| Citation: |
Yue Li, Ming Gong, Hualing Zeng. Atomically thin α-In2Se3: an emergent two-dimensional room temperature ferroelectric semiconductor[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2019, 40(6): 061002. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/40/6/061002
****
Y Li, M Gong, H L Zeng, Atomically thin α-In2Se3: an emergent two-dimensional room temperature ferroelectric semiconductor[J]. J. Semicond., 2019, 40(6): 061002. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/40/6/061002.
|
Atomically thin α-In2Se3: an emergent two-dimensional room temperature ferroelectric semiconductor
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/40/6/061002
More Information
-
Abstract
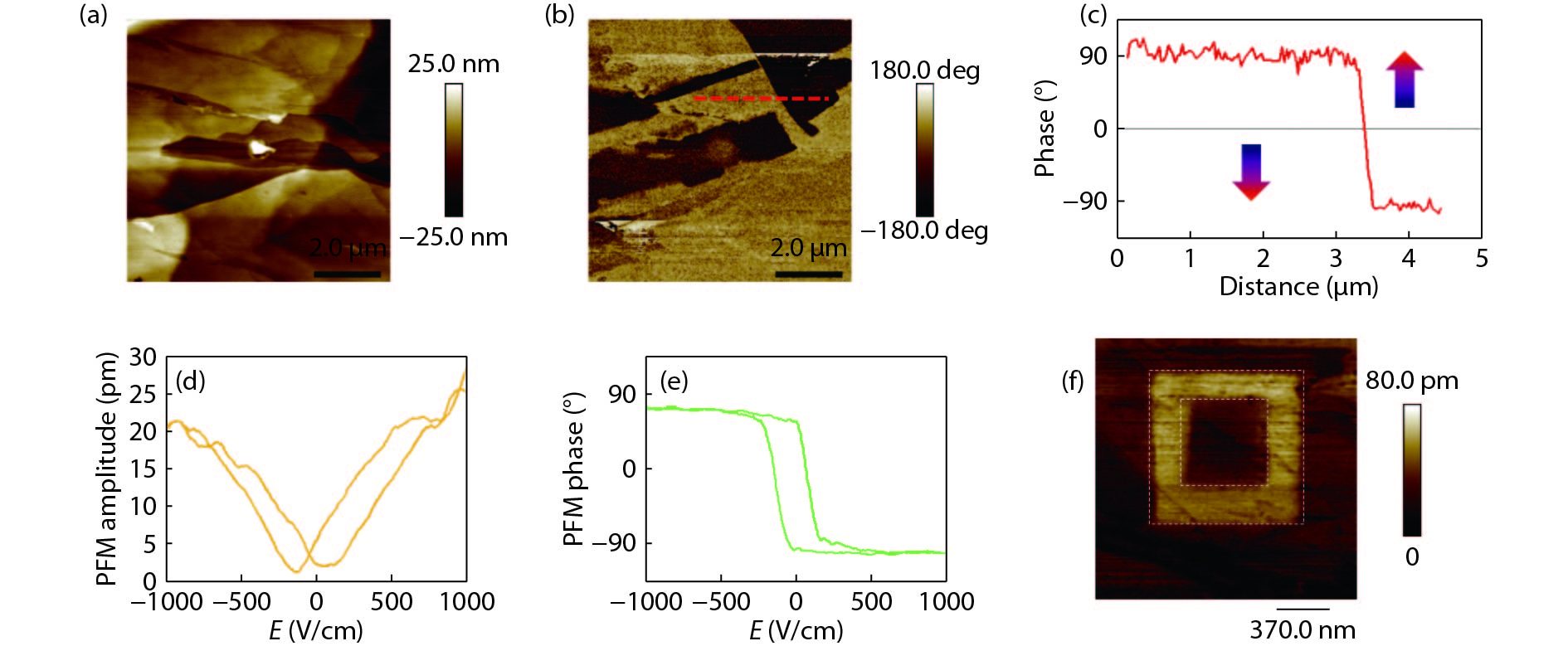
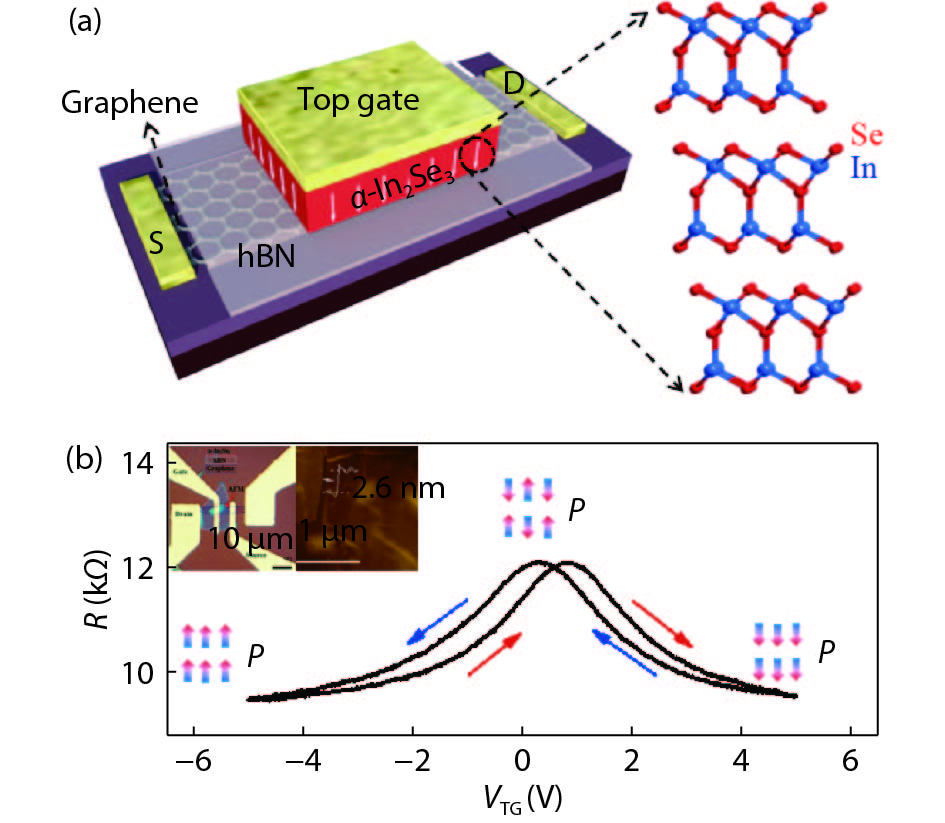
Room temperature ferroelectric thin films are the key element of high-density nonvolatile memories in modern electronics. However, with the further miniaturization of the electronic devices beyond the Moore’s law, conventional ferroelectrics suffer great challenge arising from the critical thickness effect, where the ferroelectricity is unstable if the film thickness is reduced to nanometer or single atomic layer limit. Two-dimensional (2D) materials, thanks to their stable layered structure, saturate interfacial chemistry, weak interlayer couplings, and the benefit of preparing stable ultra-thin film at 2D limit, are promising for exploring 2D ferroelectricity and related device applications. Therefore, it provides an effective approach to overcome the limitation in conventional ferroelectrics with the study of 2D ferroelectricity in van der Waals (vdW) materials. In this review article, we briefly introduce recent progresses on 2D ferroelectricity in layered vdW materials. We will highlight the study on atomically thin α-In2Se3, which is an emergent ferroelectric semiconductor with the coupled in-plane and out-of-plane ferroelectricity. Furthermore, two prototype ferroelectric devices based on ferroelectric α-In2Se3 will also be reviewed.-
Keywords:
- electric polarization,
- 2D materials,
- 2D ferroelectrics
-
References
[1] de Araujo C A P, Cuchiaro J D, McMillan L D, et al. Fatigue-free ferroelectric capacitors with platinum electrodes. Nature, 1995, 374(6523), 627 doi: 10.1038/374627a0[2] Choi T, Lee S, Choi Y J, et al. Switchable ferroelectric diode and photovoltaic effect in BiFeO3. Science, 2009, 324(5923), 63 doi: 10.1126/science.1168636[3] Lu H, Lipatov A, Ryu S, et al. Ferroelectric tunnel junctions with graphene electrodes. Nat Commun, 2014, 5, 5518 doi: 10.1038/ncomms6518[4] Scott J F, Paz de Araujo C A. Ferroelectric memories. Science, 1989, 246(4936), 1400 doi: 10.1126/science.246.4936.1400[5] Chu M W, Szafraniak I, Scholz R, et al. Impact of misfit dislocations on the polarization instability of epitaxial nanostructured ferroelectric perovskites. Nat Mater, 2004, 3(2), 87 doi: 10.1038/nmat1057[6] Stengel M, Vanderbilt D, Spaldin N A. Enhancement of ferroelectricity at metal–oxide interfaces. Nat Mater, 2009, 8, 392 doi: 10.1038/nmat2429[7] Lu H, Liu X, Burton J D, et al. Enhancement of ferroelectric polarization stability by interface engineering. Adv Mater, 2012, 24(9), 1209 doi: 10.1002/adma.v24.9[8] Junquera J, Ghosez P. Critical thickness for ferroelectricity in perovskite ultrathin films. Nature, 2003, 422(6931), 506 doi: 10.1038/nature01501[9] Gao P, Zhang Z Y, Li M Q, et al. Possible absence of critical thickness and size effect in ultrathin perovskite ferroelectric films. Nat Commun, 2017, 8, 15549 doi: 10.1038/ncomms15549[10] Xi X X, Wang Z F, Zhao W W, et al. Ising pairing in superconducting NbSe2 atomic layers. Nat Phys, 2015, 12, 139 doi: 10.1038/nphys3538[11] Xi X X, Zhao L, Wang Z F, et al. Strongly enhanced charge-density-wave order in monolayer NbSe2. Nature Nanotech, 2015, 10, 765 doi: 10.1038/nnano.2015.143[12] Zeng H L, Dai J F, Yao W, et al. Valley polarization in MoS2 monolayers by optical pumping. Nat Nanotech, 2012, 7, 490 doi: 10.1038/nnano.2012.95[13] Deng Y, Yu Y, Song Y, et al. Gate-tunable room-temperature ferromagnetism in two-dimensional Fe3GeTe2. Nature, 2018, 563(7729), 94 doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0626-9[14] Geim A K, Novoselov K S. The rise of graphene. Nat Mater, 2007, 6, 183 doi: 10.1038/nmat1849[15] Mak K F, Lee C G, Hone J, et al. Atomically thin MoS2 : a new direct-gap semiconductor. Phys Rev Lett, 2010, 105(13), 136805 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.105.136805[16] Zeng H L, Cui X D. An optical spectroscopic study on two-dimensional group-VI transition metal dichalcogenides. Chem Soc Rev, 2015, 44(9), 2629 doi: 10.1039/C4CS00265B[17] Belianinov A, He Q, Dziaugys A, et al. CuInP2S6 room temperature layered ferroelectric. Nano Lett, 2015, 15(6), 3808 doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.5b00491[18] Liu F C, You L, Seyler K L, et al. Room-temperature ferroelectricity in CuInP2S6 ultrathin flakes. Nat Commun, 2016, 7, 12357 doi: 10.1038/ncomms12357[19] Chang K, Liu J W, Lin H C, et al. Discovery of robust in-plane ferroelectricity in atomic-thick SnTe. Science, 2016, 353(6296), 274 doi: 10.1126/science.aad8609[20] Ding W J, Zhu J B, Wang Z, et al. Prediction of intrinsic two-dimensional ferroelectrics in In2Se3 and other III2–VI3 van der Waals materials. Nat Commun, 2017, 8, 14956 doi: 10.1038/ncomms14956[21] Zhou Y, Wu D, Zhu Y H, et al. Out-of-plane piezoelectricity and ferroelectricity in layered α-In2Se3 nanoflakes. Nano Lett, 2017, 17(9), 5508 doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.7b02198[22] Cui C J, Hu W J, Yan X X, et al. Intercorrelated in-plane and out-of-plane ferroelectricity in ultrathin two-dimensional layered semiconductor In2Se3. Nano Lett, 2018, 18(2), 1253 doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.7b04852[23] Poh S M, Tan S J R, Wang H, et al. Molecular-beam epitaxy of two-dimensional In2Se3 and its giant electroresistance switching in ferroresistive memory junction. Nano Lett, 2018, 18(10), 6340 doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.8b02688[24] Wan S Y, Li Y, Li W, et al. Room-temperature ferroelectricity and a switchable diode effect in two-dimensional α-In2Se3 thin layers. Nanoscale, 2018, 10(31), 14885 doi: 10.1039/C8NR04422H[25] Xiao J, Zhu H, Wang Y, et al. Intrinsic two-dimensional ferroelectricity with dipole locking. Phys Rev Lett, 2018, 120(22), 227601 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.120.227601[26] Xue F, Hu W, Lee K C, et al. Room-temperature ferroelectricity in hexagonally layered α-In2Se3 nanoflakes down to the monolayer limit. Adv Funct Mater, 2018, 0(0), 1803738 doi: 10.1002/adfm.201803738[27] Xue F, Zhang J, Hu W, et al. Multidirection piezoelectricity in mono- and multilayered hexagonal α-In2Se3. ACS Nano, 2018, 12(5), 4976 doi: 10.1021/acsnano.8b02152[28] Zheng C, Yu L, Zhu L, et al. Room temperature in-plane ferroelectricity in van der Waals In2Se3. Sci Adv, 2018, 4(7), eaar7720 doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aar7720[29] Wan S Y, Li Y, Li W, et al. Nonvolatile ferroelectric memory effect in ultrathin α-In2Se3. Adv Funct Mater, 2018, 29, 1808606 doi: 10.1002/adfm.201808606[30] Si M W, Gao S J, Qiu G, et all. A ferroelectric semiconductor field-effect transistor. arXiv: 1812.02933[31] Tao X, Gu Y. Crystalline–crystalline phase transformation in two-dimensional In2Se3 thin layers. Nano Lett, 2013, 13(8), 3501 doi: 10.1021/nl400888p[32] Wu D, Pak A J, Liu Y N, et al. Thickness-dependent dielectric constant of few-layer In2Se3 nanoflakes. Nano Lett, 2015, 15(12), 8136 doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.5b03575[33] Zhou J D, Zeng Q S, Lv D H, et al. Controlled synthesis of high-quality monolayered α-In2Se3 via physical vapor deposition. Nano Lett, 2015, 15(10), 6400 doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.5b01590[34] Jacobs-Gedrim R B, Shanmugam M, Jain N, et al. Extraordinary photoresponse in two-dimensional In2Se3 nanosheets. ACS Nano, 2014, 8(1), 514 doi: 10.1021/nn405037s[35] Nilanthy B, Christopher R S, Emily F S, et al. Quantum confinement and photoresponsivity of β -In2Se3 nanosheets grown by physical vapour transport. 2D Mater, 2016, 3(2), 025030 doi: 10.1088/2053-1583/3/2/025030[36] Choi M S, Cheong B K, Ra C H, et al. Electrically driven reversible phase changes in layered In2Se3 crystalline film. Adv Mater, 2017, 29(42), 1703568 doi: 10.1002/adma.201703568[37] Lewandowska R, Bacewicz R, Filipowicz J, et al. Raman scattering in α-In2Se3 crystals. Mater Res Bull, 2001, 36(15), 2577 doi: 10.1016/S0025-5408(01)00746-2[38] Debbichi L, Eriksson O, Lebègue S. Two-dimensional indium selenides compounds: an ab initio study. J Phys Chem Lett, 2015, 6(15), 3098 doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.5b01356[39] Zhou S, Tao X, Gu Y. Thickness-dependent thermal conductivity of suspended two-dimensional single-crystal In2Se3 layers grown by chemical vapor deposition. J Phys Chem C, 2016, 120(9), 4753 doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.5b10905[40] Eisuke T, Kojiro O, Hiroshi I. Low voltage operation of nonvolatile metal–ferroelectric–metal–insulator–semiconductor (MFMIS) field-effect-transistors (FETs) using Pt/SrBi2Ta2O9/Pt/SrTa2O6/SiON/Si structures. Jpn J Appl Phys, 2001, 40(4S), 2917 doi: 10.1143/JJAP.40.2917[41] Eisuke T, Gen F, Hiroshi I. Electrical properties of metal–ferroelectric–insulator–semiconductor (MFIS) and metal–ferroelectric–metal–insulator–semiconductor (MFMIS)-FETs using ferroelectric SrBi2Ta2O9 film and SrTa2O6/SiON buffer layer. Jpn J Appl Phys, 2000, 39(4S), 2125 doi: 10.1143/JJAP.39.2125 -
Proportional views






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: