| Citation: |
Xiaowu He, Yifeng Song, Ying Yu, Ben Ma, Zesheng Chen, Xiangjun Shang, Haiqiao Ni, Baoquan Sun, Xiuming Dou, Hao Chen, Hongyue Hao, Tongtong Qi, Shushan Huang, Hanqing Liu, Xiangbin Su, Xinliang Su, Yujun Shi, Zhichuan Niu. Quantum light source devices of In(Ga)As semiconductor self-assembled quantum dots[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2019, 40(7): 071902. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/40/7/071902
****
X W He, Y F Song, Y Yu, B Ma, Z S Chen, X J Shang, H Q Ni, B Q Sun, X M Dou, H Chen, H Y Hao, T T Qi, S S Huang, H Q Liu, X B Su, X L Su, Y J Shi, Z C Niu, Quantum light source devices of In(Ga)As semiconductor self-assembled quantum dots[J]. J. Semicond., 2019, 40(7): 071902. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/40/7/071902.
|
Quantum light source devices of In(Ga)As semiconductor self-assembled quantum dots
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/40/7/071902
More Information
-
Abstract
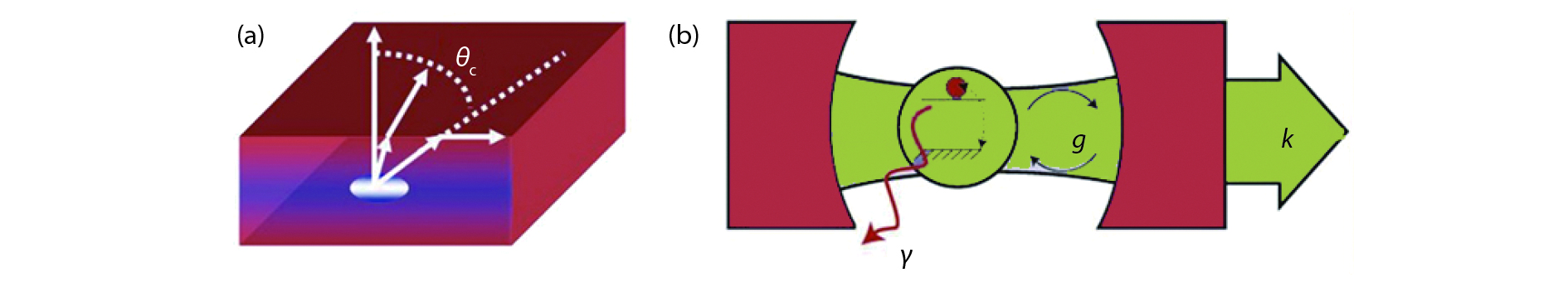
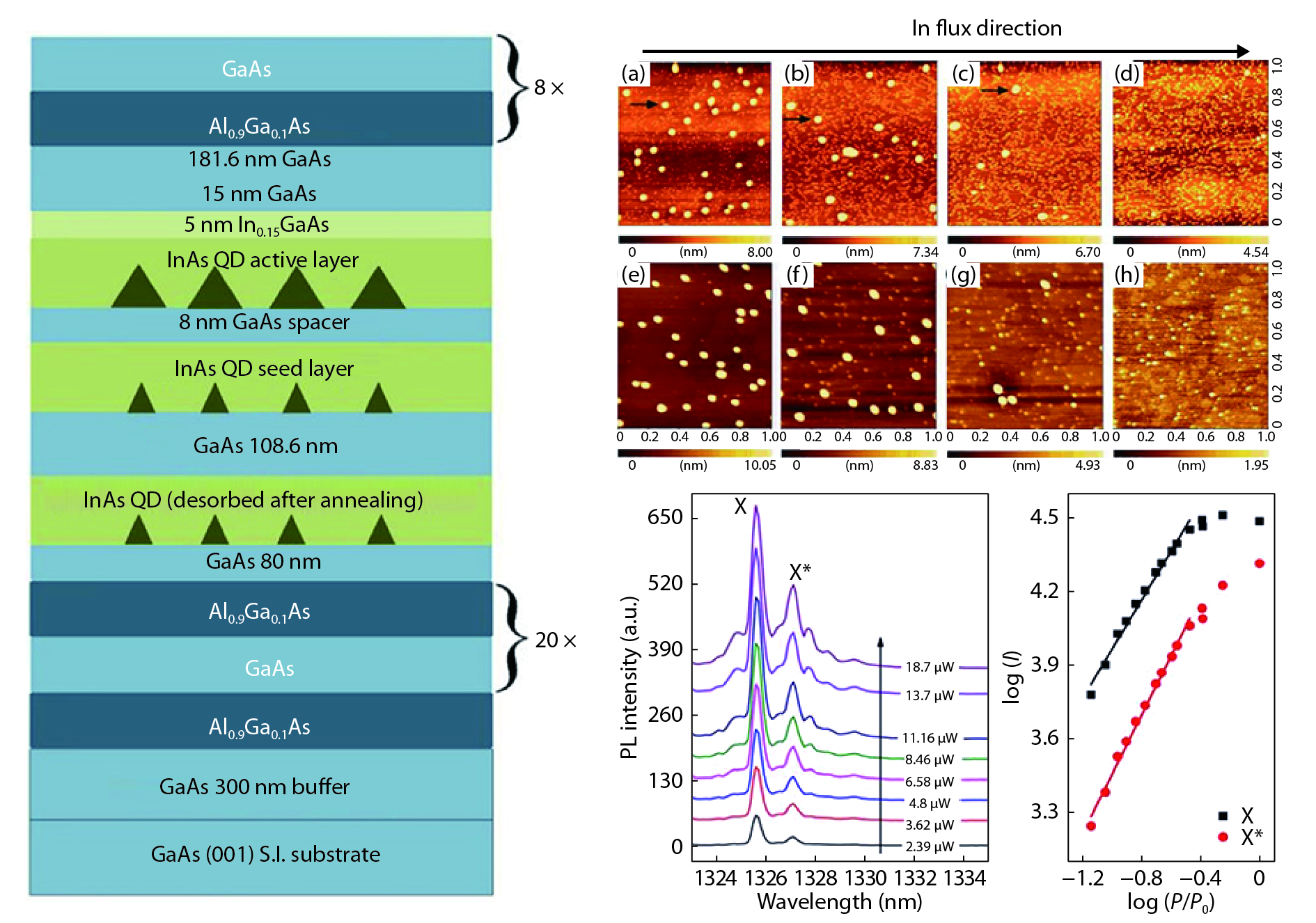
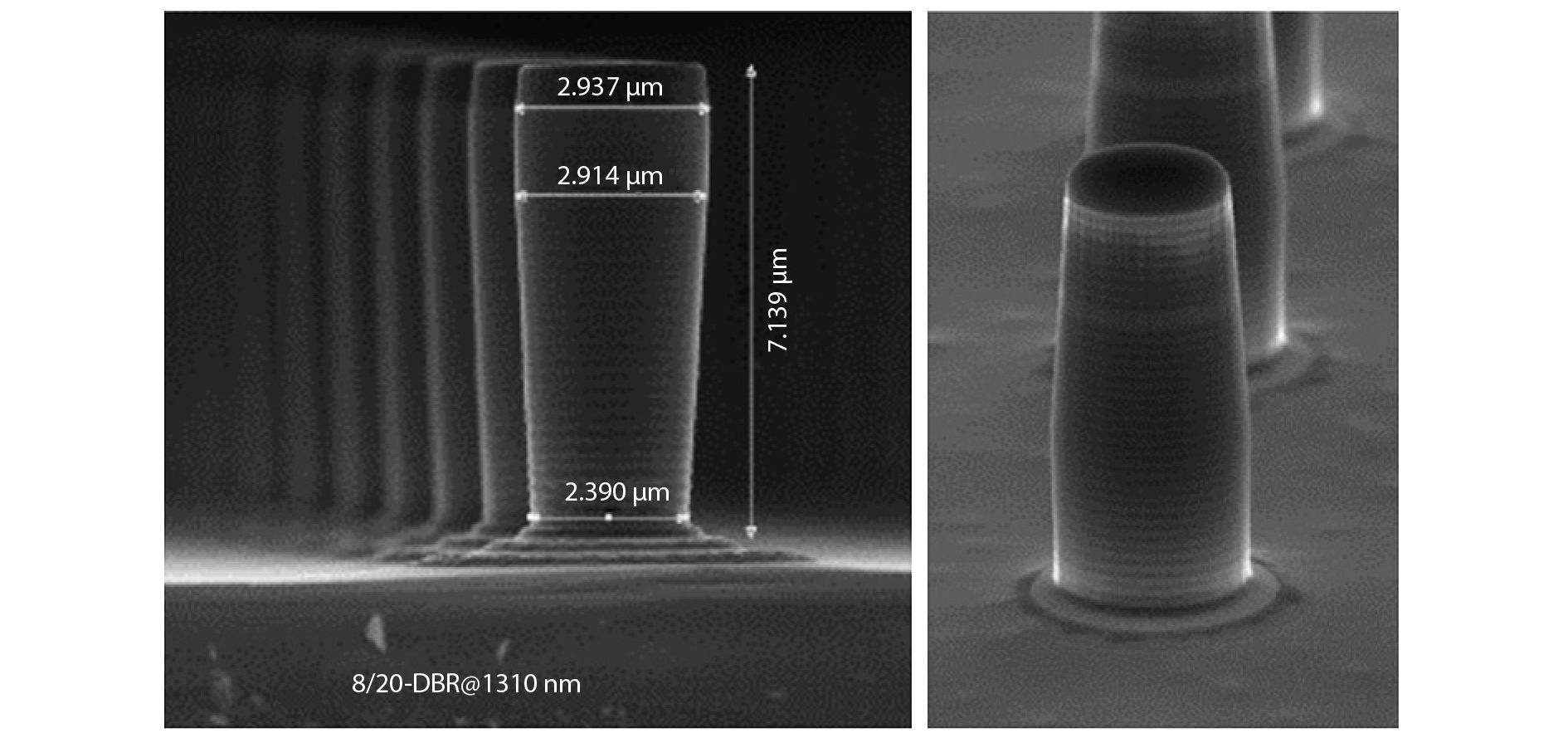
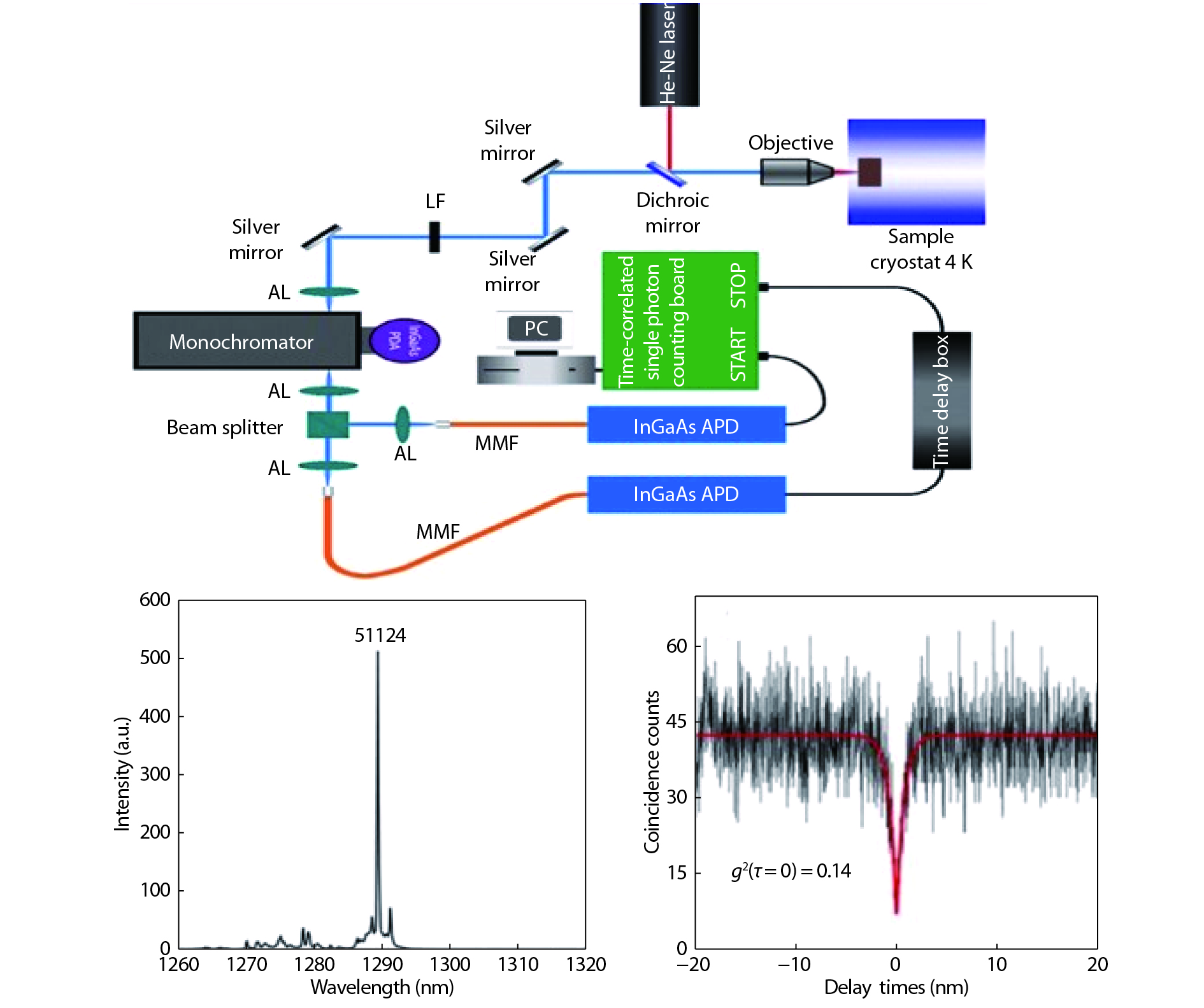
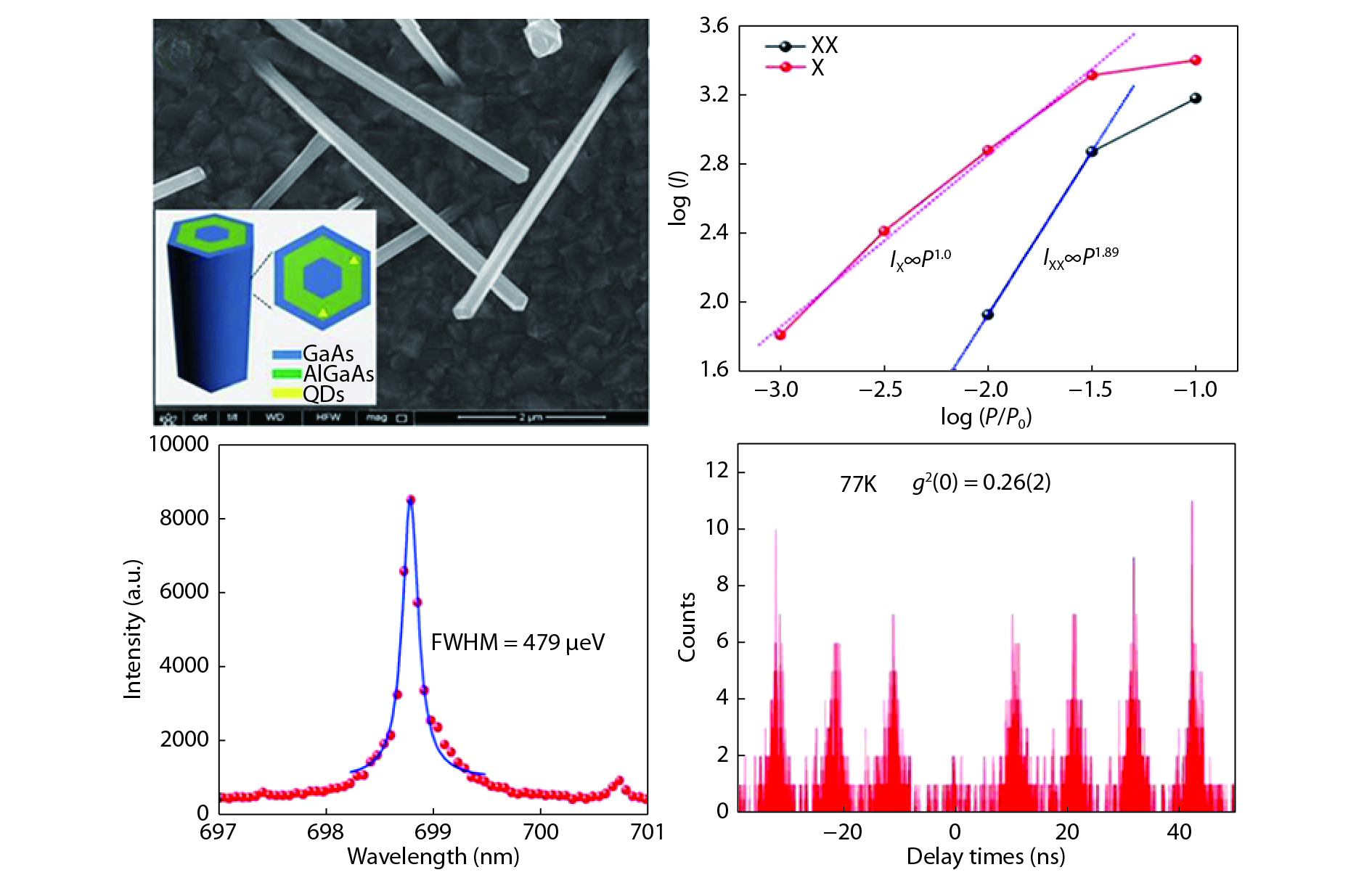
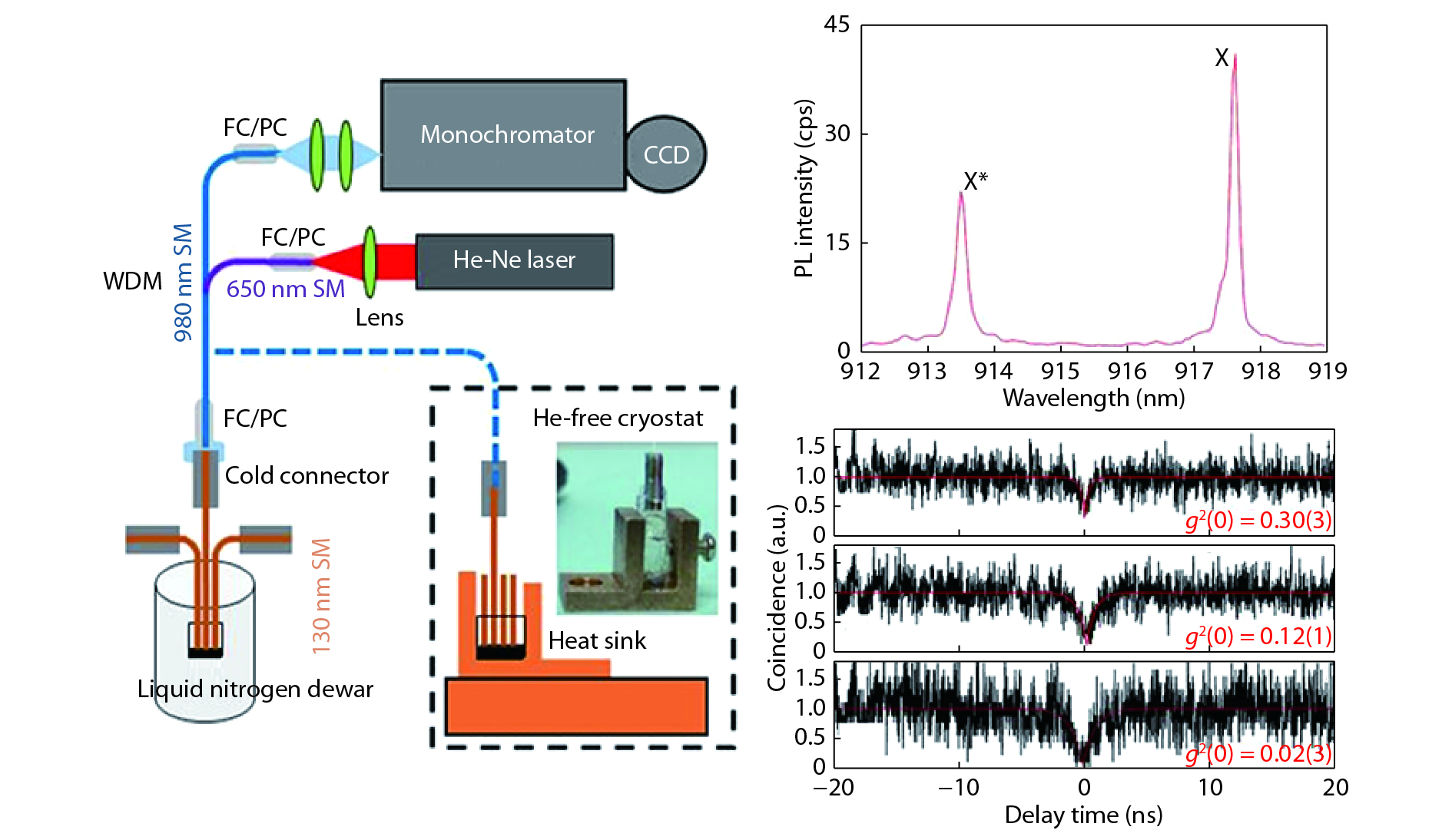
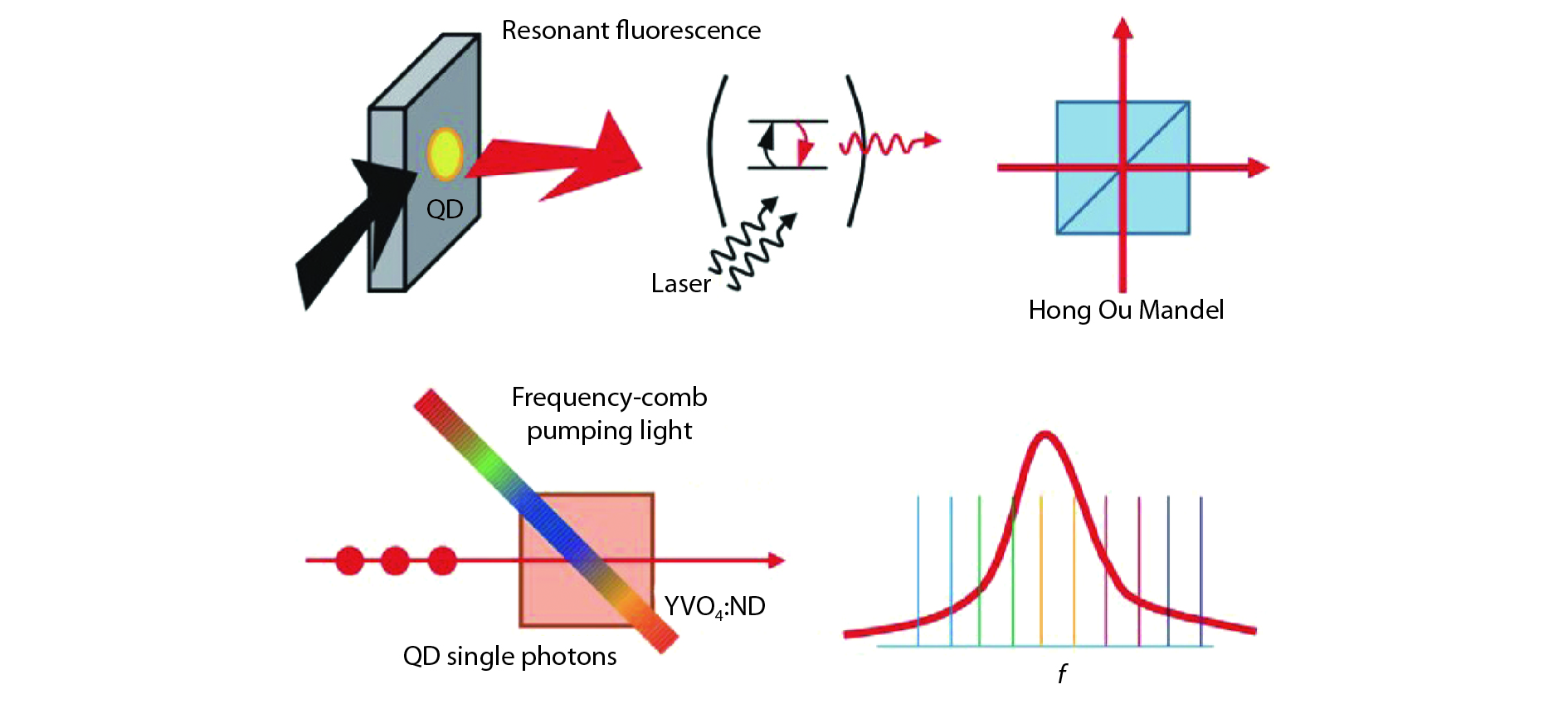
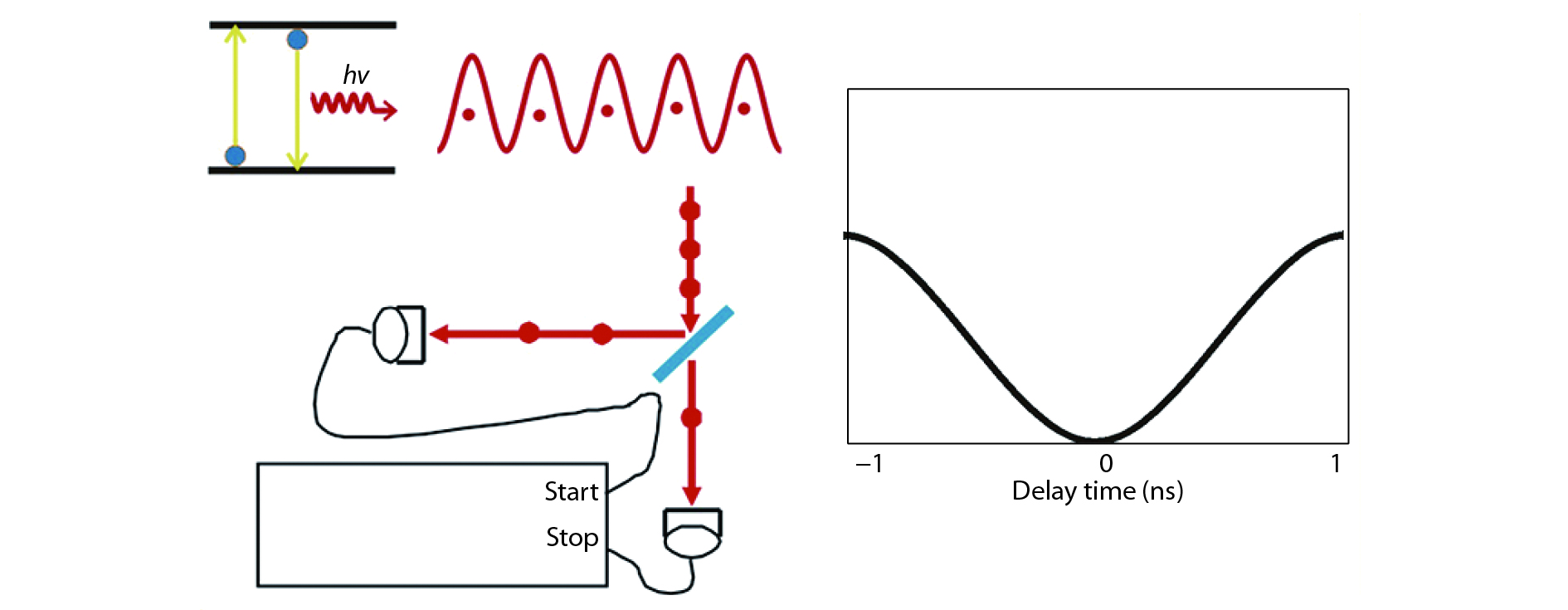
A brief introduction of semiconductor self-assembled quantum dots (QDs) applied in single-photon sources is given. Single QDs in confined quantum optical microcavity systems are reviewed along with their optical properties and coupling characteristics. Subsequently, the recent progresses in In(Ga)As QDs systems are summarized including the preparation of quantum light sources, multiple methods for embedding single QDs into different microcavities and the scalability of single-photon emitting wavelength. Particularly, several In(Ga)As QD single-photon devices are surveyed including In(Ga)As QDs coupling with nanowires, InAs QDs coupling with distributed Bragg reflection microcavity and the In(Ga)As QDs coupling with micropillar microcavities. Furthermore, applications in the field of single QDs technology are illustrated, such as the entangled photon emission by spontaneous parametric down conversion, the single-photon quantum storage, the chip preparation of single-photon sources as well as the single-photon resonance-fluorescence measurements.-
Keywords:
- quantum optics,
- quantum dots,
- nanowires,
- light sources
-
References
[1] Schneider C, Rahimi-Iman A, Kim N Y, et al. An electrically pumped polariton laser. Nature, 2013, 497(7449), 348 doi: 10.1038/nature12036[2] Pelton M, Santori C, Vuckovic J, et al. Efficient source of single photons: A single quantum dot in a micropost microcavity. Phys Rev Lett, 2002, 89(23), 233602 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.89.233602[3] Yoshie T, Scherer A, Hendrickson J, et al. Vacuum Rabi splitting with a single quantum dot in a photonic crystal nanocavity. Nature, 2004, 432(7014), 200 doi: 10.1038/nature03119[4] Peter E, Senellart P, Martrou D, et al. Exciton-photon strong-coupling regime for a single quantum dot embedded in a microcavity. Phys Rev Lett, 2005, 95(6), 067401 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.95.067401[5] Pelton M, Yamamoto Y. Ultralow threshold laser using a single quantum dot and a microsphere cavity. Phys Rev A, 1999, 59(3), 2418 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.59.2418[6] Gerard J M, Gayral B. InAs quantum dots: artificial atoms for solid-state cavity-quantum electrodynamics. Physica E, 2001, 9(1), 131 doi: 10.1016/S1386-9477(00)00187-9[7] Hargart F, Roy-Choudhury K, John T, et al. Probing different regimes of strong field light-matter interaction with semiconductor quantum dots and few cavity photons. New J Phys, 2016, 18, 123031 doi: 10.1088/1367-2630/aa5198[8] Liao S K, Cai W Q, Liu W Y, et al. Satellite-to-ground quantum key distribution. Nature, 2017, 549(7670), 43 doi: 10.1038/nature23655[9] Harrow A W, Montanaro A. Quantum computational supremacy. Nature, 2017, 549(7671), 203 doi: 10.1038/nature23458[10] Ren J G, Xu P, Yong H L, et al. Ground-to-satellite quantum teleportation. Nature, 2017, 549(7670), 70 doi: 10.1038/nature23675[11] Knill E, Laflamme R, Milburn G J. A scheme for efficient quantum computation with linear optics. Nature, 2001, 409(6816), 46 doi: 10.1038/35051009[12] Divincenzo D P. Quantum computation. Science, 1995, 270(5234), 255 doi: 10.1126/science.270.5234.255[13] Ekert A K. Quantum cryptography based on Bell’s theorem. Phys Rev Lett, 1991, 67(6), 661 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.67.661[14] Gisin N, Ribordy G G, Tittel W, et al. Quantum cryptography. Rev Mod Phys, 2002, 74(1), 145 doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.74.145[15] Wang X L, Cai X D, Su Z E, et al. Quantum teleportation of multiple degrees of freedom of a single photon. Nature, 2015, 518(7540), 516 doi: 10.1038/nature14246[16] Gisin N, Thew R. Quantum communication. Nat Photonics, 2007, 1(3), 165 doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2007.22[17] Oxborrow M, Sinclair A G. Single-photon sources. Contemp Phys, 2005, 46(3), 173 doi: 10.1080/00107510512331337936[18] Muller A, Herzog T, Huttner B, et al. ''Plug and play'' systems for quantum cryptography. Appl Phys Lett, 1997, 70(7), 793 doi: 10.1063/1.118224[19] Brassard G, Lutkenhaus N, Mor T, et al. Limitations on practical quantum cryptography. Phys Rev Lett, 2000, 85(6), 1330 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.85.1330[20] Yao P J, Rao V, Hughes S. On-chip single photon sources using planar photonic crystals and single quantum dots. Laser Photon Rev, 2010, 4(4), 499 doi: 10.1002/lpor.200810081[21] Shan G C, Yin Z Q, Shek C H, et al. Single photon sources with single semiconductor quantum dots. Front Phys, 2014, 9(2), 170 doi: 10.1007/s11467-013-0360-6[22] Lounis B, Moerner W E. Single photons on demand from a single molecule at room temperature. Nature, 2000, 407(6803), 491 doi: 10.1038/35035032[23] Keller M, Lange B, Hayasaka K, et al. Continuous generation of single photons with controlled waveform in an ion-trap cavity system. Nature, 2004, 431(7012), 1075 doi: 10.1038/nature02961[24] Kuhn A, Hennrich M, Rempe G. Deterministic single-photon source for distributed quantum networking. Phys Rev Lett, 2002, 89(6), 4 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.89.067901[25] Kurtsiefer C, Mayer S, Zarda P, et al. Stable solid-state source of single photons. Phys Rev Lett, 2000, 85(2), 290 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.85.290[26] Liang B L, Wang Z M, Wang X Y, et a. Energy transfer within ultralow density twin InAs quantum dots grown by droplet epitaxy. ACS Nano, 2008, 2(11), 2219 doi: 10.1021/nn800224p[27] He Y M, He Y, Wei Y J, et al. On-demand semiconductor single-photon source with near-unity indistinguishability. Nat Nanotechnol, 2013, 8(3), 213 doi: 10.1038/nnano.2012.262[28] Badolato A, Hennessy K, Atature M, et al. Deterministic coupling of single quantum dots to single nanocavity modes. Science, 2005, 308(5725), 1158 doi: 10.1126/science.1109815[29] Aharonovich I, Englund D, Toth M. Solid-state single-photon emitters. Nat Photonics, 2016, 10(10), 631 doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2016.186[30] Chen Y, Zhang J X, Zopf M, et al. Wavelength-tunable entangled photons from silicon-integrated III–V quantum dots. Nat Commun, 2016, 7, 10387 doi: 10.1038/ncomms10387[31] Yu Y, Shang X J, Li M F, et al. Single InAs quantum dot coupled to different " environments” in one wafer for quantum photonics. Appl Phys Lett, 2013, 102(20), 201103 doi: 10.1063/1.4807502[32] Brown R H, Twiss R Q. Correlation between photons in two coherent beams of light. Nature, 1956, 177(4497), 27 doi: 10.1038/177027a0[33] Michler P, Kiraz A, Becher C, et al. A quantum dot single-photon turnstile device. Science, 2000, 290(5500), 2282 doi: 10.1126/science.290.5500.2282[34] Mar J D, Xu X L, Baumberg J J, et al. Bias-controlled single-electron charging of a self-assembled quantum dot in a two-dimensional-electron-gas-based n-i-Schottky diode. Phys Rev B, 2011, 83(7), 075306 doi: 10.1063/1.3633216[35] Warburton R J, Schaflein C, Haft D, et al. Optical emission from a charge-tunable quantum ring. Nature, 2000, 405(6789), 926 doi: 10.1038/35016030[36] Benson O, Santori C, Pelton M, et al. Regulated and entangled photons from a single quantum dot. Phys Rev Lett, 2000, 84(11), 2513 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.84.2513[37] Mano T, Watanabe K, Tsukamoto S, et al. Fabrication of InGaAs quantum dots on GaAs(001) by droplet epitaxy. J Cryst Growth, 2000, 209(2/3), 504 doi: 10.1016/S0022-0248(99)00606-5[38] Ding X, He Y, Duan Z C, et al. On-demand single photons with high extraction efficiency and near-unity indistinguishability from a resonantly driven quantum dot in a micropillar. Phys Rev Lett, 2016, 116(2), 020401 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.116.020401[39] Yu Y, Dou X M, Wei B, et al. Self-assembled quantum dot structures in a hexagonal nanowire for quantum photonics. Adv Mater, 2014, 26(17), 2710 doi: 10.1002/adma.201304501[40] Xie X M, Xu Q, Shen B Z, et al. InGaAsP/InP micropillar cavities for 1.55 μm quantum-dot single photon sources. 6th Conference on Advances in Optoelectronics and Micro/Nano-Optics, Bristol: Iop Publishing Ltd, Bristol, 2017, 844[41] Heindel T, Schneider C, Lermer M, et al. Electrically driven quantum dot-micropillar single photon source with 34% overall efficiency. Appl Phys Lett, 2010, 96(1), 011107 doi: 10.1063/1.3284514[42] Xu T, Zhu N, Xu M Y C, et al. A pillar-array based two-dimensional photonic crystal microcavity. Appl Phys Lett, 2009, 94(24), 241110 doi: 10.1063/1.3152245[43] Vahala K J. Optical microcavities. Nature, 2003, 424(6950), 839 doi: 10.1038/nature01939[44] Javadi A, Mahmoodian S, Sollner I, et al. Numerical modeling of the coupling efficiency of single quantum emitters in photonic-crystal waveguides. J Opt Soc Am B, 2018, 35(3), 514 doi: 10.1364/JOSAB.35.000514[45] Ali H, Zhang Y Y, Tang J, et al. High-responsivity photodetection by a self-catalyzed phase-pure p-GaAs nanowire. Small, 2018, 14(17), 9 doi: 10.1002/smll.201704429[46] Ward M B, Farrow T, See P, et al. Electrically driven telecommunication wavelength single-photon source. Appl Phys Lett, 2007, 90(6), 063512 doi: 10.1063/1.2472172[47] Salter C L, Stevenson R M, Farrer I, et al. An entangled-light-emitting diode. Nature, 2010, 465(7298), 594 doi: 10.1038/nature09078[48] Dou X M, Chang X Y, Sun B Q, et al. Single-photon-emitting diode at liquid nitrogen temperature. Appl Phys Lett, 2008, 93(10), 101107 doi: 10.1063/1.2980517[49] Hargart F, Kessler C A, Schwarzback T, et al. Electrically driven quantum dot single-photon source at 2 GHz excitation repetition rate with ultra-low emission time jitter. Appl Phys Lett, 2013, 102(1), 011126 doi: 10.1063/1.4774392[50] Gerard J M, Solid-state cavity-quantum electrodynamics with self-assembled quantum dots. In: Single Quantum Dots: Fundamentals, Applications and New Concepts. Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 2003, 90, 269[51] P Michler. Single quantum dots: Fundamentals, applications and new concepts. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer Publishing Company, Incorporated, 2003[52] Muller M, Bounouar S, Jons K D, et al. On-demand generation of indistinguishable polarization-entangled photon pairs. Nat Photonics, 2014, 8(3), 224 doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2013.377[53] Wang H, Duan Z C, Li Y H, et al. Near-transform-limited single photons from an efficient solid-state quantum emitter. Phys Rev Lett, 2016, 116(21), 213601 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.116.213601[54] He Y, He Y M, Wei Y J, et al. Indistinguishable tunable single photons emitted by spin-flip raman transitions in InGaAs quantum dots. Phys Rev Lett, 2013, 111(23), 237403 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.111.237403[55] Zhang J X, Zallo E, Hofer B, et al. Electric-field-induced energy tuning of on-demand entangled-photon emission from self-assembled quantum dots. Nano Lett, 2017, 17(1), 501 doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.6b04539[56] Chen Z S, Ma B, Shang X J, et al. Bright single-photon source at 1.3 μm based on InAs bilayer quantum dot in micropillar. Nanoscale Res Lett, 2017, 12(1), 378 doi: 10.1186/s11671-017-2153-2[57] Ma B, Chen Z S, Wei S H, et al. Single photon extraction from self-assembled quantum dots via stable fiber array coupling. Appl Phys Lett, 2017, 110(14), 142104 doi: 10.1063/1.4979827[58] Zha G W, Shang X J, Su D, et al. Self-assembly of single "square" quantum rings in gold-free GaAs nanowires. Nanoscale, 2014, 6(6), 3190 doi: 10.1039/c3nr05634a[59] Yu Y, Li M F, He J F, et al. Single InAs quantum dot grown at the junction of branched gold-free GaAs nanowire. Nano Lett, 2013, 13(4), 1399 doi: 10.1021/nl304157d[60] Zha G W, Shang X J, Ni H Q, et al. In situ probing and integration of single self-assembled quantum dots-in-nanowires for quantum photonics. Nanotechnology, 2015, 26(38), 385706 doi: 10.1088/0957-4484/26/38/385706[61] Tang J S, Zhou Z Q, Wang Y T, et al. Storage of multiple single-photon pulses emitted from a quantum dot in a solid-state quantum memory. Nat Commun, 2015, 6, 8652 doi: 10.1038/ncomms9652[62] Konthasinghe K, Peiris M, Yu Y, et al. Field-field and photon-photon correlations of light scattered by two remote two-level InAs quantum dots on the same substrate. Phys Rev Lett, 2012, 109(26), 267402 doi: 10.1103/physrevlett.109.267402[63] Konthasinghe K, Walker J, iris, et al. Coherent versus incoherent light scattering from a quantum dot. Phys Rev B, 2012, 85(23), 235315 doi: 10.1103/physrevb.85.235315[64] Peiris M, Konthasinghe K, Yu Y, et al. Bichromatic resonant light scattering from a quantum dot. Phys Rev B, 2014, 89(15), 155305 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.89.155305[65] Chen G, Zou Y, Xu X Y, et al. Experimental test of the state estimation-reversal tradeoff relation in general quantum measurements. Phys Rev X, 2014, 4(5), 021043 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevX.4.021043[66] Chen G, Zou Y, Zhang W H, et al. Experimental demonstration of a hybrid-quantum-emitter producing individual entangled photon Pairs in the telecom band. Sci Rep, 2016, 6, 26680 doi: 10.1038/srep26680[67] Buckley S, Rivoire K, Vuckovic J. Engineered quantum dot single-photon sources. Rep Prog Phys, 2012, 75(12), 126503 doi: 10.1088/0034-4885/75/12/126503[68] Franchi S, Trevisi G, Seravalli L, et al. Quantum dot nanostructures and molecular beam epitaxy. Prog Cryst Growth Charact Mater, 2003, 47(2/3), 166 doi: 10.1016/j.pcrysgrow.2005.01.002[69] Purcell E M. Spontaneous emission probabilities at radio frequencies. Phys Rev, 1946, 69, 681 doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-1963-8_40[70] Bozhevolnyi S I, Khurgin J B. Fundamental limitations in spontaneous emission rate of single-photon sources. Optica, 2016, 3(12), 1418 doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.3.001418[71] Zhao Y P, Li C C, Chen M M, et al. Growth of aligned ZnO nanowires via modified atmospheric pressure chemical vapor deposition. Phys Lett A, 2016, 380(47), 3993 doi: 10.1016/j.physleta.2016.06.030[72] Shang X J, Xu J X, Ma B, et al. Proper In deposition amount for on-demand epitaxy of InAs/GaAs single quantum dots. Chin Phys B, 2016, 25(10), 107805 doi: 10.1088/1674-1056/25/10/107805[73] Zhou P Y, Dou X M, Wu X F, et al. Single-photon property characterization of 1.3 μm emissions from InAs/GaAs quantum dots using silicon avalanche photodiodes. Sci Rep, 2014, 4, 3633 doi: 10.1038/srep03633[74] Michler P, Kiraz A, Zhang L D, et al. Laser emission from quantum dots in microdisk structures. Appl Phys Lett, 2000, 77(2), 184 doi: 10.1063/1.126918[75] Benson O. Assembly of hybrid photonic architectures from nanophotonic constituents. Nature, 2011, 480(7376), 193 doi: 10.1038/nature10610[76] Chen Z S, Ma B, Shang X J, et al. Telecommunication wavelength-band single-photon emission from single large InAs quantum dots nucleated on low-density seed quantum dots. Nanoscale Res Lett, 2016, 11(1), 382 doi: 10.1186/s11671-016-1597-0 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: