| Citation: |
P Mallika Bramaramba Devi, G. Phaneendra Reddy, K. T. Ramakrishna Reddy. Structural and optical studies on PVA capped SnS films grown by chemical bath deposition for solar cell application[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2019, 40(5): 052101. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/40/5/052101
****
P M B Devi, G P Reddy, K T R Reddy, Structural and optical studies on PVA capped SnS films grown by chemical bath deposition for solar cell application[J]. J. Semicond., 2019, 40(5): 052101. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/40/5/052101.
|
Structural and optical studies on PVA capped SnS films grown by chemical bath deposition for solar cell application
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/40/5/052101
More Information
-
Abstract
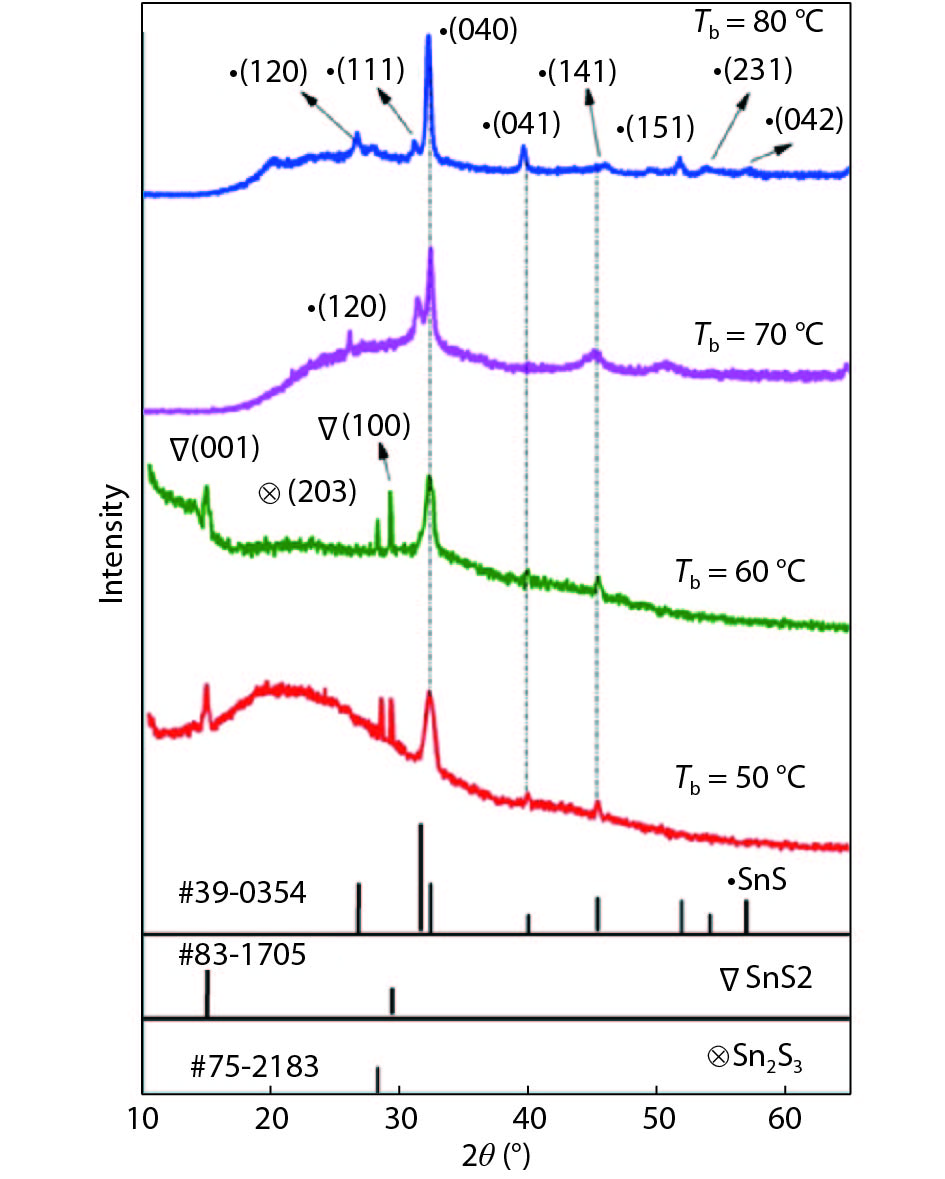
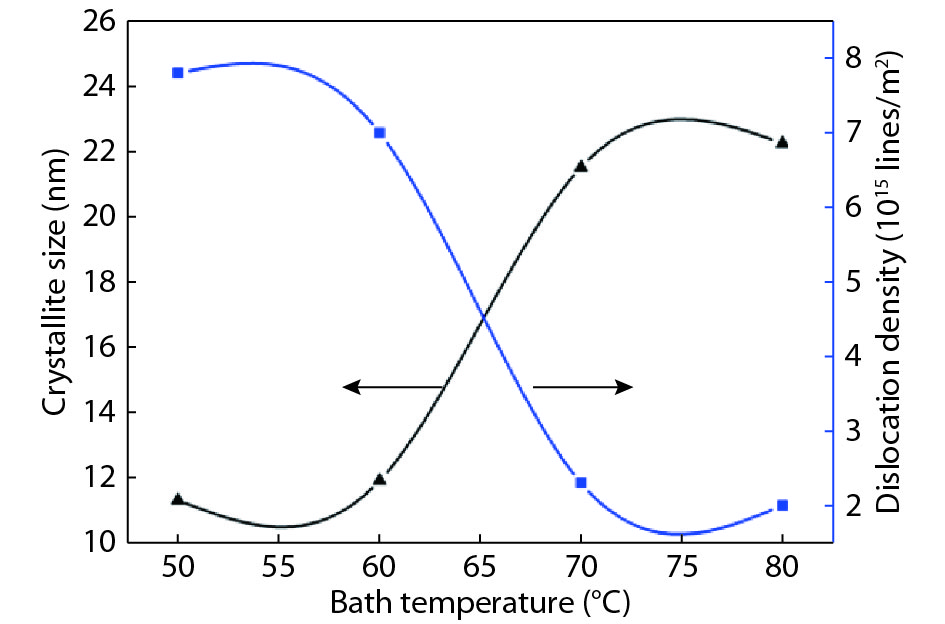
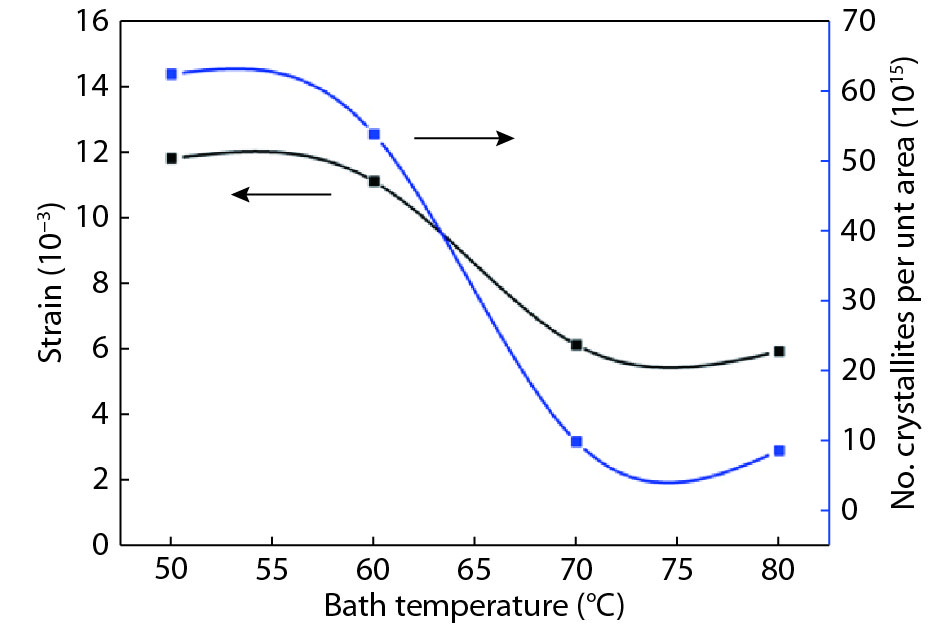
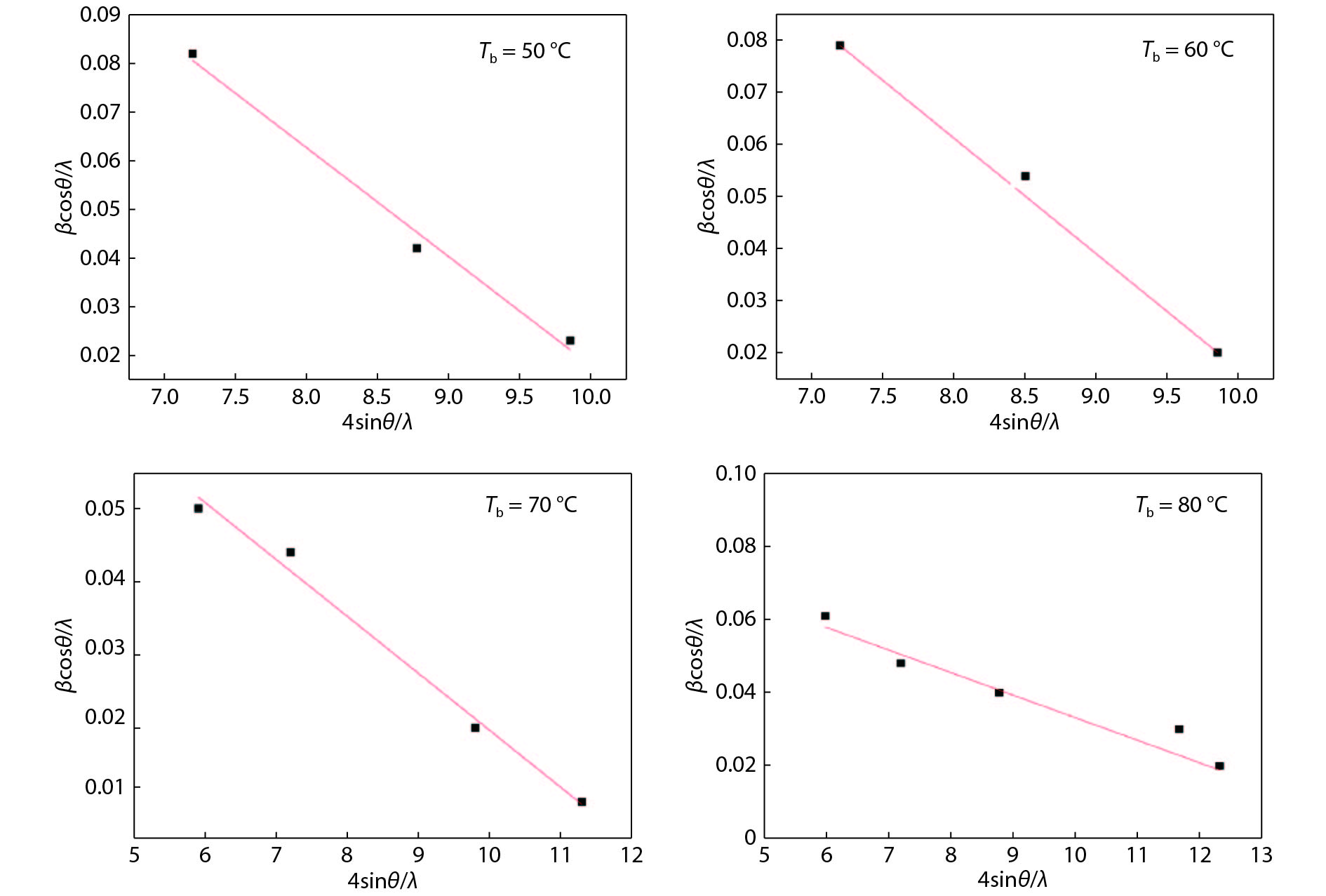
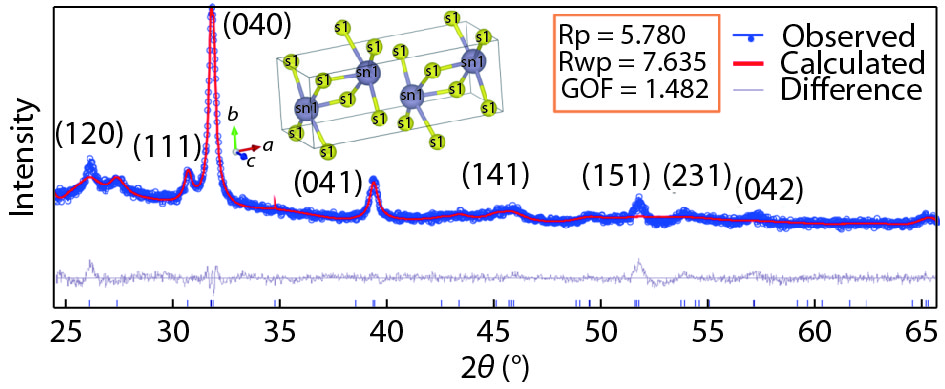
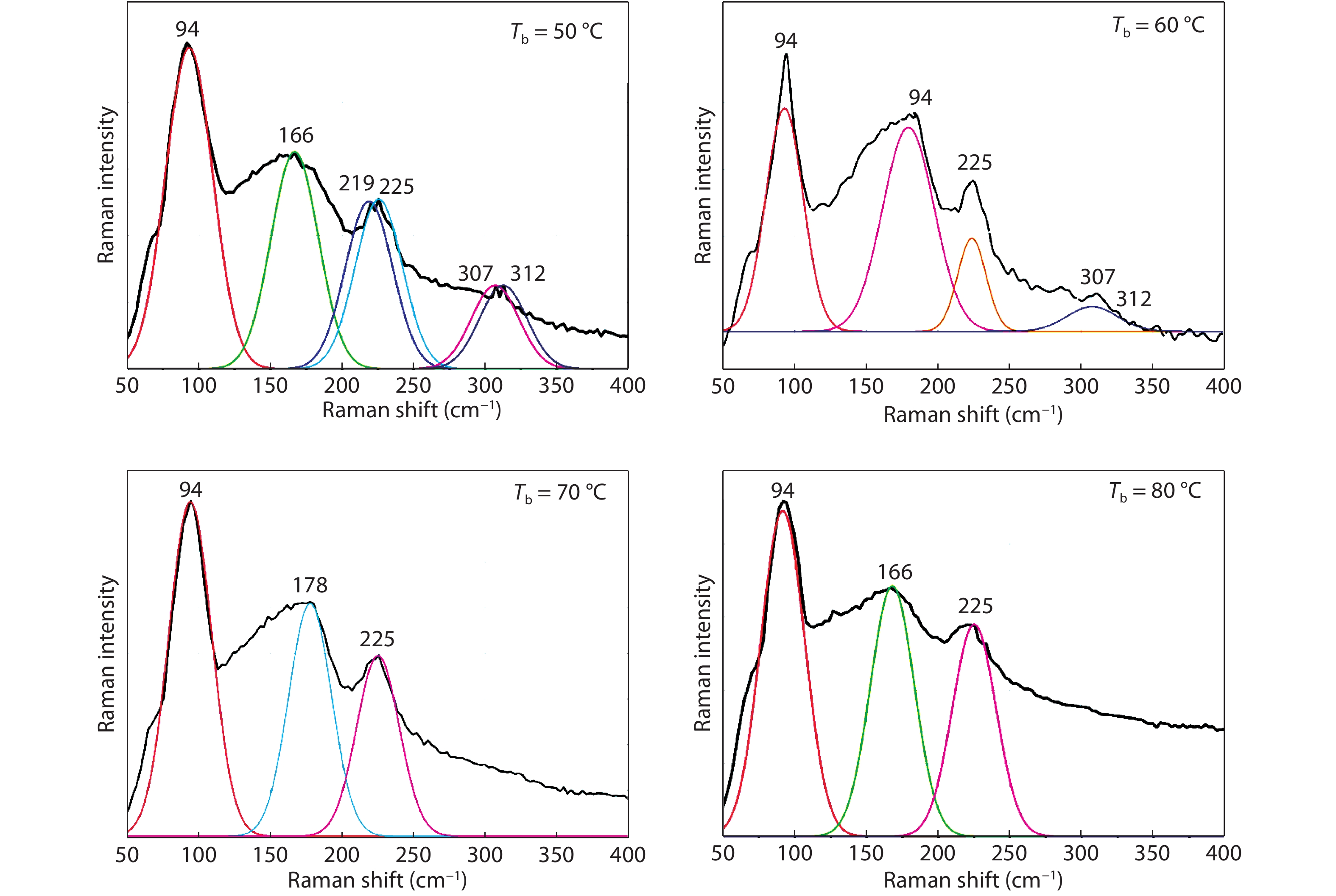
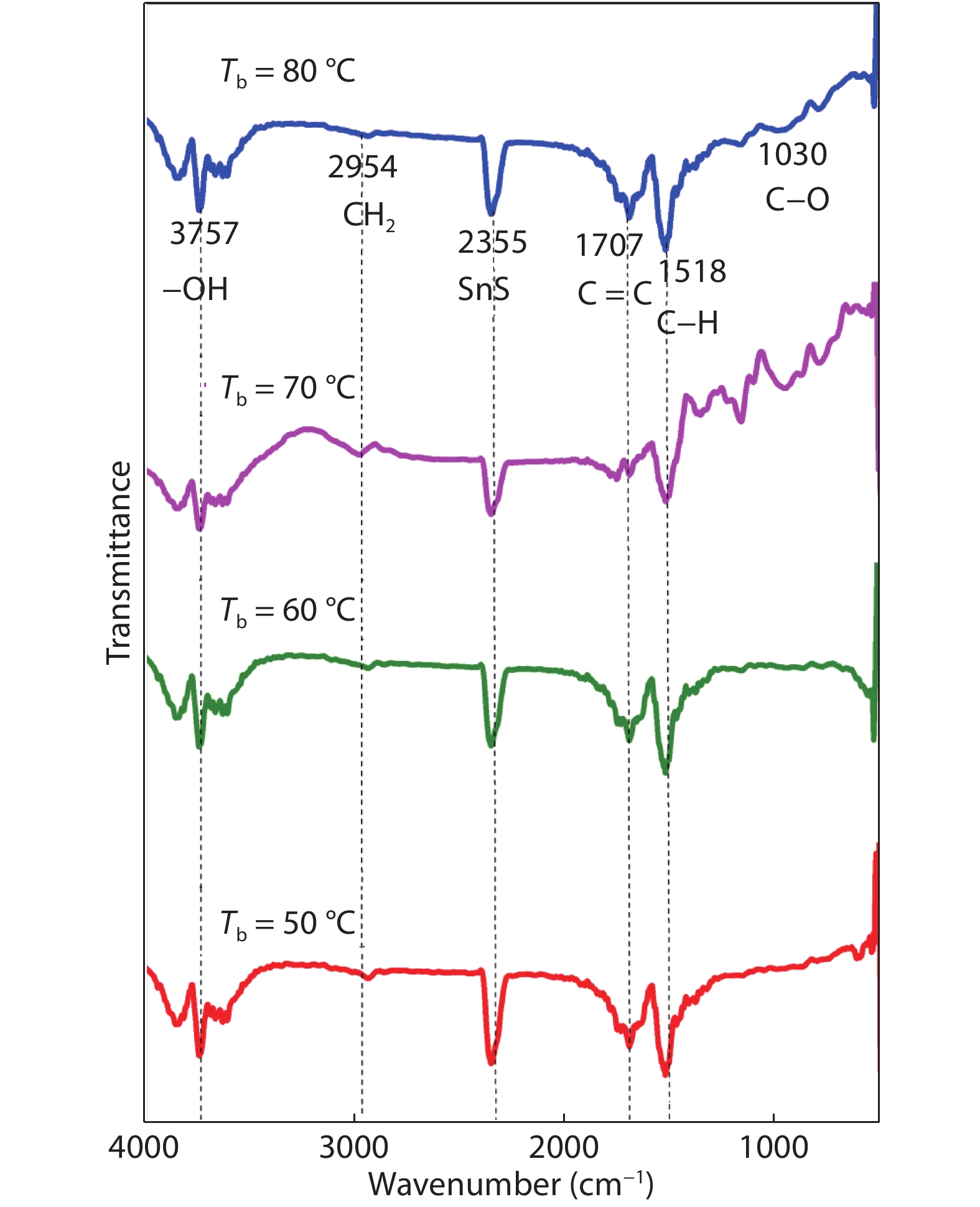
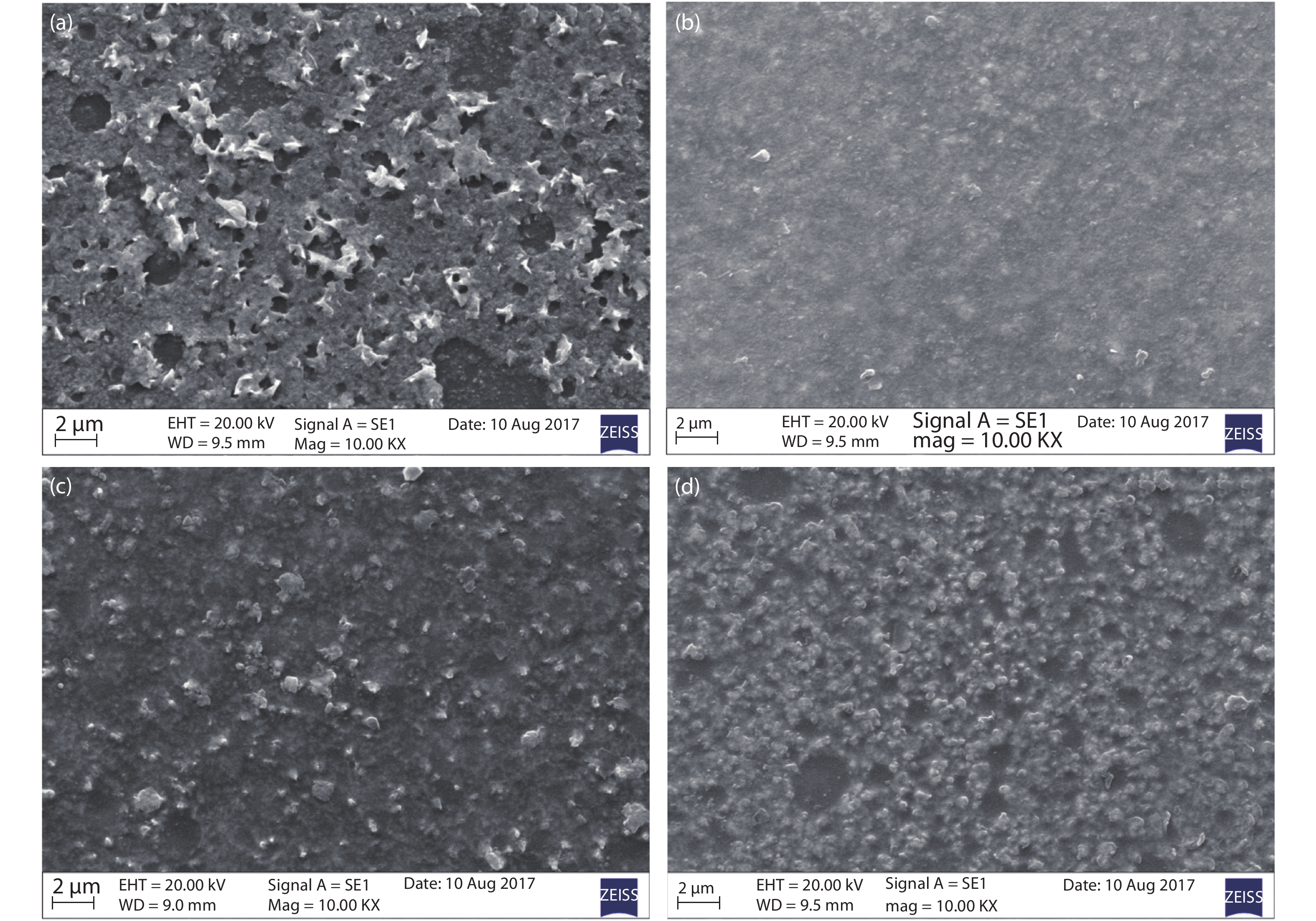
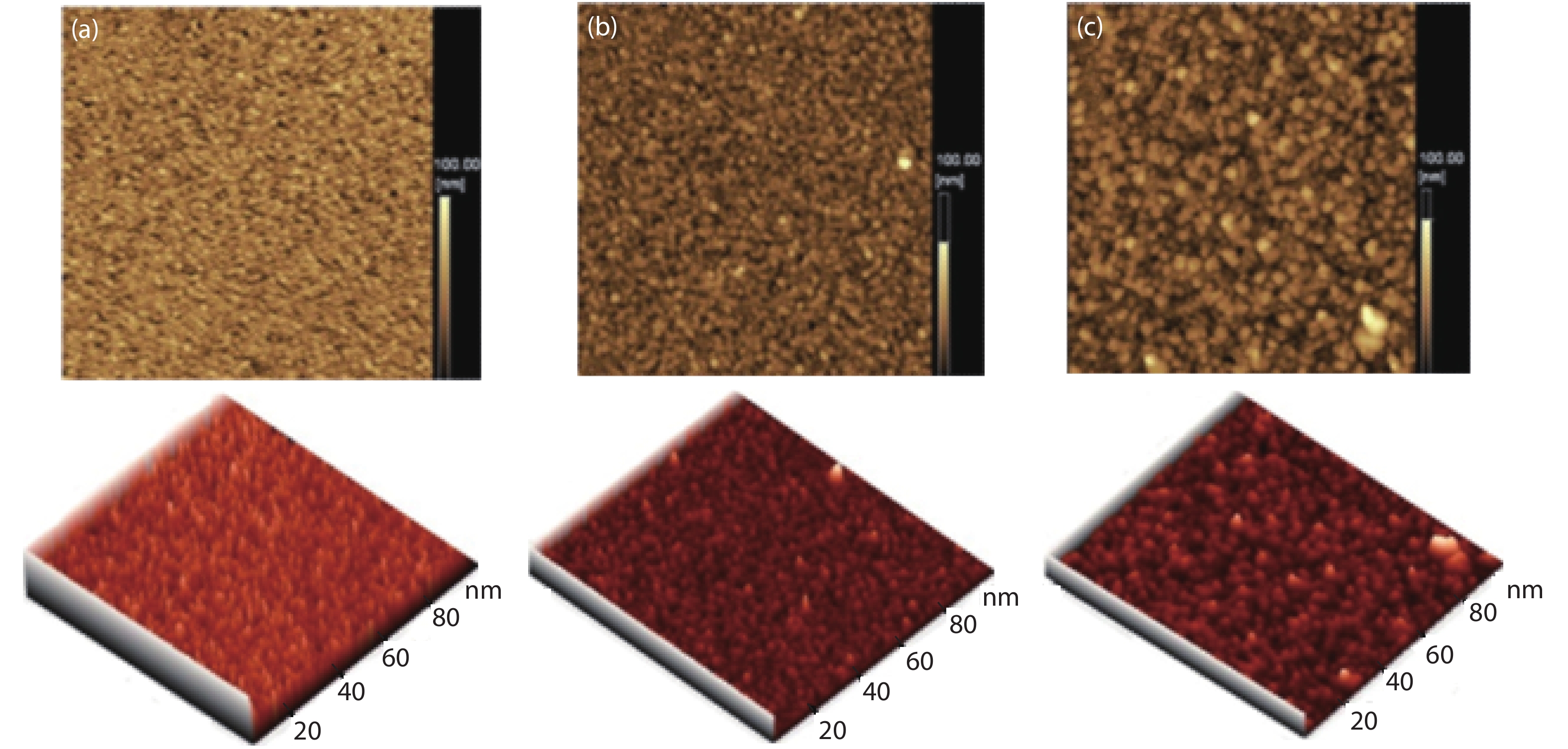
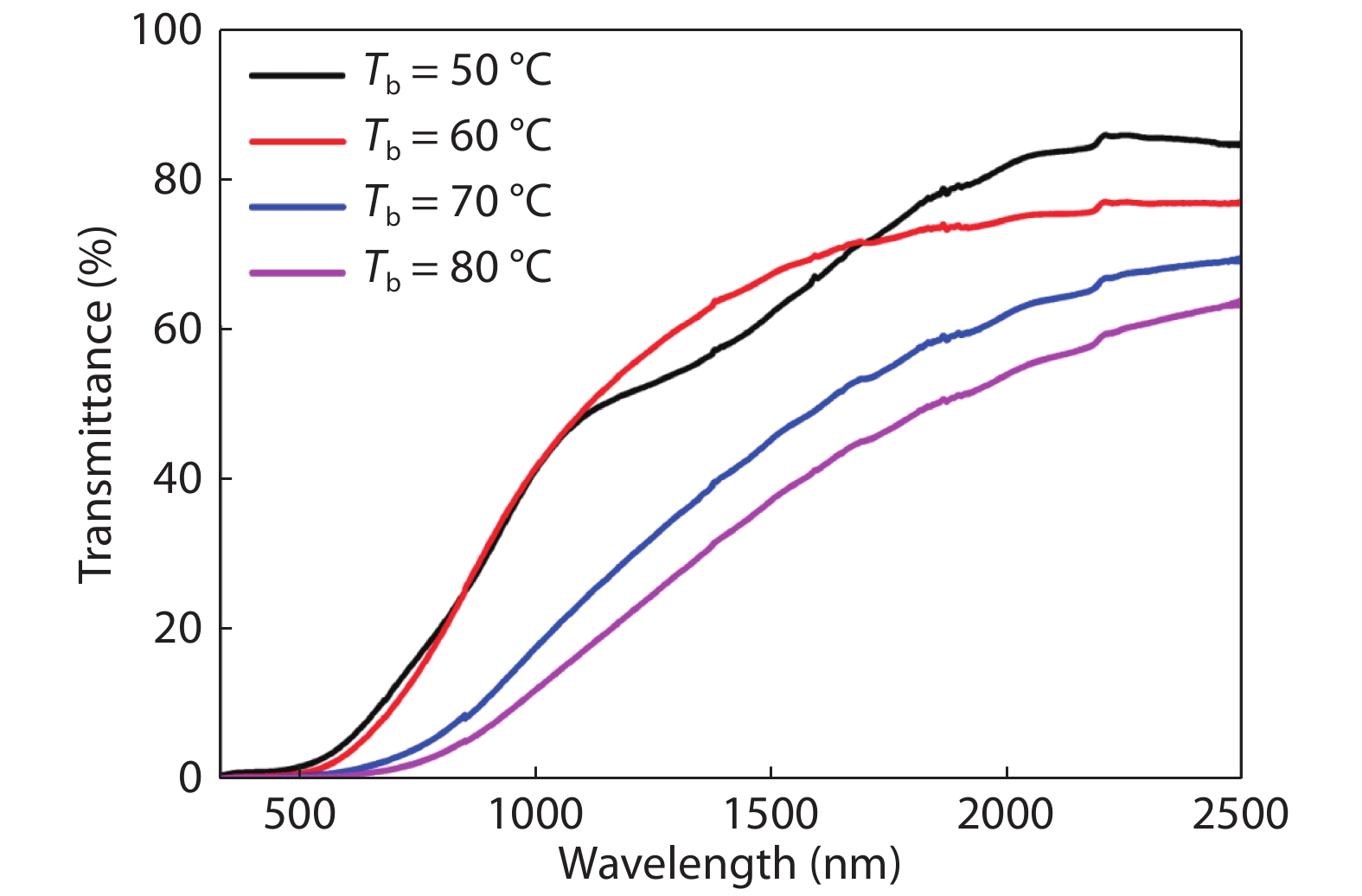
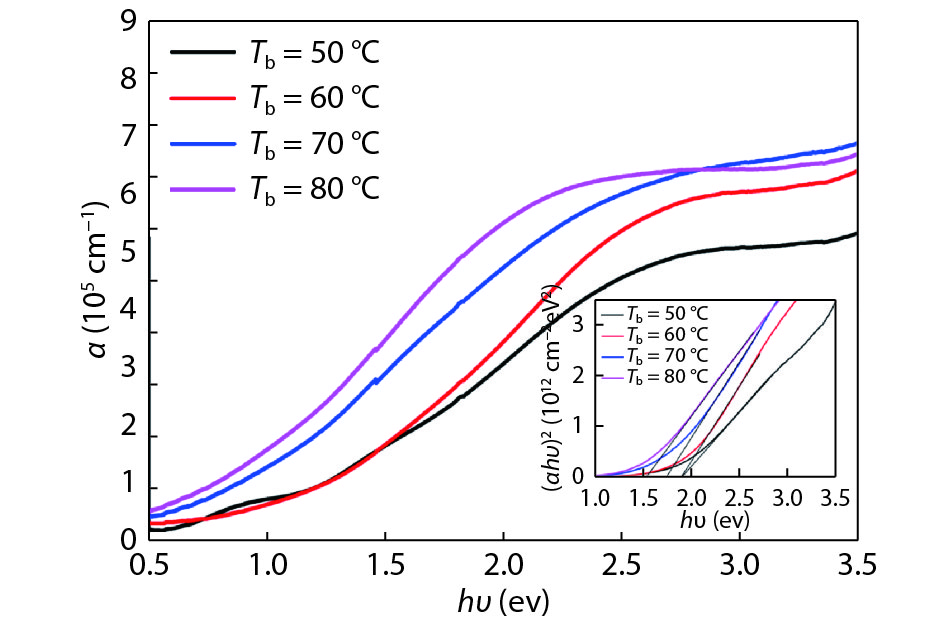
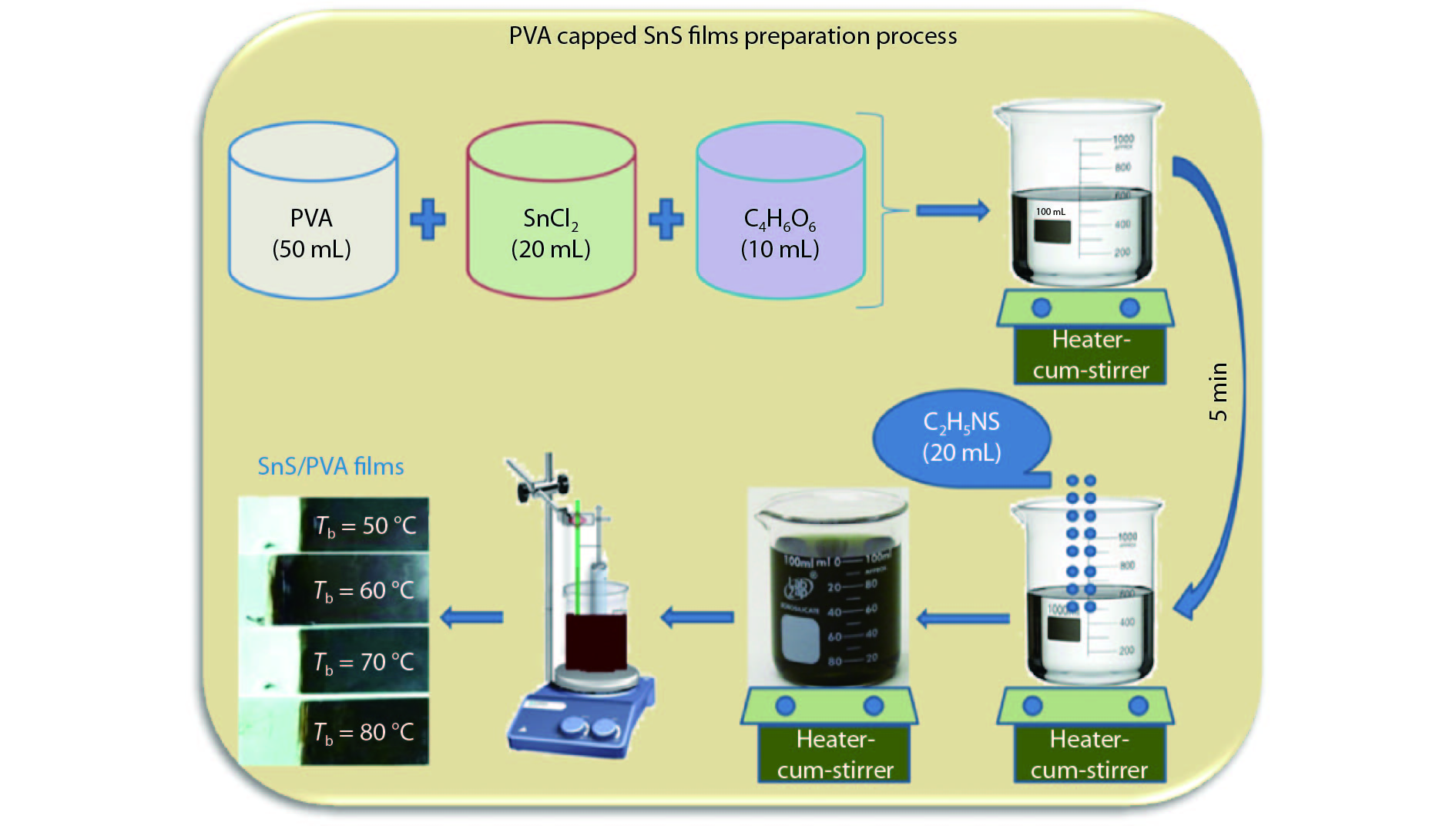
Tin monosulphide (SnS) thin films capped by PVA have been successfully deposited on glass substrates for cost effective photovoltaic device applications by a simple and low-cost wet chemical process, chemical bath deposition (CBD) at different bath temperatures varying in the range, 50–80 °C. X–ray diffraction analysis showed that the deposited films were polycrystalline in nature, showing orthorhombic structure with an intense peak corresponding to (040) plane of SnS. These observations were further confirmed by Raman analysis. FTIR spectra showed the absorption bands which corresponds to PVA in addition to SnS. The scanning electron microscopy and atomic force microscopy studies revealed that the deposited SnS films were uniform and nanostructured with an average particle size of 4.9 to 7.6 nm. The optical investigations showed that the layers were highly absorbing with the optical absorption coefficient ~105 cm–1. A decrease in optical band gap from 1.92 to 1.55 eV with an increase of bath temperature was observed. The observed band gap values were higher than the bulk value of 1.3 eV, which might be due to quantum confinement effect. The optical band gap values were also used to calculate particle size and the results are discussed. -
References
[1] Kana A T, Hibbert T G, Mahon M F, et al. Organotin unsymmetric dithiocarbamates: Synthesis, formation and characterization of tin (II) sulphide films by atmospheric pressure chemical vapour deposition. Polyhedron, 2001, 20, 2989 doi: 10.1016/S0277-5387(01)00908-1[2] Reddy K T R, Reddy N K, Miles R W, et al. Photovoltaic properties of SnS based solar cells. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells, 2006, 90, 3041 doi: 10.1016/j.solmat.2006.06.012[3] Guneri E, Gode F, Ultas C, et al. Effect of deposition time on structural, electrical, optical properties of SnS thin films deposited by chemical bath deposition. App Surf Sci, 2010, 257, 1189 doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2010.07.104[4] Reddy N K, Reddy K T R. Optical behaviour of sprayed tin sulphide thin films. Mater Res Bull, 2006, 41, 414 doi: 10.1016/j.materresbull.2005.08.001[5] Kawano Y, Chantana J, Minemoto T, et al. Impact of growth temperature on the properties of SnS films prepared by thermal evaporation and its photovoltaic performance. Curr Appl Phys, 2015, 15, 897 doi: 10.1016/j.cap.2015.03.026[6] Ganchev M, Vitanvov P, Sendova-Vassileva M, et al. Properties of SnS thin films grown by physical vapour deposition. J Phys: Conf Ser, 2016, 682, 012019 doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/682/1/012019[7] Cheng S, Chen Y, He Y, et al. The structure and properties of SnS thin films prepared by pulse electro deposition. Mater Lett, 2007, 61, 1408 doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2006.07.067[8] EI-Nahass M M, Zeyada H M, Aziz M S, et al. Optical properties of thermally evaporated SnS thin films. Opt Mater, 2002, 20, 159 doi: 10.1016/S0925-3467(02)00030-7[9] Andrade-Arvizu J A, Garcia-Sanchez M F, Courel-Piedrahita M, et al. Suited growth parameters including type of conductivity conversions on chemical spray pyrolysis synthesized SnS thin films. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis, 2016, 121, 347 doi: 10.1016/j.jaap.2016.08.016[10] Haraa K O, Suzuki S, Usami N, et al. Formation of metastable cubic phase in SnS thin films fabricated by thermal evaporation. Thin Solid Films, 2017, 639, 7 doi: 10.1016/j.tsf.2017.08.025[11] Tanusevski A, Poelman D. Optical and photoconductive properties of SnS thin films prepared by electron beam evaporation. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells, 2003, 80, 297 doi: 10.1016/j.solmat.2003.06.002[12] Ana V, Dronova M, Zakharov A, et al. Optical and AFM studies on p-SnS films deposited by magnetron sputtering. Chalcogenide Lett, 2015, 12, 483[13] Banu S, Ahn S J, Eo Y J, et al. Thin monosulphide (SnS) thin films grown by liquid-phase deposition. Solar Energy, 2017, 145, 33 doi: 10.1016/j.solener.2016.12.013[14] Jana S, Thapa R, Maity R, et al. Optical and dielectric properties of PVA capped nanocrystalline PbS thin films synthesized by chemical bath depostition. Physica E, 2008, 40, 3121 doi: 10.1016/j.physe.2008.04.015[15] Subramaniam E P, Rajesh G, Muthukumarasamy N, et al. Solar cells of Cu2ZnSnS4 thin films prepared by chemical bath deposition method. Indian J Pure Ap Phy, 2014, 52, 620[16] Jing J, Cao M, Wu C, et al. Chemical bath deposition of SnS nanosheet thin films for FTO/SnS/CdS/Pt photocathode. J Alloys Compd, 2017, 726, 720 doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.07.303[17] Chalapathi U, Poornaprakash B, Park S H, et al. Chemically deposited cubic SnS thin films for solar cell applications. Solar Energy, 2016, 139, 238 doi: 10.1016/j.solener.2016.09.046[18] Chaki S H, Chaudhary M D, Deshpande M P. SnS thin films deposited by chemical bath deposition, dip coating and SILAR. J Semicond, 2016, 37, 053001 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/37/5/053001[19] Nair M T S, Nair P K. Simplified chemical bath deposition for good quality SnS thin films. Semicond Sci Technol, 1991, 6, 132 doi: 10.1088/0268-1242/6/2/014[20] Nair P K, Nair M T S, Garcia V M, et al. Semiconductor thin films by chemical bath deposition for solar energy related applications. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells, 1998, 52, 313 doi: 10.1016/S0927-0248(97)00237-7[21] Reighima M, Akkari A, Guasch C, Kamoun N T, et al. Synthesis and characterization of Fe-doped SnS thin films by chemical bath deposition technique for solar cell applications. J Renew Sustain Energy, 2013, 5, 063109 doi: 10.1063/1.4830256[22] Kumar K S, Manoharan C, Dhanapandian S, et al. Effect of Sb dopant on the structural, optical and electrical properties of SnS thin films by spray pyrolysis technique. Spectrochimica Acta A, 2013, 115, 840 doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2013.06.112[23] Chaki S H, Chaudhary M D, Deshpande M P, et al. Effect of indium and antimony doping in SnS single crystal. Mater Res Bull, 2015, 63, 173 doi: 10.1016/j.materresbull.2014.12.013[24] Kafasham H, Ebrahimi-Kahrizsangi R, Jamali-Sheini F, et al. Effect of Al doping on the structural and optical properties of electrodeposited SnS thin films. Phys Status Solidi A, 2016, 5, 1302 doi: 10.1002/pssa.201532920[25] Deepa K G, Nagaraju J. Growth and photovoltaic performance of SnS quantum dots. Mater Sci Eng B, 2012, 177, 1023 doi: 10.1016/j.mseb.2012.05.006[26] Alam F, Dutta V. Tin sulphide (SnS) nanostructured films deposited by continuous spray pyrolysis (CoSP) technique for dye-sensitized solar cell applications. Appl Surf Sci, 2015, 358, 491 doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.07.211[27] Park J, Hwang C H, Young Lee W, et al. Preparation of size tunable SnS nanoparticles by a sonochemical method under multibubble sonoluminescence conditions. Mater Lett, 2014, 117, 188 doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2013.11.115[28] Azizian-Kalandaragh Y, Khodayari A, Zeng Z, et al. Strong quantum confinement effects in SnS nanocrystals produced by ultrasound-assisted method. J Nanoparticle Res, 2013, 15, 1388 doi: 10.1007/s11051-012-1388-1[29] Babu P, Reddy M V, Sreedevi G, et al. Status review on earth-abundant and environmentally green Sn–X (X = Se, S) nanoparticle synthesis by solution methods for photovoltaic applications. Int J Hydrog Energy, 2017, 42, 2790 doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.11.084[30] Bala V, Sharma M, Tripathi S K, et al. Investigations of AI: CdS/PVA nanocomposites: A joint theoretical and experimental approach. Mater Chem Phys, 2014, 146, 523 doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2014.04.003[31] Ramrakhiani M, Nogriya V. Photo and electro-luminescence of cadmium selenide nanocrystals and nanocomposites. J Lumin, 2013, 133, 129 doi: 10.1016/j.jlumin.2011.09.046[32] Hmar J J L, Majumder T, Mondal S P, et al. Growth and characteristics of PbS/polyvinyl alcohol nanocomposites for flexible high dielectric thin film applications. Thin Solid Films, 2016, 598, 243 doi: 10.1016/j.tsf.2015.12.032[33] Elashmawi I S, Abdelghany A M, Hakeema N A, et al. Quantum confinement effects of CdS nanoparticles dispersed within PVP/PVA nanocomposites. J Mater Sci Mater Electron, 2014, 24, 2956 doi: 10.1007/s10854-013-1197-z[34] Begum S K M, Nirmala G, Ravindranadh K, et al. Physical and spectral investigations of Mn2+ ions doped poly vinyl alcohol capped ZnSe nanoparticles. J Mol Struct, 2011, 1006, 344 doi: 10.1016/j.molstruc.2011.09.030[35] Zakaria A, Zamiri R, Vaziri P, et al. Thermal diffusivity measurement of cadmium sulphide nanoparticles prepared by γ-radiation technique. Int J Phys Math Sci, 2011, 5, 928 doi: psasir.upm.edu.my/id/eprint/25034[36] Sagitha P, Sarada K, Muralidharan K, et al. One pot synthesis of poly vinyl alcohol (PVA) supported silver nanoparticles and its efficiency in catalytic reduction of methylene blue. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China, 2016, 26, 2693 doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(16)64397-2[37] Murugadoss G, Rajesh kumar M. Synthesis and optical properties of monodispersed Ni2+ doped ZnS nanopaarticles. Appl Nanosci, 2014, 4, 67 doi: 10.1007/s13204-012-0167-8[38] Osuntokun J, Ajibade P A. Morphology and thermal studies of zinc sulphide and cadmium sulphide nanoparticles in polyvinyl alcohol matrix. Physica B, 2016, 496, 106 doi: 10.1016/j.physb.2016.05.024[39] Mohamed S A, AI-Ghamdi A A, Sharma G D, et al. Effect of ethylene carbonate as a plasticizer on CuI/PVA nanocomposite: Structure, optical and electrical properties. J Adv Res, 2014, 5, 79 doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2012.11.008[40] Seoudi R, EI Mongy S A, Shabaka A A, et al. Effect of polyvinyl alocohol matrices on the structural and spectroscopic studies of CdSe nanoparticles. Physica B, 2008, 403, 1781 doi: 10.1016/j.physb.2007.10.108[41] Sharma M, Tripathi S K. Optical and electrical properties of polyvinyl alcohol doped CdS nanoparticles prepared by sol–gel method. J Mater Sci Mater Electron, 2015, 26, 2760 doi: 10.1007/s10854-015-2756-2[42] Elashmawi I S, Hakeema N A, Soliman Selim M, et al. Optimization and spectroscopic studies of CdS/polyvinyl alcohol nanocomposites. Mater Chem Phys, 2009, 115, 132 doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2008.11.034[43] Tamgadge Y S, Sunatkari A L , S, Talwatkar S, et al. Linear and nonlinear optical properties of nanostructured Zn(1– x)Sr xO-PVA composite thin films. Opt Mater, 2014, 37, 42 doi: 10.1016/j.optmat.2014.04.036[44] Singh N, Mehra R M, Kapoor A. ZnO based quantum dot sensitized solar cell using CdS quantum dots. J Renew Sustain Energy, 2012, 4, 013110 doi: 10.1063/1.3683531[45] Phukan P, Saikia D. Optical and structural investigation of CdSe quantum dots dispersed in PVA matrix and photovoltaic applications. Int J Photoenergy, 2013, 2013, 728280 doi: dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/728280[46] Saikia D, Phukan P. Fabrication and evaluation of CdS/PbS thin film solar cell by chemical bath deposition technique. Thin Solid Films, 2014, 562, 239 doi: 10.1016/j.tsf.2014.04.065[47] Sreedevi G, Reddy M V, Park C, et al. Comprehensive optical studies on SnS layers synthesized by chemical bath deposition. Opt Mater, 2015, 42, 468 doi: 10.1016/j.optmat.2015.01.043[48] Reddy V R M, Sreedevi G, Park C, et al. Development of sulphurized SnS thin film solar cells. Curr Appl Phys, 2015, 15, 588 doi: 10.1016/j.cap.2015.01.022[49] Nwankwo S N, Campbell S, Reddy K T R, et al. Temperature controlled properties of sub-micron thin SnS films. Semicond Sci Technol, 2018, 33, 065002 doi: 10.1088/1361-6641/aabc6f[50] Hwang D H, Shin J Y, Lee S, et al. Substrate temperature effects on the properties of radio-frequency sputtered SnS thin films. Nanosci Nanotechnol Lett, 2018, 10, 696 doi: 10.1166/nnl.2018.2715[51] Clayton A J, Charbonneau C M E, Tsoi W C, et al. One-step growth of thin film SnS with large grains using MOCVD. Sci Technol Adv Mater, 2018, 19, 153 doi: 10.1080/14686996.2018.1428478[52] Sall T, Soucase B M, Mollar M, et al. SnS thin films prepared by chemical spray pyrolysis at different substrate temperatures for photovoltaic applications. J Electron Mater, 2017, 46, 1714 doi: 10.1007/s11664-016-5215-9[53] Assilli K, Alouani K, Vilanova X. Impact of deposition temperature on the properties of SnS thin films grown over silicon substrate- comparative study of structural and optical properties with films grown on glass substrates. Semicond Sci Technol, 2017, 32, 115005 doi: 10.1088/1361-6641/aa8b2c[54] Al Shakban M, Xie Z, Savjani N, et al. A facile method for the production of SnS thin films from melt reactions. J Mater Sci, 2016, 51, 6166 doi: 10.1007/s10853-016-9906-7[55] Saenk N S. The X-ray diffraction study of three-dimensional disordered network of nanographites: experiment and theory. Physics Procedia, 2012, 23, 102 doi: 10.1016/j.phpro.2012.01.026[56] Purohit A, Chander S, Nehra S P, et al. Effect of air annealing on structural, optical, morphological and electrical properties of thermally evaporated CdSe thin films. Physica E, 2015, 69, 342 doi: 10.1016/j.physe.2015.01.028[57] Sarmah K, Sarma R, Das H L. Structural characterization of thermally evaporated CdSe thin films. Chalcogenide Lett, 2008, 5, 153 doi: hdl.handle.net/10603/66250[58] Jassim S A J, Ali Zumaila A A R, et al. Influence of substrate temperature on the structural, optical and electrical properties of CdS thin films deposited by thermal evaporation. Results in Physics, 2013, 3, 173 doi: 10.1016/j.rinp.2013.08.003[59] Prabhu Y T, Rao K V, Kumar V S S, et al. X-ray analysis by Williamson-Hall and size-strain methods of ZnO nanoparticles with fuel variation. World J Nano Sci Eng, 2014, 4, 21 doi: 10.4236/wjnse.2014.41004[60] Baby B H, Vaisakh V M, Mohan D B, et al. Fabrication and phase characterization study of SnS thin films under controlled sulfur deposition temperature. Mater Today, 2016, 3, 2077 doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2016.04.111[61] Ali S, Wang F, Zafar S, et al. Characterization and Raman vibrations of chalcogenide SnS nanorods. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 2017, 275, 012007 doi: 10.1088/1757-899X/275/1/012007[62] Jayasree Y, Chalapathi U, Bhaskar P U, et al. Effect of precursor concentration and bath temperature on the growth of chemical bath deposited tin sulphide thin films. Appl Surf Sci, 2012, 258, 2732 doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2011.10.124[63] Arulanantham A M S, Valanarasu S, Jeyadheepan K, et al. Development of SnS (FTO/CdS/SnS) thin films by nebulizer spray pyrolysis (NSP) for solar cell applications. J Mol Struct, 2018, 1152, 137 doi: 10.1016/j.molstruc.2017.09.077[64] Das D, Dutta R K. A novel method of synthesis of small band gap SnS nanorods and its efficient photocatalytic dye degradation. J Colloid Interface Sci, 2015, 457, 339 doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2015.07.002[65] Onwudiwe D C, Kruger T P J, Oluwatobi O S, et al. Nanosecond laser irradiation synthesis of CdS nanoparticles in a PVA system. Appl Surf Sci, 2014, 290, 18 doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.10.165[66] Guddeti P R, Gedi S, Reddy K T R, et al. Sulfurization temperature dependent physical properties of Cu2SnS3 films grown by a two-stage process. Mater Sci Semicond Process, 2018, 86, 164 doi: 10.1016/j.mssp.2018.06.021[67] Ojha K S. Structural and optical properties of PVA doped zinc sulphide thin films. Optik, 2016, 127, 2586 doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2015.11.233[68] Brus L. Electronic wave functions in semiconductor clusters: experiment and theory. J Phys Chem, 1986, 90, 2555 doi: 10.1021/j100403a003[69] Xu J, Yang Y. Study on the performances of SnS heterojunctions by numerical analysis. Energy Convers Manag, 2014, 78, 260 doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2013.10.062 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: