| Citation: |
Qian Yang, Yongzhou Xue, Hao Chen, Xiuming Dou, Baoquan Sun. Photo-induced doping effect and dynamic process in monolayer MoSe2[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2020, 41(8): 082004. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/41/8/082004
****
Q Yang, Y Z Xue, H Chen, X M Dou, B Q Sun, Photo-induced doping effect and dynamic process in monolayer MoSe2[J]. J. Semicond., 2020, 41(8): 082004. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/41/8/082004.
|
Photo-induced doping effect and dynamic process in monolayer MoSe2
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/41/8/082004
More Information
-
Abstract
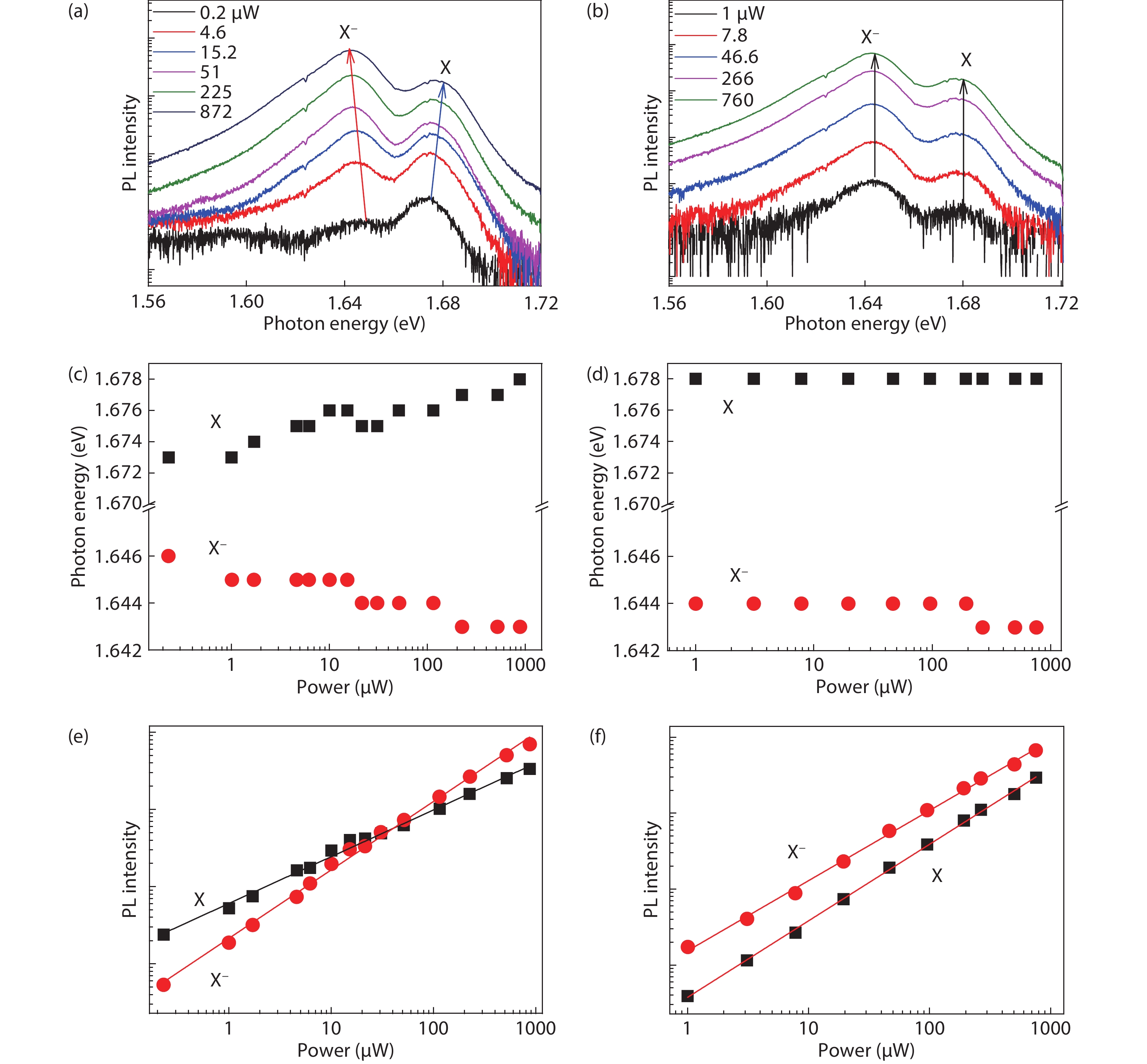
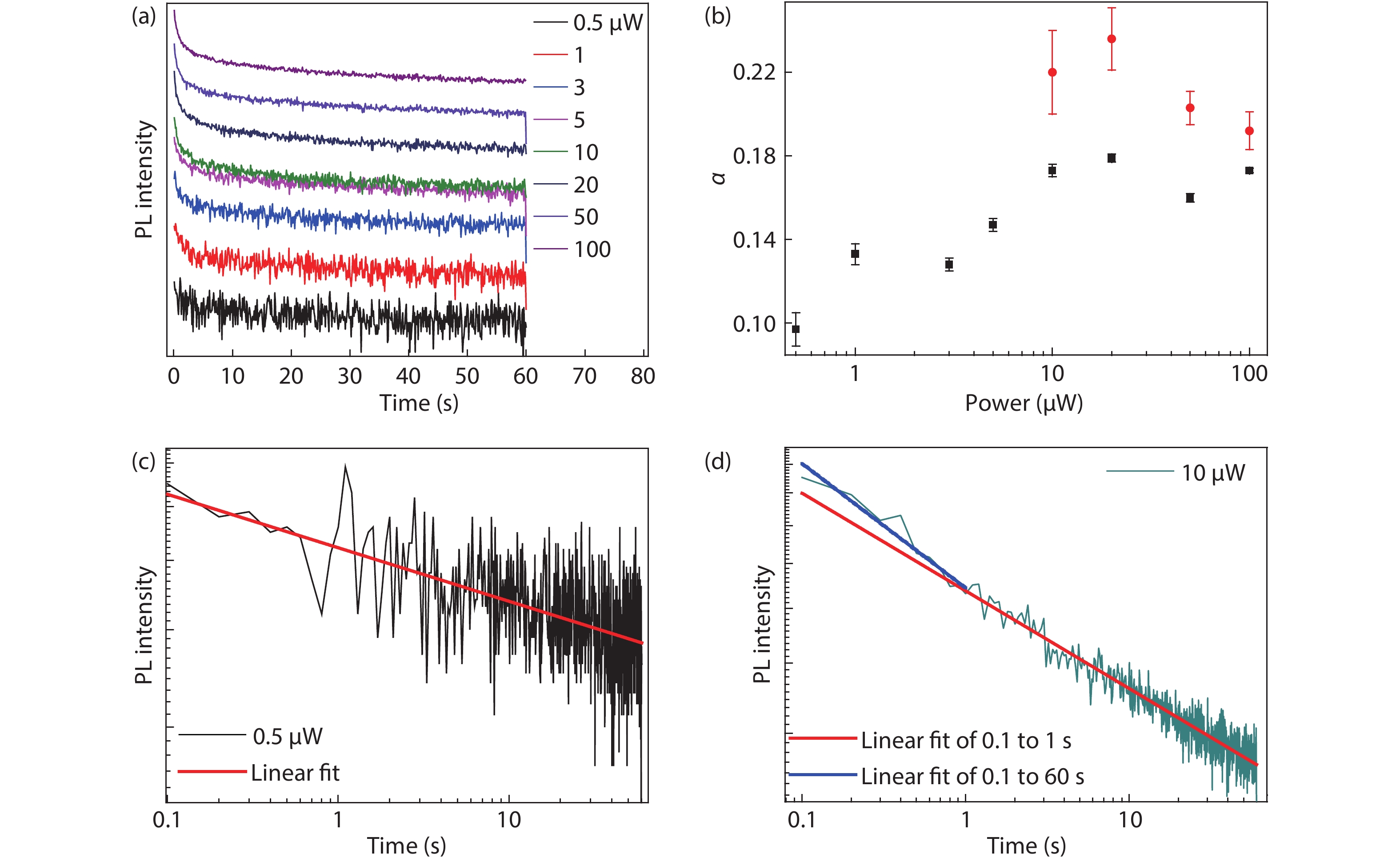
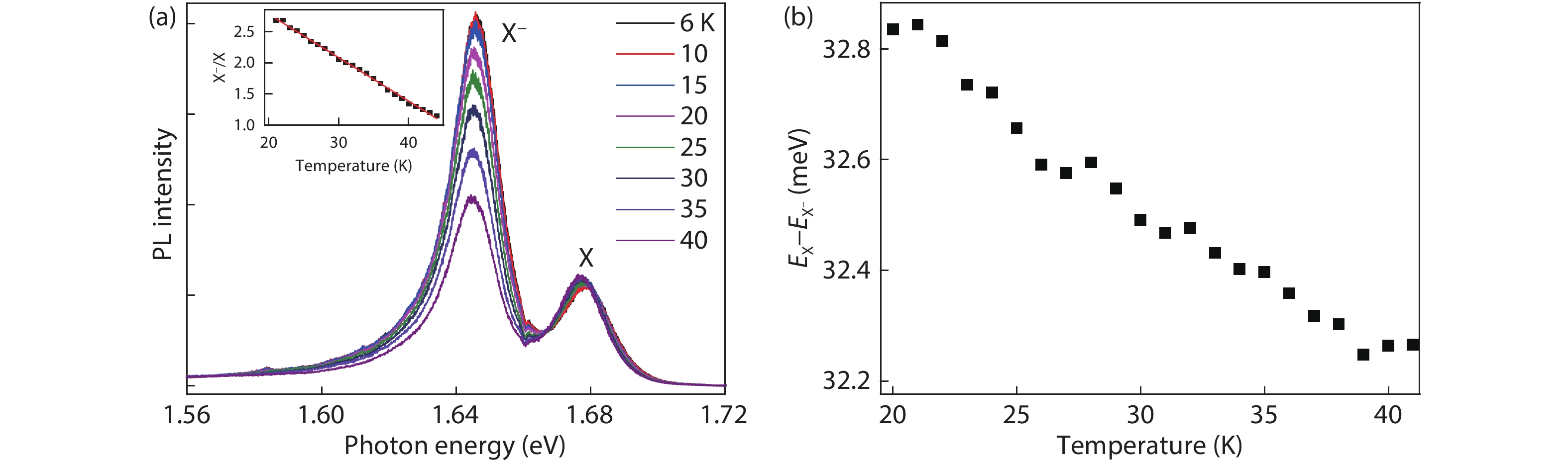
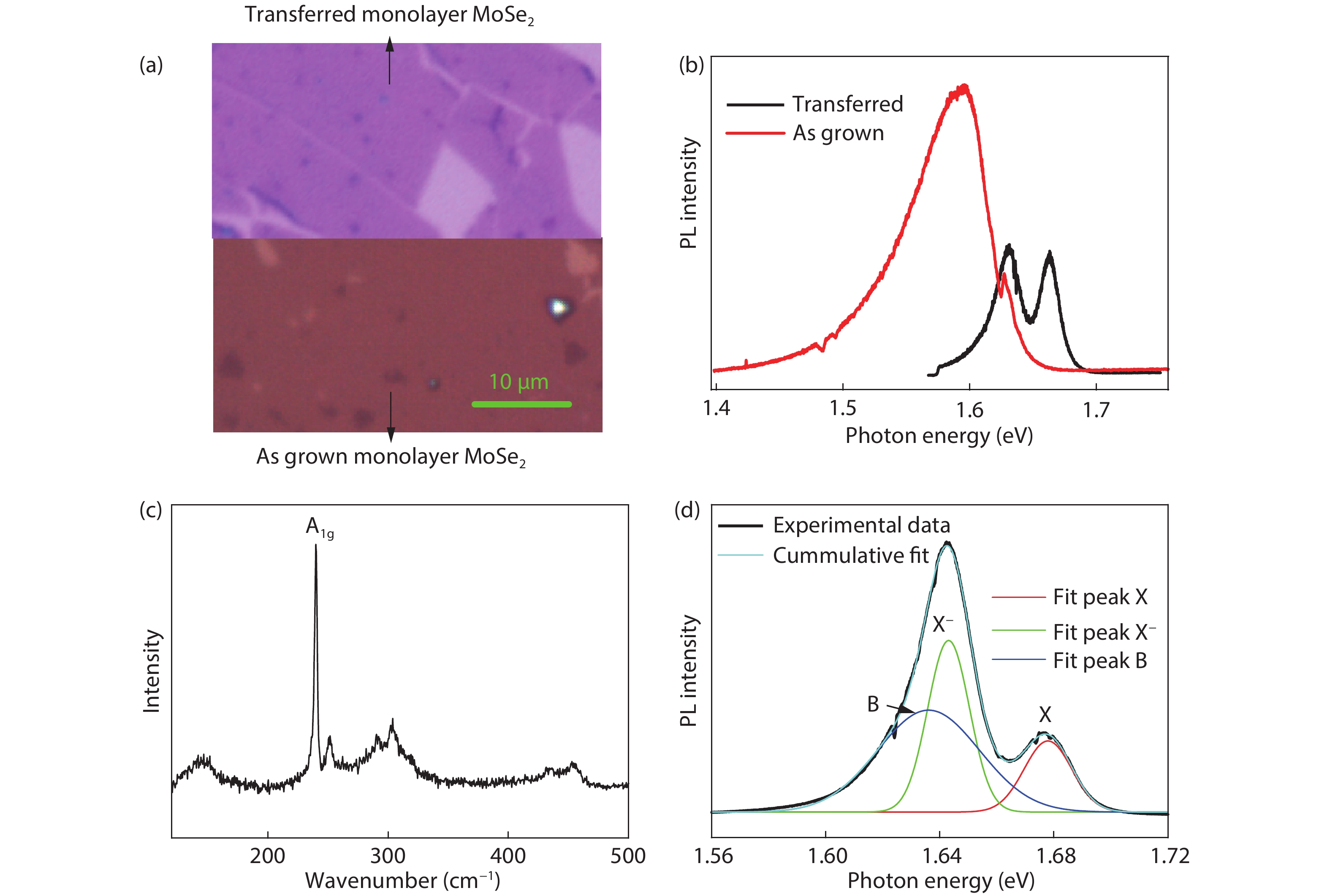
Dynamic processes of electron transfer by optical doping in monolayer MoSe2 at 6 K are investigated via measuring time resolved photoluminescence (PL) traces under different excitation powers. Time-dependent electron transfer process can be analyzed by a power-law distribution of t−α with α = 0.1–0.24, depending on the laser excitation power. The average electron transfer time of approximately 27.65 s is obtained in the excitation power range of 0.5 to 100 μW. As the temperature increases from 20 to 44 K, the energy difference between the neutral and charged excitons is observed to decrease.-
Keywords:
- photodoping,
- monolayer MoSe2,
- dynamic process,
- temperature
-
References
[1] Salehzadeh O, Djavid M, Tran N H, et al. Optically pumped two-dimensional MoS2 lasers operating at room-temperature. Nano Lett, 2015, 15, 5302 doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.5b01665[2] Ye Y, Wong Z J, Lu X F, et al. Monolayer excitonic laser. Nat Photon, 2015, 9, 733 doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2015.197[3] Wu S, Buckley S, Schaibley J R, et al. Monolayer semiconductor nanocavity lasers with ultralow thresholds. Nature, 2015, 520, 69 doi: 10.1038/nature14290[4] Pospischil A, Furchi M M, Mueller T. Solar-energy conversion and light emission in an atomic monolayer p–n diode. Nat Nanotechnol, 2014, 9, 257 doi: 10.1038/nnano.2014.14[5] Withers F, del Pozo-Zamudio O, Mishchenko A, et al. Light-emitting diodes by band-structure engineering in van der Waals heterostructures. Nat Mater, 2015, 14, 301 doi: 10.1038/nmat4205[6] Koperski M, Nogajewski K, Arora A, et al. Single photon emitters in exfoliated WSe2 structures. Nat Nanotechnol, 2015, 10, 503 doi: 10.1038/nnano.2015.67[7] He Y M, Clark G, Schaibley J R, et al. Single quantum emitters in monolayer semiconductors. Nat Nanotechnol, 2015, 10, 497 doi: 10.1038/nnano.2015.75[8] Roldán R, Silva-Guillén J A, López-Sancho M P, et al. Electronic properties of single-layer and multilayer transition metal dichalcogenides MX2 (M = Mo, W and X = S, Se). Ann Der Physik, 2014, 526, 347 doi: 10.1002/andp.201400128[9] Currie M, Hanbicki A T, Kioseoglou G, et al. Optical control of charged exciton states in tungsten disulfide. Appl Phys Lett, 2015, 106, 201907 doi: 10.1063/1.4921472[10] Singh A, Moody G, Tran K, et al. Trion formation dynamics in monolayer transition metal dichalcogenides. Phys Rev B, 2016, 93, 041401 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.93.041401[11] Godde T, Schmidt D, Schmutzler J, et al. Exciton and trion dynamics in atomically thin MoSe2 and WSe2: Effect of localization. Phys Rev B, 2016, 94, 165301 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.94.165301[12] Liu T, Xiang D, Zheng Y, et al. Nonvolatile and programmable photodoping in MoTe2 for photoresist-free complementary electronic devices. Adv Mater, 2018, 30, 1804470 doi: 10.1002/adma.201804470[13] Quereda J, Ghiasi T S, van der Wal C H, et al. Semiconductor channel-mediated photodoping in h-BN encapsulated monolayer MoSe2 phototransistors. 2D Mater, 2019, 6, 025040 doi: 10.1088/2053-1583/ab0c2d[14] Ross J S, Wu S F, Yu H Y, et al. Electrical control of neutral and charged excitons in a monolayer semiconductor. Nat Commun, 2013, 4, 1474 doi: 10.1038/ncomms2498[15] Cadiz F, Robert C, Wang G, et al. Ultra-low power threshold for laser induced changes in optical properties of 2D molybdenum dichalcogenides. 2D Mater, 2016, 3, 045008 doi: 10.1088/2053-1583/3/4/045008[16] Atkin P, Lau D M, Zhang Q, et al. Laser exposure induced alteration of WS2 monolayers in the presence of ambient moisture. 2D Mater, 2017, 5, 015013 doi: 10.1088/2053-1583/aa91b8[17] Liu Z, Amani M, Najmaei S, et al. Strain and structure heterogeneity in MoS2 atomic layers grown by chemical vapour deposition. Nat Commun, 2014, 5, 5246 doi: 10.1038/ncomms6246[18] Fu X, Li F, Lin J F, et al. Pressure-dependent light emission of charged and neutral excitons in monolayer MoSe2. J Phys Chem Lett, 2017, 8, 3556 doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.7b01374[19] Pei J, Yang J, Wang X, et al. Excited state biexcitons in atomically thin MoSe2. ACS Nano, 2017, 11, 7468 doi: 10.1021/acsnano.7b03909[20] Lundt N, Cherotchenko E, Iff O, et al. The interplay between excitons and trions in a monolayer of MoSe2. Appl Phys Lett, 2018, 112, 031107 doi: 10.1063/1.5019177[21] Pelant I, Valenta J. Luminescence spectroscopy of semiconductors. London: Oxford University Press, 2012[22] Scher H, Montroll E W. Anomalous transit-time dispersion in amorphous solids. Phys Rev B, 1975, 12, 2455 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.12.2455[23] Kakalios J, Street R A, Jackson W B. Stretched-exponential relaxation arising from dispersive diffusion of hydrogen in amorphous silicon. Phys Rev Lett, 1987, 59, 1037 doi: 10.1063/1.4933331 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: