| Citation: |
Tongqiang Gao, Zhenxiong Chen, Siqi Zhao, Haigang Yang, Xinxia Cai. A BFSK and OOK IF demodulation circuit with 2.8 μs settling time and re-configurable image rejection functions for MICS/BCC applications[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2018, 39(7): 075001. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/39/7/075001
****
T Q Gao, Z X Chen, S Q Zhao, H G Yang, X X Cai, A BFSK and OOK IF demodulation circuit with 2.8 μs settling time and re-configurable image rejection functions for MICS/BCC applications[J]. J. Semicond., 2018, 39(7): 075001. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/39/7/075001.
|
A BFSK and OOK IF demodulation circuit with 2.8 μs settling time and re-configurable image rejection functions for MICS/BCC applications
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/39/7/075001
More Information
-
Abstract
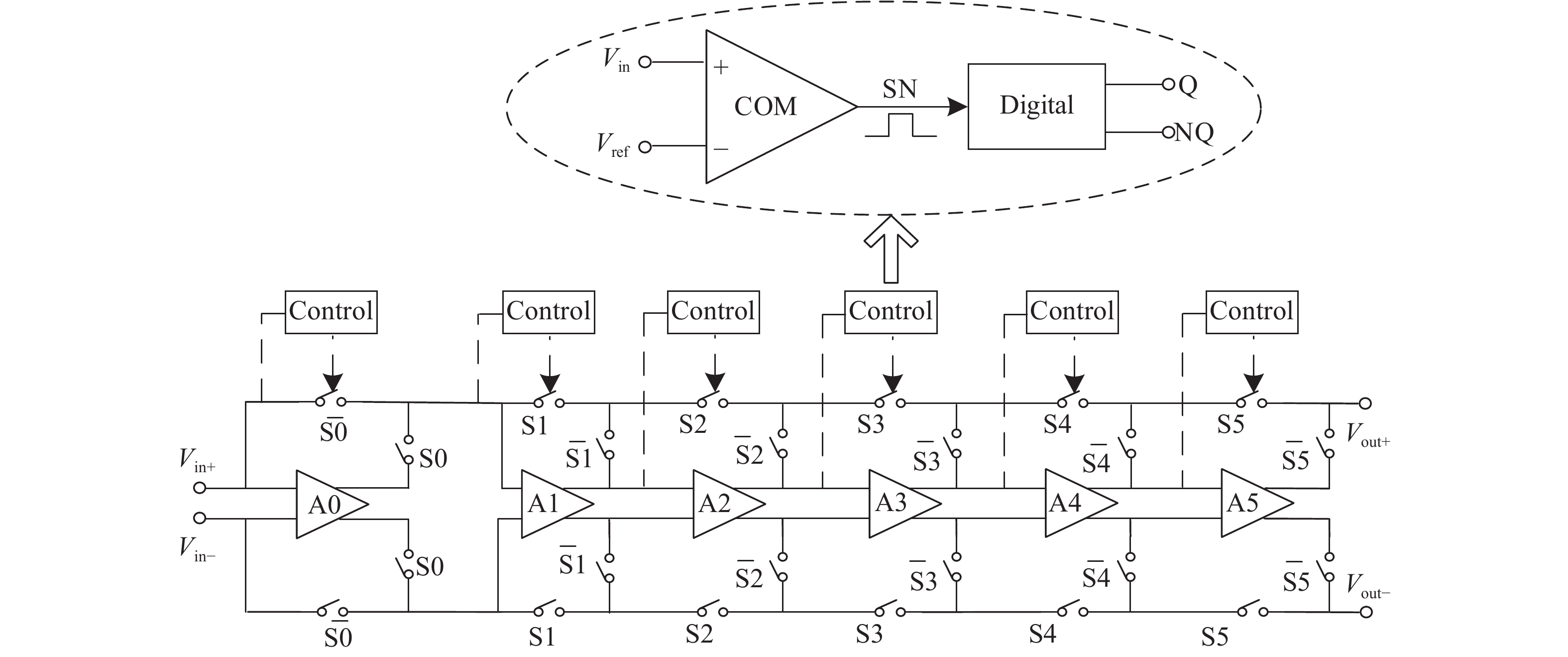
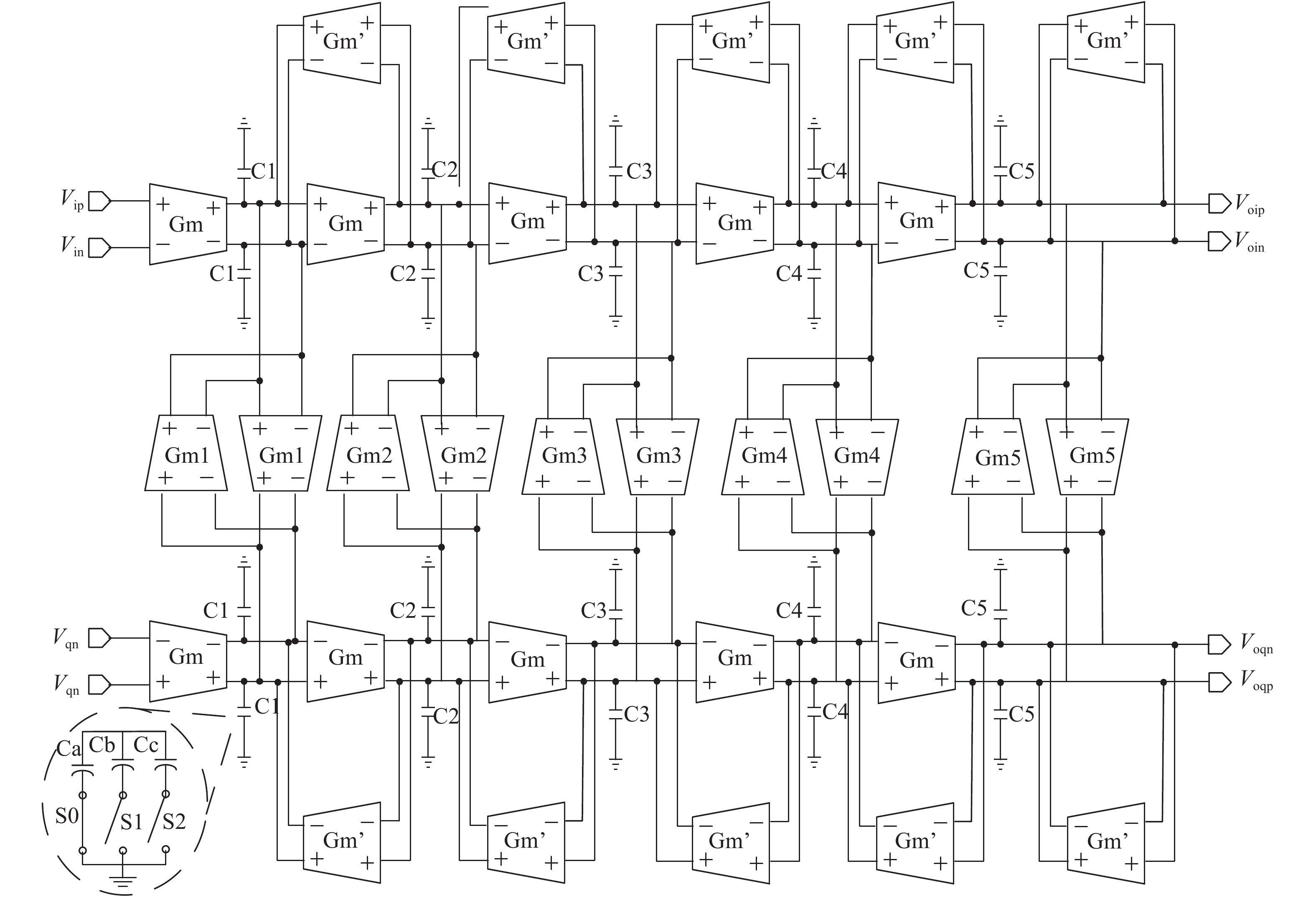
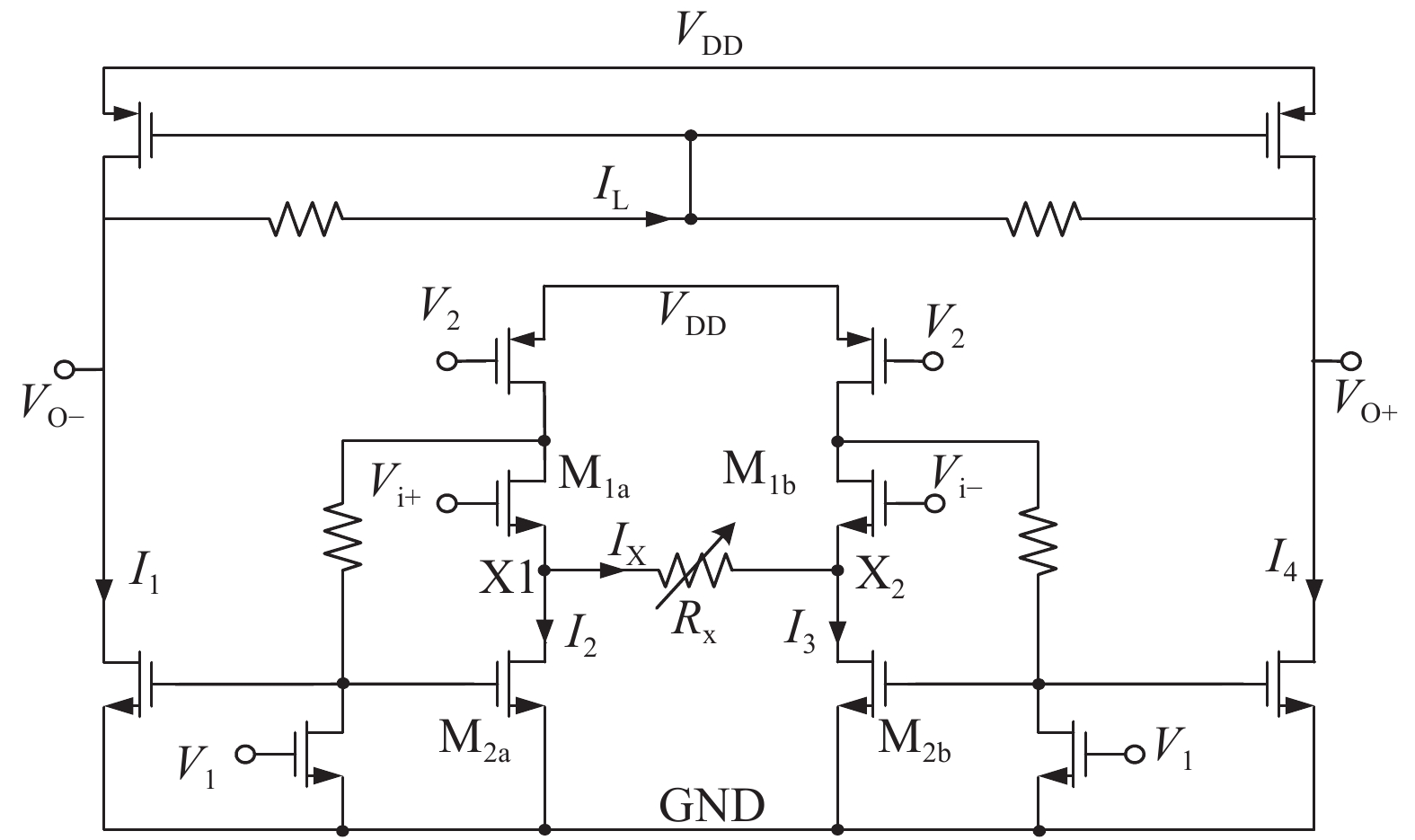
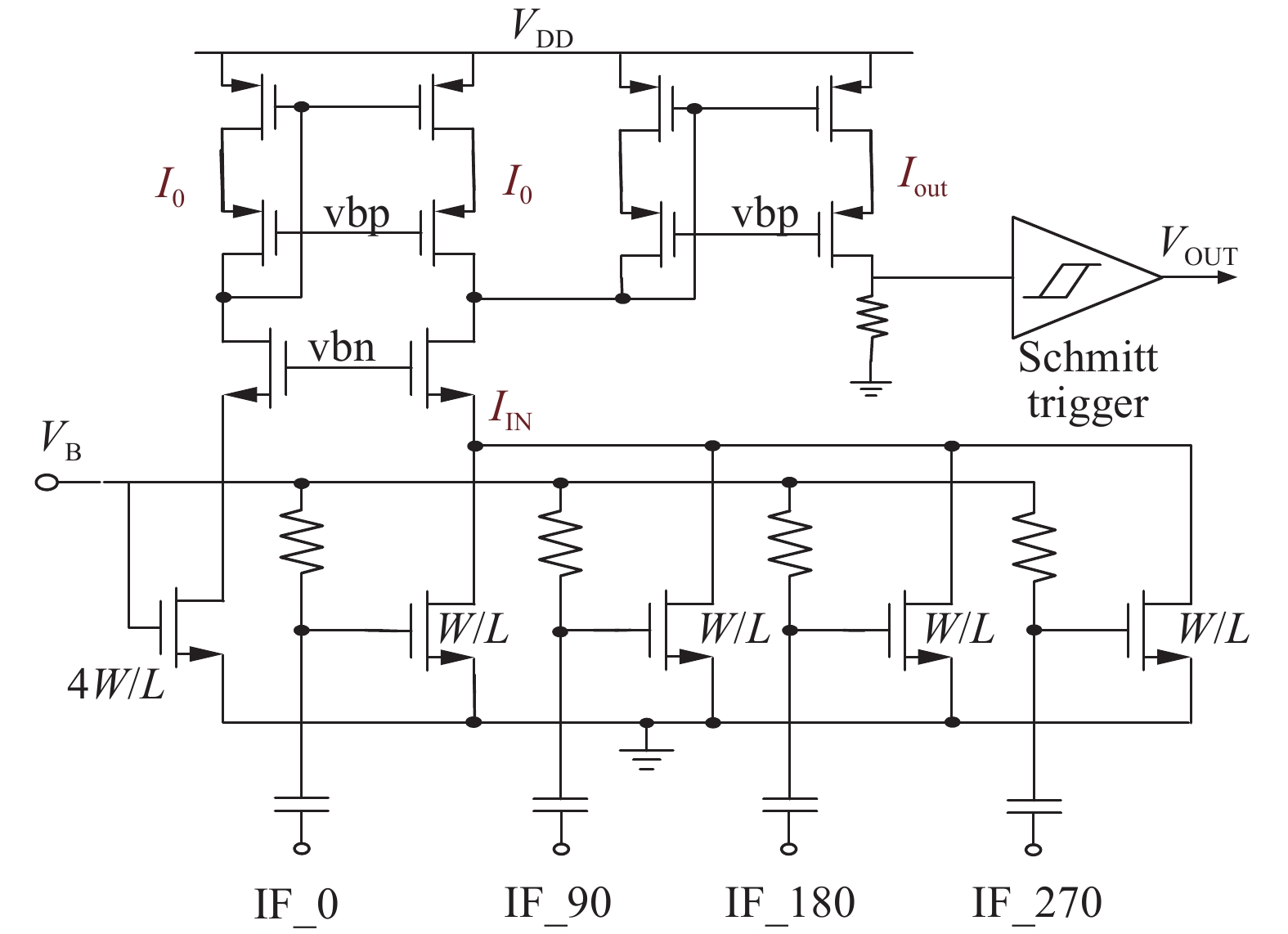
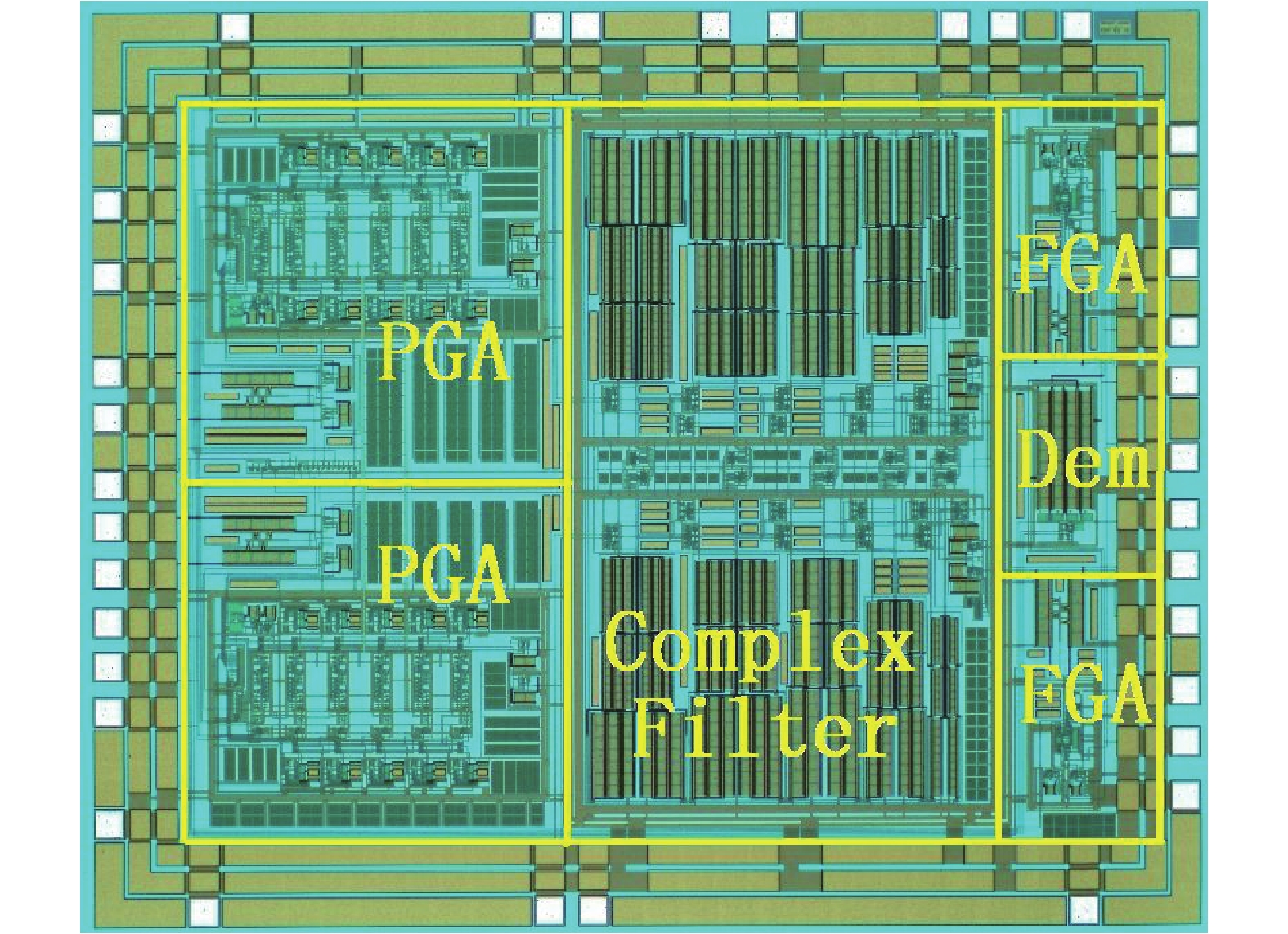
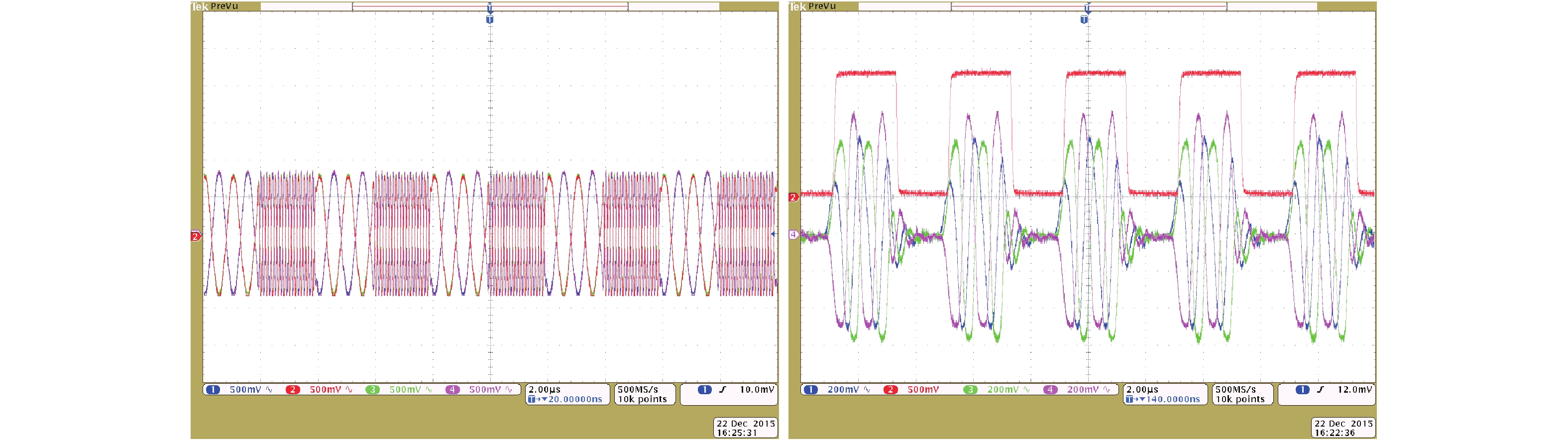
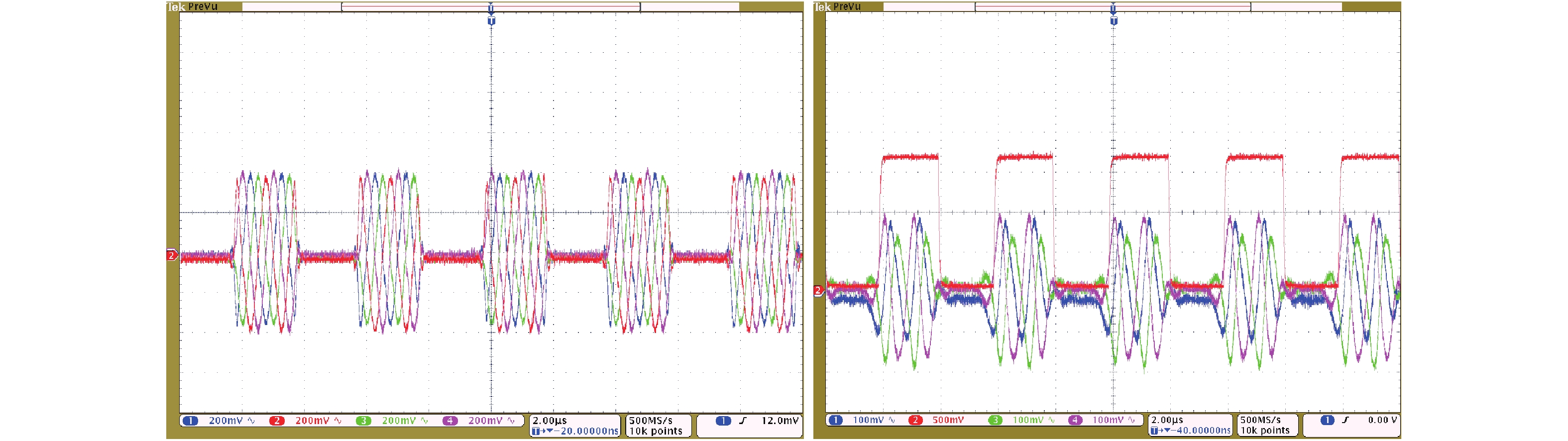
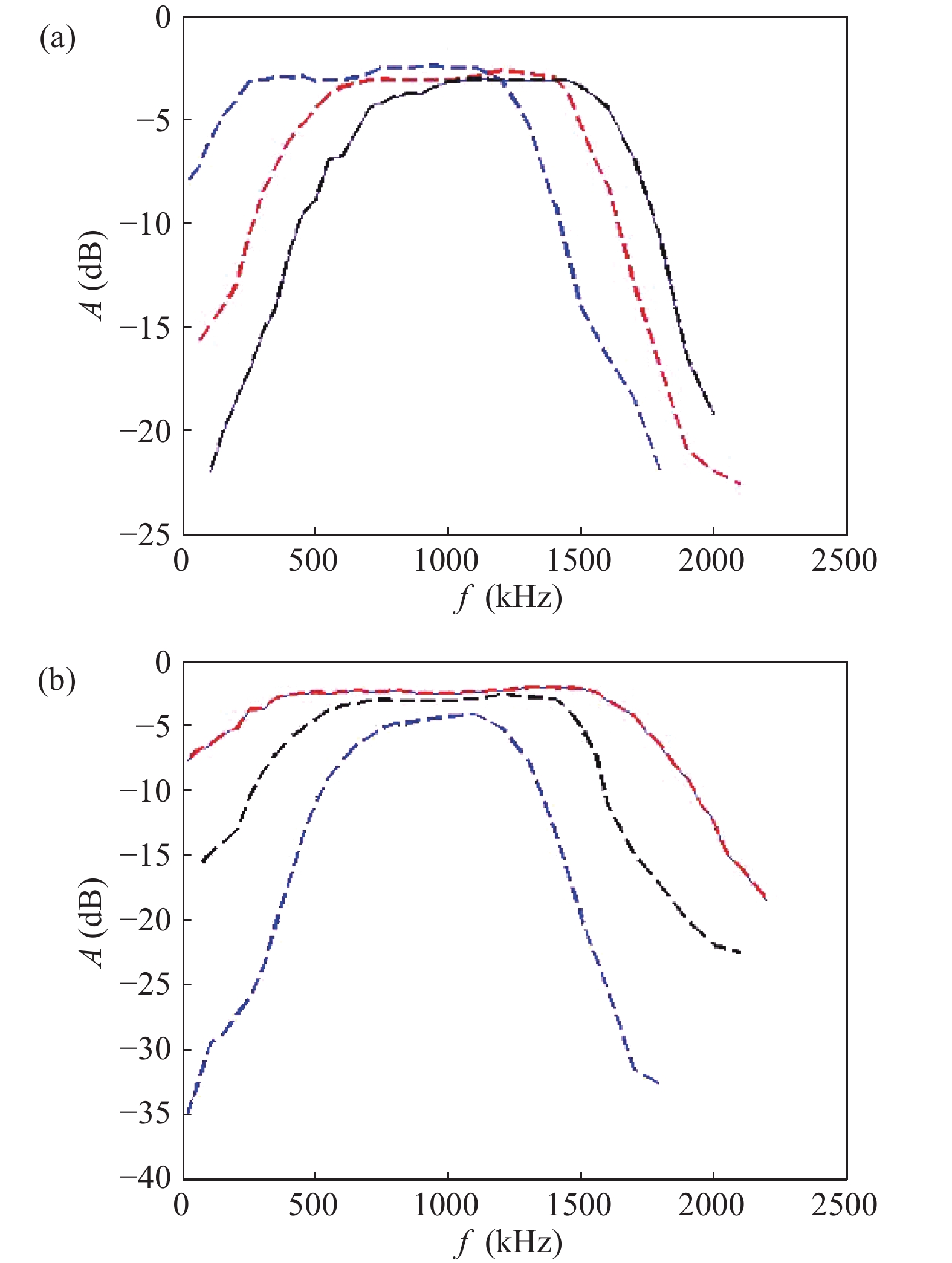
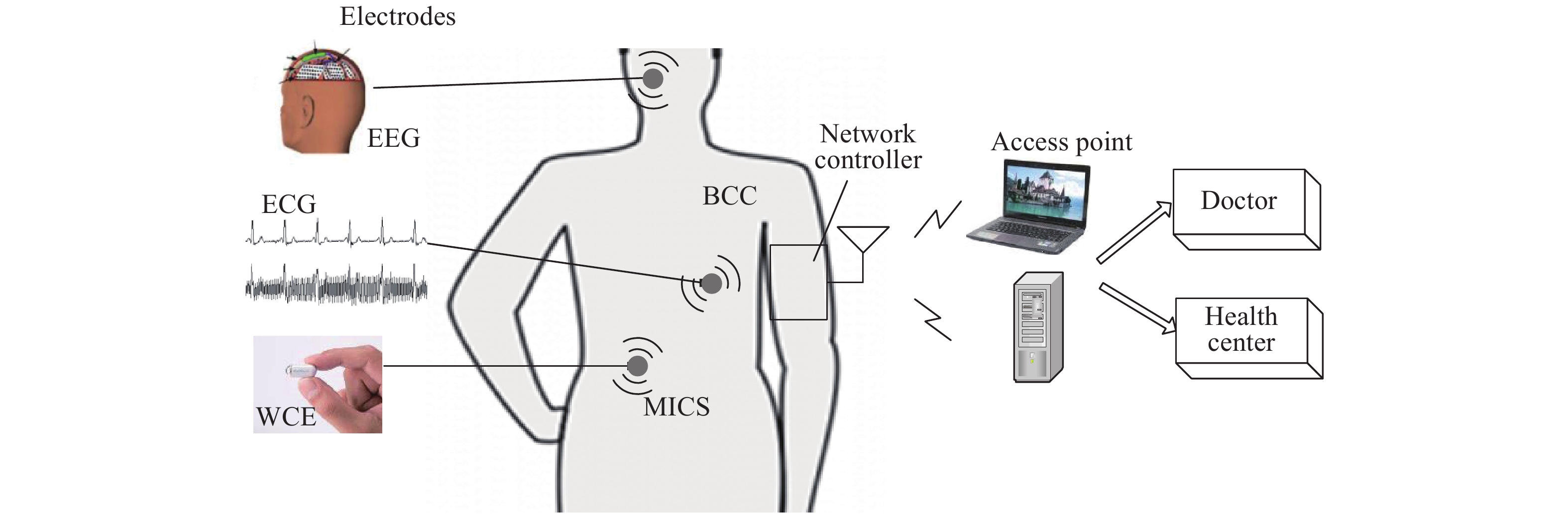
A BFSK and OOK IF base-band circuit is provided to implement the low-IF RF receivers for a dual-band MICS/BCC network controller. In order to transfer the massive vital data immediately, the IF circuit is comprised of the fast-settling feed-forward programmable gain amplifier (PGA), a Gm–C complex filter, the fixed gain amplifier (FGA) and a 4-input " quadratic sum” demodulator. A novel auto-switched coarse gain-setting method is adopted in the PGA to enhance the reaction speed and narrow the output signal range. Also the PGA does not suffer the same stability constraint as open-loop topologies. The complex filter fulfills the function of image rejection, in which the center frequency and bandwidth can be adjusted individually. The FGA is used to ameliorate the linearity and the ‘quadratic sum’ demodulator can reduce the overall power consumption. The designed IF circuit is fabricated with SMIC 0.18 μm CMOS process. The chip area is about 5.36 mm2. Measurement results are given to verify the design goals.-
Keywords:
- low-IF receiver,
- VGA,
- complex filter,
- MICS,
- BCC
-
References
[1] Body Area Network (BAN), IEEE 802.15 WPANTM Task Group 6, Nov. 2007[2] Tino C, Seungkee M, Sridhar S, et al. A CMOS low-power transceiver with reconfigurable antenna interface for medical implant applications. IEEE Trans Microwave Theory Tech, 2011, 59(5): 1369 doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2011.2116036[3] Cho N, Bae J, Yoo H J. A 10.8 mW, body channel communication/MICS dual-band transceiver for a unified body sensor network controller. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2009, 44(12): 3459 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2009.2032592[4] Hsieh J Y, Huang Y C, Kuo P H, et al. A 0.45-V low-power OOK/FSK RF receiver in 0.18 μm CMOS technology for implantable medical applications. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I, 2016, 63(8): 1123 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2016.2589338[5] Mohamed Z, Mohamed S. A low-power dual-injection-locked RF receiver with FSK-to-OOK conversion for biomedical implants. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I, 2015, 62(11): 2748 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2015.2477577[6] FCC Rules and Regulations, MICS Band Plan, Part 95, 2003[7] Ilku N, Kyudon C, Joonhee L, et al. A 2.4 GHz low-power low-IF receiver and direct-conversion transmitter in 0.18-μm CMOS for IEEE 802.15.4 WPAN applications. IEEE Trans Microwave Theory Tech, 2007, 55(4): 682 doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2007.893646[8] Masaki K, Takashi T, Tadashi M, et al. A low-IF/Zero-IF re-configurable analog baseband IC with an I/Q imbalance cancellation scheme. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2011, 46(3): 572 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2010.2102510[9] Juan P A P, Belen C, Santiago C. A high-performance CMOS feedforward AGC circuit for a WLAN receiver. IEEE Trans Ind Electron, 2010, 57(8): 2851 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2009.2036021[10] Cheng X, Yang H G, Gao T Q, et al. A feed-forward AGC Circuits with 48 dB-gain range, 1.2 μs minimum settling time for WiMAX receiver. Analog Integr Cir Sig Process, 2013, 76(1): 61 doi: 10.1007/s10470-013-0076-0[11] OKjune J, Robert M F, Brent A M. Analog AGC circuitry for a CMOS WLAN receiver. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits, 2006, 41(10): 2291 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2006.881548[12] Cheng X, Yang H G, Gao T Q, et al. A CMOS Gm–C complex filter with re-configurable centre and cutoff frequencies in wimax receivers. J Semicond, 2013, 34(7): 075004 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/7/075004[13] Liu J H, Li C, Chen L, et al. An ultra-low power 400 MHz OOK transceiver for medical implanted applications. ESSCIRC, 2011: 175[14] Wang X M, Chi N Y, Wang Z H. A low-power high-data-rate ASK IF receiver with a digital-control AGC loop. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Ⅱ, 2010, 57(8): 617[15] Yin Y, Yang Y, Zhang L. A low-power low-cost 780 MHz CMOS FSK receiver for short-range wireless communication. Chin J Electron, 2016, 25(2): 220 doi: 10.1049/cje.2016.03.005 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: