| Citation: |
Zeguo Song, Yunkun Wang, Yunke Zhu, Peng Bai, An Hu, Yunan Gao. Targeted transfer of self-assembled CdSe nanoplatelet film onto WS2 flakes to construct hybrid heterostructures[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2021, 42(8): 082901. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/42/8/082901
****
Z G Song, Y K Wang, Y K Zhu, P Bai, A Hu, Y N Gao, Targeted transfer of self-assembled CdSe nanoplatelet film onto WS2 flakes to construct hybrid heterostructures[J]. J. Semicond., 2021, 42(8): 082901. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/42/8/082901.
|
Targeted transfer of self-assembled CdSe nanoplatelet film onto WS2 flakes to construct hybrid heterostructures
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/42/8/082901
More Information
-
Abstract
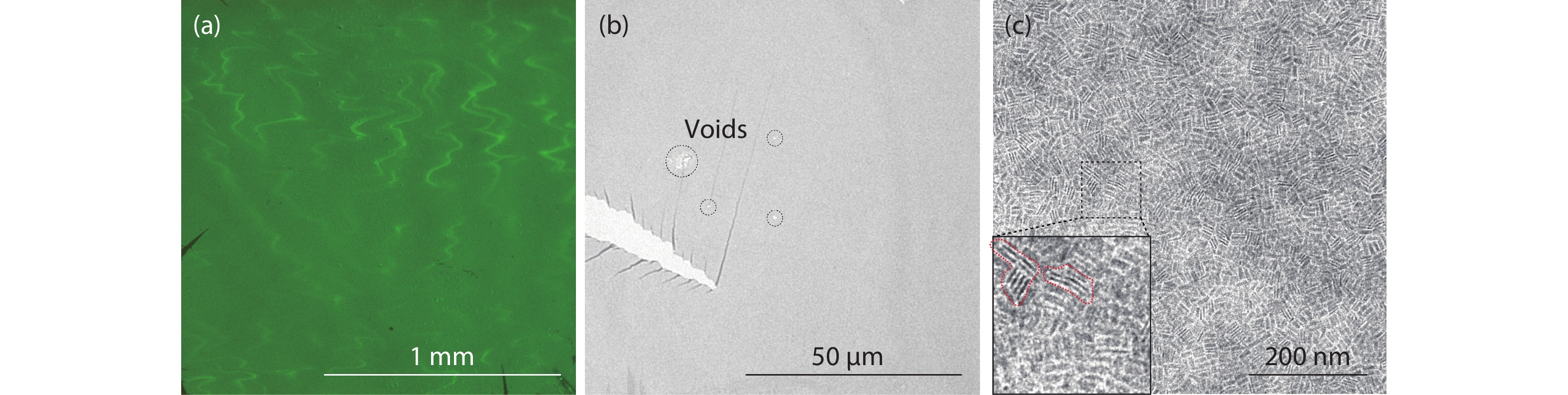
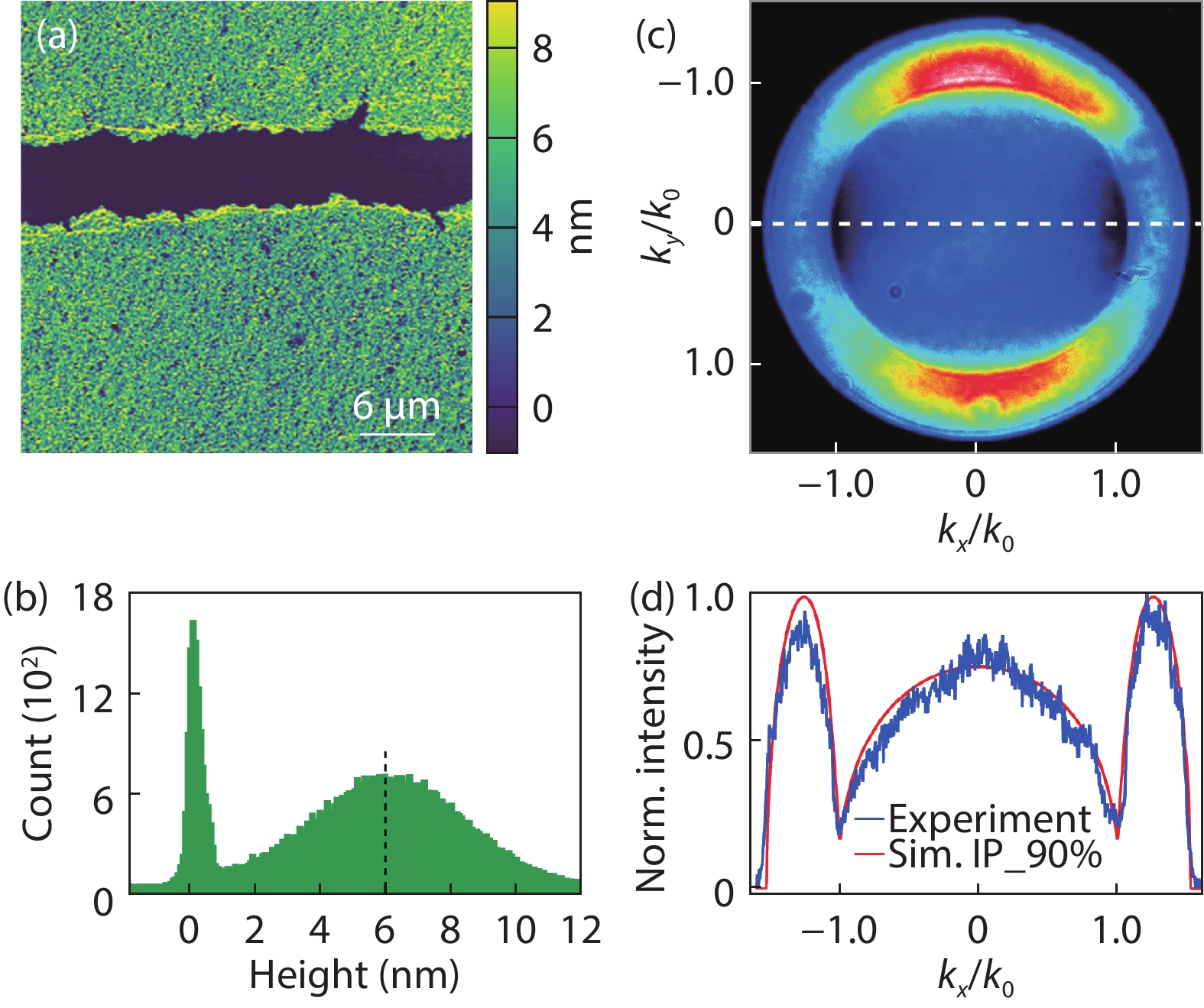
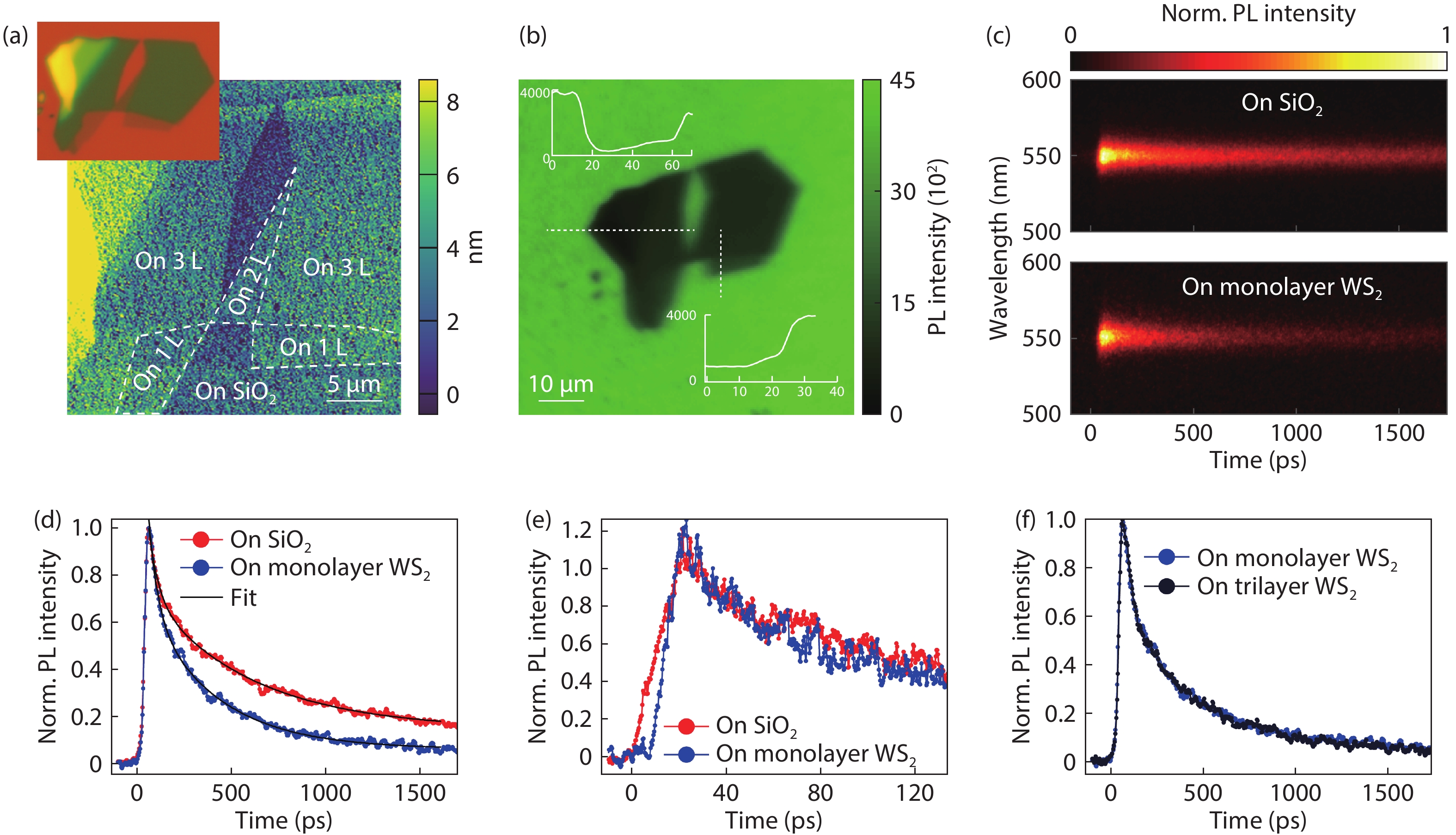
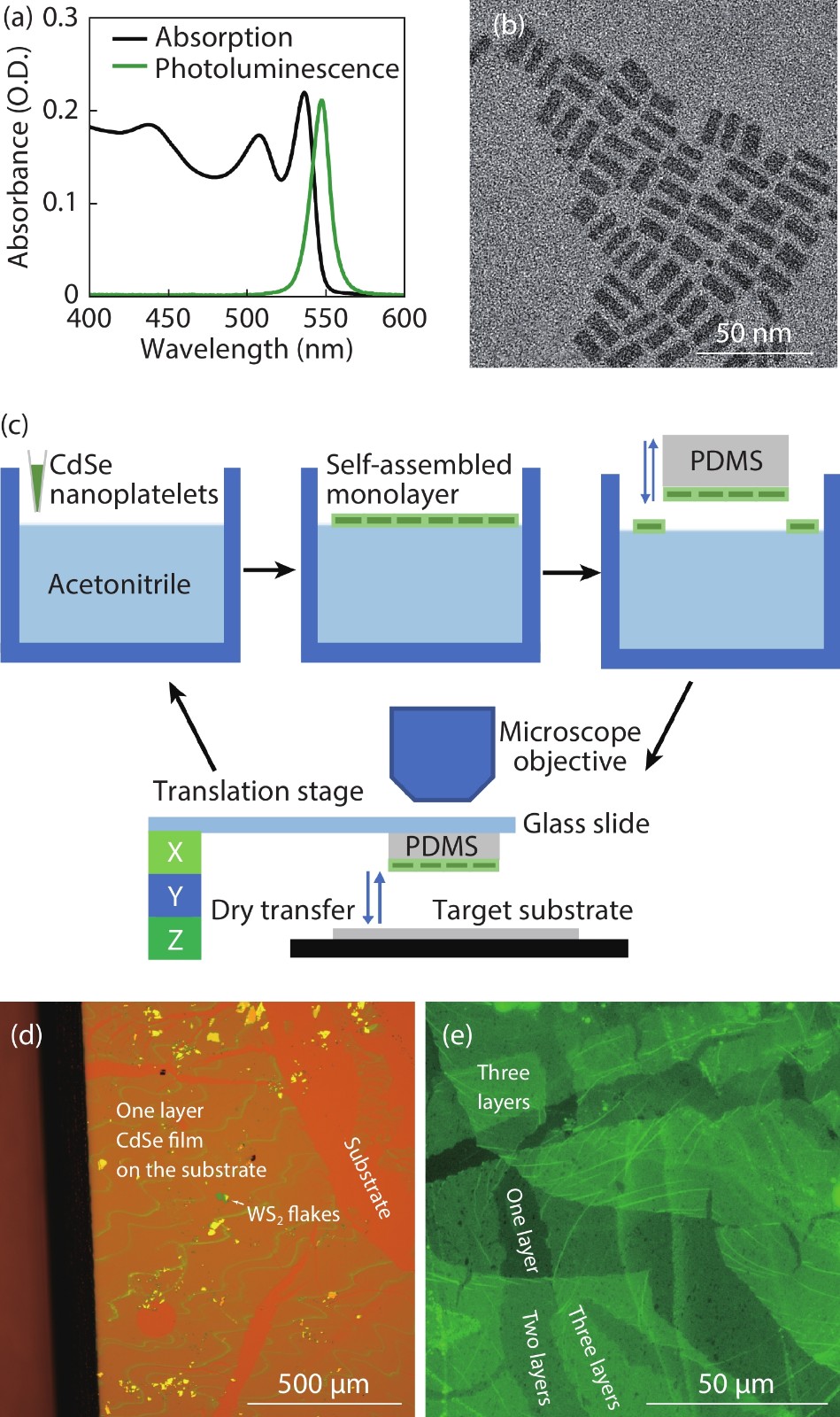
Colloidal CdSe nanoplatelets are thin semiconductor materials with atomic flatness surfaces and one-dimensional strong quantum confinement, and hence they own very narrow and anisotropic emission. Here, we present a polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) assisted transferring method that can pick up single layer CdSe nanoplatelet films self-assembled on a liquid surface and then precisely transfer to a target. By layer-by-layer picking up and transferring, multiple layers of CdSe films can be built up to form CdSe stacks with each single layer having dominant in-plane transition dipole distribution, which both material and energic structures are analogous to traditional multiple quantum wells grown by molecular-beam epitaxy. Additionally, with the great flexibility of colloidal nanoplatelets and this transferring method, CdSe nanoplatelets films can be combined with other materials to form hybrid heterostructures. We transferred a single-layer CdSe film onto WS2 flakes, and precisely studied the fast energy transfer rate with controlled CdSe nanoplatelet orientation and by using a streak camera with a ps time resolution.-
Keywords:
- CdSe nanoplatelets,
- self-assembly,
- transfer,
- energy transfer,
- hybrid heterostructures,
- WS2
-
References
[1] Kovalenko M V, Manna L, Cabot A, et al. Prospects of nanoscience with nanocrystals. ACS Nano, 2015, 9, 1012 doi: 10.1021/nn506223h[2] Gao Y N, Weidman M C, Tisdale W A. CdSe nanoplatelet films with controlled orientation of their transition dipole moment. Nano Lett, 2017, 17, 3837 doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.7b01237[3] Ithurria S, Tessier M D, Mahler B, et al. Colloidal nanoplatelets with two-dimensional electronic structure. Nat Mater, 2011, 10, 936 doi: 10.1038/nmat3145[4] Scott R, Heckmann J, Prudnikau A V, et al. Directed emission of CdSe nanoplatelets originating from strongly anisotropic 2D electronic structure. Nat Nanotechnol, 2017, 12, 1155 doi: 10.1038/nnano.2017.177[5] Kim W D, Kim D, Yoon D E, et al. Pushing the efficiency envelope for semiconductor nanocrystal-based electroluminescence devices using anisotropic nanocrystals. Chem Mater, 2019, 31, 3066 doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.8b05366[6] Yang Z, Pelton M, Fedin I, et al. A room temperature continuous-wave nanolaser using colloidal quantum wells. Nat Commun, 2017, 8, 143 doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-00198-z[7] Grim J Q, Christodoulou S, Di Stasio F, et al. Continuous-wave biexciton lasing at room temperature using solution-processed quantum wells. Nat Nanotechnol, 2014, 9, 891 doi: 10.1038/nnano.2014.213[8] Giovanella U, Pasini M, Lorenzon M, et al. Efficient solution-processed nanoplatelet-based light-emitting diodes with high operational stability in air. Nano Lett, 2018, 18, 3441 doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.8b00456[9] Zhang F J, Wang S J, Wang L, et al. Super color purity green quantum dot light-emitting diodes fabricated by using CdSe/CdS nanoplatelets. Nanoscale, 2016, 8, 12182 doi: 10.1039/C6NR02922A[10] Boles M A, Engel M, Talapin D V. Self-assembly of colloidal nanocrystals: From intricate structures to functional materials. Chem Rev, 2016, 116, 11220 doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00196[11] Li X, Lu Z L, Wang T. Self-assembly of semiconductor nanoparticles toward emergent behaviors on fluorescence. Nano Res, 2021, 14, 1233 doi: 10.1007/s12274-020-3140-y[12] Vanmaekelbergh D. Self-assembly of colloidal nanocrystals as route to novel classes of nanostructured materials. Nano Today, 2011, 6, 419 doi: 10.1016/j.nantod.2011.06.005[13] Dong A, Chen J, Vora P M, et al. Binary nanocrystal superlattice membranes self-assembled at the liquid-air interface. Nature, 2010, 466, 474 doi: 10.1038/nature09188[14] Abécassis B, Tessier M D, Davidson P, et al. Self-assembly of CdSe nanoplatelets into giant micrometer-scale needles emitting polarized light. Nano Lett, 2014, 14, 710 doi: 10.1021/nl4039746[15] Erdem O, Foroutan S, Gheshlaghi N, et al. Thickness-tunable self-assembled colloidal nanoplatelet films enable ultrathin optical gain media. Nano Lett, 2020, 20, 6459 doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.0c02153[16] Momper R, Zhang H, Chen S, et al. Kinetic control over self-assembly of semiconductor nanoplatelets. Nano Lett, 2020, 20, 4102 doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.9b05270[17] Erdem O, Gungor K, Guzelturk B, et al. Orientation-controlled nonradiative energy transfer to colloidal nanoplatelets: Engineering dipole orientation factor. Nano Lett, 2019, 19, 4297 doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.9b00681[18] Bai P, Hu A, Liu Y, et al. Printing and in situ assembly of CdSe/CdS nanoplatelets as uniform films with unity in-plane transition dipole moment. J Phys Chem Lett, 2020, 11, 4524 doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.0c00748[19] Özdemir O, Ramiro I, Gupta S, et al. High sensitivity hybrid PbS CQD-TMDC photodetectors up to 2 μm. ACS Photonics, 2019, 6, 2381 doi: 10.1021/acsphotonics.9b00870[20] Prins F, Kim D K, Cui J, et al. Direct patterning of colloidal quantum-dot thin films for enhanced and spectrally selective out-coupling of emission. Nano Lett, 2017, 17, 1319 doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.6b03212[21] He Z, Chen B, Hua Y, et al. CMOS compatible high-performance nanolasing based on perovskite-SiN hybrid integration. Adv Opt Mater, 2020, 8, 2000453 doi: 10.1002/adom.202000453[22] Prasai D, Klots A R, Newaz A, et al. Electrical control of near-field energy transfer between quantum dots and two-dimensional semiconductors. Nano Lett, 2015, 15, 4374 doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.5b00514[23] Dutta A, Medda A, Bera R, et al. Hybrid nanostructures of 2D CdSe nanoplatelets for high-performance photodetector using charge transfer process. ACS Appl Nano Mater, 2020, 3, 4717 doi: 10.1021/acsanm.0c00728[24] Rowland C E, Fedin I, Zhang H, et al. Picosecond energy transfer and multiexciton transfer outpaces Auger recombination in binary CdSe nanoplatelet solids. Nat Mater, 2015, 14, 484 doi: 10.1038/nmat4231[25] She C X, Fedin I, Dolzhnikov D S, et al. Low-threshold stimulated emission using colloidal quantum wells. Nano Lett, 2014, 14, 2772 doi: 10.1021/nl500775p[26] Paik T, Ko D K, Gordon T R, et al. Studies of liquid crystalline self-assembly of GdF3 nanoplates by in-plane, out-of-plane SAXS. ACS Nano, 2011, 5, 8322 doi: 10.1021/nn203049t[27] Schuller J A, Karaveli S, Schiros T, et al. Orientation of luminescent excitons in layered nanomaterials. Nat Nanotechnol, 2013, 8, 271 doi: 10.1038/nnano.2013.20[28] Taghipour N, Hernandez Martinez P L, Ozden A, et al. Near-unity efficiency energy transfer from colloidal semiconductor quantum wells of CdSe/CdS nanoplatelets to a monolayer of MoS2. ACS Nano, 2018, 12, 8547 doi: 10.1021/acsnano.8b04119[29] Prins F, Goodman A J, Tisdale W A. Reduced dielectric screening and enhanced energy transfer in single- and few-layer MoS2. Nano Lett, 2014, 14, 6087 doi: 10.1021/nl5019386[30] Raja A, Montoya−Castillo A, Zultak J, et al. Energy transfer from quantum dots to graphene and MoS2: The role of absorption and screening in two-dimensional materials. Nano Lett, 2016, 16, 2328 doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.5b05012[31] Liu H, Wang T, Wang C, et al. Exciton radiative recombination dynamics and nonradiative energy transfer in two-dimensional transition-metal dichalcogenides. J Phys Chem C, 2019, 123, 10087 doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.8b12179 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: