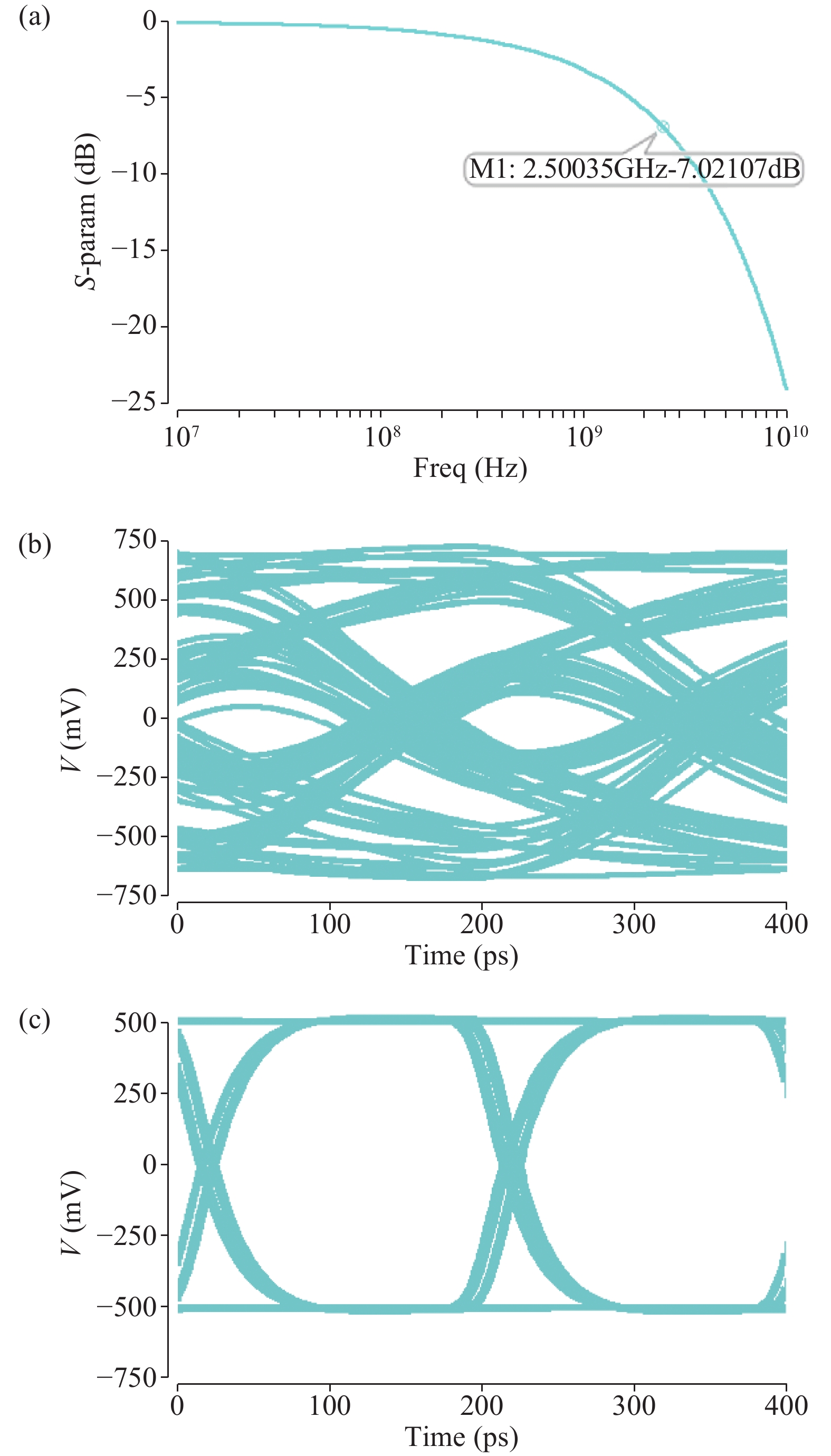
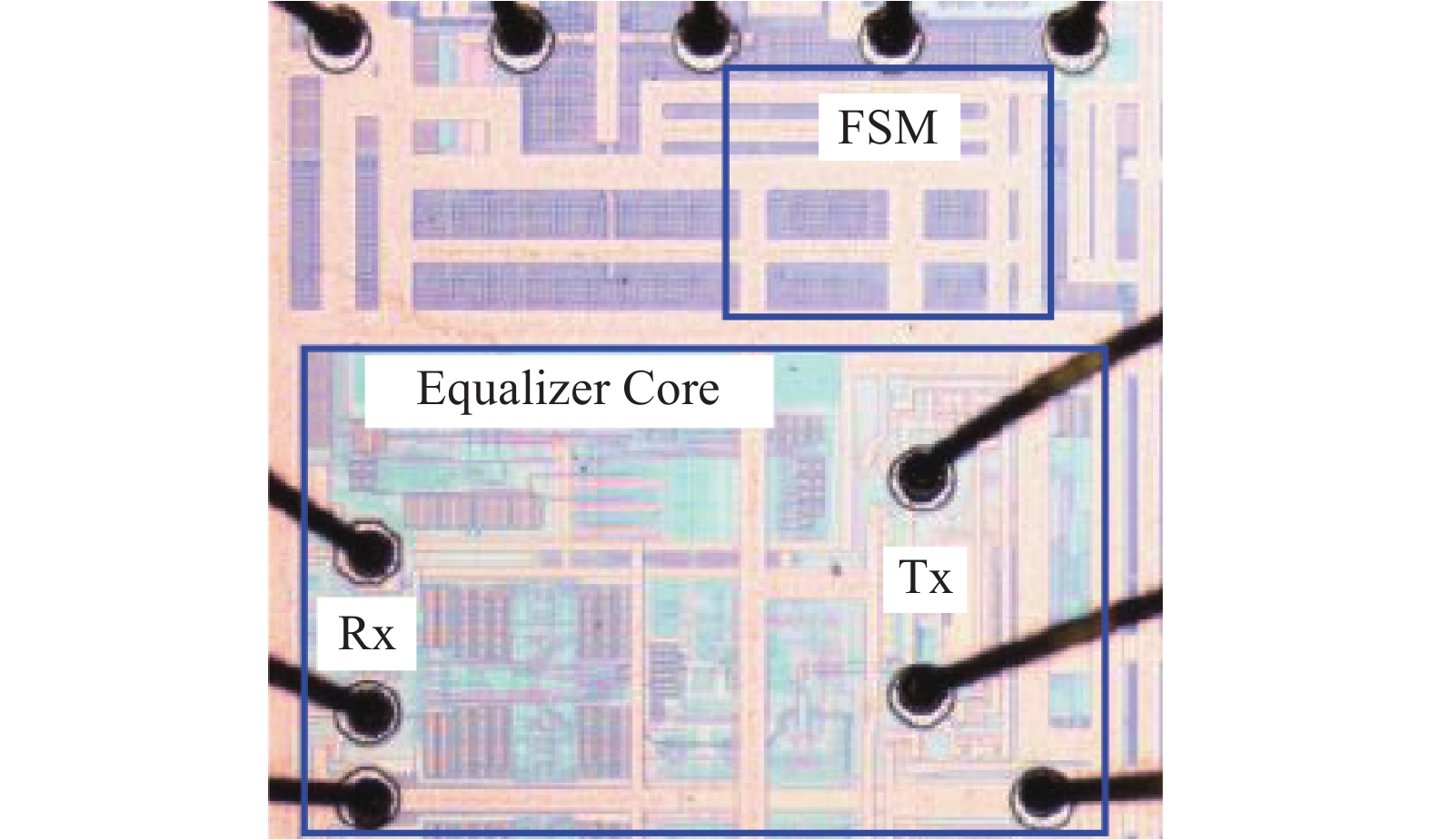
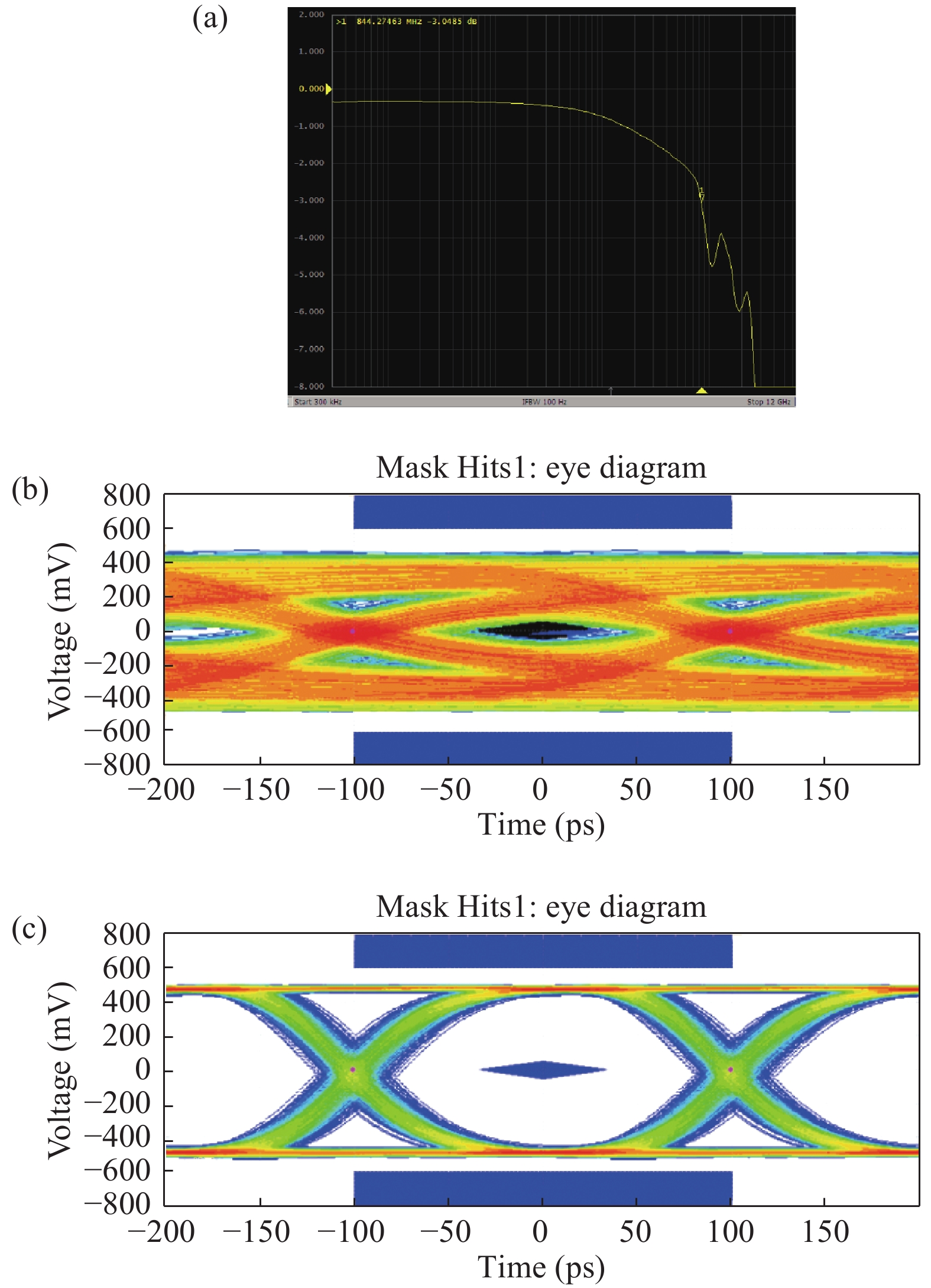
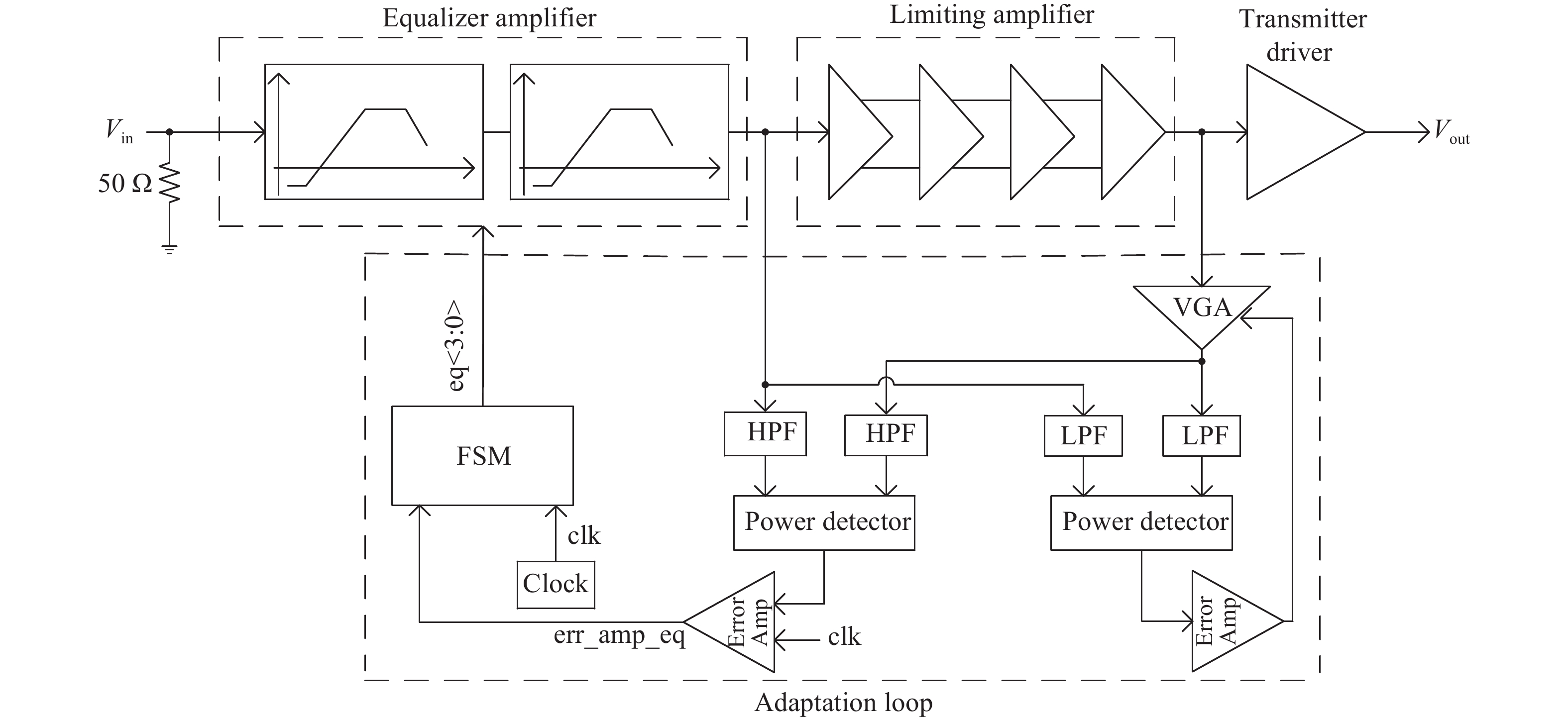
A 5 Gb/s adaptive equalizer with a new adaptation scheme is presented here by using 0.13 μm CMOS process. The circuit consists of the combination of equalizer amplifier, limiter amplifier and adaptation loop. The adaptive algorithm exploits both the low frequency gain loop and the equalizer loop to minimize the inter-symbol interference (ISI) for a variety of cable characteristics. In addition, an offset cancellation loop is used to alleviate the offset influence of the signal path. The adaptive equalizer core occupies an area of 0.3567 mm2 and consumes a power consumption of 81.7 mW with 1.8 V power supply. Experiment results demonstrate that the equalizer could compensate for a designed cable loss with 0.23 UI peak-to-peak jitter. -
References
[1] Fayed A A, Ismail M. A low-voltage low-power CMOS analog adaptive equalizer for UTP-5 cables. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I, 2008, 55(2): 480 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2008.916440[2] Gimeno C, Guerrero E, Sanchez-Azqueta C, et al. Multi-rate adaptive equalizer for transmission over up to 50-m SI-POF. IEEE Photonics Technol Lett, 2017, 29: 587 doi: 10.1109/LPT.2017.2670023[3] Gimeno C, Guerrero. A 1-V CMOS double loop continuous-time adaptive equalizer for short-haul optical networks. International Multi-Conference on Systems, Signals & Devices, 2014: 1[4] Ray S, Hella M. A 0.622–10 Gb/s inductorless adaptive linear equalizer with spectral tracking for data rate adaptation in 0.13-μm CMOS. Custom Integrated Circuits Conference, 2015: 1[5] Ajjaiah H B M, Hunagund P V, Rajesh R B. Adaptive filters in digital transmission based on improved LMS algorithm. International Conference on Wireless Communications, Signal Processing and Networking, 2016: 985[6] Gimeno C, Sanchez-Azqueta C, Guerrero E, et al. A 2.5-Gb/s multi-rate continuous-time adaptive equalizer for short reach optical links. European Solid-State Circuits Conference, 2015: 44[7] Gondi S, Lee J, Takeuchi D, et al. A 10 Gb/s CMOS adaptive equalizer for backplane applications. ISSCC Dig Tech Papers, 2005: 328[8] Liu H, Wang Y, Xu C, et al. A 5-Gb/s serial-link redriver with adaptive equalizer and transmitter swing enhancement. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I, 2014, 61(4): 1001 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2013.2283675[9] Tsai Y, Cheng K, Wu Y. A CMOS adaptive equalizer using low-voltage zero generators technique. Proc IEEE, 2010: 546[10] Gasca C G, Pueyo S C, Chagoyen C A. CMOS continuous-time adaptive equalizers for high-speed serial links. Springer, 2015[11] Sonna P, Carrer H. Broadband programmable equalizer and limiting amplifier for an XFI interface in 45 nm CMOS. Argentine School of Micro-Nanoelectronics, Technology and Applications, 2009: 77[12] Sackinger E, Fischer W C. A 3-GHz 32-dB CMOS limiting amplifier for SONET OC-48 receivers. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2000, 35(12): 1884 doi: 10.1109/4.890301[13] Kim Y H, Kim Y J, Lee T, et al. A 21-gbit/s 1.63-pj/bit adaptive CTLE and one-tap DFE with single loop spectrum balancing method. IEEE Trans Very Large Scale Integr Syst, 2016, 24(2): 789 doi: 10.1109/TVLSI.2015.2418579[14] Lin Y F, Huang C C, Lee J Y M, et al. A 5–20 Gb/s power scalable adaptive linear equalizer using edge counting. Solid-State Circuits Conference, 2015: 273[15] Pan Q, Wang Y, Lu Y, et al. An 18-Gb/s fully integrated optical receiver with adaptive cascaded equalizer. IEEE J Sel Topics Quantum Electron, 2016, 22(6): 1[16] Gimeno C, Guerrero E, Sánchez-Azqueta C, et al. Continuous-time linear equalizer for multigigabit transmission through SI-POF in factory area networks. IEEE Trans Ind Electron, 2015, 62(10): 6530 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2015.2427123 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: