| Citation: |
Chenyun Lin, Xiaotong Fan, Yuxuan Gu, Siting Cai, Zhong Chen, Shuli Wang, Yue Lin. Electrohydrodynamic inkjet printing of perovskite quantum dots for color-conversion micro-LED displays[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2026, In Press. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/25120014
****
C Y Lin, X T Fan, Y X Gu, S T Cai, Z Chen, S L Wang, and Y Lin, Electrohydrodynamic inkjet printing of perovskite quantum dots for color-conversion micro-LED displays[J]. J. Semicond., 2026, accepted doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/25120014
|
Electrohydrodynamic inkjet printing of perovskite quantum dots for color-conversion micro-LED displays
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/25120014
CSTR: 32376.14.1674-4926.25120014
More Information-
Abstract
Electrohydrodynamic (EHD) inkjet printing has emerged as a powerful micro-/nanofabrication technique for high-resolution perovskite quantum dot (PeQD) color-conversion layers, offering precise control over pixel morphology, dimensions, and composition. This review systematically examines the mechanisms of cone-jet and electrostatic-attraction modes in EHD printing, highlighting recent advances in PeQD ink design, solvent and ligand engineering, and printing parameter optimization. Perovskite precursor and colloidal inks are discussed in detail, emphasizing strategies to enhance droplet ejection stability, suppress coffee-ring effects, and achieve uniform, high-luminescence pixels. Ligand exchange, dual-ligand passivation, and core−shell or polymer encapsulation are shown to effectively mitigate ion migration, surface defects, and environmental degradation, thereby improving photoluminescence efficiency and stability. Multi-channel and multi-nozzle EHD printing systems enable dynamic halide composition control and parallel RGB pixel deposition, facilitating ultrahigh-resolution patterning down to submicron feature sizes. Finally, the review highlights future directions, including synergistic PeQD material synthesis, advanced ink formulation, scalable high-throughput printing, and integration of PeQD color-conversion pixels into full-color micro-LED displays with minimal crosstalk and robust operational stability. These developments collectively demonstrate the immense potential of EHD inkjet printing for next-generation high-performance display technologies. -
References
[1] Yin K, Hsiang E L, Zou J Y, et al. Advanced liquid crystal devices for augmented reality and virtual reality displays: Principles and applications. Light Sci Appl, 2022, 11(1): 161 doi: 10.1038/s41377-022-00851-3[2] Chen H W, Lee J H, Lin B Y, et al. Liquid crystal display and organic light-emitting diode display: Present status and future perspectives. Light Sci Appl, 2018, 7: 17168 doi: 10.1038/lsa.2017.168[3] Wang D W. OLED industrialization review and issue analysis. Chin J Liq Cryst Disp, 2022, 37(6): 709 doi: 10.37188/cjlcd.2022-0049[4] Anwar A R, Sajjad M T, Ali Johar M, et al. Recent progress in micro-LED-based display technologies. Laser Photonics Rev, 2022, 16(6): 2100427[5] Chen D B, Chen Y C, Zeng G, et al. Integration technology of micro-LED for next-generation display. Research, 2023, 6: 0047 doi: 10.34133/research.0047[6] Chen F R, Bian J, Hu J L, et al. Mass transfer techniques for large-scale and high-density microLED arrays. Int J Extrem Manuf, 2022, 4(4): 042005 doi: 10.1088/2631-7990/ac92ee[7] Sun W G, Ji L F, Lin Z Y, et al. 20 µm micro-LEDs mass transfer via laser-induced in situ nanoparticles resonance enhancement. Small, 2024, 20(27): 2309877[8] Geum D M, Kim S K, Kang C M, et al. Strategy toward the fabrication of ultrahigh-resolution micro-LED displays by bonding-interface-engineered vertical stacking and surface passivation. Nanoscale, 2019, 11(48): 23139 doi: 10.1039/C9NR04423J[9] Huang J H, Li Z W, Zhu Y L, et al. Monolithic integration of full-color microdisplay screen with sub-5 µm quantum-dot pixels. Adv Mater, 2024, 36(45): 2409025[10] Qi L H, Li P A, Zhang X, et al. Monolithic full-color active-matrix micro-LED micro-display using InGaN/AlGaInP heterogeneous integration. Light Sci Appl, 2023, 12(1): 258 doi: 10.1038/s41377-023-01298-w[11] Guo Y, Yu J C, Huang L, et al. Monolithic full-color micro-LED displays featuring three-dimensional chip bonding and quantum dot-based color conversion layer. Opt Express, 2024, 32(16): 27662 doi: 10.1364/OE.530687[12] Wang Y H, Luo Y S, Kong X M, et al. Patterning technologies of quantum dots for color-conversion micro-LED display applications. Nanoscale, 2025, 17(4): 1764 doi: 10.1039/D4NR03925D[13] Yan Z J, University X, Wang Y H, et al. Microfluidic-based patterning of high-resolution, uniform luminescent, and low optical crosstalk quantum dot arrays for full-color micro-LED displays. ACS Photonics, 2025, 12(10): 5443 doi: 10.1021/acsphotonics.5c01016[14] Zhang X, Liu N, Du H N, et al. Metal halide perovskite as down-cvonversion materials for advanced display. Adv Mater, 2025, 37(25): e2410194[15] Fan X T, Wang S L, Yang X, et al. Brightened bicomponent perovskite nanocomposite based on Förster resonance energy transfer for micro-LED displays. Adv Mater, 2023, 35(30): e2300834[16] Kong L M, Zhang X Y, Zhang C X, et al. Stability of perovskite light-emitting diodes: existing issues and mitigation strategies related to both material and device aspects. Adv Mater, 2022, 34(43): e2205217 doi: 10.1002/adma.202205217[17] Lin Y, Zheng X, Shangguan Z B, et al. All-inorganic encapsulation for remarkably stable cesium lead halide perovskite nanocrystals: Toward full-color display applications. J Mater Chem C, 2021, 9(36): 12303 doi: 10.1039/D1TC02685B[18] Zhang P P, Yang G L, Li F, et al. Direct in situ photolithography of perovskite quantum dots based on photocatalysis of lead bromide complexes. Nat Commun, 2022, 13(1): 6713 doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-34453-9[19] Li Y, Tao J, Wang Q, et al. Microfluidics-based quantum dot color conversion layers for full-color micro-LED display. Appl Phys Lett, 2021, 118(17): 173501 doi: 10.1063/5.0047854[20] Viola I, Matteocci F, De Marco L, et al. Microfluidic-assisted growth of perovskite single crystals for photodetectors. Adv Mater Technol, 2023, 8(14): 2300023[21] Huang R X, Yao D Y, Sun K C, et al. Flexible quantum dots color conversion layer fabricated via laser direct writing technique for micro-LED. J Lumin, 2025, 277: 120902 doi: 10.1016/j.jlumin.2024.120902[22] Tian X Y, Wang L, Li W, et al. Whispering gallery mode lasing from perovskite polygonal microcavities via femtosecond laser direct writing. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2021, 13(14): 16952 doi: 10.1021/acsami.0c21824[23] Lin Y H, Huang W J, Zhanghu M Y, et al. Ultra-thick inkjet-printed quantum dots layer for full-color micro-LED displays. Opt Express, 2023, 31(20): 31818 doi: 10.1364/OE.498974[24] Wang Y X, Yin Y M, Liu M, et al. One-step synthesis of UV-curable CsPbX3 (X = Cl, Br, and I) nanocrystal inks for printing. Laser Photonics Rev, 2024, 18(10): 2300962[25] Long Z S, Li H J, Cao Q L, et al. Large-scale synthesis of perovskite quantum dots and their application to inkjet-printed highly stable microarray. Small, 2025, 21(15): e2410935[26] Yin Z P, Wang D Z, Guo Y L, et al. Electrohydrodynamic printing for high resolution patterning of flexible electronics toward industrial applications. InfoMat, 2024, 6(2): e12505 doi: 10.1002/inf2.12505[27] Coppola S, Vespini V, Behal J, et al. Drop-on-demand pyro-electrohydrodynamic printing of nematic liquid crystal microlenses. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2024, 16(15): 19453 doi: 10.1021/acsami.4c00215[28] Lin Y, Yang X, Wang S L, et al. Electrohydrodynamic inkjet specialized perovskite non-polar ink for printing color conversion layer of micro-LED display. Symp Digest Tech Papers, 2024, 55(S1): 425[29] Iranshahi K, Defraeye T, Rossi R M, et al. Electrohydrodynamics and its applications: Recent advances and future perspectives. Int J Heat Mass Transf, 2024, 232: 125895 doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2024.125895[30] Wang S L, Kong X M, Cai S T, et al. Solvent engineering in perovskite nanocrystal colloid inks for super-fine electrohydrodynamic inkjet printing of color conversion microstructures in micro-LED displays. Chin Chem Lett, 2025, 36(8): 110976 doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2025.110976[31] Huang C Y, Li H C, Wu Y, et al. Inorganic halide perovskite quantum dots: A versatile nanomaterial platform for electronic applications. Nanomicro Lett, 2022, 15(1): 16 doi: 10.1007/s40820-022-00983-6[32] Ren X X, Zhang X, Xie H X, et al. Perovskite quantum dots for emerging displays: Recent progress and perspectives. Nanomaterials, 2022, 12(13): 2243 doi: 10.3390/nano12132243[33] Shi Y X, Chang S E, Lee T W. Sustainable perovskite light emitters. Chem Soc Rev, 2025, 54(22): 10316 doi: 10.1039/D5CS00620A[34] Dey A, Ye J Z, De A, et al. State of the art and prospects for halide perovskite nanocrystals. ACS Nano, 2021, 15(7): 10775 doi: 10.1021/acsnano.0c08903[35] Zhu M H, Duan Y Q, Liu N, et al. Electrohydrodynamically printed high-resolution full-color hybrid perovskites. Adv Funct Materials, 2019, 29(35): 1903294[36] Wang Q L, Zhang G N, Zhang H Y, et al. High-resolution, flexible, and full-color perovskite image photodetector via electrohydrodynamic printing of ionic-liquid-based ink. Adv Funct Materials, 2021, 31(28): 2100857[37] Huang Q S, Wang W, Vikesland P J. Implications of the coffee-ring effect on virus infectivity. Langmuir, 2021, 37(38): 11260 doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.1c01610[38] Poulichet V, Morel M, Rudiuk S, et al. Liquid-liquid coffee-ring effect. J Colloid Interface Sci, 2020, 573: 370 doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2020.03.094[39] Zhang G N, Zhang H Y, Yu R, et al. Critical size/viscosity for coffee-ring-free printing of perovskite micro/nanopatterns. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2022, 14(12): 14712 doi: 10.1021/acsami.1c23630[40] Kang G , Lee H , Moon J, et al. Electrohydrodynamic jet-printed MAPbBr3 perovskite/polyacrylonitrile nanostructures for water-stable, flexible, and transparent displays. ACS Appl Nano Mater, 2022, 5(5): 6726[41] Chen Y H, Yang X, Fan X T, et al. Electrohydrodynamic inkjet printing of three-dimensional perovskite nanocrystal arrays for full-color micro-LED displays. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2024, 16(19): 24908 doi: 10.1021/acsami.4c02594[42] Cohen T A, Sharp D, Kluherz K T, et al. Direct patterning of perovskite nanocrystals on nanophotonic cavities with electrohydrodynamic inkjet printing. Nano Lett, 2022, 22(14): 5681 doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.2c00473[43] Yang X, Yan Z J, Zhong C M, et al. Electrohydrodynamically printed high-resolution arrays based on stabilized CsPbBr3 quantum dot inks. Adv Opt Mater, 2023, 11(9): 2202673[44] Zhang X, Cai J H, Yang L W, et al. Ligand strategy for perovskite displays: A review. ACS Energy Lett, 2024, 9(4): 1587 doi: 10.1021/acsenergylett.3c02454[45] Luo Y N, Wang S, Li W Q, et al. Dual ligand strategy to manipulate growth kinetics of FAPbBr3 nanocrystals for high-performance light-emitting diodes. Small Methods, 2025: e2401694[46] Li Y W, Alam A, Zhou T, et al. Functional ligand-modified perovskite quantum dots for stable full-color microarrays via photopolymerization. Adv Funct Materials, 2025, 35(4): 2413963[47] Li G M, Cai J H, Zhang T Q, et al. Förster resonance energy transfer-based design of high-brightness CdSe/ZnS-CsPb(BrI)3 nanocrystals for high-performance micro-LED color conversion pixels. Laser Photonics Rev, 2025: e01630[48] Yang X, Wang S L, Hou Y Q, et al. Dual-ligand red perovskite ink for electrohydrodynamic printing color conversion arrays over 2540 dpi in near-eye micro-LED display. Nano Lett, 2024, 24(12): 3661 doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.3c04927[49] Cai S T, Chen X, Wang S L, et al. Silica coating of quantum dots and their applications in optoelectronic fields. Chin Chem Lett, 2025, 36(6): 110798 doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2024.110798[50] He Y Y, Zhang L L, Chen G T, et al. ZnO/SiO2 encapsulation of perovskite nanocrystals for efficient and stable light-emitting diodes. Appl Surf Sci, 2023, 611: 155724 doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2022.155724[51] Liu M L, Lin C Q, Ou W C, et al. Electrohydrodynamic printing of PCL@CsPbBr3 composite fibers with high luminescence for flexible displays. Coatings, 2023, 13(3): 500 doi: 10.3390/coatings13030500[52] Wang S J, Chen D J, Xu K Y, et al. Boosting stability and inkjet printability of pure-red CsPb(Br/I)3 quantum dots through dual-shell encapsulation for micro-LED displays. ACS Energy Lett, 2024, 9(6): 2517 doi: 10.1021/acsenergylett.4c00803[53] Moon I, Woo Jung J, Kim S, et al. EHD spinning process for QD color converting display. J Inf Disp, 2025, 26(3): 293 doi: 10.1080/15980316.2025.2465565[54] Jin J H, Yeom S H, Lee H J, et al. The effect of nozzle spacing on the electric field and fiber size distribution in a multi-nozzle electrospinning system. J Appl Polym Sci, 2023, 140(16): e53764 doi: 10.1002/app.53764[55] Duan Y Q, Yu R, Zhang H Y, et al. Programmable, high-resolution printing of spatially graded perovskites for multispectral photodetectors. Adv Mater, 2024, 36(24): e2313946[56] Zhang H H, Ye R F, Wu D H, et al. Efficient multi-needle electrospinning based on regulating multiple geometric factors to optimize electric-field uniformity. Mater Today Commun, 2025, 48: 113657 doi: 10.1016/j.mtcomm.2025.113657 -
Proportional views





 Chenyun Lin received her BS degree from Henan University of Science and Technology. She is currently pursuing a Master’s degree at the School of Electronic Science and Engineering, Xiamen University, under the supervision of Dr. Yue Lin and Dr. Shuli Wang. Her research is concentrated on micro-LED display technology.
Chenyun Lin received her BS degree from Henan University of Science and Technology. She is currently pursuing a Master’s degree at the School of Electronic Science and Engineering, Xiamen University, under the supervision of Dr. Yue Lin and Dr. Shuli Wang. Her research is concentrated on micro-LED display technology. Xiaotong Fan currently serves as the Program Director of the Integrated Circuit Major at Wuxi Taihu University. He obtained his Ph.D. degree from Xiamen University in June 2024. His current research interests include perovskite nanocrystals, micro-LED display technology, integrated circuit packaging and testing technology, and semiconductor device design.
Xiaotong Fan currently serves as the Program Director of the Integrated Circuit Major at Wuxi Taihu University. He obtained his Ph.D. degree from Xiamen University in June 2024. His current research interests include perovskite nanocrystals, micro-LED display technology, integrated circuit packaging and testing technology, and semiconductor device design. Shuli Wang serves as associate professor in School of Electronic Science and Engineering, Xiamen University. He received his B.S. degree in June 2013 and his Ph. D. in June 2018 from Jilin University, under the supervision of Professor Junhu Zhang. His current research interests mainly focused on perovskite-based micro-LED displays and photodetectors.
Shuli Wang serves as associate professor in School of Electronic Science and Engineering, Xiamen University. He received his B.S. degree in June 2013 and his Ph. D. in June 2018 from Jilin University, under the supervision of Professor Junhu Zhang. His current research interests mainly focused on perovskite-based micro-LED displays and photodetectors. Yue Lin currently serves as associate professor in School of Electronic Science and Engineering, Xiamen University. He obtained his Ph.D. from Xiamen University. His main research interests include micro-LED display technology; photoelectric properties of GaN-based semiconductor materials and devices; optoelectronic characteristics of all-inorganic and hybrid organic−inorganic perovskite quantum dots; and semiconductor lighting testing technologies.
Yue Lin currently serves as associate professor in School of Electronic Science and Engineering, Xiamen University. He obtained his Ph.D. from Xiamen University. His main research interests include micro-LED display technology; photoelectric properties of GaN-based semiconductor materials and devices; optoelectronic characteristics of all-inorganic and hybrid organic−inorganic perovskite quantum dots; and semiconductor lighting testing technologies.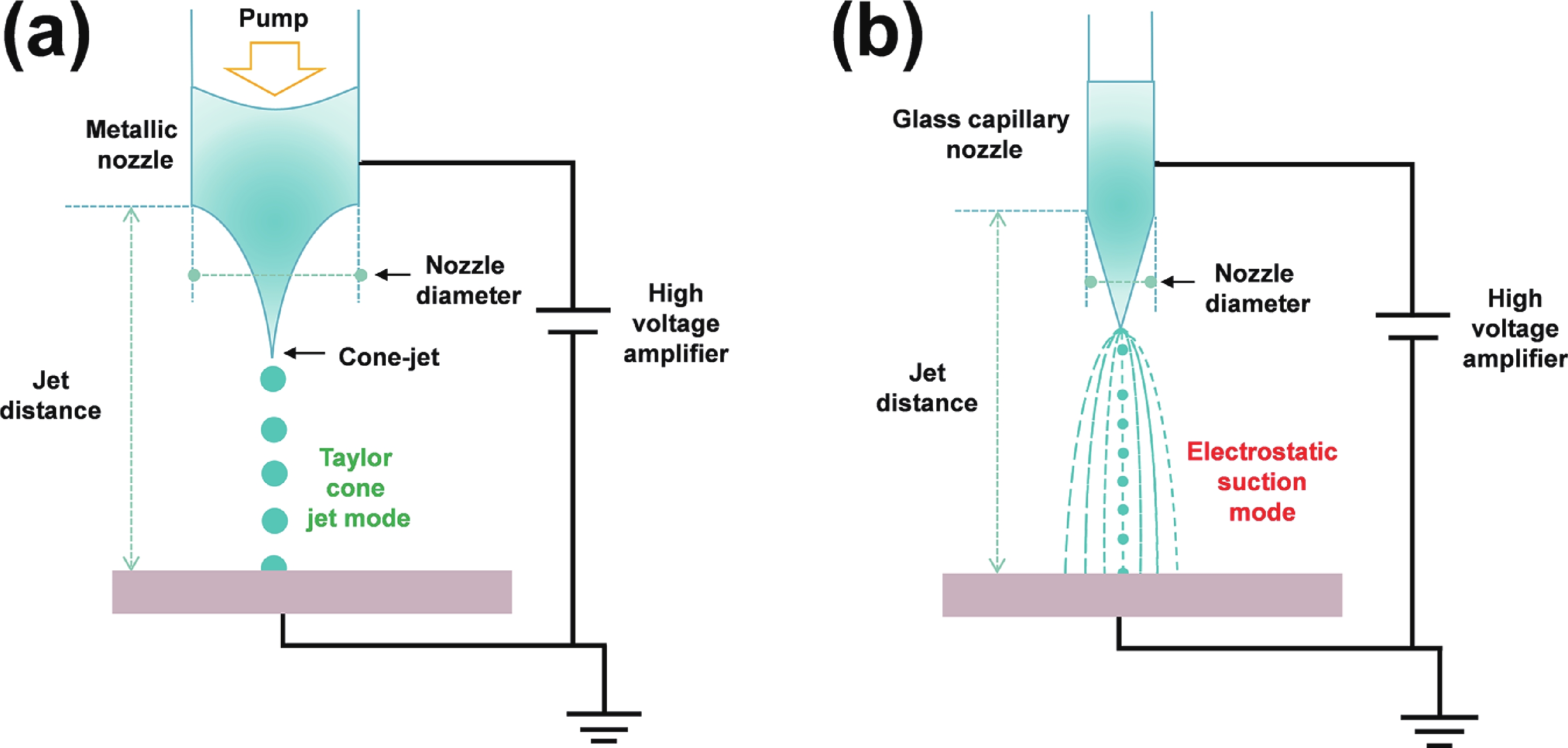
 DownLoad:
DownLoad:




















