| Citation: |
K. S. Zhuravlev, A. L. Chizh, K. B. Mikitchuk, A. M. Gilinsky, I. B. Chistokhin, N. A. Valisheva, D. V. Dmitriev, A. I. Toropov, M. S. Aksenov. High-power InAlAs/InGaAs Schottky barrier photodiodes for analog microwave signal transmission[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2022, 43(1): 012302. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/43/1/012302
****
K S Zhuravlev, A L Chizh, K B Mikitchuk, A M Gilinsky, I B Chistokhin, N A Valisheva, D V Dmitriev, A I Toropov, M S Aksenov, High-power InAlAs/InGaAs Schottky barrier photodiodes for analog microwave signal transmission[J]. J. Semicond., 2022, 43(1): 012302. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/43/1/012302.
|
High-power InAlAs/InGaAs Schottky barrier photodiodes for analog microwave signal transmission
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/43/1/012302
More Information
-
Abstract
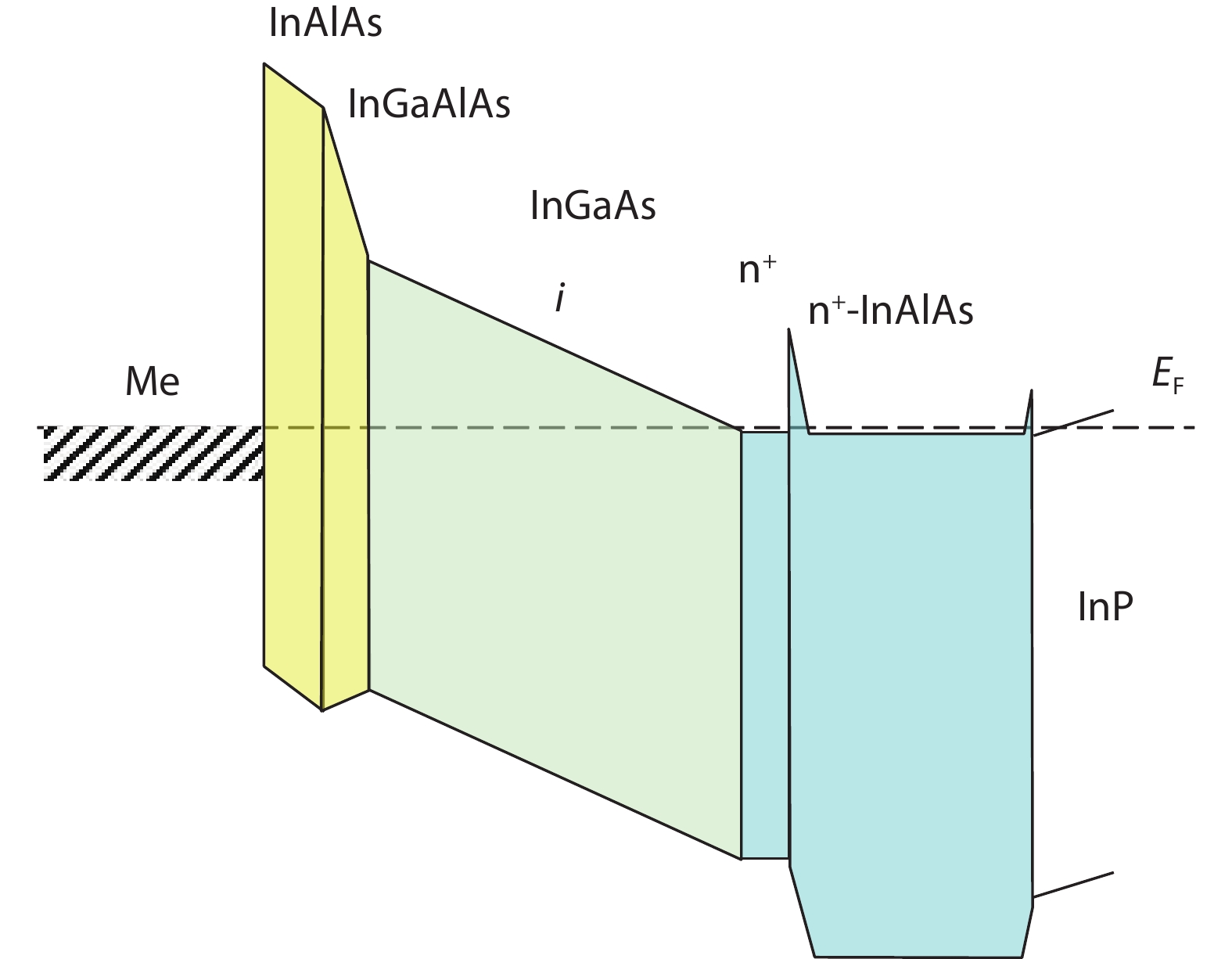
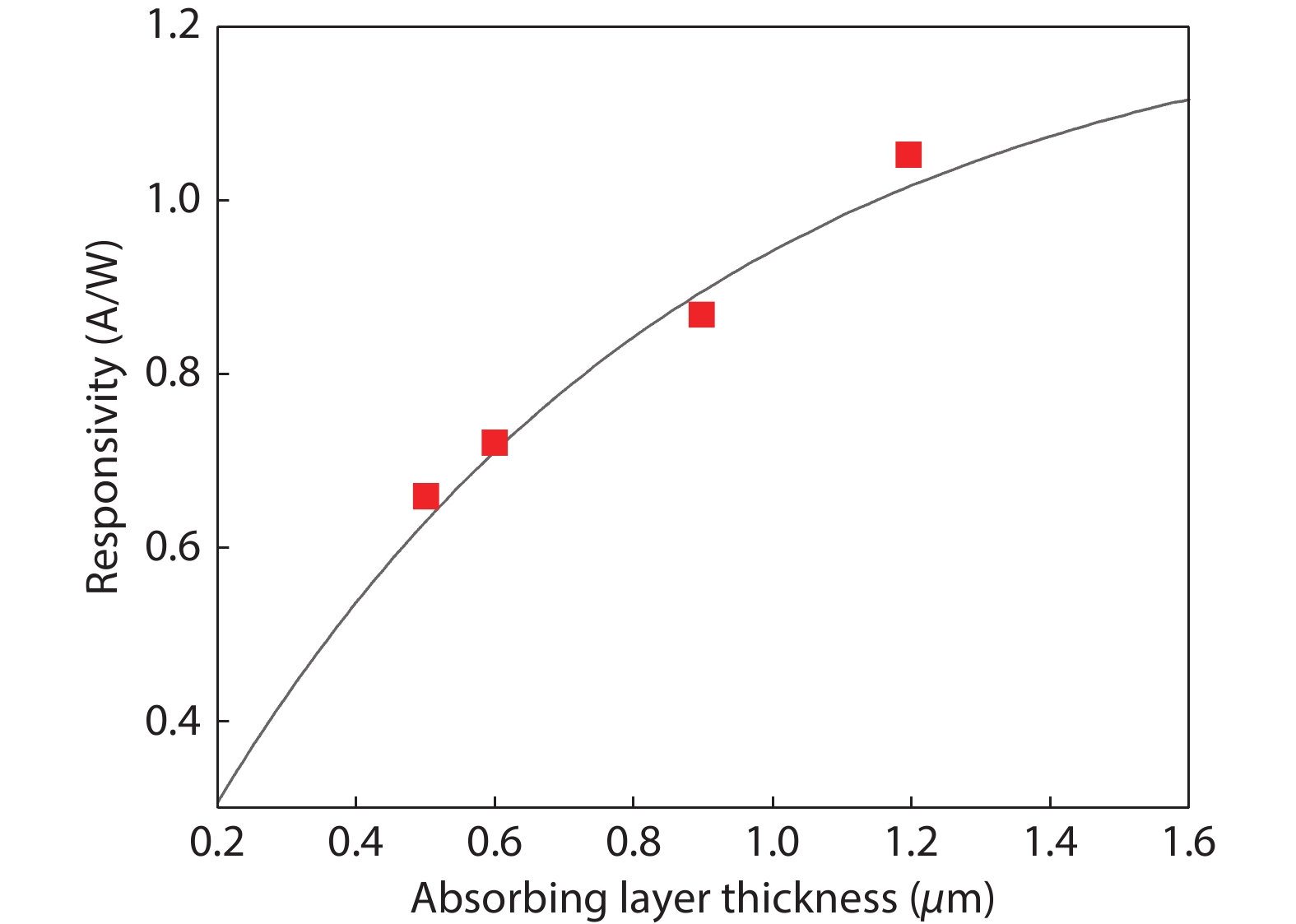
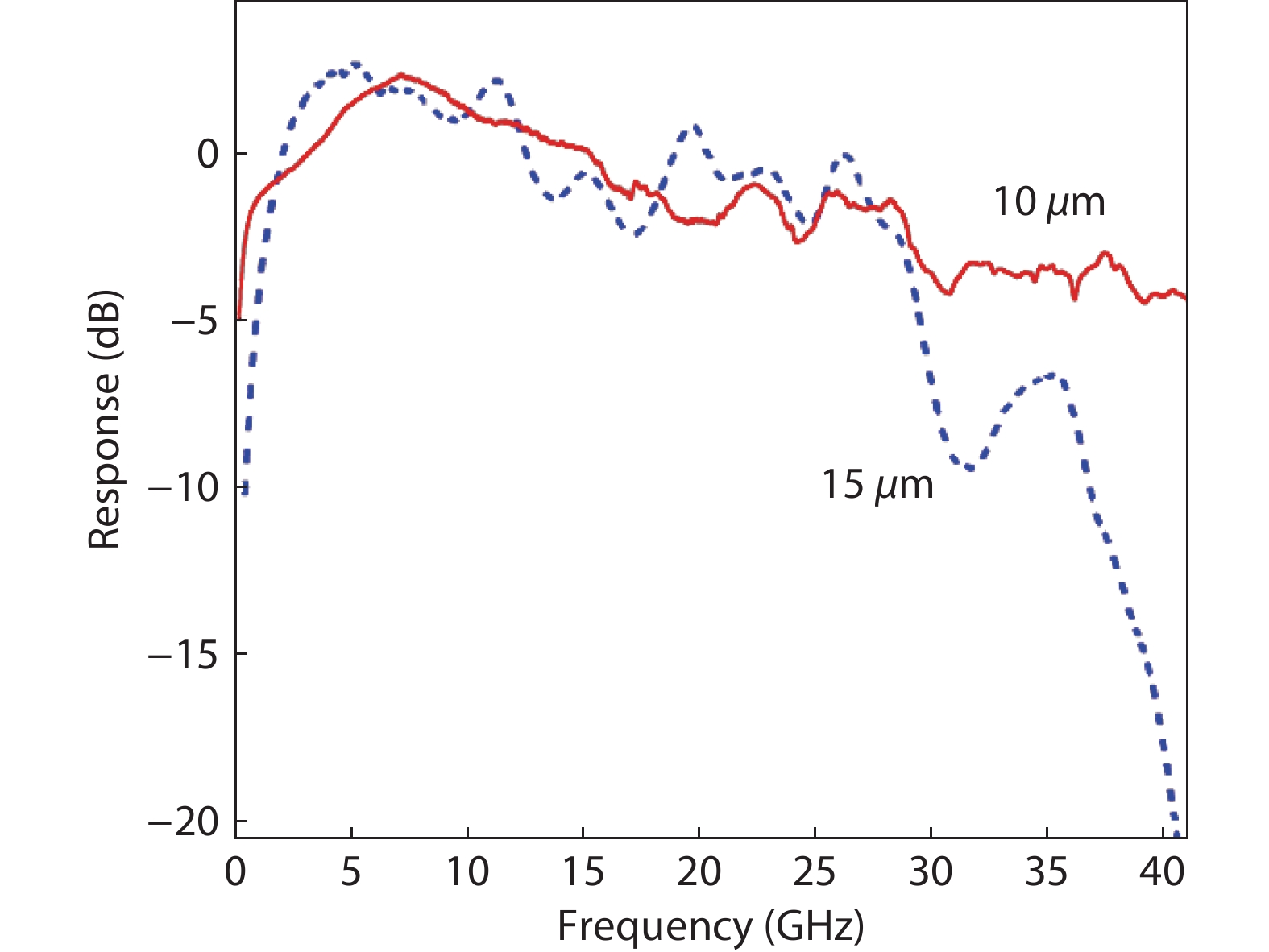
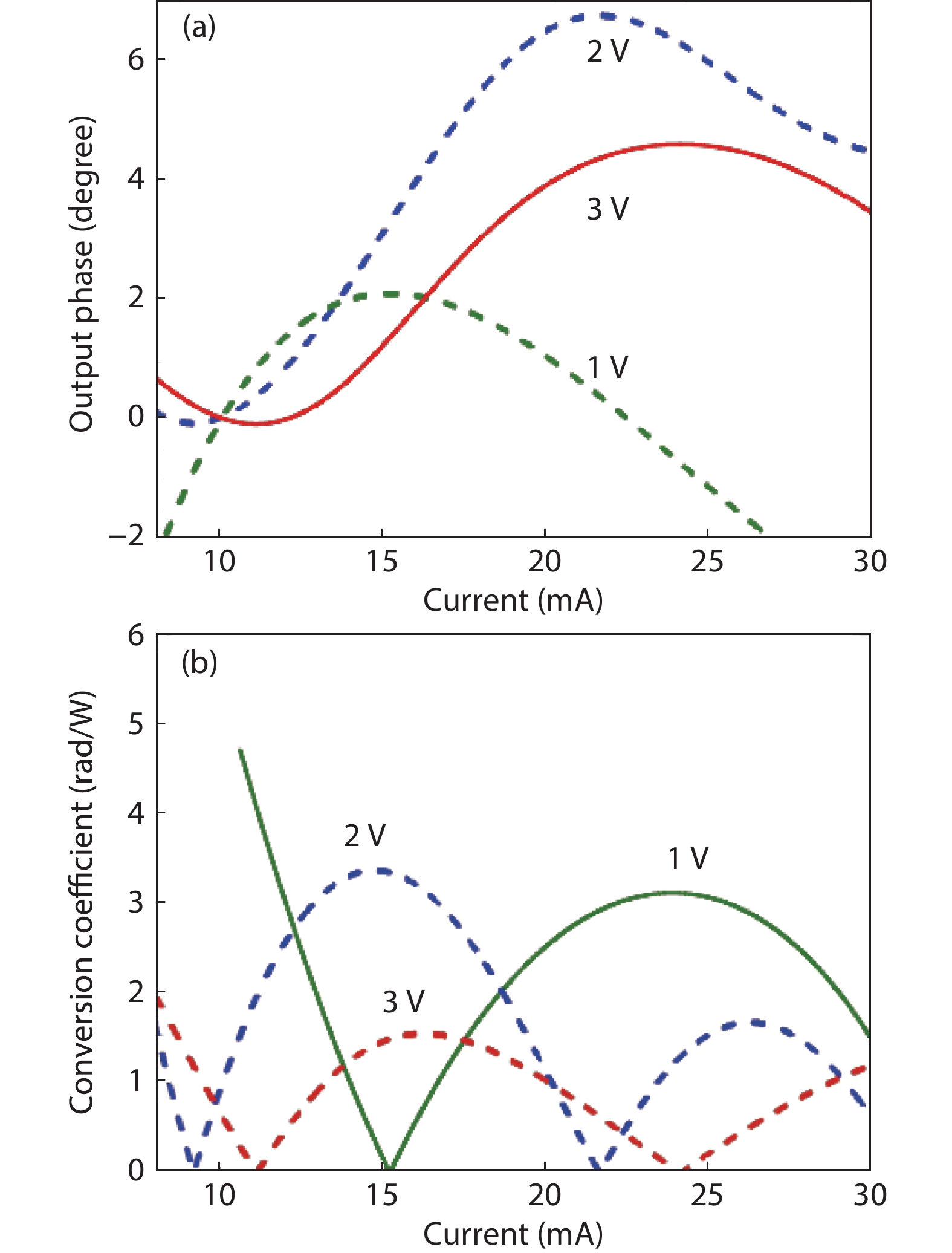
The design, manufacturing and DC and microwave characterization of high-power Schottky barrier InAlAs/InGaAs back-illuminated mesa structure photodiodes are presented. The photodiodes with 10 and 15 μm mesa diameters operate at ≥40 and 28 GHz, respectively, have the output RF power as high as 58 mW at a frequency of 20 GHz, the DC responsivity of up to 1.08 A/W depending on the absorbing layer thickness, and a photodiode dark current as low as 0.04 nA. We show that these photodiodes provide an advantage in the amplitude-to-phase conversion factor which makes them suitable for use in high-speed analog transmission lines with stringent requirements for phase noise. -
References
[1] Liu P L, Williams K J, Frankel M Y, et al. Saturation characteristics of fast photodetectors. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech, 1999, 47, 1297 doi: 10.1109/22.775469[2] Li X W, Li N, Demiguel S, et al. A partially depleted absorber photodiode with graded doping injection regions. IEEE Photonics Technol Lett, 2004, 16, 2326 doi: 10.1109/LPT.2004.834563[3] Seeds A J, Williams K J. Microwave photonics. J Light Technol, 2006, 24, 4628 doi: 10.1109/JLT.2006.885787[4] Nagatsuma T, Ito H, Ishibashi T. High-power RF photodiodes and their applications. Laser Photonics Rev, 2009, 3, 123 doi: 10.1002/lpor.200810024[5] Rouvalis E, Baynes F N, Xie X J, et al. High-power and high-linearity photodetector modules for microwave photonic applications. J Light Technol, 2014, 32, 3810 doi: 10.1109/JLT.2014.2310252[6] Chizh A, Malyshev S, Mikitchuk K. High-speed high-power InAlAs/InGaAs/InP Schottky photodiode. 2015 International Topical Meeting on Microwave Photonics (MWP), 2015, 1[7] Chizh A L, Mikitchuk K B, Zhuravlev K S, et al. High-power high-speed Schottky photodiodes for analog fiber-optic microwave signal transmission lines. Tech Phys Lett, 2019, 45, 739 doi: 10.1134/S1063785019070204[8] Dmitriev D V, Kolosovsky D A, Gavrilova T A, et al. Transformation of the InP(001) surface upon annealing in an arsenic flux. Surf Sci, 2021, 710, 121861 doi: 10.1016/j.susc.2021.121861[9] Dmitriev D V, Valisheva N A, Gilinsky A M, et al. InAlAs/InGaAs/InP heterostructures for microwave photodiodes grown by molecular beam epitaxy. IOP Conf Ser: Mater Sci Eng, 2019, 475, 012022 doi: 10.1088/1757-899X/475/1/012022[10] Aksenov M S, Valisheva N A, Chistokhin I B, et al. About the nature of the barrier inhomogeneities at Au/Ti/n-InAlAs(001) Schottky contacts. Appl Phys Lett, 2019, 114, 221602 doi: 10.1063/1.5091598[11] Born M, Wolf E. Principles of optics. 7th ed. Cambridge University Press, 1999, 64[12] Rogalski A. Infrared detectors. 2nd ed. CRC Press, 2010, 182[13] Zielinski E, Schweizer H, Streubel K, et al. Excitonic transitions and exciton damping processes in InGaAs/InP. J Appl Phys, 1986, 59, 2196 doi: 10.1063/1.336358[14] Kato K, Hata S, Kawano K, et al. Design of ultrawide-band, high-sensitivity p–i–n photodetectors. IEICE Trans Electron, 1993, E76-C, 214[15] Chtioui M, Enard A, Carpentier D, et al. High-power high-linearity uni-traveling-carrier photodiodes for analog photonic links. IEEE Photonics Technol Lett, 2008, 20, 202 doi: 10.1109/LPT.2007.913260[16] Rubiola E, Salik E, Yu N, et al. Flicker noise in high-speed p-i-n photodiodes. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech, 2006, 54, 816 doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2005.863062[17] Eliyahu D, Seidel D, Maleki L. RF amplitude and phase-noise reduction of an optical link and an opto-electronic oscillator. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech, 2008, 56, 449 doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2007.914640[18] Hu Y, Menyuk C R, Xie X J, et al. Computational study of amplitude-to-phase conversion in a modified unitraveling carrier photodetector. IEEE Photonics J, 2017, 9, 1 doi: 10.1109/JPHOT.2017.2682251[19] -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: