| Citation: |
Hua Fan, Huichao Yue, Jiangmin Mao, Ting Peng, Siming Zuo, Quanyuan Feng, Qi Wei, Hadi Heidari. Modelling and fabrication of wide temperature range Al0.24Ga0.76As/GaAs Hall magnetic sensors[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2022, 43(3): 034101. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/43/3/034101
****
H Fan, H C Yue, J Mao, T Peng, S M Zuo, Q Feng, Q Wei, H Heidari, Modelling and fabrication of wide temperature range Al0.24Ga0.76As/GaAs Hall magnetic sensors[J]. J. Semicond., 2022, 43(3): 034101. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/43/3/034101.
|
Modelling and fabrication of wide temperature range Al0.24Ga0.76As/GaAs Hall magnetic sensors
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/43/3/034101
More Information
-
Abstract
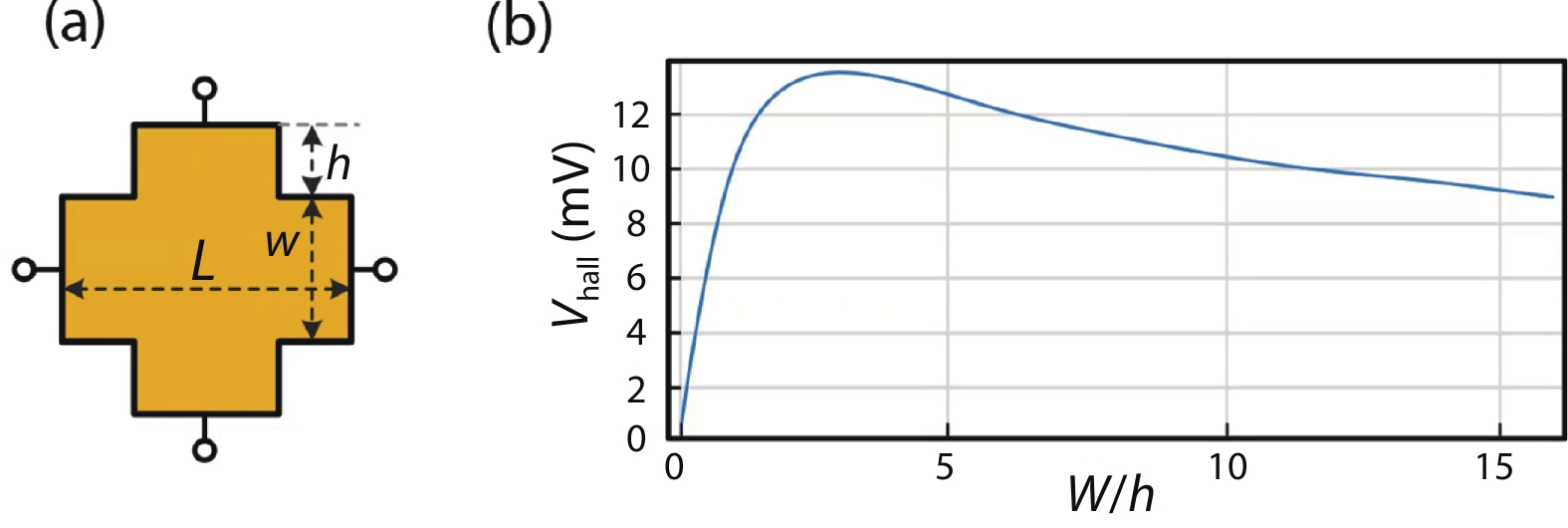
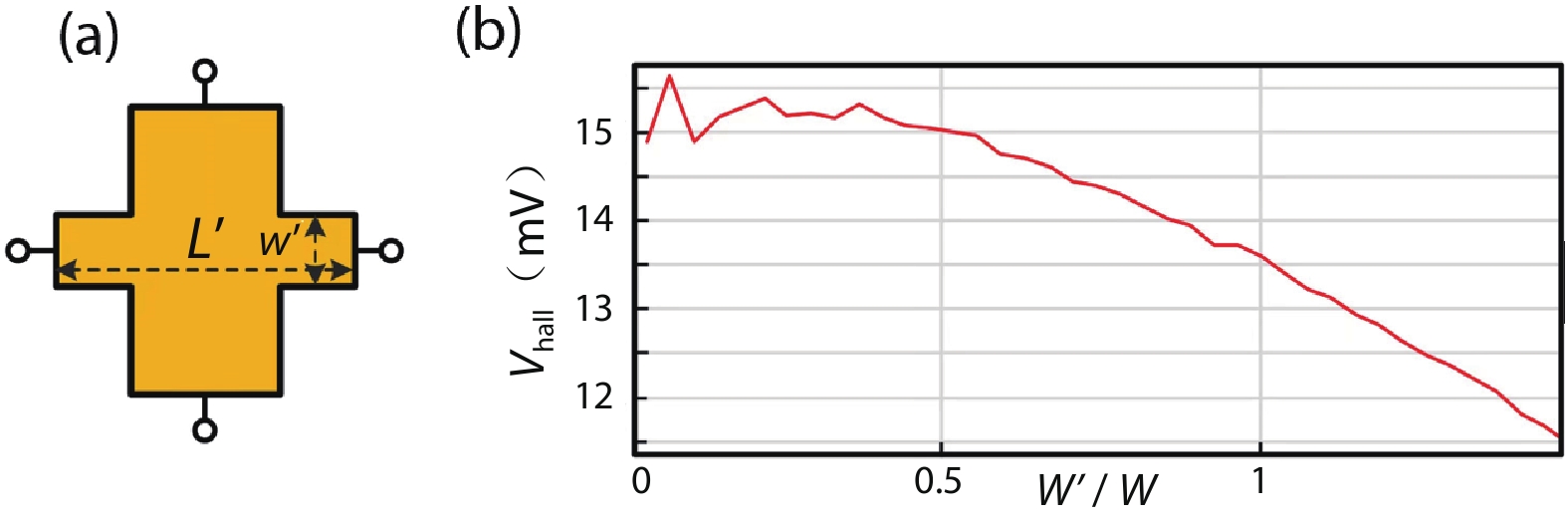
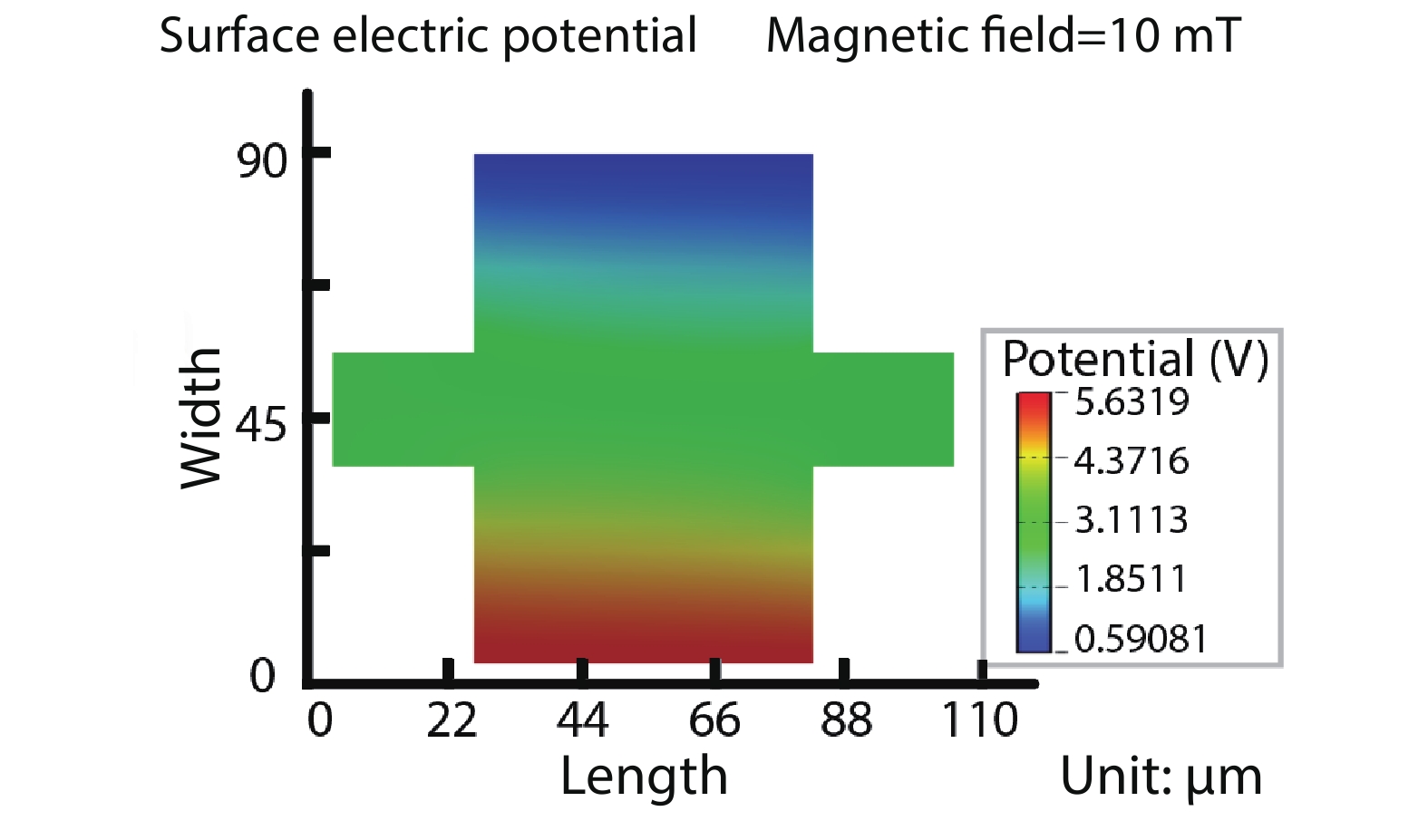
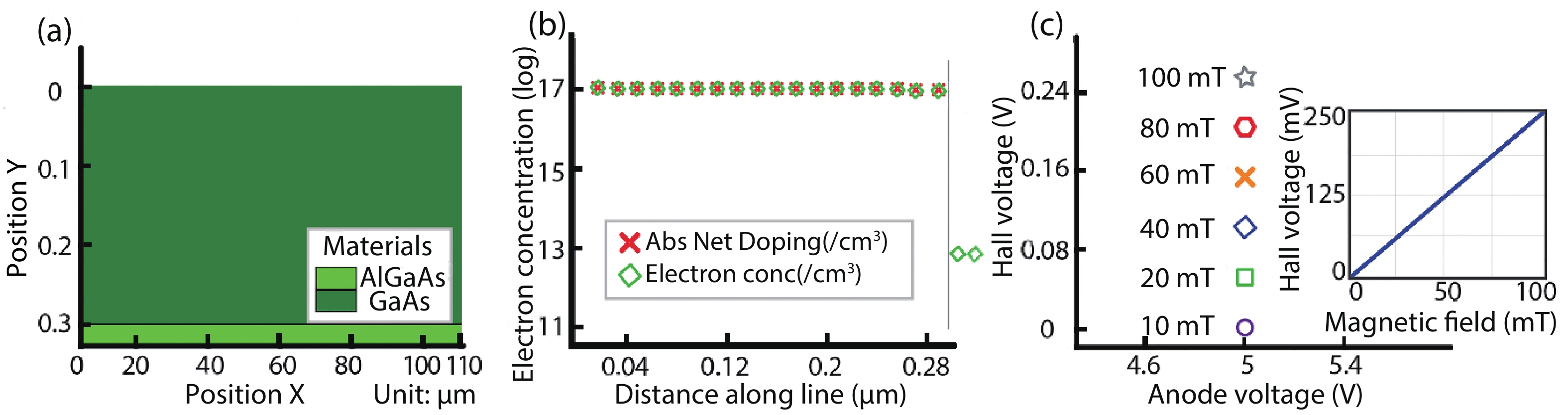
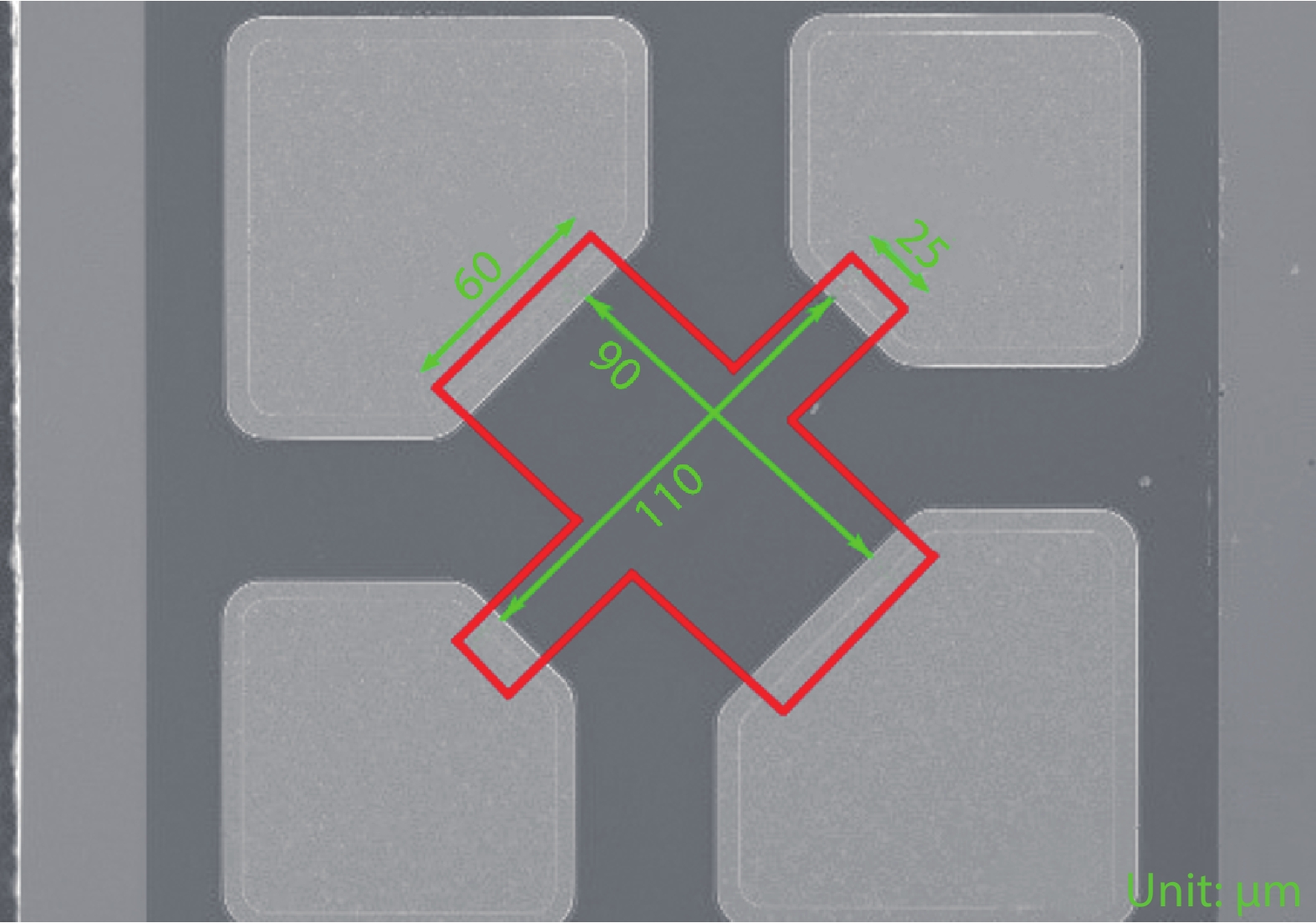
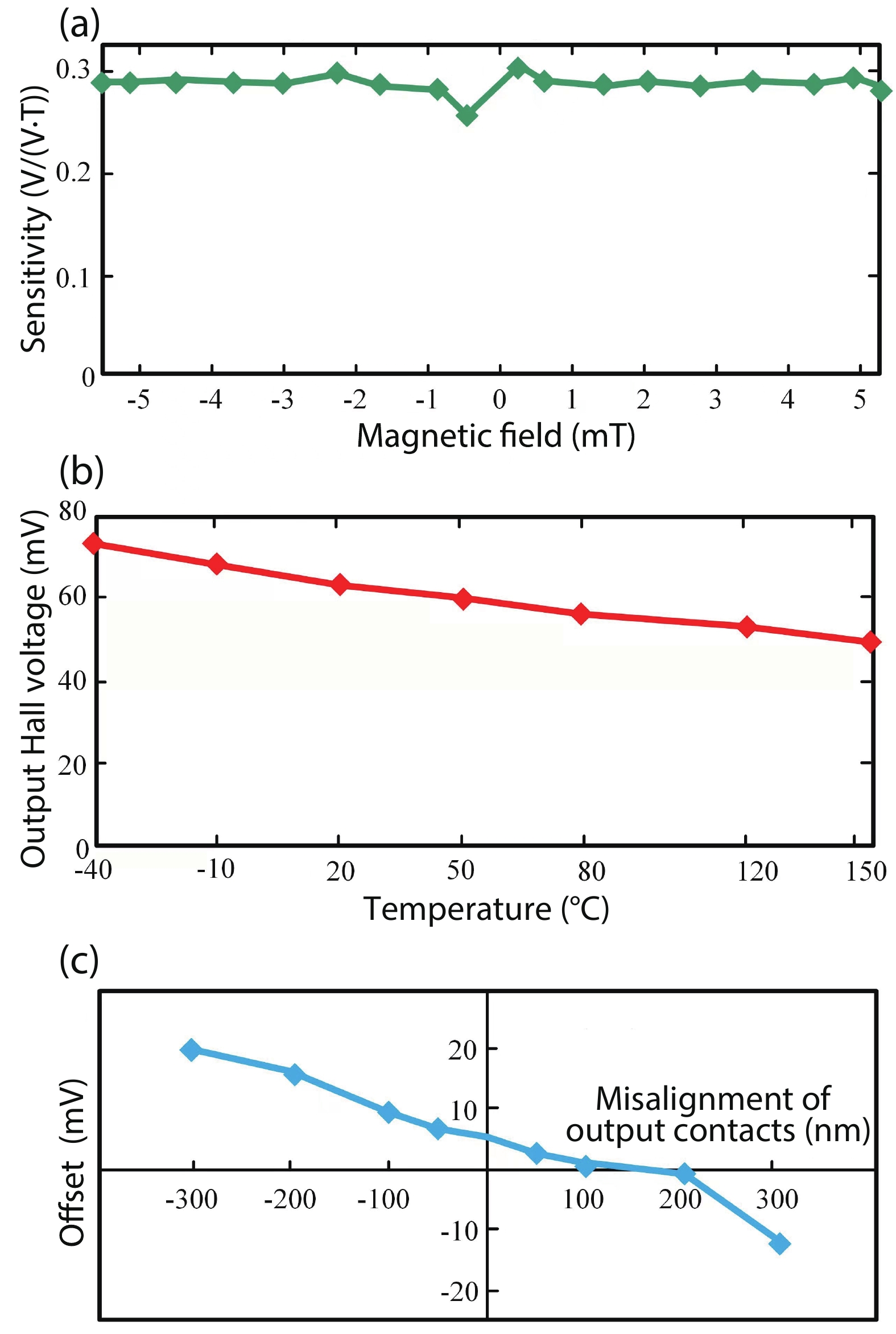
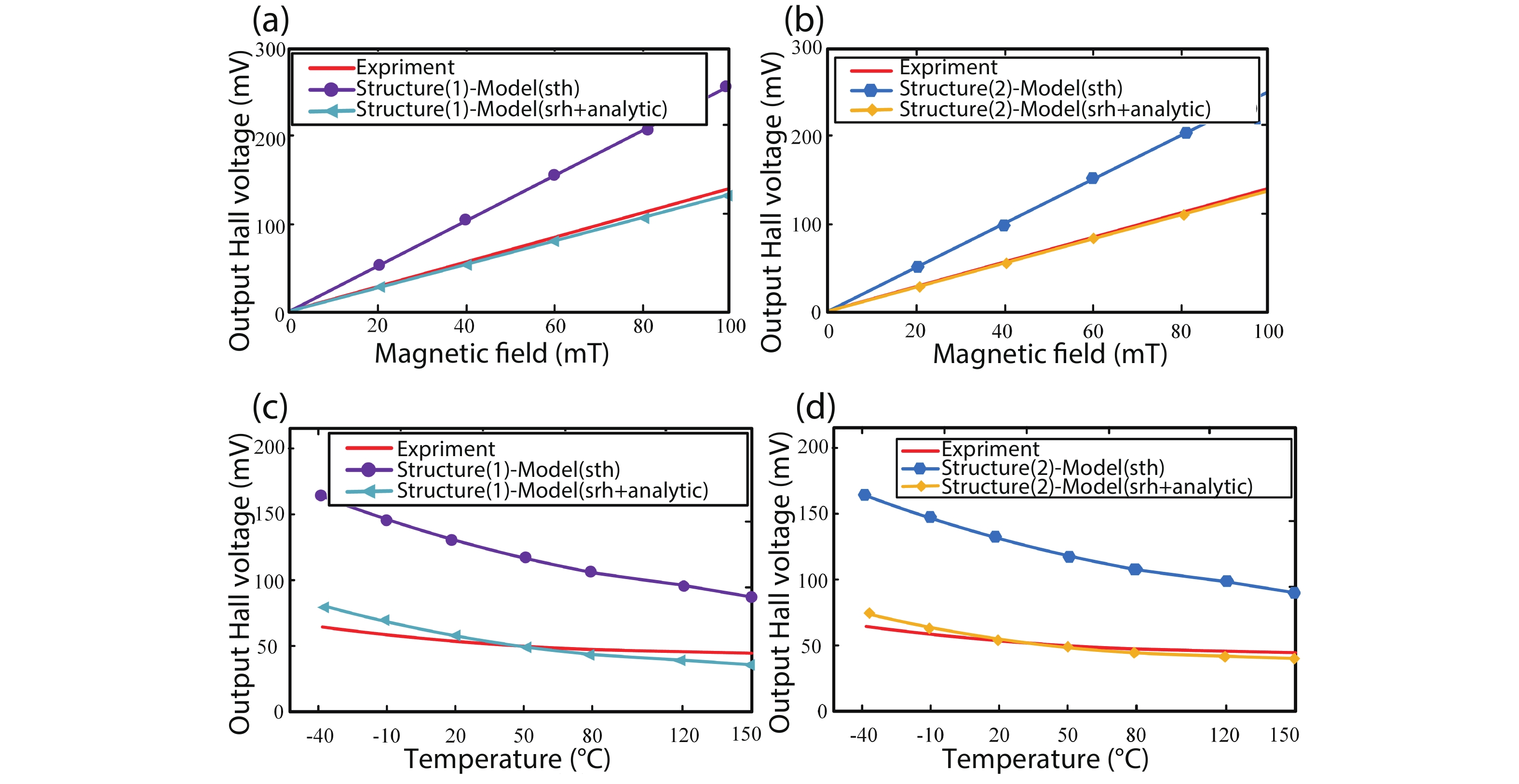
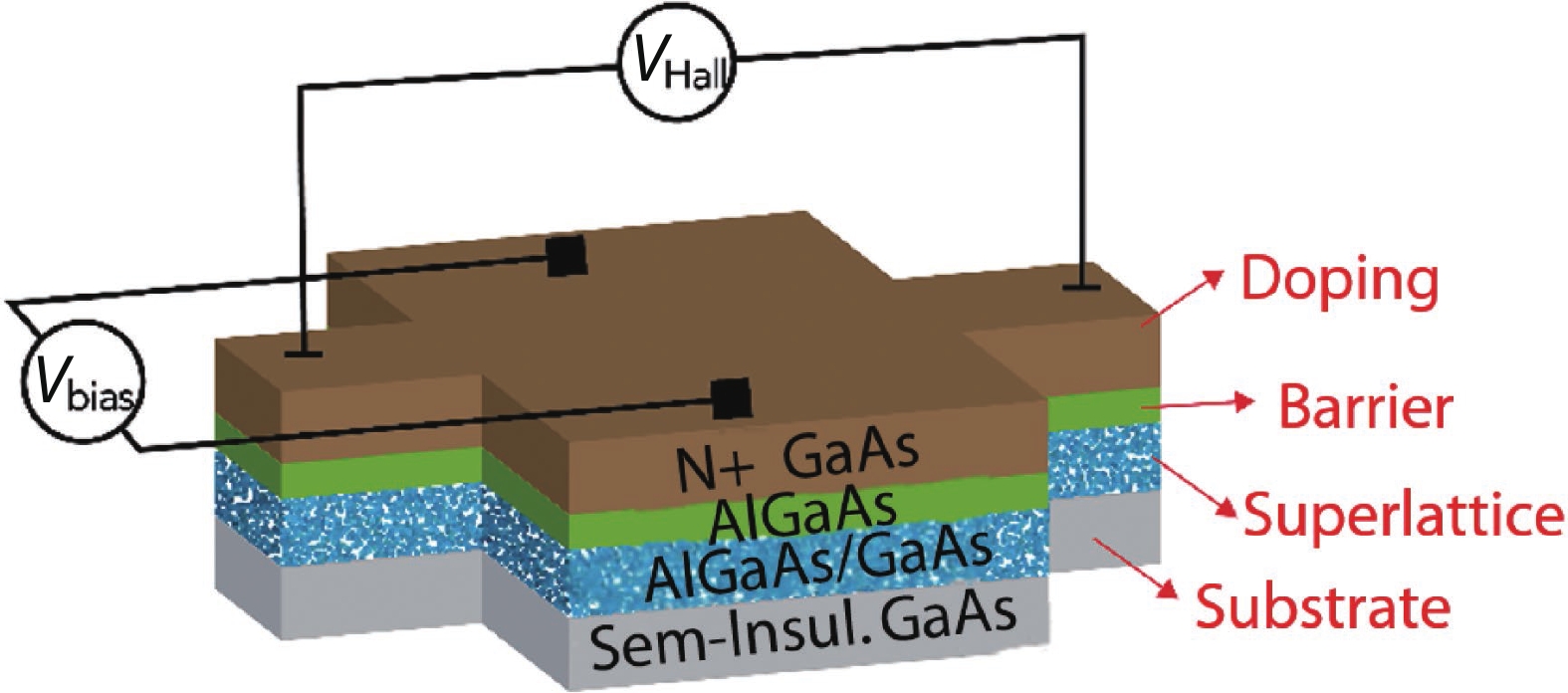
Silicon Hall-effect sensors have been widely used in industry and research fields due to their straightforward fabrication process and CMOS compatibility. However, as their material property limitations, technicians usually implement complex CMOS circuits to improve the sensors’ performance including temperature drift and offset compensation for fitting tough situation, but it is no doubt that it increases the design complexity and the sensor area. Gallium arsenide (GaAs) is a superior material of Hall-effect device because of its large mobility and stable temperature characteristics. Concerning there is no specified modelling of GaAs Hall-effect device, this paper investigated its modelling by using finite element method (FEM) software Silvaco TCAD® to help and guide GaAs Hall-effect device fabrication. The modeled sensor has been fabricated and its experimental results are in agreement with the simulation results. Comparing to our previous silicon Hall-effect sensor, the GaAs Hall-effect sensor demonstrates potential and reliable benchmark for the future Hall magnetic sensor developments. -
References
[1] Popovic R S, Randjelovic Z, Manic D. Integrated Hall-effect magnetic sensors. Sens Actuat A, 2001, 91, 46 doi: 10.1016/S0924-4247(01)00478-2[2] Heidari H, Bonizzoni E, Gatti U, et al. A CMOS current-mode magnetic hall sensor with integrated front-end. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I, 2015, 62, 1270 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2015.2415173[3] Pastre M, Kayal M, Blanchard H. A hall sensor analog front end for current measurement with continuous gain calibration. IEEE Sens J, 2007, 7, 860 doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2007.894902[4] Ajbl A, Pastre M, Kayal M. A fully integrated hall sensor microsystem for contactless current measurement. IEEE Sens J, 2013, 13, 2271 doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2013.2251971[5] Randjelovic Z B, Kayal M, Popovic R, et al. Highly sensitive Hall magnetic sensor microsystem in CMOS technology. IEEE J Solid State Circuits, 2002, 37, 151 doi: 10.1109/4.982421[6] Dowling K M, Alpert H S, Yalamarthy A S, et al. Micro-tesla offset in thermally stable AlGaN/GaN 2DEG hall plates using current spinning. IEEE Sens Lett, 2019, 3, 1 doi: 10.1109/LSENS.2019.2898157[7] Dowling K M, Alpert H A, Zhang P, et al. The effect of bias conditions ON AlGaN/GaN 2DEG hall plates. 2018 Solid-State, Actuators, and Microsystems Workshop, 2018[8] Sze S. Physics of semiconductor devices. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 1981[9] Haned N, Missous M. Nano-tesla magnetic field magnetometry using an InGaAs-AlGaAs-GaAs 2DEG Hall sensor. Sens Actuat A, 2003, 102, 216 doi: 10.1016/S0924-4247(02)00386-2[10] Mosser V, Matringe N, Haddab Y. A spinning current circuit for Hall measurements down to the nanotesla range. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas, 2017, 66, 637 doi: 10.1109/TIM.2017.2649858[11] Heidari H, Bonizzoni E, Gatti U, et al. CMOS vertical Hall magnetic sensors on flexible substrate. IEEE Sens J, 2016, 16, 8736 doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2016.2575802[12] Heidari H, Bonizzoni E, Gatti U, et al. A 0.18-µm CMOS current-mode Hall magnetic sensor with very low bias current and high sensitive front-end. Sensors, 2014, 1467 doi: 10.1109/ICSENS.2014.6985291[13] Allegretto W, Nathan A, Baltes H. Numerical analysis of magnetic-field-sensitive bipolar devices. IEEE Trans Comput Aided Des Integr Circuits Syst, 1991, 10, 501 doi: 10.1109/43.75633[14] Sotoodeh M, Khalid A H, Rezazadeh A A. Empirical low-field mobility model for III-V compounds applicable in device simulation codes. J Appl Phys, 2000, 87, 2890 doi: 10.1063/1.372274[15] Jovanovic E, Pesic T, Pantic D. 3D simulation of cross-shaped Hall sensor and its equivalent circuit model. 2004 24th International Conference on Microelectronics, 2004, 235[16] Heidari H, Gatti U, Bonizzoni E, et al. Low-noise low-offset current-mode Hall sensors. Proceedings of the 2013 9th Conference on Ph. D. Research in Microelectronics and Electronics, 2013, 325[17] Jankowski J, El-Ahmar S, Oszwaldowski M. Hall sensors for extreme temperatures. Sensors, 2011, 11, 876 doi: 10.3390/s110100876[18] Wouters C, Vranković V, Rössler C, et al. Design and fabrication of an innovative three-axis Hall sensor. Sens Actuat A, 2016, 237, 62 doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2015.11.022 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: