| Citation: |
Uma Devi Godavarti, P. Nagaraju, Vijayakumar Yelsani, Yamuna Pushukuri, P. S. Reddy, Madhavaprasad Dasari. Synthesis and characterization of ZnS-based quantum dots to trace low concentration of ammonia[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2021, 42(12): 122901. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/42/12/122901
****
U D Godavarti, P Nagaraju, V Yelsani, Y Pushukuri, P S Reddy, M Dasari, Synthesis and characterization of ZnS-based quantum dots to trace low concentration of ammonia[J]. J. Semicond., 2021, 42(12): 122901. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/42/12/122901.
|
Synthesis and characterization of ZnS-based quantum dots to trace low concentration of ammonia
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/42/12/122901
More Information
-
Abstract
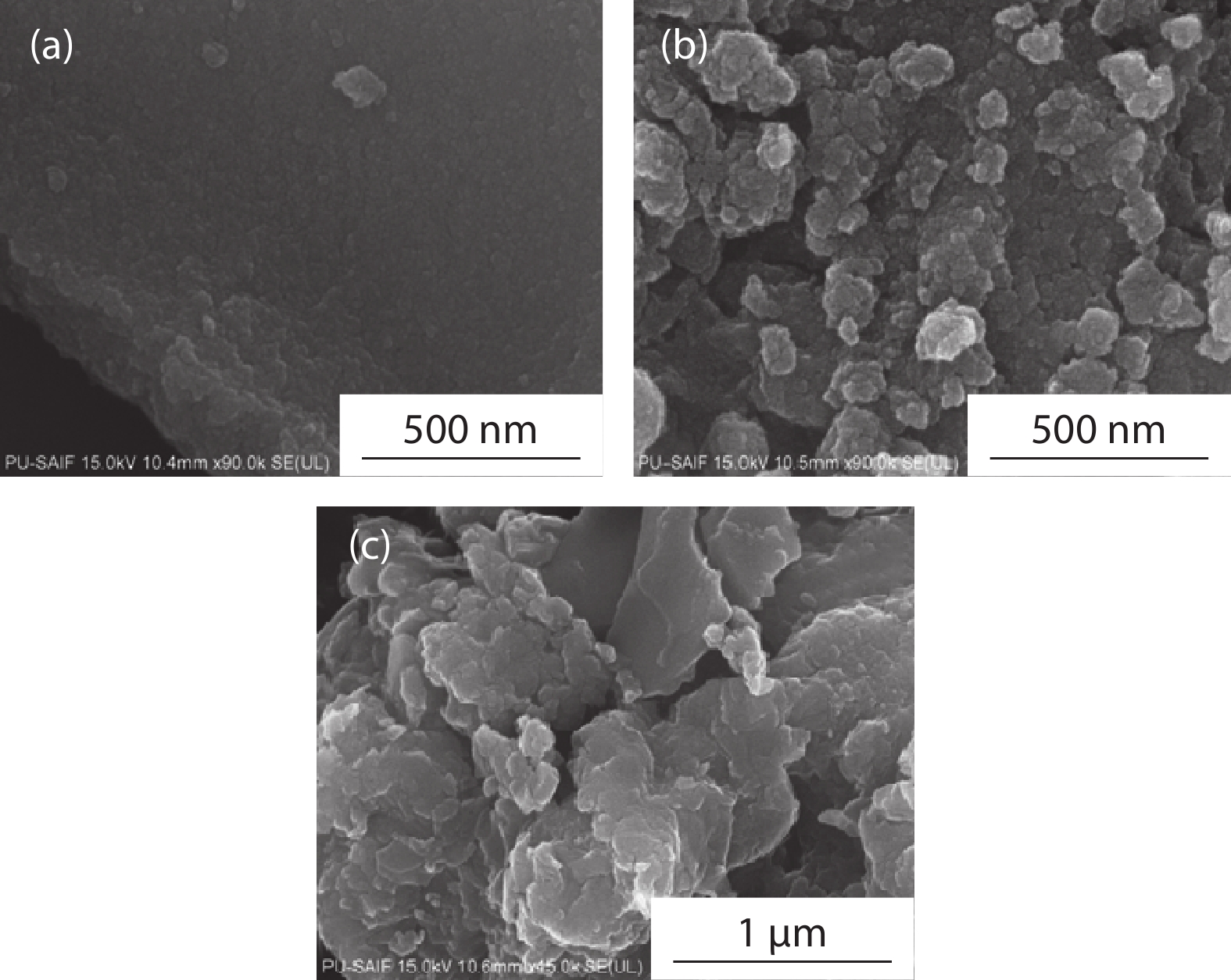
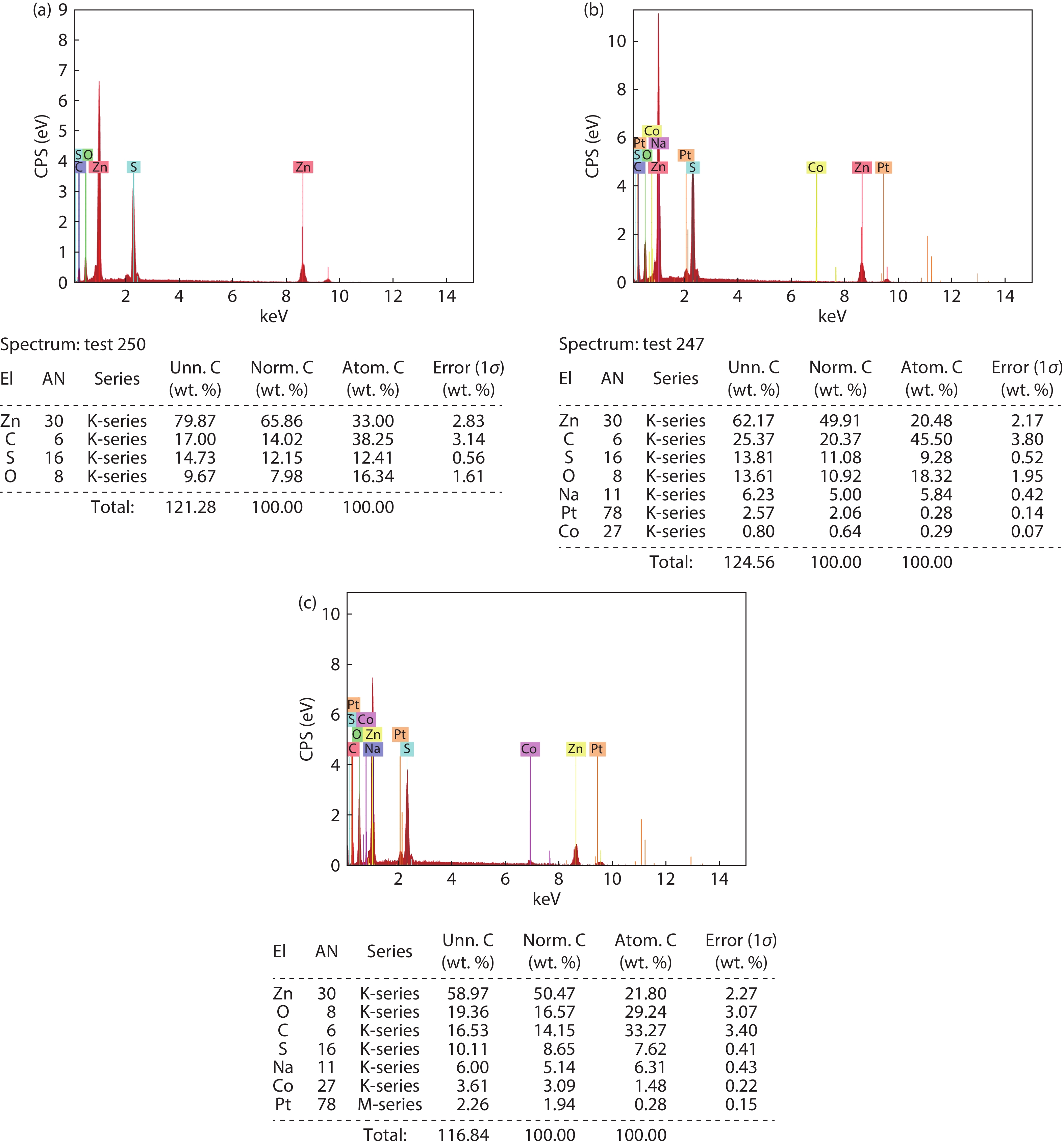
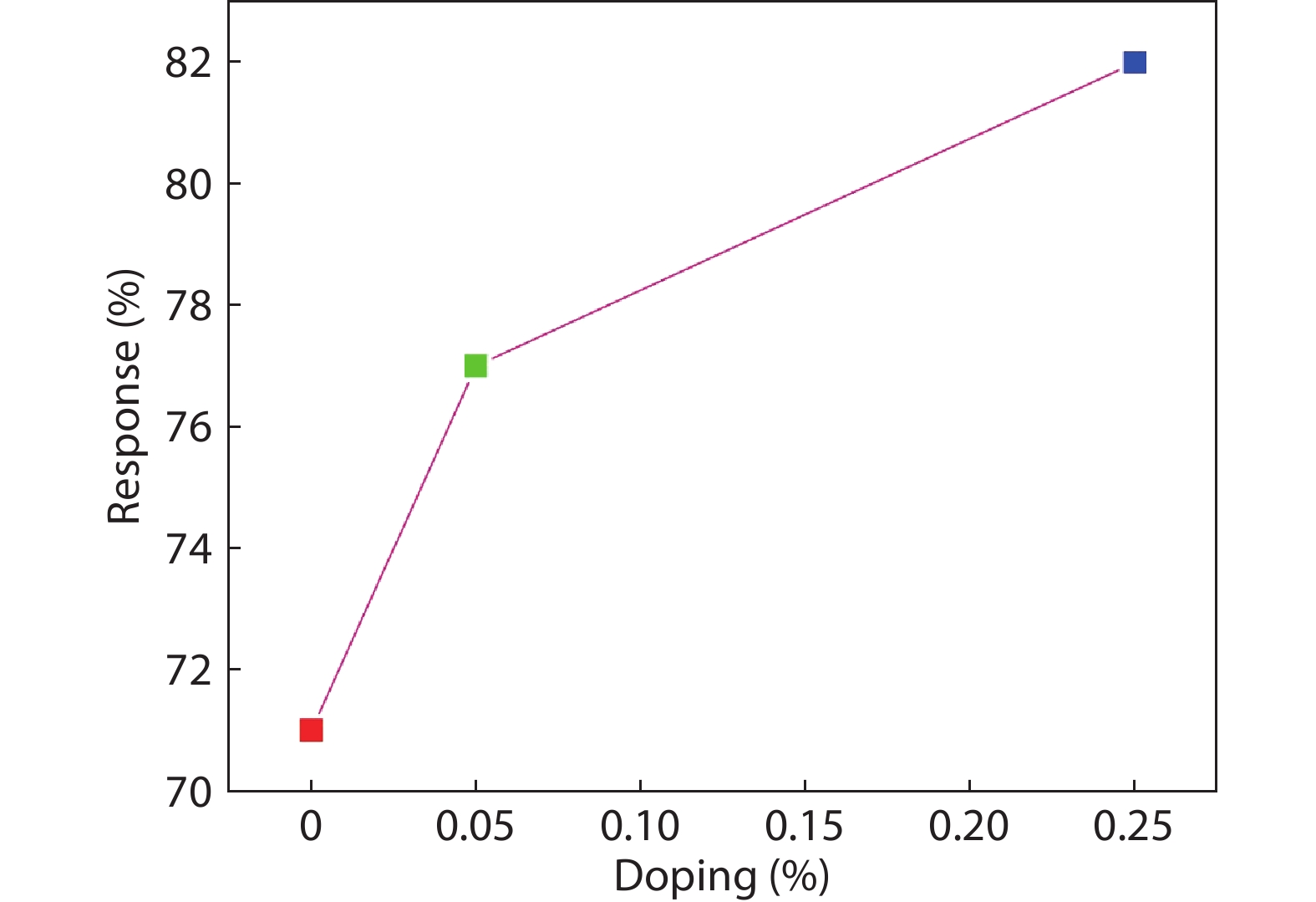
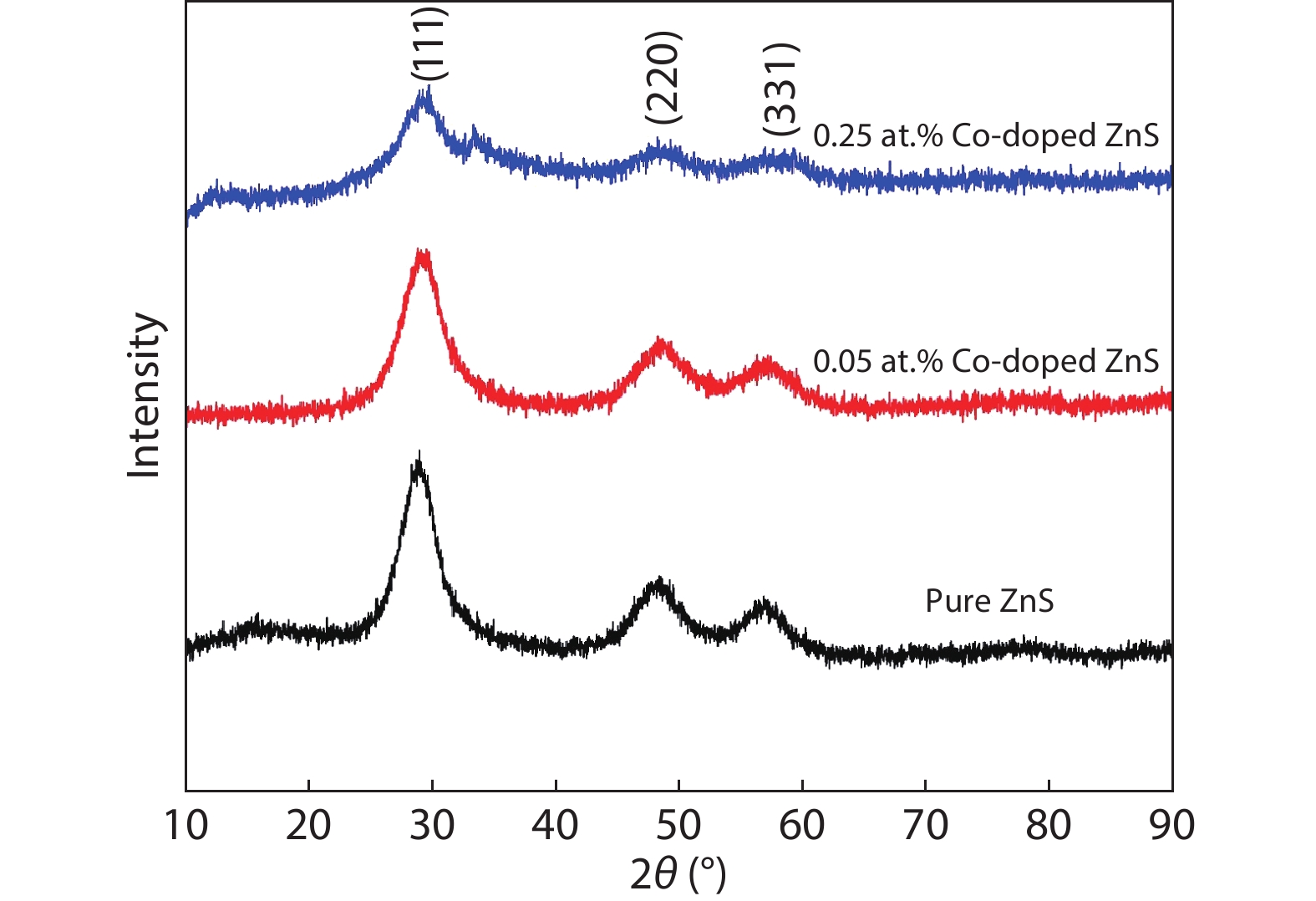
In the present work, a solution-based co-precipitation method has been adopted to synthesize pure and cobalt-doped ZnS quantum dots and characterized by XRD, SEM, TEM with EDX, FTIR and gas sensing properties. XRD analysis has shown a single phase of ZnS quantum dots having a zinc blend structure. TEM and XRD line broadening indicated that the average crystallite size in the sample is in the range of 2 to 5 nm. SEM micrographs show spherical-shaped quantum dots. FTIR studies show that cobalt has been successfully doped into the ZnS cubic lattice. EDX spectra have analyzed the elemental presence in the samples and it is evident that the spectra confirmed the presence of cobalt (Co), zinc (Zn), oxygen (O), and sulphur (S) elements only and no other impurities are observed. The ZnS-based quantum dot sensors reveal high sensitivity towards 50 ppm of ammonia vapors at an operating temperature of 70 °C. Hence, ZnS-based quantum dots can be a promising and quick traceable sensor towards ammonia sensing applications with good response and recovery time.-
Keywords:
- ZnS,
- co-precipitation,
- cobalt doped ZnS,
- XRD,
- quantum dots,
- gas sensor,
- ammonia,
- response
-
References
[1] Fan G Y, Wang C Y, Fang J Y. Solution-based synthesis of III-V quantum dots and their applications in gas sensing and bio-imaging. Nano Today, 2014, 9, 69 doi: 10.1016/j.nantod.2014.02.007[2] Xiang D H, Zhu Y B, He Z J, et al. A simple one-step synthesis of ZnS nanoparticles via salt-alkali-composited-mediated method and investigation on their comparative photocatalytic activity. Mater Res Bull, 2013, 48, 188 doi: 10.1016/j.materresbull.2012.09.070[3] Fang X S, Zhai T Y, Gautam U K, et al. ZnS nanostructures: From synthesis to applications. Prog Mater Sci, 2011, 56, 175 doi: 10.1016/j.pmatsci.2010.10.001[4] Liu H, Hu L F, Watanabe K, et al. Cathodoluminescence modulation of ZnS nanostructures by morphology, doping, and temperature. Adv Funct Mater, 2013, 23, 3701 doi: 10.1002/adfm.201203711[5] Xu X J, Li S Y, Chen J X, et al. Design principles and material engineering of ZnS for optoelectronic devices and catalysis. Adv Funct Mater, 2018, 28, 1802029 doi: 10.1002/adfm.201802029[6] Fang X S, Gautam U K, Bando Y, et al. Multiangular branched ZnS nanostructures with needle-shaped tips: potential luminescent and field-emitter nanomaterial. J Phys Chem C, 2008, 112, 4735 doi: 10.1021/jp711498m[7] Fang X S, Bando Y, Liao M Y, et al. Single-crystalline ZnS nanobelts as ultraviolet-light sensors. Adv Mater, 2009, 21, 2034 doi: 10.1002/adma.200802441[8] Jadraque M, Evtushenko A B, Ávila-Brande D, et al. Co-doped ZnS clusters and nanostructures produced by pulsed laser ablation. J Phys Chem C, 2013, 117, 5416 doi: 10.1021/jp3108792[9] Poornaprakash B, Amaranatha Reddy D, Murali G, et al. Composition dependent room temperature ferromagnetism and PL intensity of cobalt doped ZnS nanoparticles. J Alloys Compd, 2013, 577, 79 doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.04.106[10] Fang W J, Liu Y S, Guo B Z, et al. Room temperature ferromagnetism and cooling effect in dilute Co-doped ZnS nanoparticles with zinc blende structure. J Alloys Compd, 2014, 584, 240 doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.08.215[11] Tang L J, Huang G F, Tian Y, et al. Efficient ultraviolet emission of ZnS nanospheres: Co doping enhancement. Mater Lett, 2013, 100, 237 doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2013.03.036[12] Akhtar M S, Malik M A, Riaz S, et al. Optimising conditions for the growth of nanocrystalline ZnS thin films from acidic chemical baths. Mater Sci Semicond Process, 2015, 30, 292 doi: 10.1016/j.mssp.2014.10.019[13] Hou Q T, Chen K, Zhang H G, et al. Magnetic properties of co doped ZnS diluted magnetic semiconductor. J Phys: Conf Ser, 2013, 430, 012076 doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/430/1/012076[14] Zhang L, Qin D Z, Yangand G R, et al. The investigation on synthesis and optical properties of ZnS:Co nanocrystals by using hydrothermal method. Chalcog Lett, 2012, 9, 93[15] Liu L Y, Yang L, Pu Y T, et al. Optical properties of water-soluble Co2+:ZnS semiconductor nanocrystals synthesized by a hydrothermal process. Mater Lett, 2012, 66, 121 doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2011.08.025[16] Chen X B, Yang N, Liu X F, et al. Structure dependent photoluminescence and magnetic properties of Co:ZnS nanostructures. Phys Scr, 2013, 88, 035703 doi: 10.1088/0031-8949/88/03/035703[17] Ehsan M A, Peiris T A N, Wijayantha K G U, et al. Surface morphological and photoelectrochemical studies of ZnS thin films developed from single source precursors by aerosol assisted chemical vapour deposition. Thin Solid Films, 2013, 540, 1 doi: 10.1016/j.tsf.2013.05.117[18] Sullivan H, Parish J D, Thongchai P, et al. Aerosol-assisted chemical vapor deposition of ZnS from thioureide single source precursors. Inorg Chem, 2019, 58, 2784 doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.8b03363[19] Parkin I P, Price L S, Hibbert T G, et al. The first single source deposition of tin sulfide coatings on glass: Aerosol-assisted chemical vapour deposition using [Sn(SCH2CH2S)2]. J Mater Chem, 2001, 11, 1486 doi: 10.1039/b009923f[20] Memon A A, Afzaal M, Malik M A, et al. The N-alkyldithiocarbamato complexes [M(S2CNHR)2] (M = Cd(ii) Zn(ii); R = C2H5, C4H9, C6H13, C12H25); their synthesis, thermal decomposition and use to prepare of nanoparticles and nanorods of CdS. Dalton Trans, 2006, 37, 4499 doi: 10.1039/b606661e[21] Istas J R, de Borger R, de Temmerman L, et al. Effect of ammonia on the acidification of the environment. European Communities Report No. EUR 11857 EN, 1988[22] Timmer B, Olthuis W, van den Berg A. Ammonia sensors and their applications—a review. Sens Actuat B, 2005, 107, 666 doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2004.11.054[23] Binks D J, Bant S P, West D P, et al. CdSe/CdS core/shell quantum dots as sensitizer of a photorefractive polymer composite. J Mod Opt, 2003, 50, 299 doi: 10.1080/09500340210149714[24] Nguyen C Q, Adeogun A, Afzaal M, et al. Metal complexes of selenophosphinates from reactions with (R2PSe)2Se: [M(R2PSe2)n] (M = ZnII, CdII, PbII, InIII, GaIII, CuI, BiIII, NiII; R = iPr, Ph) and [MoV2O2Se2(Se2PiPr2)2. Chem Commun, 2006, 2182 doi: 10.1039/b603198f[25] Derbali A, Saidi H, Attaf A, et al. Solution flow rate influence on ZnS thin films properties grown by ultrasonic spray for optoelectronic application. J Semicond, 2018, 39, 093001 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/39/9/093001[26] Panneerselvam A, Nguyen C Q, Malik M A, et al. The CVD of silver selenide films from dichalcogenophosphinato and imidodichalcogenodiphosphinatosilver(I) single-source precursors. J Mater Chem, 2009, 19, 419 doi: 10.1039/B812074A[27] Singhal S, Chawla A K, Gupta H O, et al. Influence of cobalt doping on the physical properties of Zn0.9Cd0.1S nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res Lett, 2009, 5, 323 doi: 10.1007/s11671-009-9483-7[28] Salem J K, Hammad T M, Kuhn S, et al. Structural and optical properties of Co-doped ZnS nanoparticles synthesized by a capping agent. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron, 2014, 25, 2177 doi: 10.1007/s10854-014-1856-8[29] Sarte P M, Cowley R A, Rodriguez E E, et al. Disentangling orbital and spin exchange interactions for Co2+ on a rocksalt lattice. Phys Rev B, 2018, 98, 024415 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.98.024415[30] Yang A M, Sheng Y H, Farid M A, et al. Copper doped EuMnO3: Synthesis, structure and magnetic properties. RSC Adv, 2016, 6, 13928 doi: 10.1039/C5RA27426E[31] Nagaraju P, Vijayakumar Y, Ramana Reddy M V. Room-temperature BTEX sensing characterization of nanostructured ZnO thin films. J Asian Ceram Soc, 2019, 7, 141 doi: 10.1080/21870764.2019.1579401[32] Abbas N K, Al-Rasoul K T, Shanan Z J. New method of preparation ZnS nano size at low pH. Int J Electrochem Sci, 2013, 8, 3049[33] Kumar S, Mandal P, Singh A, et al. Magnetization properties of Co incorporated ZnS nanocrystals synthesized at low temperature via chemical route. J Alloys Compd, 2020, 830, 154640 doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.154640[34] Nagaraju P, Vijayakumar Y, Phase D M, et al. Microstructural, optical and gas sensing characterization of laser ablated nanostructured ceria thin films. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron, 2016, 27, 651 doi: 10.1007/s10854-015-3801-x[35] Ghosh G, Kanti Naskar M, Patra A, et al. Synthesis and characterization of PVP-encapsulated ZnS nanoparticles. Opt Mater, 2006, 28, 1047 doi: 10.1016/j.optmat.2005.06.003[36] Rema Devi B S, Raveendran R, Vaidyan A V. Synthesis and characterization of Mn2+-doped ZnS nanoparticles. Pramana, 2007, 68, 679 doi: 10.1007/s12043-007-0068-7[37] Manjunath G, Vardhan R V, Praveen L L, et al. Room-temperature detection of ammonia and formaldehyde gases by LaxBa1− xSnO3− δ (x = 0 and 0.05) screen printed sensors: Effect of ceria and ruthenate sensitization. Appl Phys A, 2021, 127, 116 doi: 10.1007/s00339-021-04284-4[38] Godavarti U, Mote V D, Reddy M V R, et al. Precipitated cobalt doped ZnO nanoparticles with enhanced low temperature xylene sensing properties. Phys B, 2019, 553, 151 doi: 10.1016/j.physb.2018.10.034[39] Bhat P, K N K S, Nagaraju P. Synthesis and characterization of ZnO-MWCNT nanocomposites for 1-butanol sensing application at room temperature. Phys B, 2019, 570, 139 doi: 10.1016/j.physb.2019.06.008[40] Liu Y L, Wang L L, Wang H R, et al. Highly sensitive and selective ammonia gas sensors based on PbS quantum dots/TiO2 nanotube arrays at room temperature. Sens Actuators B, 2016, 236, 529 doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2016.06.037[41] Li Z P, Zhao Q Q, Fan W L, et al. Porous SnO2 nanospheres as sensitive gas sensors for volatile organic compounds detection. Nanoscale, 2011, 3, 1646 doi: 10.1039/c0nr00728e[42] Chen Z G, Zou J, Liu G, et al. Silicon-induced oriented ZnS nanobelts for hydrogen sensitivity. Nanotechnology, 2008, 19, 055710 doi: 10.1088/0957-4484/19/05/055710[43] Liu Y G, Feng P, Xue X Y, et al. Room-temperature oxygen sensitivity of ZnS nanobelts. Appl Phys Lett, 2007, 90, 042109 doi: 10.1063/1.2432278[44] Liu X W, Wang F Y, Zhen F, et al. In situ growth of Au nanoparticles on the surfaces of Cu2O nanocubes for chemical sensors with enhanced performance. RSC Adv, 2012, 2, 7647 doi: 10.1039/c2ra20789c[45] Batzill M, Diebold U. Surface studies of gas sensing metal oxides. Phys Chem Chem Phys, 2007, 9, 2307 doi: 10.1039/b617710g[46] Wang X F, Xie Z, Huang H T, et al. Gas sensors, thermistor and photodetector based on ZnS nanowires. J Mater Chem, 2012, 22, 6845 doi: 10.1039/c2jm16523f[47] Park S, An S, Ko H, et al. Synthesis, structure, and UV-enhanced gas sensing properties of Au-functionalized ZnS nanowires. Sens Actuators B, 2013, 188, 1270 doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2013.07.076[48] Hussain S, Liu T M, Javed M S, et al. Highly reactive 0D ZnS nanospheres and nanoparticles for formaldehyde gas-sensing properties. Sens Actuators B, 2017, 239, 1243 doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2016.09.128[49] Zhang L P, Dong R, Zhu Z Y, et al. Au nanoparticles decorated ZnS hollow spheres for highly improved gas sensor performances. Sens Actuators B, 2017, 245, 112 doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2017.01.179[50] Mani G K, Rayappan J B B. Selective detection of ammonia using spray pyrolysis deposited pure and nickel doped ZnO thin films. Appl Surf Sci, 2014, 311, 405 doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.05.075[51] Kalyamwar V S. TiO2 modified ZnO thick film resistors as ammonia gas sensors. Adv Mater Lett, 2013, 4, 895 doi: 10.5185/amlett.2013.4456 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: