| Citation: |
Qiao Wang, Donglin Zhang, Yulin Zhao, Chao Liu, Xiaoxin Xu, Jianguo Yang, Hangbing Lv. Low-cost dual-stage offset-cancelled sense amplifier with hybrid read reference generator for improved read performance of RRAM at advanced technology nodes[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2021, 42(8): 082401. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/42/8/082401
****
Q Wang, D L Zhang, Y L Zhao, C Liu, X X Xu, J G Yang, H B Lv, Low-cost dual-stage offset-cancelled sense amplifier with hybrid read reference generator for improved read performance of RRAM at advanced technology nodes[J]. J. Semicond., 2021, 42(8): 082401. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/42/8/082401.
|
Low-cost dual-stage offset-cancelled sense amplifier with hybrid read reference generator for improved read performance of RRAM at advanced technology nodes
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/42/8/082401
More Information
-
Abstract
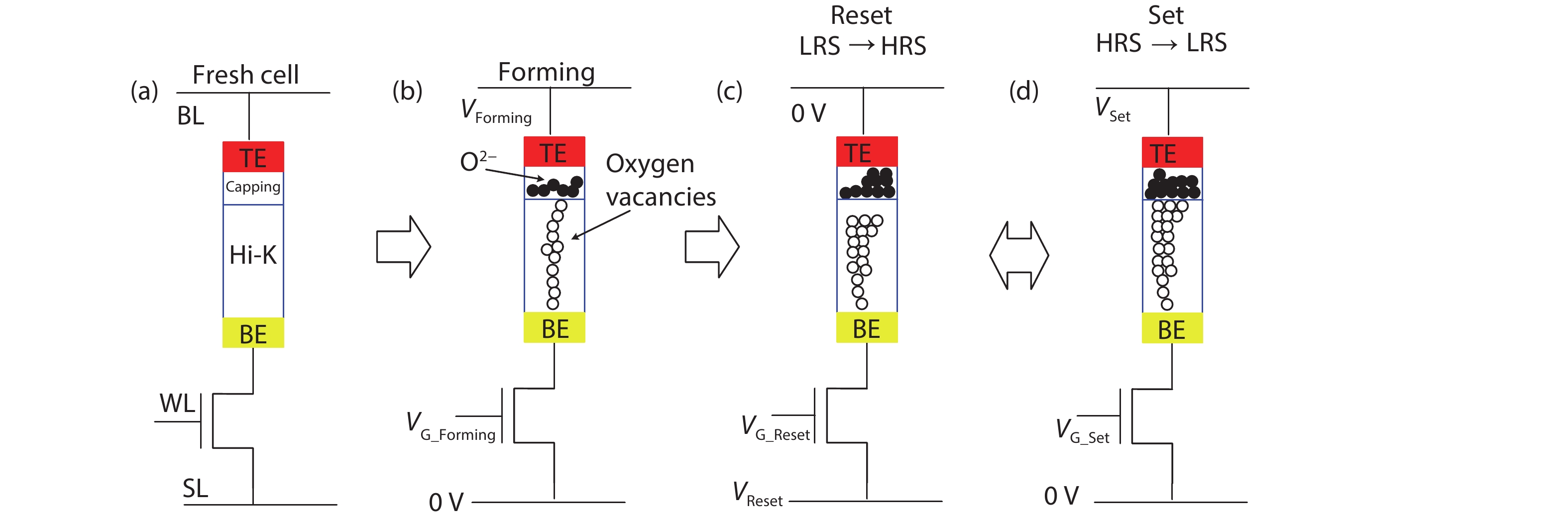
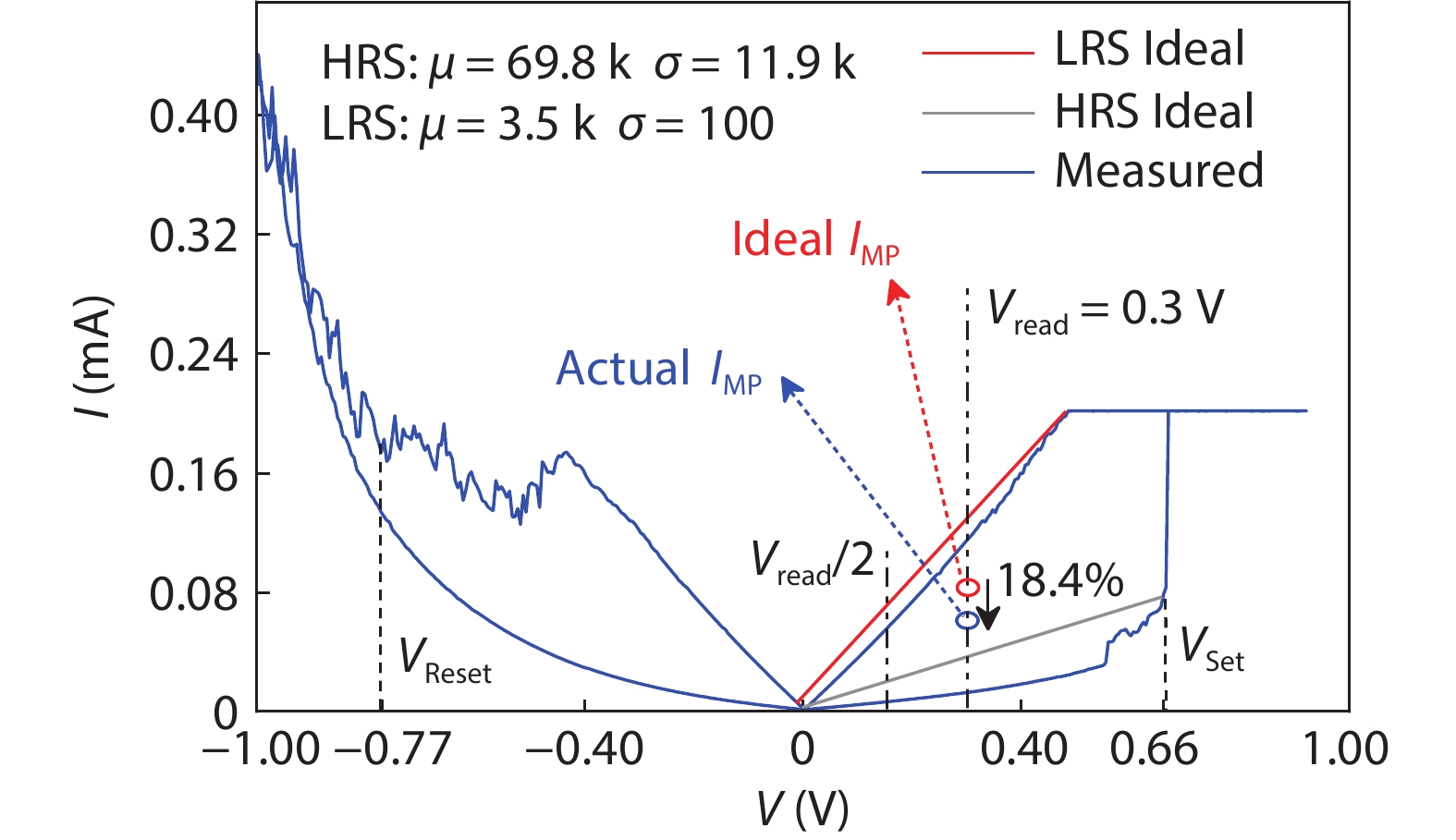
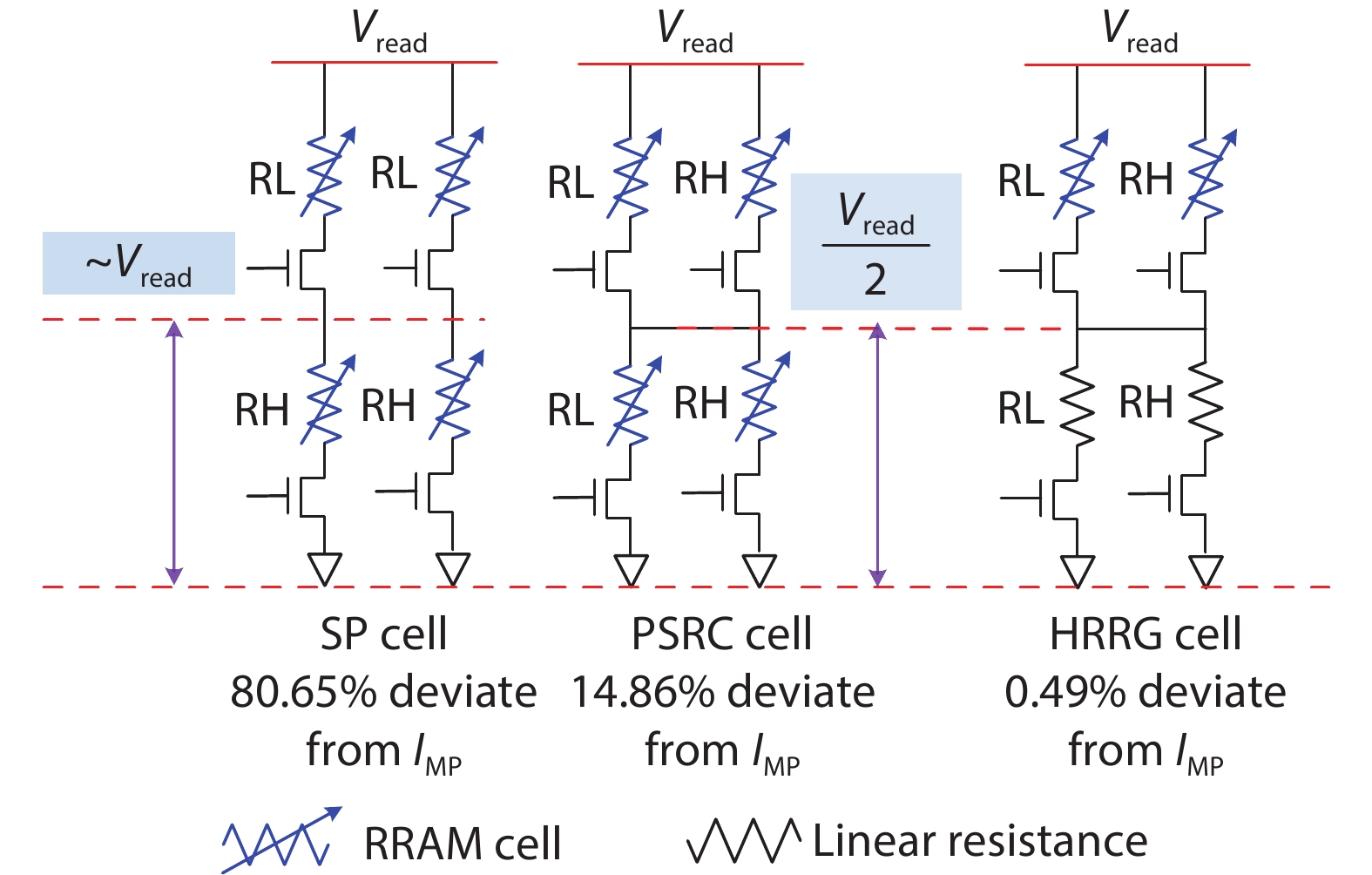
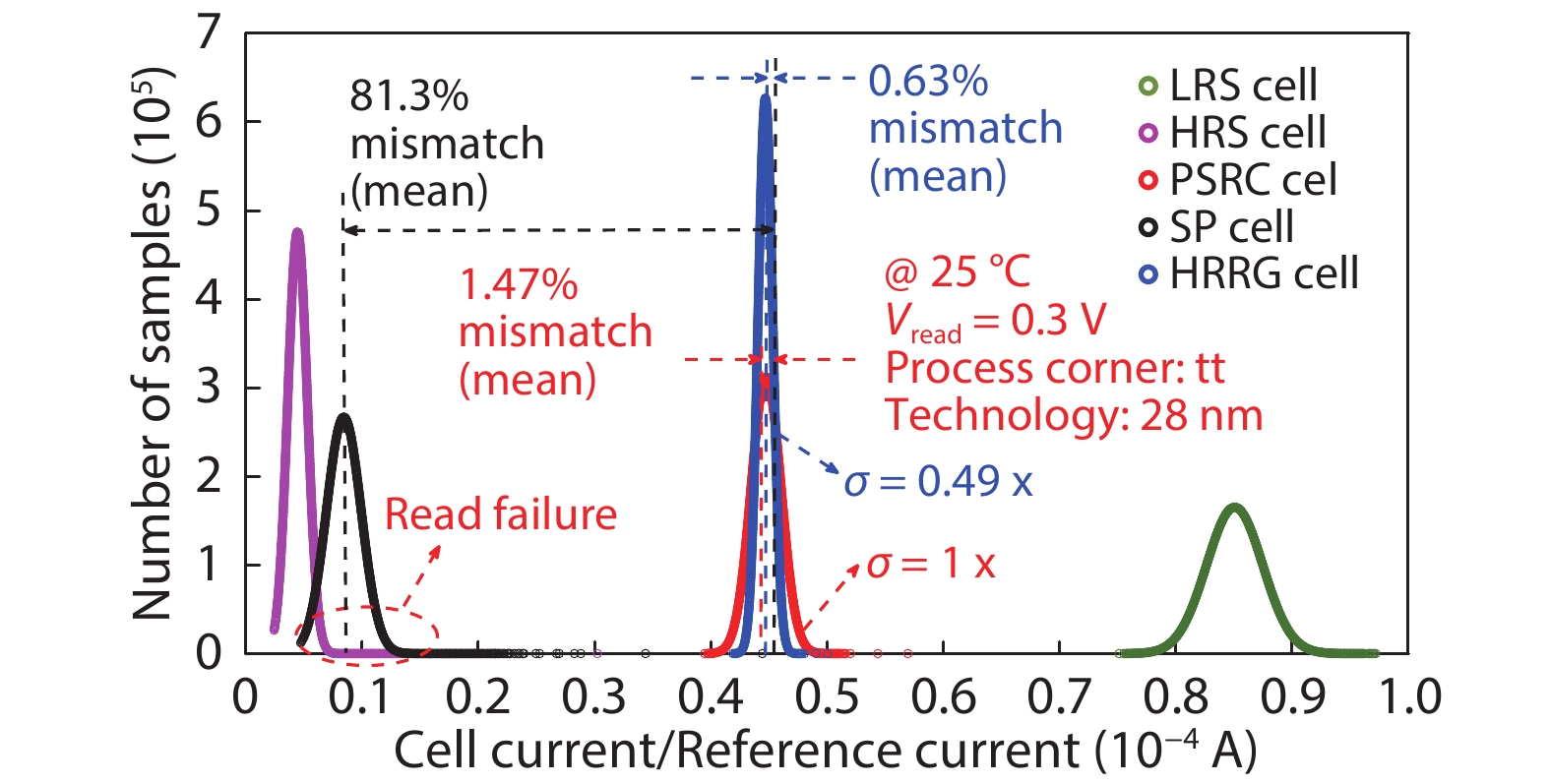
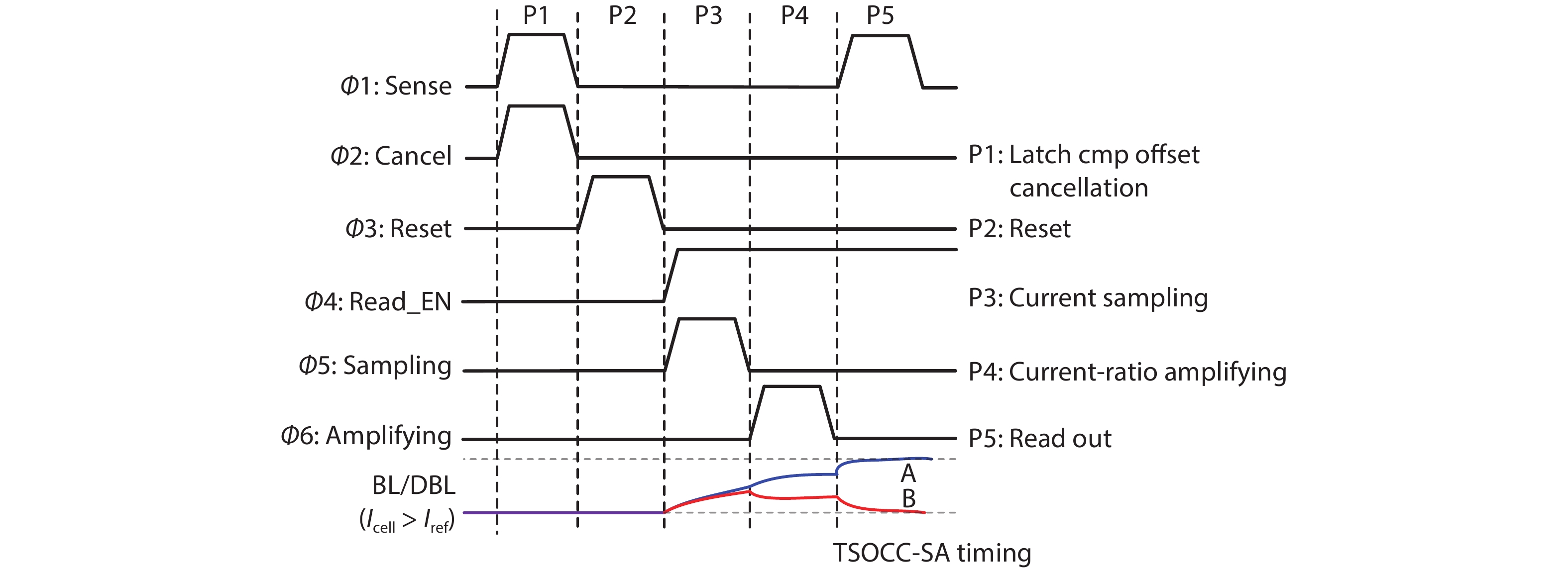
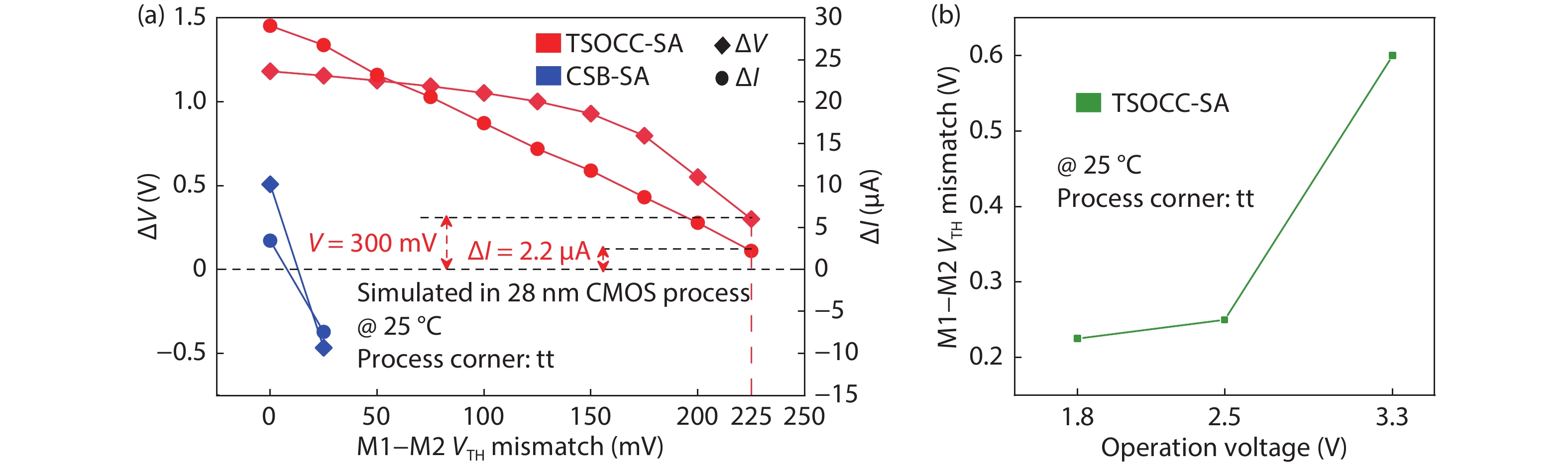
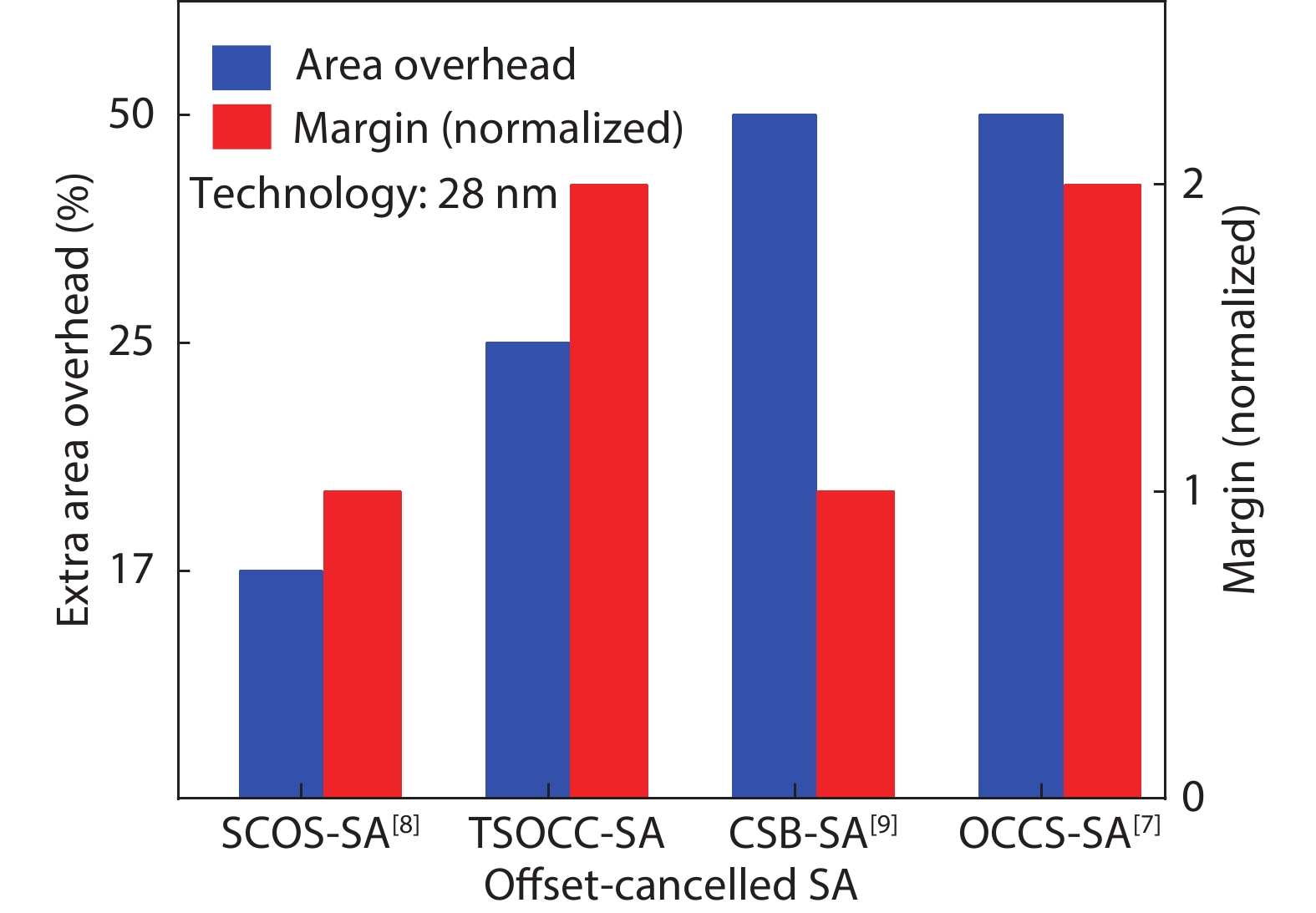
In this work, two process-variation-tolerant schemes for a current-mode sense amplifier (CSA) of RRAM were proposed: (1) hybrid read reference generator (HRRG) that tracks process-voltage-temperature (PVT) variations and solve the nonlinear issue of the RRAM cells; (2) a two-stage offset-cancelled current sense amplifier (TSOCC-SA) with only two capacitors achieves a double sensing margin and a high tolerance of device mismatch. The simulation results in 28 nm CMOS technology show that the HRRG can provide a read reference that tracks PVT variations and solves the nonlinear issue of the RRAM cells. The proposed TSOCC-SA can tolerate over 64% device mismatch. -
References
[1] Yeh C W S, Wong S S. Compact one-transistor-N-RRAM array architecture for advanced CMOS technology. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2015, 50, 1299 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2015.2402217[2] Woo J, Yu S M. Two-step read scheme in one-selector and one-RRAM crossbar-based neural network for improved inference robustness. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2018, 65, 5549 doi: 10.1109/TED.2018.2875937[3] Chang M F, Wu C W, Kuo C C, et al. A 0.5 V 4 Mb logic-process compatible embedded resistive RAM (ReRAM) in 65 nm CMOS using low-voltage current-mode sensing scheme with 45 ns random read time. 2012 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, 2012, 434[4] Jain P, Arslan U, Sekhar M, et al. 13.2 A 3.6 Mb 10.1Mb/mm2 embedded non-volatile ReRAM macro in 22 nm FinFET technology with adaptive forming/set/reset schemes yielding down to 0.5 V with sensing time of 5 ns at 0.7 V. 2019 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, 2019, 212[5] Chen W H, Dou C M, Li K X, et al. CMOS-integrated memristive non-volatile computing-in-memory for AI edge processors. Nat Electron, 2019, 2, 420 doi: 10.1038/s41928-019-0288-0[6] Chou C C, Lin Z J, Lai C A, et al. A 22nm 96K × 144 RRAM macro with a self-tracking reference and a low ripple charge pump to achieve a configurable read window and a wide operating voltage range. IEEE Symposium on VLSI Circuits, 2020, 1[7] Na T, Song B, Kim J P, et al. Offset-canceling current-sampling sense amplifier for resistive nonvolatile memory in 65 nm CMOS. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2017, 52, 496 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2016.2612235[8] Dong Q, Wang Z H, Lim J, et al. A 1Mb 28nm STT-MRAM with 2.8ns read access time at 1.2V VDD using single-cap offset-cancelled sense amplifier and in situ self-write-termination. IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, 2018, 480[9] Chang M F, Shen S J, Liu C C, et al. An offset-tolerant current-sampling-based sense amplifier for sub-100nA-cell-current nonvolatile memory. IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, 2011, 206[10] Huang Y L, Huang R, Cai Y M, et al. A TaOx based threshold switching selector for the RRAM crossbar array memory. 12th Annual Non-Volatile Memory Technology Symposium Proceedings, 2012, 85[11] Chou C C, Lin Z J, Tseng P L, et al. An N40 256K × 44 embedded RRAM macro with SL-precharge SA and low-voltage current limiter to improve read and write performance. IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, 2018, 478[12] Chakrabarti S, Jana D, Dutta M, et al. Impact of AlOx interfacial layer and switching mechanism in W/AlOx/TaOx/TiN RRAMs. 2014 IEEE 6th Int Mem Work IMW, 2014, 1[13] Na T, Kim J, Kim J P, et al. Reference-scheme study and novel reference scheme for deep submicrometer STT-RAM. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I, 2014, 61, 3376 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2014.2327337[14] Durlam M, Naji P J, Omair A, et al. A 1-Mbit MRAM based on 1T1MTJ bit cell integrated with copper interconnects. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2003, 38, 769 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2003.810048[15] Chang M F, Sheu S S, Lin K F, et al. A high-speed 7.2-ns read-write random access 4-mb embedded resistive RAM (ReRAM) macro using process-variation-tolerant current-mode read schemes. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2013, 48, 878 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2012.2230515[16] Trinh Q K, Ruocco S, Alioto M. Dynamic reference voltage sensing scheme for read margin improvement in STT-MRAMs. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I, 2018, 65, 1269 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2017.2749522[17] Kang W, Pang T T, Lv W, et al. Dynamic dual-reference sensing scheme for deep submicrometer STT-MRAM. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I, 2017, 64, 122 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2016.2606438[18] Zhou Y L, Cai H, Xie L, et al. A self-timed voltage-mode sensing scheme with successive sensing and checking for STT-MRAM. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I, 2020, 67, 1602 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2019.2960028 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: