| Citation: |
Jianyun Zhao, Xu Li, Ting Liu, Yong Lu, Jicai Zhang. First-principles study of the growth and diffusion of B and N atoms on the sapphire surface with h-BN as the buffer layer[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2021, 42(8): 082801. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/42/8/082801
****
J Y Zhao, X Li, T Liu, Y Lu, J C Zhang, First-principles study of the growth and diffusion of B and N atoms on the sapphire surface with h-BN as the buffer layer[J]. J. Semicond., 2021, 42(8): 082801. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/42/8/082801.
|
First-principles study of the growth and diffusion of B and N atoms on the sapphire surface with h-BN as the buffer layer
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/42/8/082801
More Information
-
Abstract
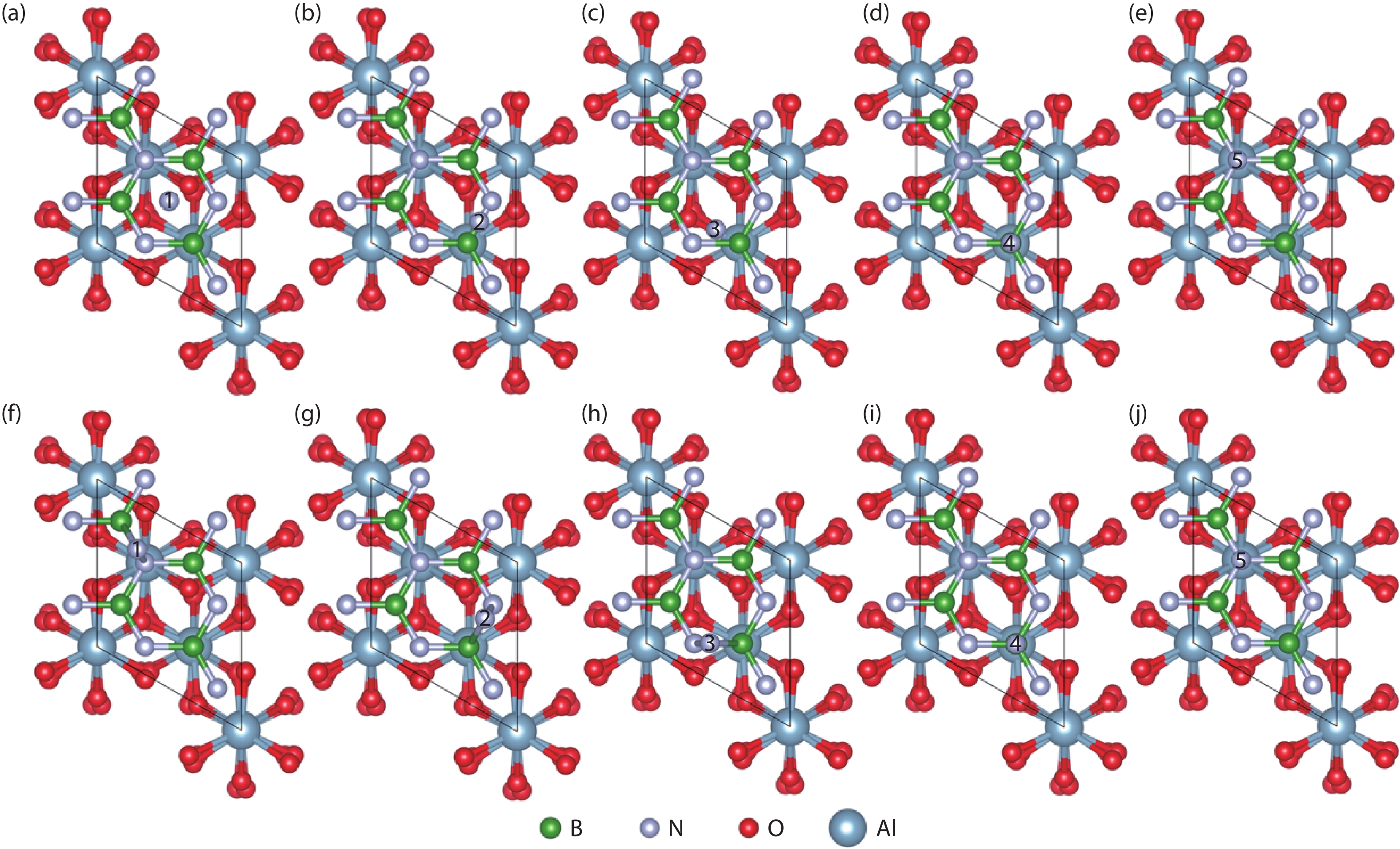
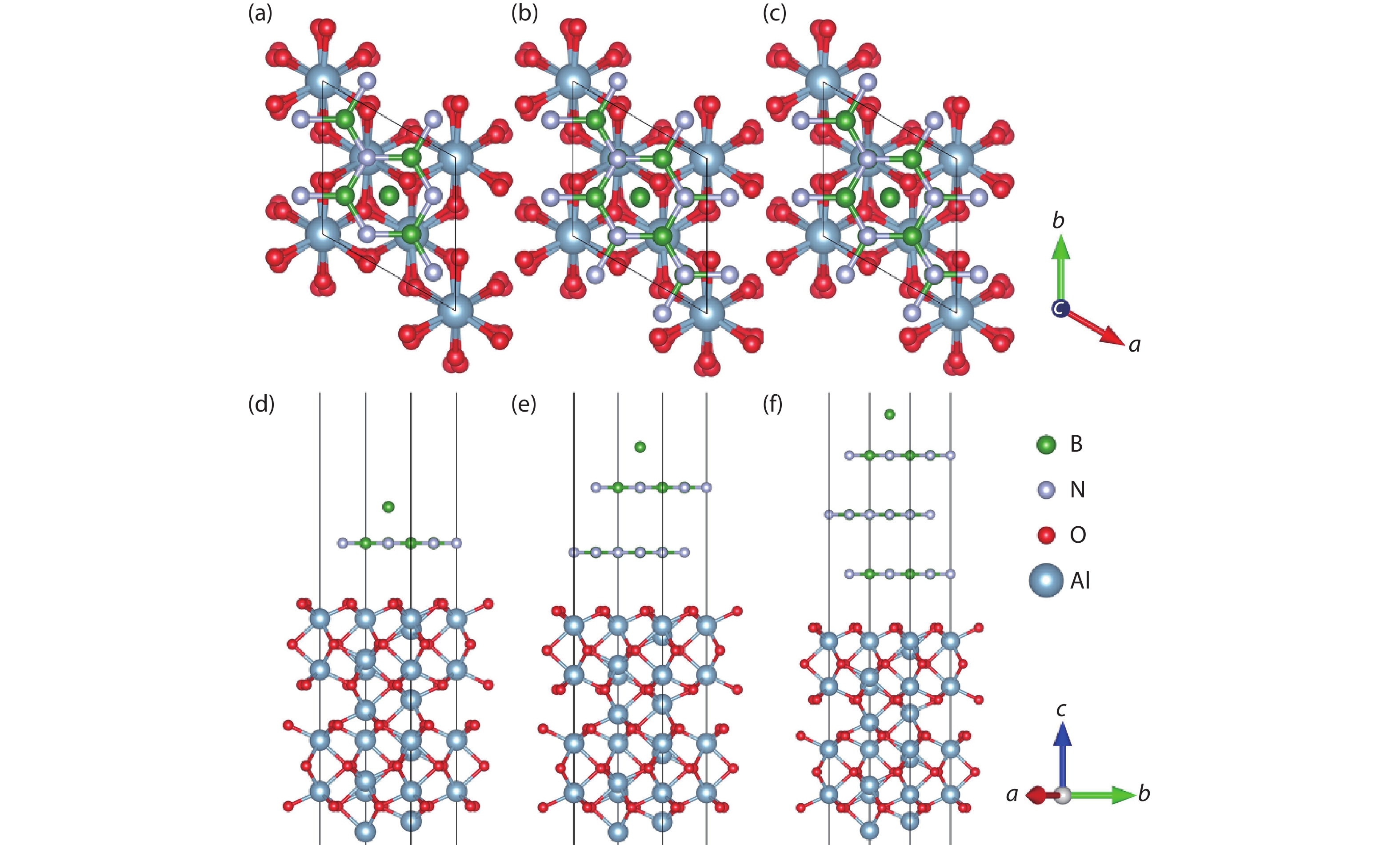
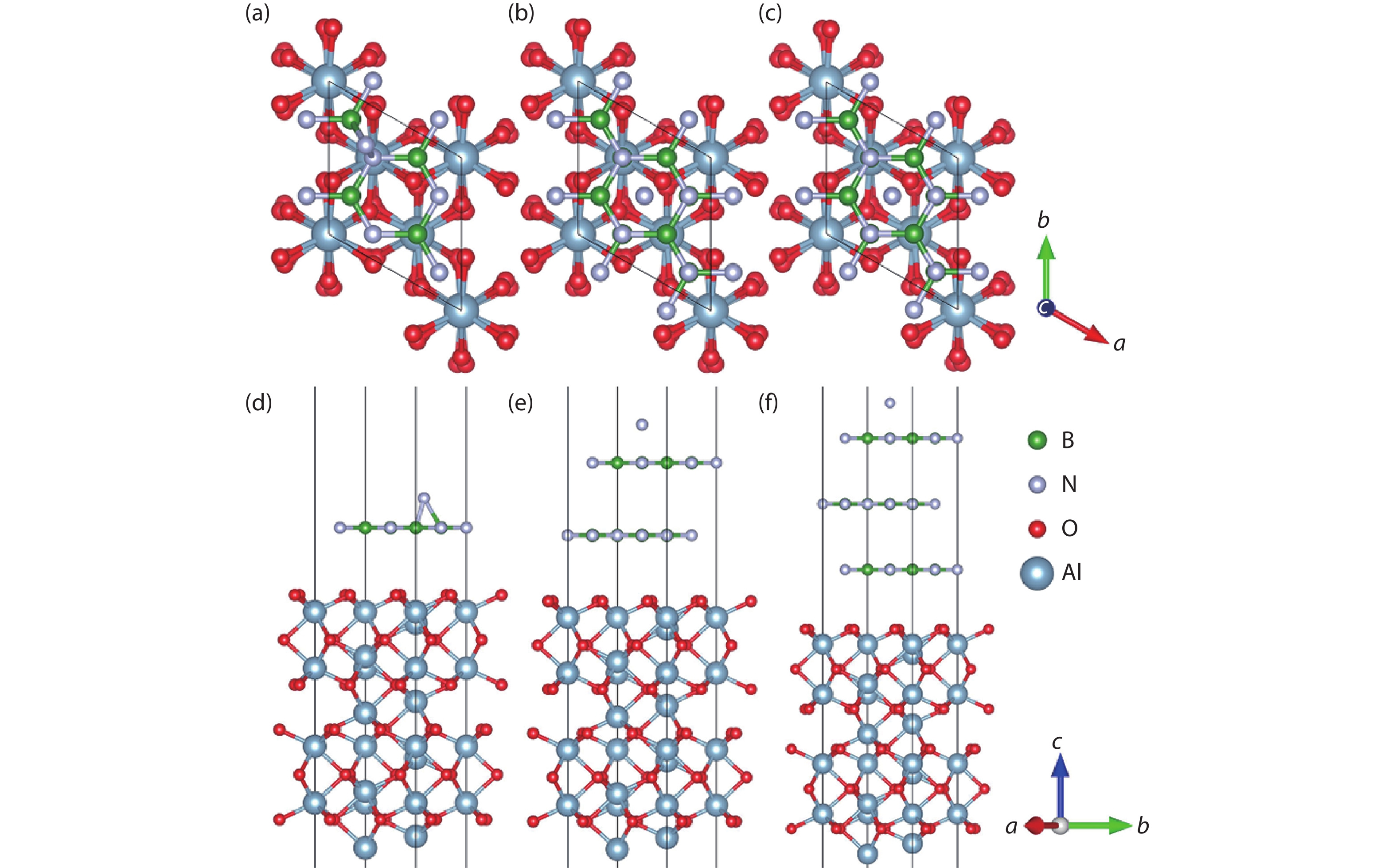
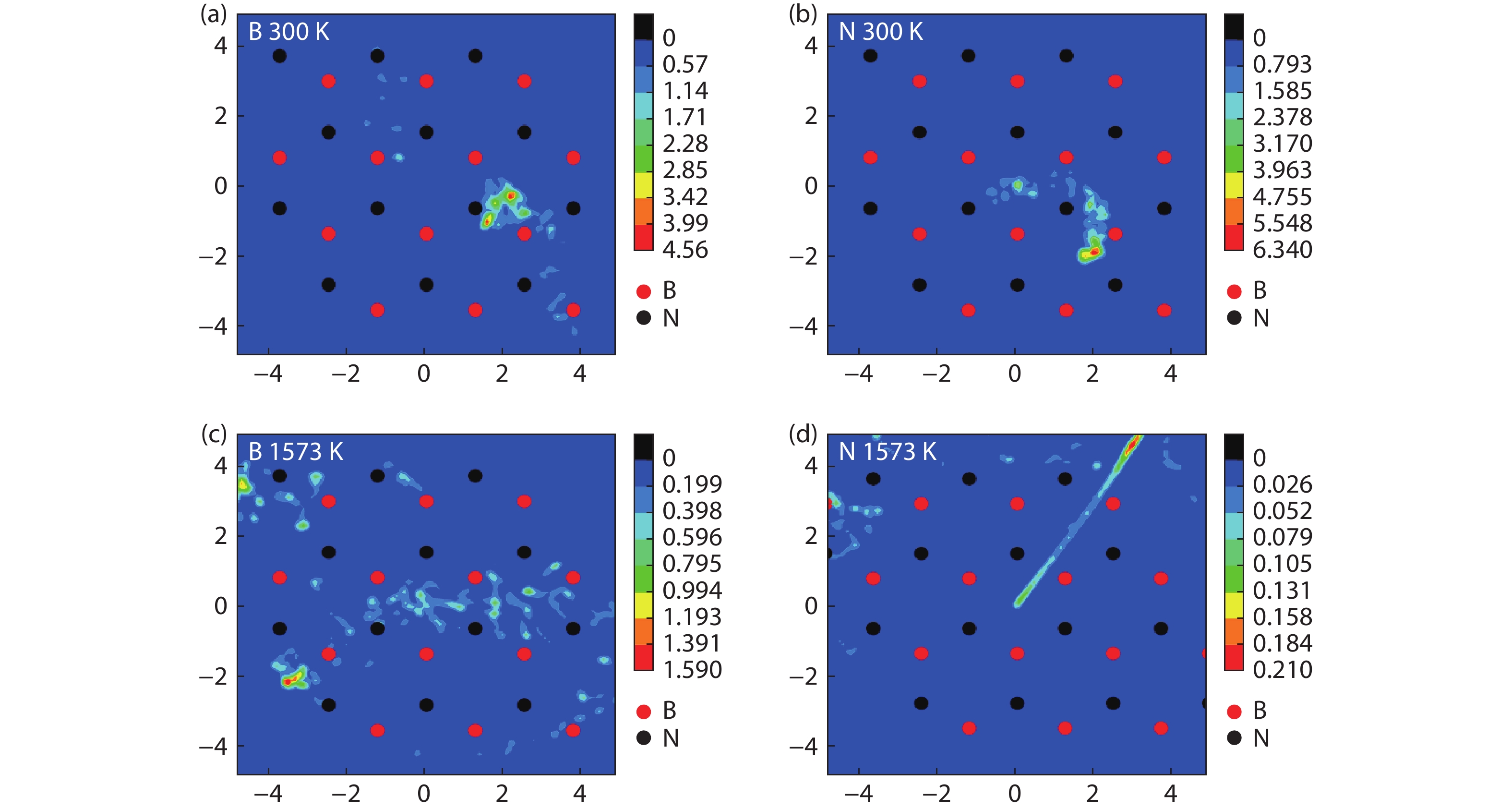
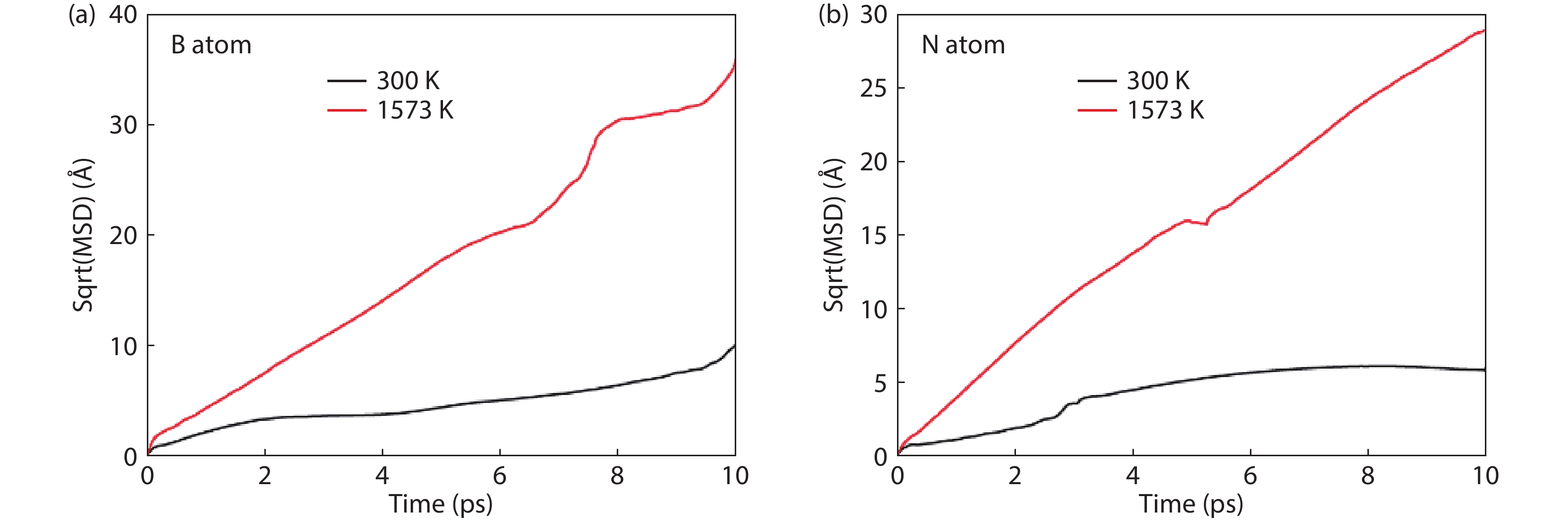
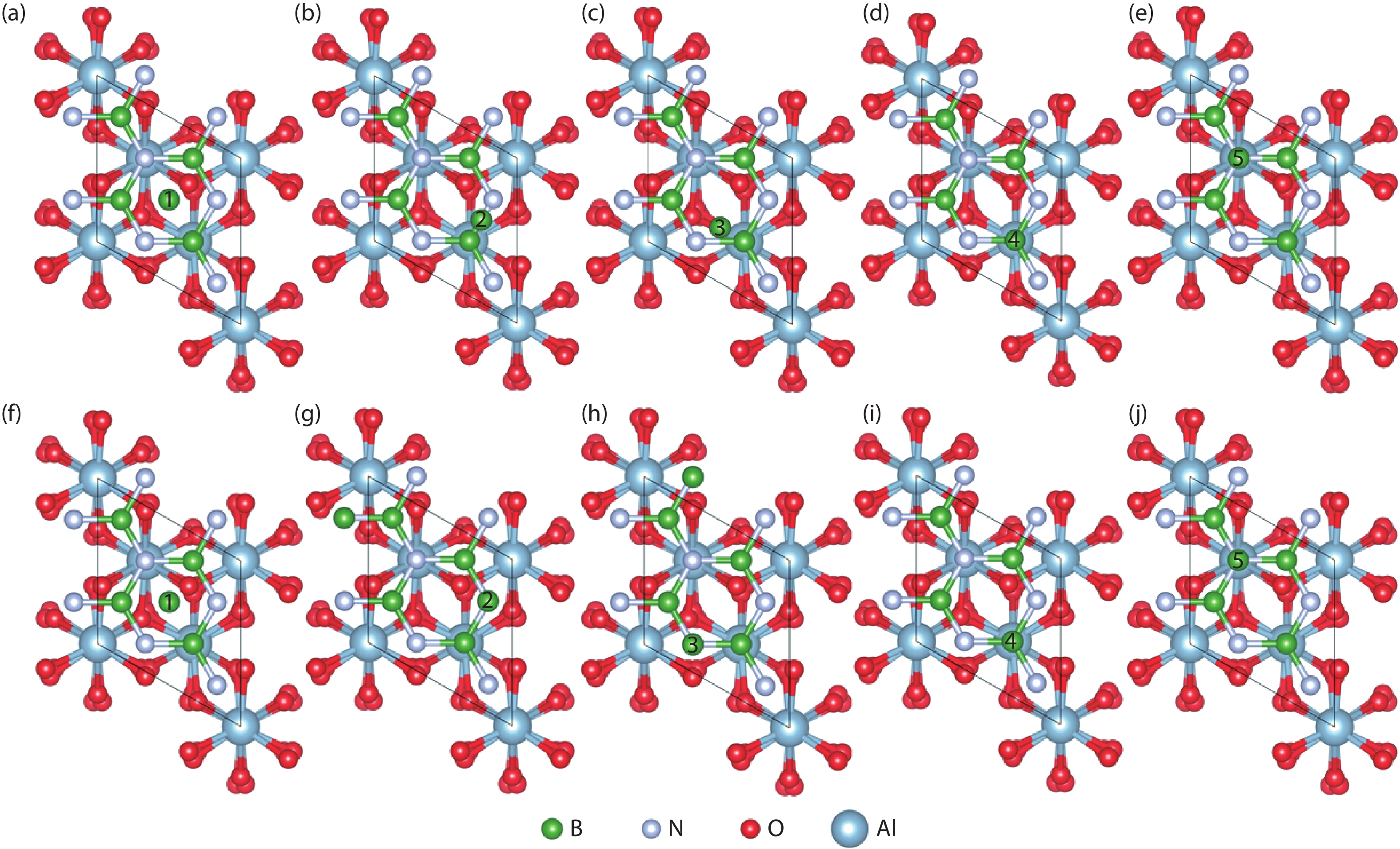
Currently, the preparation of large-size and high-quality hexagonal boron nitride is still an urgent problem. In this study, we investigated the growth and diffusion of boron and nitrogen atoms on the sapphire/h-BN buffer layer by first-principles calculations based on density functional theory. The surface of the single buffer layer provides several metastable adsorption sites for free B and N atoms due to exothermic reaction. The adsorption sites at the ideal growth point for B atoms have the lowest adsorption energy, but the N atoms are easily trapped by the N atoms on the surface to form N–N bonds. With the increasing buffer layers, the adsorption process of free atoms on the surface changes from exothermic to endothermic. The diffusion rate of B atoms is much higher than that of the N atoms thus the B atoms play a major role in the formation of B–N bonds. The introduction of buffer layers can effectively shield the negative effect of sapphire on the formation of B–N bonds. This makes the crystal growth on the buffer layer tends to two-dimensional growth, beneficial to the uniform distribution of B and N atoms. These findings provide an effective reference for the h-BN growth. -
References
[1] Geim A K, Novoselov K S. The rise of graphene. Nat Mater, 2007, 6, 183 doi: 10.1038/nmat1849[2] Wang J G, Mu X J, Wang X X, et al. The thermal and thermoelectric properties of in-plane C-BN hybrid structures and graphene/h-BN van der Waals heterostructures. Mater Today Phys, 2018, 5, 29 doi: 10.1016/j.mtphys.2018.05.006[3] Tang Q, Zhou Z. Graphene-analogous low-dimensional materials. Prog Mater Sci, 2013, 58, 1244 doi: 10.1016/j.pmatsci.2013.04.003[4] Wang J G, Ma F C, Sun M T. Graphene, hexagonal boron nitride, and their heterostructures: Properties and applications. RSC Adv, 2017, 7, 16801 doi: 10.1039/C7RA00260B[5] Song Y X, Zhang C R, Li B, et al. Triggering the atomic layers control of hexagonal boron nitride films. Appl Surf Sci, 2014, 313, 647 doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.06.040[6] Dahal R, Li J, Majety S, et al. Epitaxially grown semiconducting hexagonal boron nitride as a deep ultraviolet photonic material. Appl Phys Lett, 2011, 98, 211110 doi: 10.1063/1.3593958[7] Doan T C, Majety S, Grenadier S, et al. Fabrication and characterization of solid-state thermal neutron detectors based on hexagonal boron nitride epilayers. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res Sect A, 2014, 748, 84 doi: 10.1016/j.nima.2014.02.031[8] Jiang H X, Lin J Y. Hexagonal boron nitride for deep ultraviolet photonic devices. Semicond Sci Technol, 2014, 29, 084003 doi: 10.1088/0268-1242/29/8/084003[9] Cai L C, Fan X H, Su H T, et al. First principles calculation of the lattice constants of hexagonal and cubic boron nitride to 3000 K and 30 GPa. Ferroelectrics, 2020, 566, 136 doi: 10.1080/00150193.2020.1762437[10] Hafner J. Ab-initio simulations of materials using VASP: Density-functional theory and beyond. J Comput Chem, 2008, 29, 2044 doi: 10.1002/jcc.21057[11] Chadi D J. Special points for Brillouin-zone integrations. Phys Rev B, 1977, 16, 1746 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.16.1746[12] Yang X, Nitta S, Nagamatsu K, et al. Growth of hexagonal boron nitride on sapphire substrate by pulsed-mode metalorganic vapor phase epitaxy. J Cryst Growth, 2018, 482, 1 doi: 10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2017.10.036[13] Chikh H, SI Ahmed F, Afir A, et al. In-situ X-ray diffraction study of alumina α-Al2O3 thermal behavior under dynamic vacuum and constant flow of nitrogen. J Alloy Compd, 2016, 654, 509 doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.09.131[14] Wu J H, Hagelberg F, Sattler K. First-principles calculations of small silicon clusters adsorbed on a graphite surface. Phys Rev B, 2005, 72, 085441 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.72.085441[15] Govind Rajan A, Strano M S, Blankschtein D. Ab initio molecular dynamics and lattice dynamics-based force field for modeling hexagonal boron nitride in mechanical and interfacial applications. J Phys Chem Lett, 2018, 9, 1584 doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.7b03443[16] Zoroddu A, Bernardini F, Ruggerone P, et al. First-principles prediction of structure, energetics, formation enthalpy, elastic constants, polarization, and piezoelectric constants of AlN, GaN, and InN: Comparison of local and gradient-corrected density-functional theory. Phys Rev B, 2001, 64, 045208 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.64.045208[17] Shigemi A, Wada T. Enthalpy of formation of various phases and formation energy of point defects in perovskite-type NaNbO3 by first-principles calculation. Jpn J Appl Phys, 2004, 43, 6793 doi: 10.1143/JJAP.43.6793[18] Petrushenko I K, Petrushenko K B. Stone-Wales defects in graphene-like boron nitride-carbon heterostructures: Formation energies, structural properties, and reactivity. Comput Mater Sci, 2017, 128, 243 doi: 10.1016/j.commatsci.2016.11.039[19] Nosé S. A unified formulation of the constant temperature molecular dynamics methods. J Chem Phys, 1984, 81, 511 doi: 10.1063/1.447334[20] Wang V, Xu N, Liu J C, et al. VASPKIT: A user-friendly interface facilitating high-throughput computing and analysis using VASP code. arXiv: 1908.08269, 2019[21] Kowsari M H, Alavi S, Ashrafizaadeh M, et al. Molecular dynamics simulation of imidazolium-based ionic liquids. I. Dynamics and diffusion coefficient. J Chem Phys, 2008, 129, 224508 doi: 10.1063/1.3035978[22] Sadki K, Zanane F Z, Ouahman M, et al. Molecular dynamics study of pristine and defective hexagonal BN, SiC and SiGe monolayers. Mater Chem Phys, 2020, 242, 122474 doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2019.122474[23] Nagai T, Tsurumaki S, Urano R, et al. Position-dependent diffusion constant of molecules in heterogeneous systems as evaluated by the local mean squared displacement. J Chem Theory Comput, 2020, 16, 7239 doi: 10.1021/acs.jctc.0c00448[24] Manga V R, Poirier D R. Ab initio molecular dynamics simulation of self-diffusion in Al–Si binary melts. Model Simul Mater Sci Eng, 2018, 26, 065006 doi: 10.1088/1361-651X/aacdbc[25] Chubarov M, Högberg H, Henry A, et al. Challenge in determining the crystal structure of epitaxial 0001 oriented sp 2 -BN films. J Vac Sci Technol A, 2018, 36, 030801 doi: 10.1116/1.5024314[26] Skuridina D, Dinh D V, Pristovsek M, et al. Surface and crystal structure of nitridated sapphire substrates and their effect on polar InN layers. Appl Surf Sci, 2014, 307, 461 doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.04.057[27] Dwikusuma F, Kuech T F. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic study on sapphire nitridation for GaN growth by hydride vapor phase epitaxy: Nitridation mechanism. J Appl Phys, 2003, 94, 5656 doi: 10.1063/1.1618357 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: