| Citation: |
Shuai Yuan, Changran Hu, An Pan, Yuedi Ding, Xuanhao Wang, Zhicheng Qu, Junjie Wei, Yuheng Liu, Cheng Zeng, Jinsong Xia. Photonic devices based on thin-film lithium niobate on insulator[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2021, 42(4): 041304. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/42/4/041304
****
S Yuan, C R Hu, A Pan, Y D Ding, X H Wang, Z C Qu, J J Wei, Y H Liu, C Zeng, J S Xia, Photonic devices based on thin-film lithium niobate on insulator[J]. J. Semicond., 2021, 42(4): 041304. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/42/4/041304.
|
Photonic devices based on thin-film lithium niobate on insulator
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/42/4/041304
More Information
-
Abstract
Lithium niobate on insulator (LNOI) is rising as one of the most promising platforms for integrated photonics due to the high-index-contrast and excellent material properties of lithium niobate, such as wideband transparency from visible to mid-infrared, large electro-optic, piezoelectric, and second-order harmonic coefficients. The fast-developing micro- and nano-structuring techniques on LNOI have enabled various structure, devices, systems, and applications. In this contribution, we review the latest developments in this platform, including ultra-high speed electro-optic modulators, optical frequency combs, opto-electro-mechanical system on chip, second-harmonic generation in periodically poled LN waveguides, and efficient edge coupling for LNOI.-
Keywords:
- thin-film lithium niobate,
- modulator,
- PPLN,
- edge coupler
-
References
[1] Marpaung D, Roeloffzen C, Heideman R, et al. Integrated microwave photonics. Laser Photonics Rev, 2013, 7, 506 doi: 10.1002/lpor.201200032[2] Ye W N, Xiong Y L. Review of silicon photonics: History and recent advances. J Mod Opt, 2013, 60, 1299 doi: 10.1080/09500340.2013.839836[3] Thomson D, Zilkie A, Bowers J E, et al. Roadmap on silicon photonics. J Opt, 2016, 18, 073003 doi: 10.1088/2040-8978/18/7/073003[4] van der Tol J J G M, Jiao Y Q, Shen L F, et al. Indium phosphide integrated photonics in membranes. IEEE J Sel Top Quantum Electron, 2018, 24, 1 doi: 10.1109/JSTQE.2017.2772786[5] Wang C, Zhang M, Stern B, et al. Nanophotonic lithium niobate electro-optic modulators. Opt Express, 2018, 26, 1547 doi: 10.1364/OE.26.001547[6] Wang C, Zhang M, Chen X, et al. Integrated lithium niobate electro-optic modulators operating at CMOS-compatible voltages. Nature, 2018, 562, 101 doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0551-y[7] He Y, Yang Q F, Ling J W, et al. Self-starting bi-chromatic LiNbO3 soliton microcomb. Optica, 2019, 6, 1138 doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.6.001138[8] Sua Y, Chen J Y, Huang Y P. Ultra-wideband and high-gain parametric amplification in telecom wavelengths with an optimally mode-matched PPLN waveguide. Opt Lett, 2018, 43, 2965 doi: 10.1364/OL.43.002965[9] Wang T J, Chu C H, Lin C Y. Electro-optically tunable microring resonators on lithium niobate. Opt Lett, 2007, 32, 2777 doi: 10.1364/OL.32.002777[10] Chiles J, Fathpour S. Mid-infrared integrated waveguide modulators based on silicon-on-lithium-niobate photonics. Optica, 2014, 1, 350 doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.1.000350[11] Stenger V E, Toney J, PoNick A, et al. Low loss and low vpi thin film lithium niobate on quartz electro-optic modulators. European Conference on Optical Communication (ECOC), 2017, 1[12] Stenger V, Toney J, Pollick A, et al. Engineered thin film lithium niobate substrate for high gain-bandwidth electro-optic modulators. CLEO: 2013, OSA Technical Digest, 2013, CW3O.3[13] Wang C, Zhang M, Yu M, et al. Monolithic lithium niobate photonic circuits for Kerr frequency comb generation and modulation. Nat Commun, 2019, 10, 978 doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-08969-6[14] Li M X, Ling J W, He Y, et al. Lithium niobate photonic-crystal electro-optic modulator. Nat Commun, 2020, 11, 4123 doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-17950-7[15] Han S, Cong L, Srivastava Y K, et al. All-dielectric active terahertz photonics driven by bound states in the continuum. Adv Mater, 2019, 31, e1901921 doi: 10.1002/adma.201901921[16] Xu M, He M, Zhang H, et al. High-performance coherent optical modulators based on thin-film lithium niobate platform. Nat Commun, 2020, 11, 3911 doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-17806-0[17] Kippenberg T J, Holzwarth R, Diddams S A. Microresonator-based optical frequency combs. Science, 2011, 332, 555 doi: 10.1126/science.1193968[18] Herr T, Brasch V, Jost J D, et al. Temporal solitons in optical microresonators. Nat Photonics, 2014, 8, 145 doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2013.343[19] Marin-Palomo P, Kemal J N, Karpov M, et al. Microresonator-based solitons for massively parallel coherent optical communications. Nature, 2017, 546, 274 doi: 10.1038/nature22387[20] DeSalvo R, Said A A, Hagan D J, et al. Infrared to ultraviolet measurements of two-photon absorption and n2 in wide bandgap solids. IEEE J Quantum Electron, 1996, 32, 1324 doi: 10.1109/3.511545[21] Zhang M, Wang C, Cheng R, et al. Monolithic ultra-high-Q lithium niobate microring resonator. Optica, 2017, 4, 1536 doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.4.001536[22] Zhang M, Buscaino B, Wang C, et al. Broadband electro-optic frequency comb generation in a lithium niobate microring resonator. Nature, 2019, 568, 373 doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1008-7[23] Pan A, Hu C R, Zeng C, et al. Fundamental mode hybridization in a thin film lithium niobate ridge waveguide. Opt Express, 2019, 27, 35659 doi: 10.1364/OE.27.035659[24] Liu K, Ye C, Khan S, et al. Review and perspective on ultrafast wavelength-size electro-optic modulators. Laser Photonics Rev, 2015, 9, 172 doi: 10.1002/lpor.201400219[25] Faraon A, Vučković J. Local temperature control of photonic crystal devices via micron-scale electrical heaters. Appl Phys Lett, 2009, 95, 043102 doi: 10.1063/1.3189081[26] Bennett B R, Soref R A, del Alamo J A. Carrier-induced change in refractive index of InP, GaAs and InGaAsP. IEEE J Quantum Electron, 1990, 26, 113 doi: 10.1109/3.44924[27] Baker C, Hease W, Nguyen D T, et al. Photoelastic coupling in gallium arsenide optomechanical disk resonators. Opt Express, 2014, 22, 14072 doi: 10.1364/OE.22.014072[28] Midolo L, Schliesser A, Fiore A. Nano-opto-electro-mechanical systems. Nat Nanotechnol, 2018, 13, 11 doi: 10.1038/s41565-017-0039-1[29] Weis R S, Gaylord T K. Lithium niobate: Summary of physical properties and crystal structure. Appl Phys A, 1985, 37, 191 doi: 10.1007/BF00614817[30] Bhugra H, Piazza G. Piezoelectric MEMS resonators. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2017[31] Gong S B, Piazza G. Design and analysis of lithium–niobate-based high electromechanical coupling RF-MEMS resonators for wideband filtering. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech, 2013, 61, 403 doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2012.2228671[32] Poberaj G, Hu H, Sohler W, et al. Lithium niobate on insulator (LNOI) for micro-photonic devices. Laser Photonics Rev, 2012, 6, 488 doi: 10.1002/lpor.201100035[33] Jiang W T, Patel R N, Mayor F M, et al. Lithium niobate piezo-optomechanical crystals. Optica, 2019, 6, 845 doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.6.000845[34] Cai L T, Mahmoud A, Khan M, et al. Acousto-optical modulation of thin film lithium niobate waveguide devices. Photonics Res, 2019, 7, 1003 doi: 10.1364/PRJ.7.001003[35] Shao L B, Yu M J, Maity S, et al. Microwave-to-optical conversion using lithium niobate thin-film acoustic resonators. Optica, 2019, 6, 1498 doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.6.001498[36] Wong K K. Properties of lithium niobate. IET, 2002[37] Nagy J T, Reano R M. Reducing leakage current during periodic poling of ion-sliced x-cut MgO doped lithium niobate thin films. Opt Mater Express, 2019, 9, 3146 doi: 10.1364/OME.9.003146[38] Wang C, Langrock C, Marandi A, et al. Ultrahigh-efficiency wavelength conversion in nanophotonic periodically poled lithium niobate waveguides. Optica, 2018, 5, 1438 doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.5.001438[39] Niu Y F, Lin C, Liu X Y, et al. Optimizing the efficiency of a periodically poled LNOI waveguide using in situ monitoring of the ferroelectric domains. Appl Phys Lett, 2020, 116, 101104 doi: 10.1063/1.5142750[40] Rao A, Rao A, Rao A, et al. Actively-monitored periodic-poling in thin-film lithium niobate photonic waveguides with ultrahigh nonlinear conversion efficiency of 4600 %W−1cm−2. Opt Express, 2019, 27, 25920 doi: 10.1364/OE.27.025920[41] Lu J J, Surya J B, Liu X W, et al. Periodically poled thin-film lithium niobate microring resonators with a second-harmonic generation efficiency of 250, 000%/W. Optica, 2019, 6, 1455 doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.6.001455[42] Chen J Y, Ma Z H, Sua Y, et al. Ultra-efficient frequency conversion in quasi-phase-matched lithium niobate microrings. Optica, 2019, 6, 1244 doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.6.001244[43] Pohl D, Escalé M R, Madi M, et al. An integrated broadband spectrometer on thin-film lithium niobate. Nat Photonics, 2020, 14, 24 doi: 10.1038/s41566-019-0529-9[44] Yao N, Yao N, Zhou J X, et al. Efficient light coupling between an ultra-low loss lithium niobate waveguide and an adiabatically tapered single mode optical fiber. Opt Express, 2020, 28, 12416 doi: 10.1364/OE.391228[45] Krasnokutska I, Tambasco J L J, Peruzzo A. Nanostructuring of LNOI for efficient edge coupling. Opt Express, 2019, 27, 16578 doi: 10.1364/OE.27.016578[46] He L Y, He L Y, Zhang M, et al. Low-loss fiber-to-chip interface for lithium niobate photonic integrated circuits. Opt Lett, 2019, 44, 2314 doi: 10.1364/OL.44.002314[47] Pan Y, Sun S H, Xu M Y, et al. Low fiber-to-fiber loss, large bandwidth and low drive voltage lithium niobate on insulator modulators. Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics, 2020, JTh2B.10[48] Hu C R, Pan A, Li T, et al. High-efficient and polarization independent edge coupler for thin-film lithium niobite waveguide devices. arXiv: 2009.02855, 2020 -
Proportional views





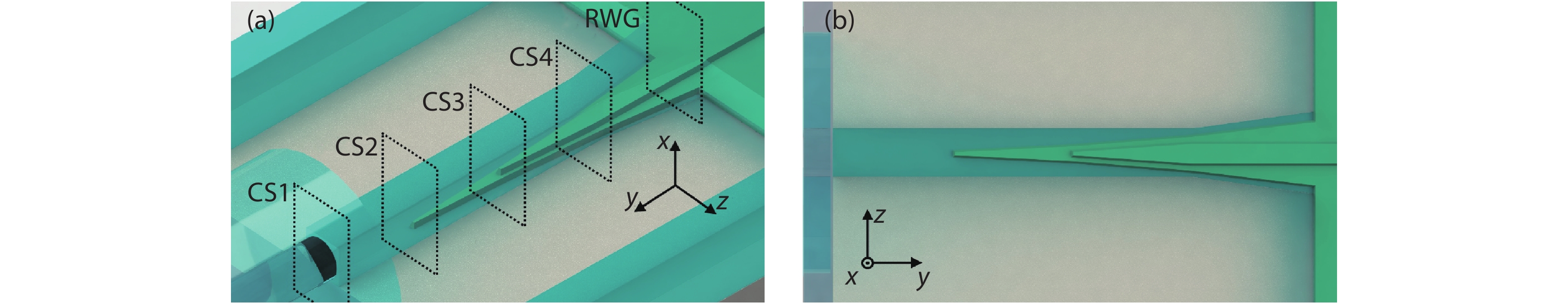
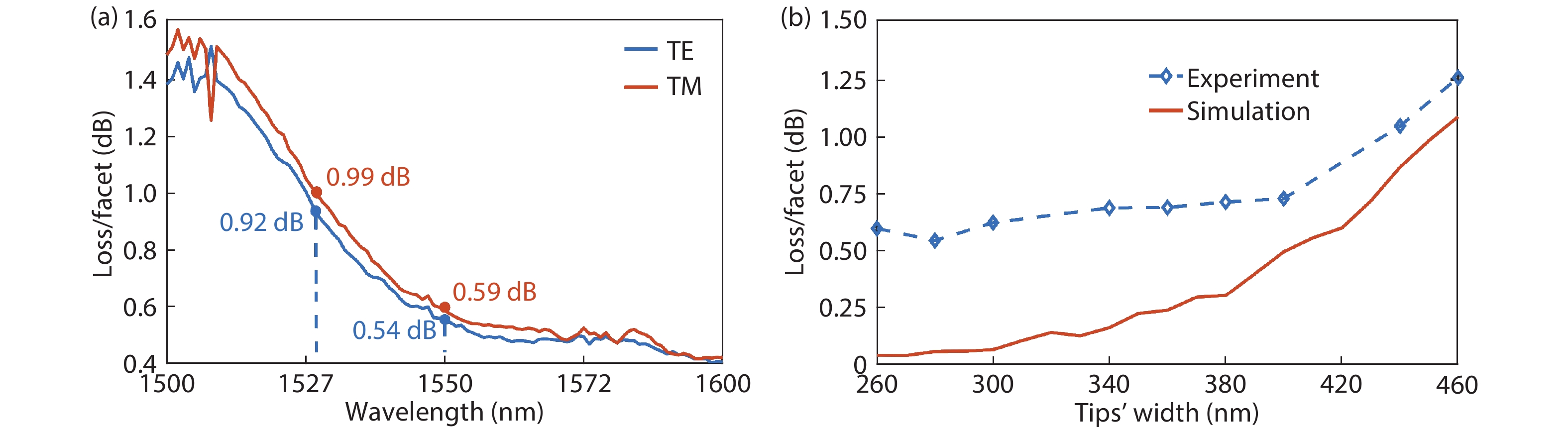
 DownLoad:
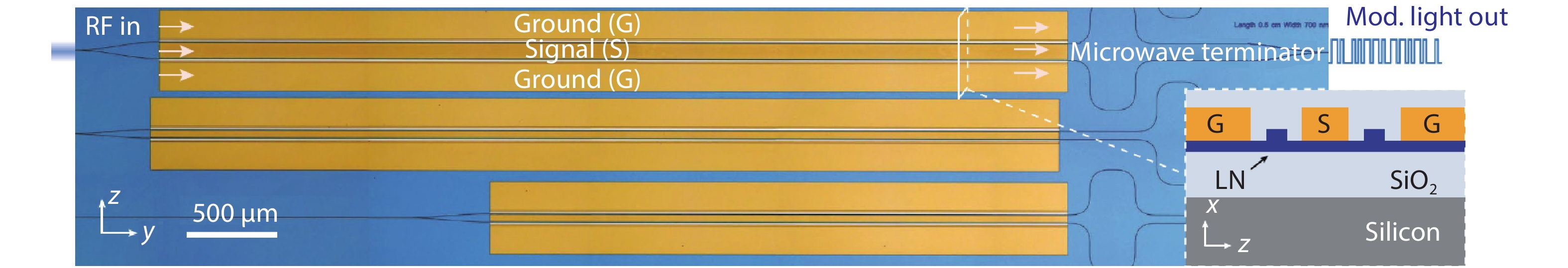
DownLoad: