| Citation: |
Adnan Shariah, Feda Mahasneh. Emitter layer optimization in heterojunction bifacial silicon solar cells[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2022, 43(12): 122701. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/43/12/122701
****
A Shariah, F Mahasneh. Emitter layer optimization in heterojunction bifacial silicon solar cells[J]. J. Semicond, 2022, 43(12): 122701. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/43/12/122701
|
Emitter layer optimization in heterojunction bifacial silicon solar cells
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/43/12/122701
More Information
-
Abstract
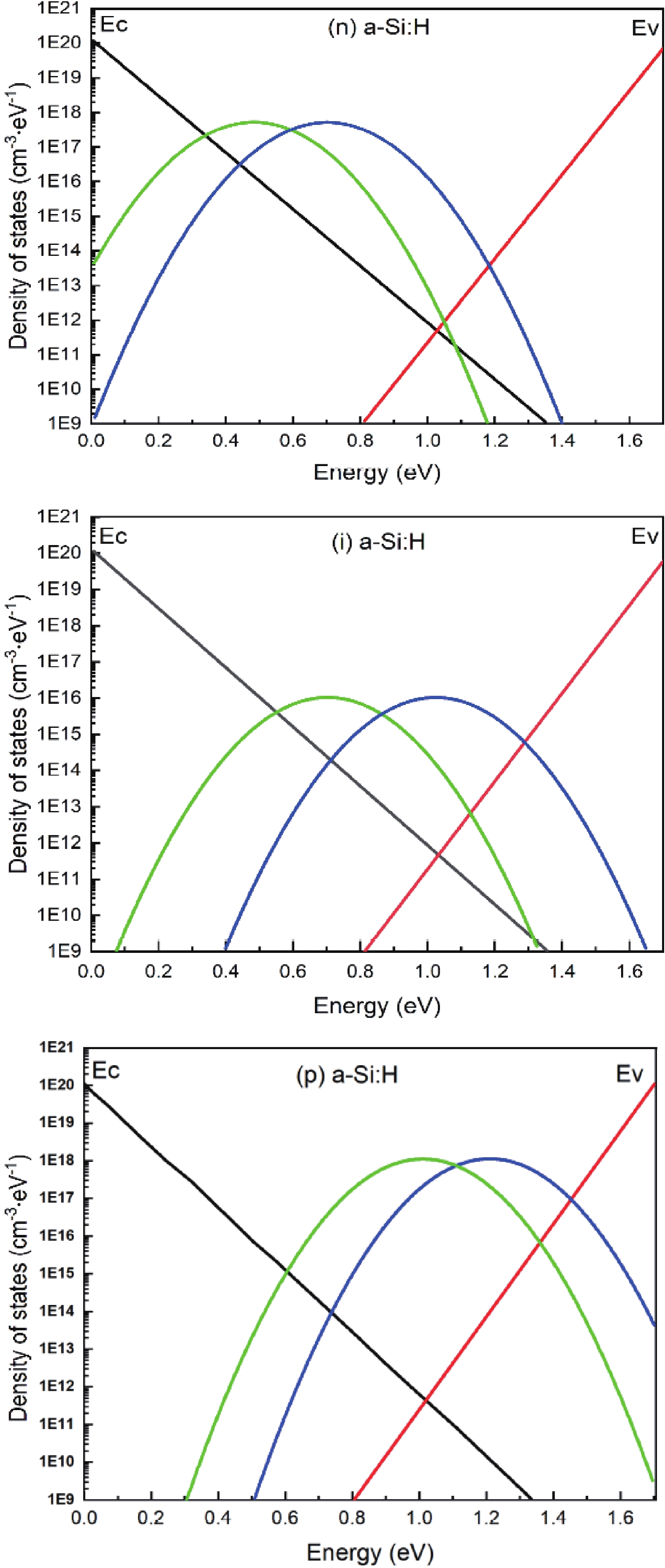
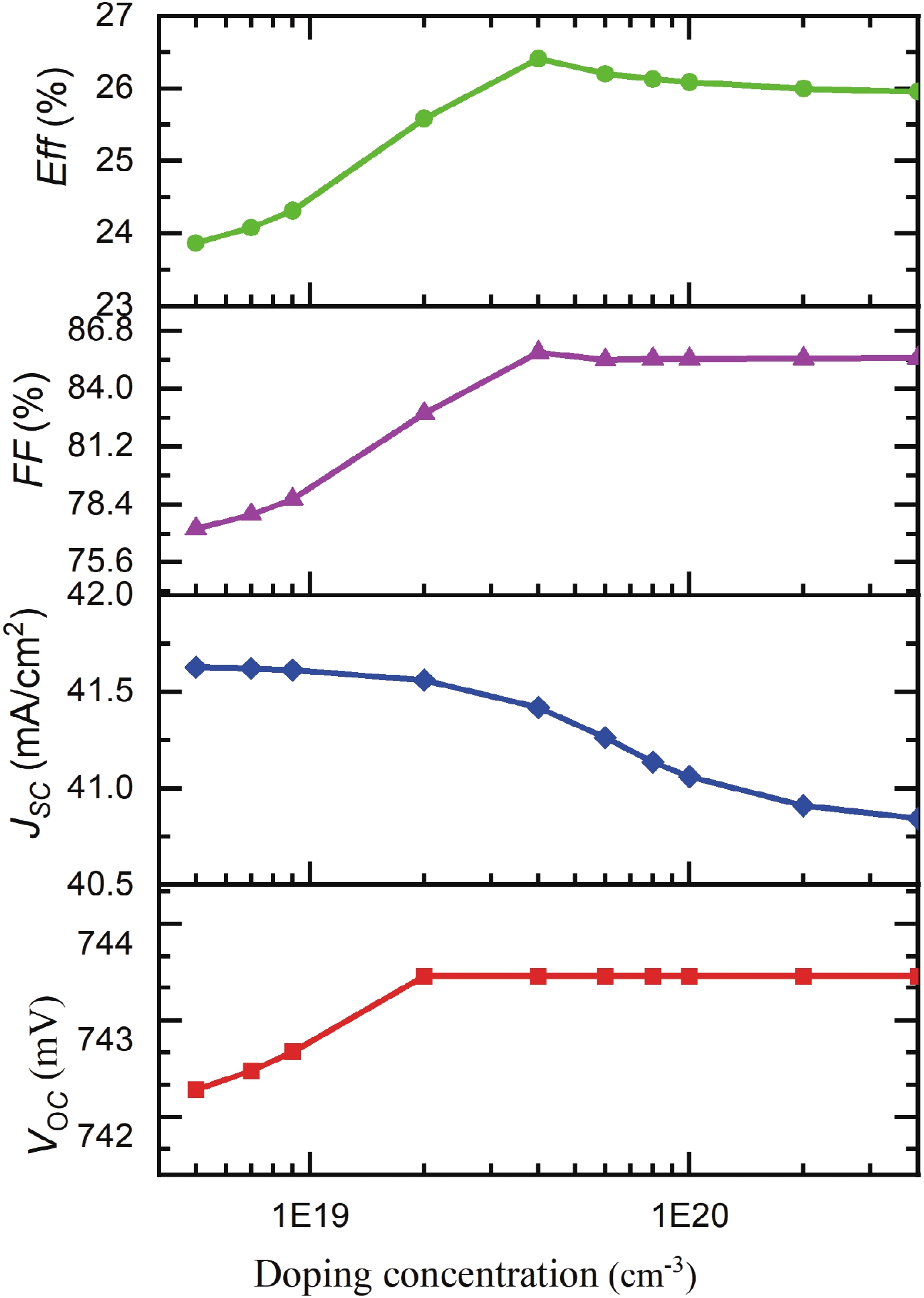
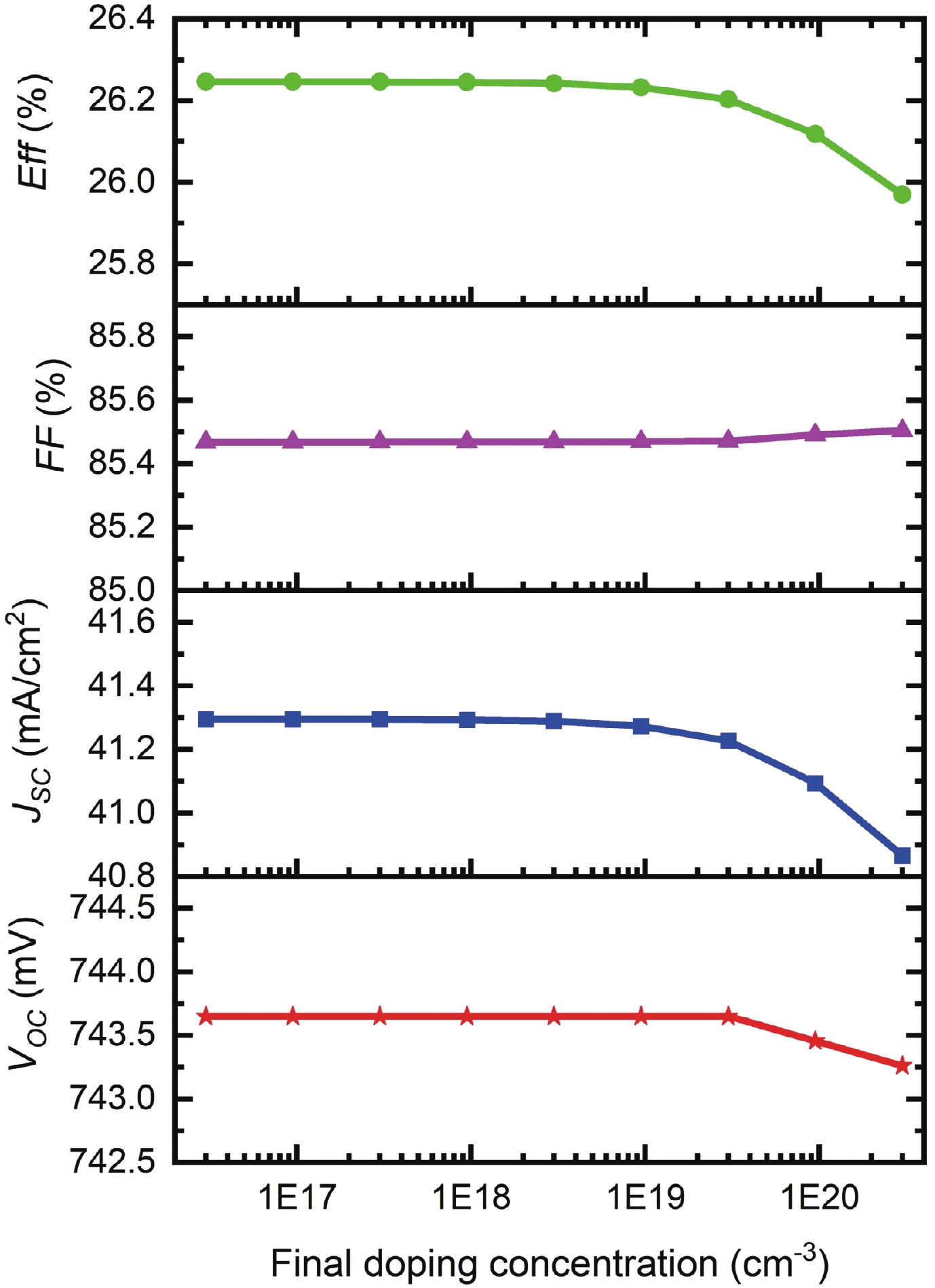
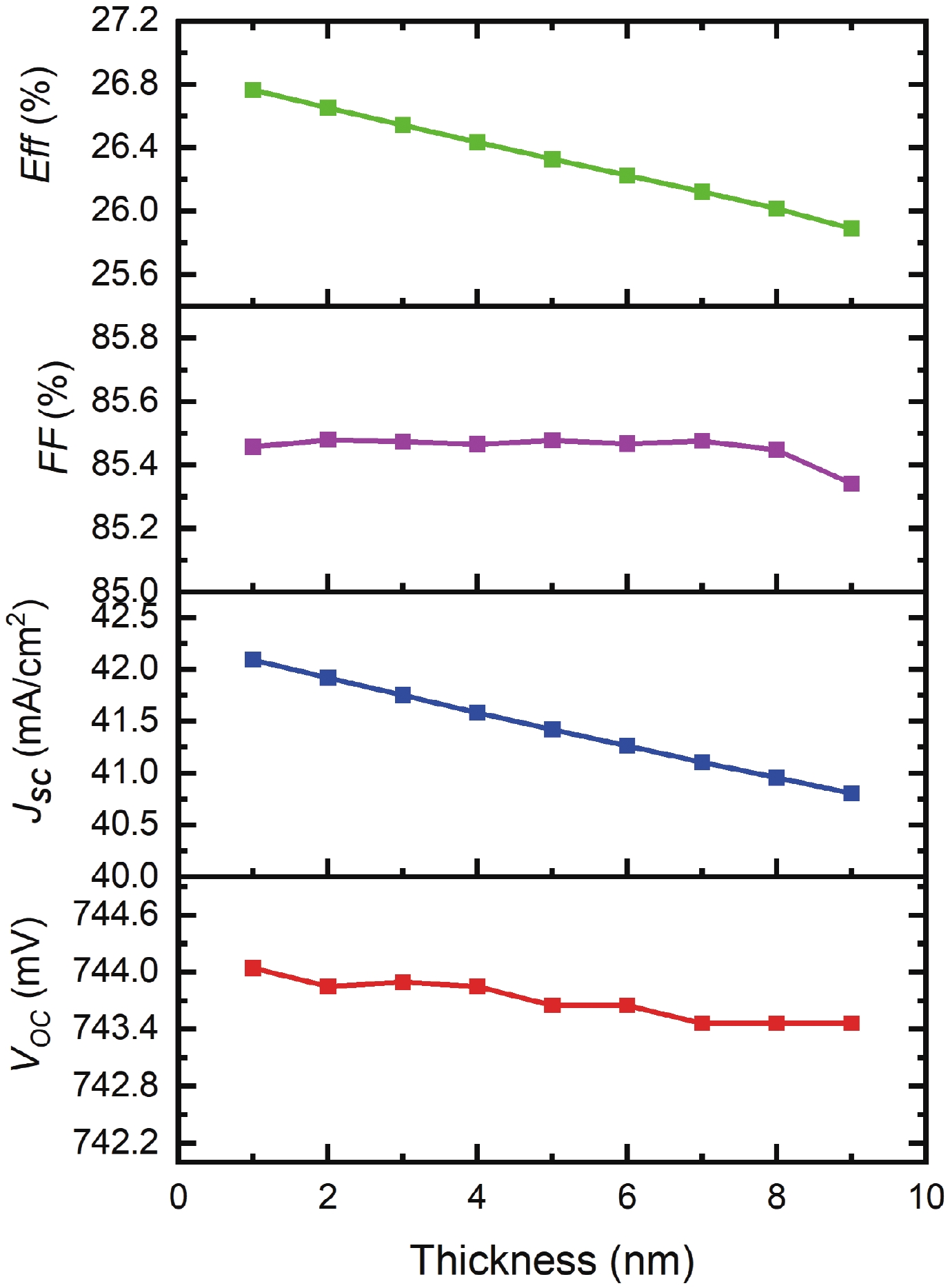
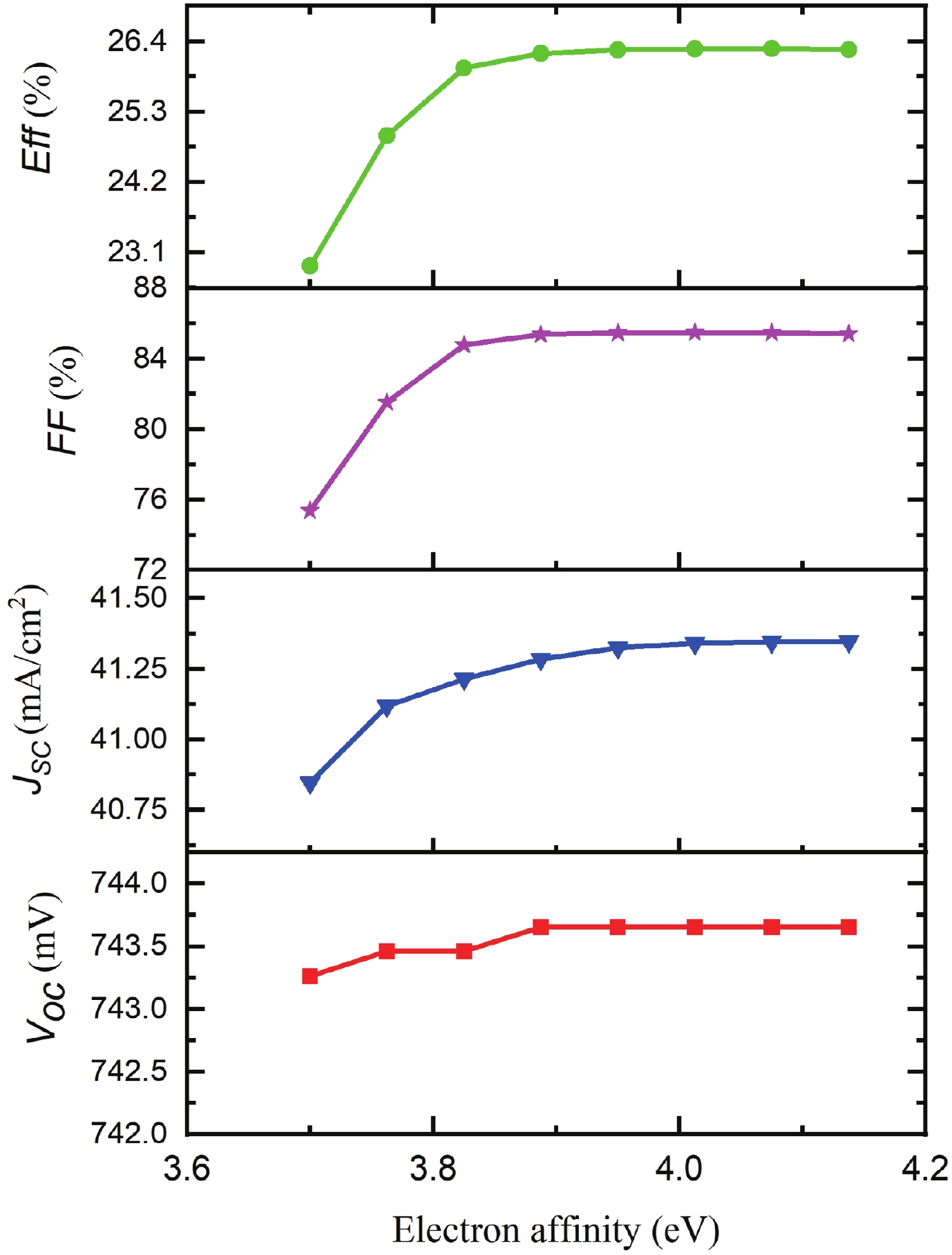
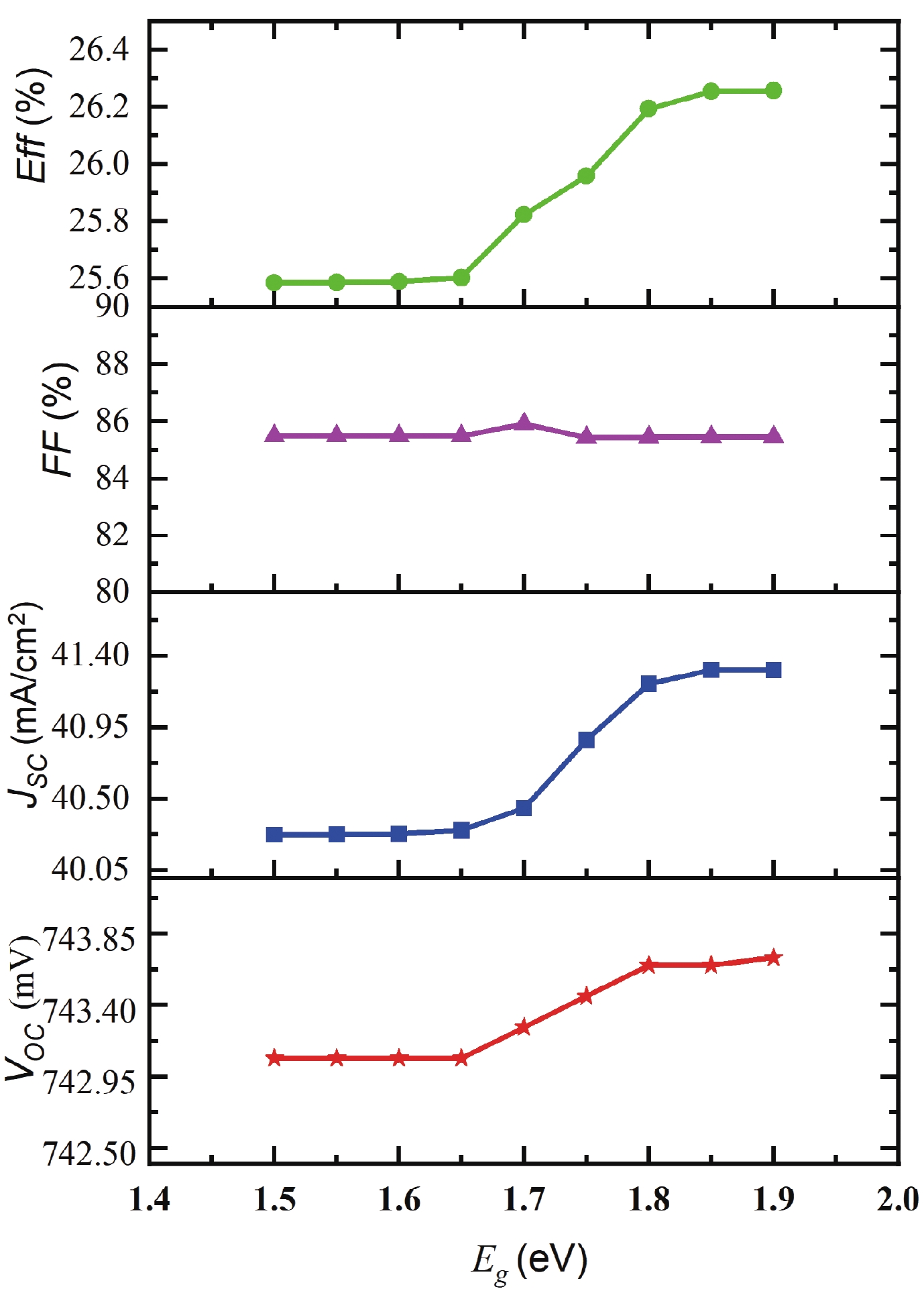
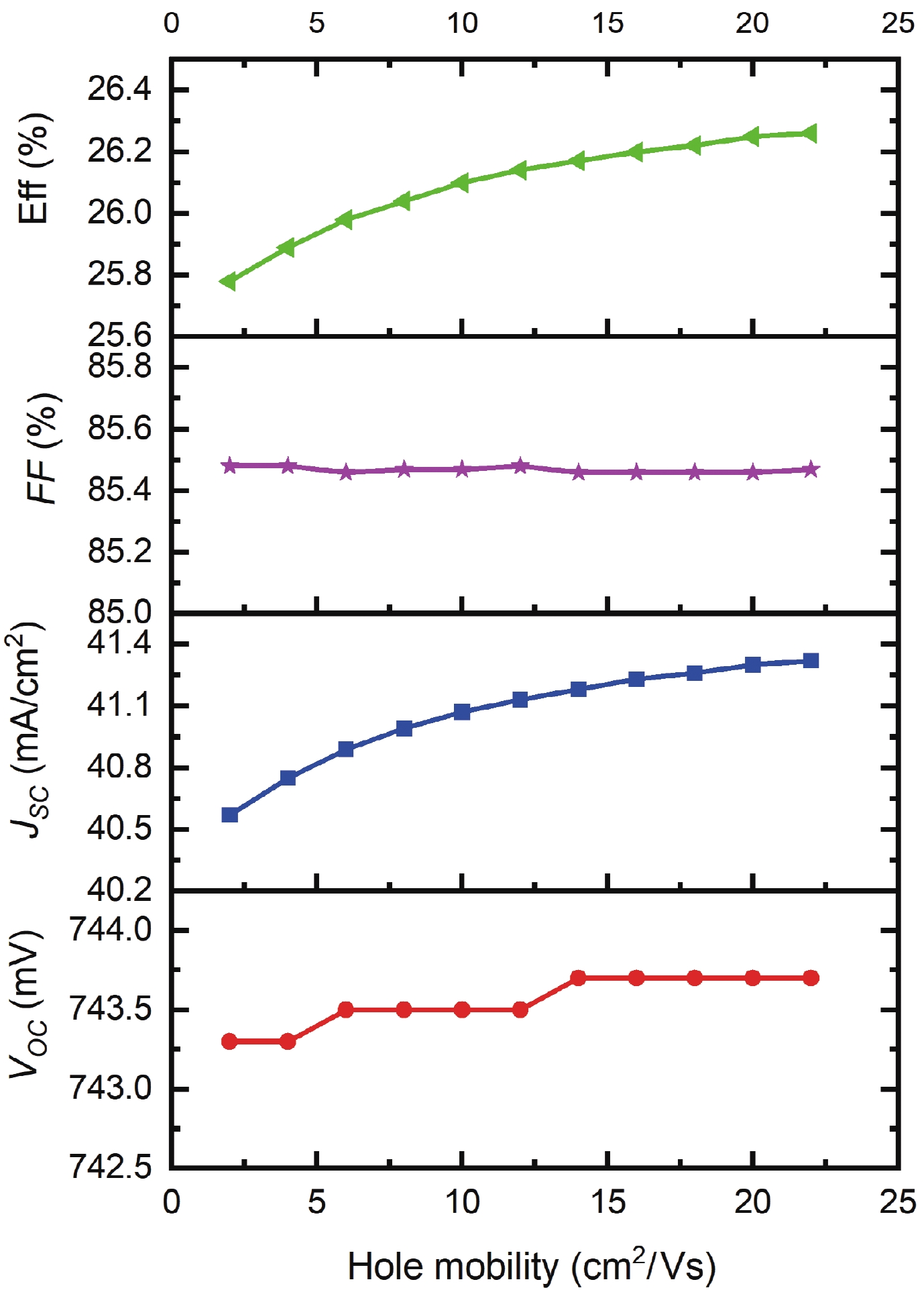
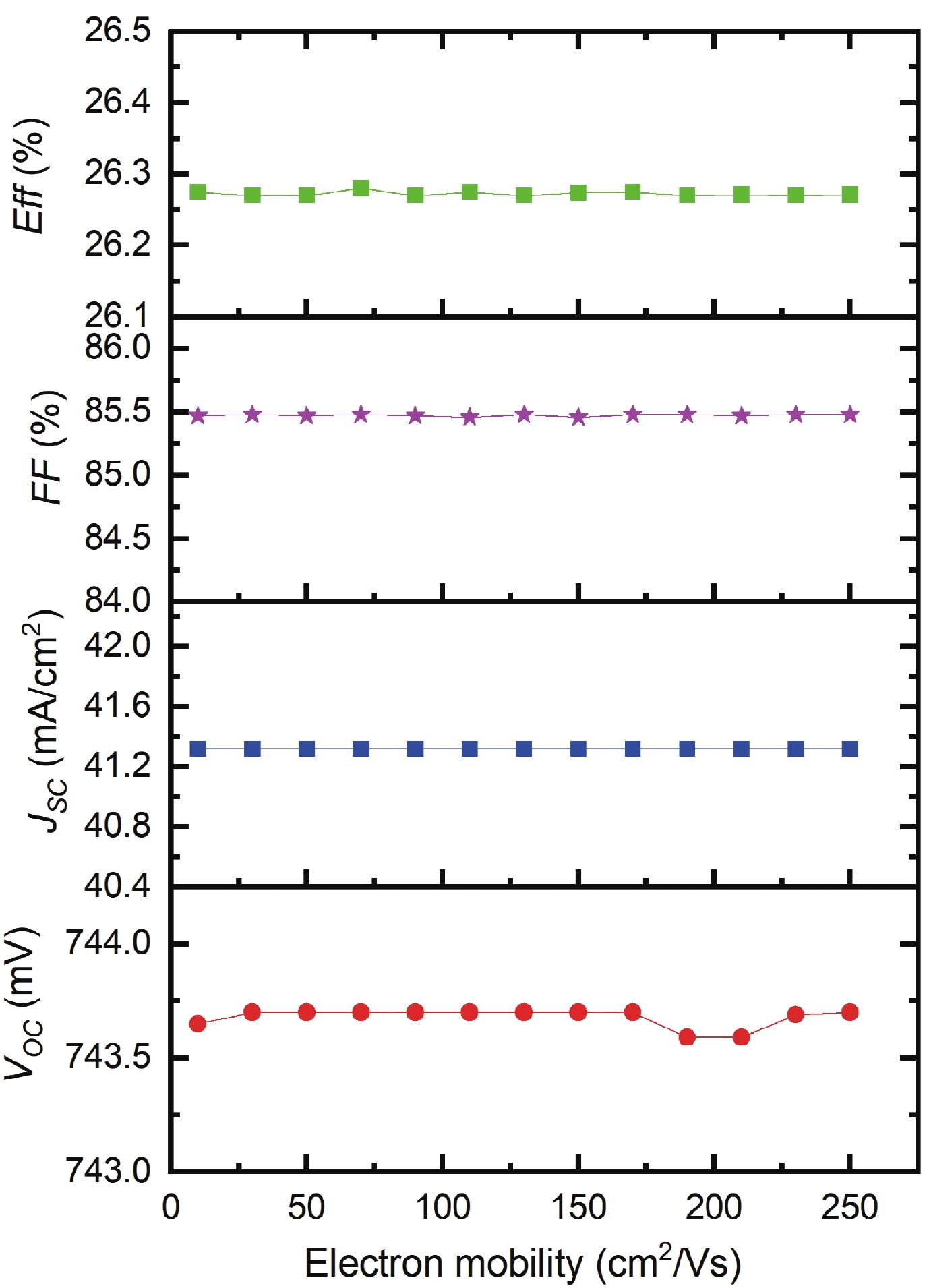
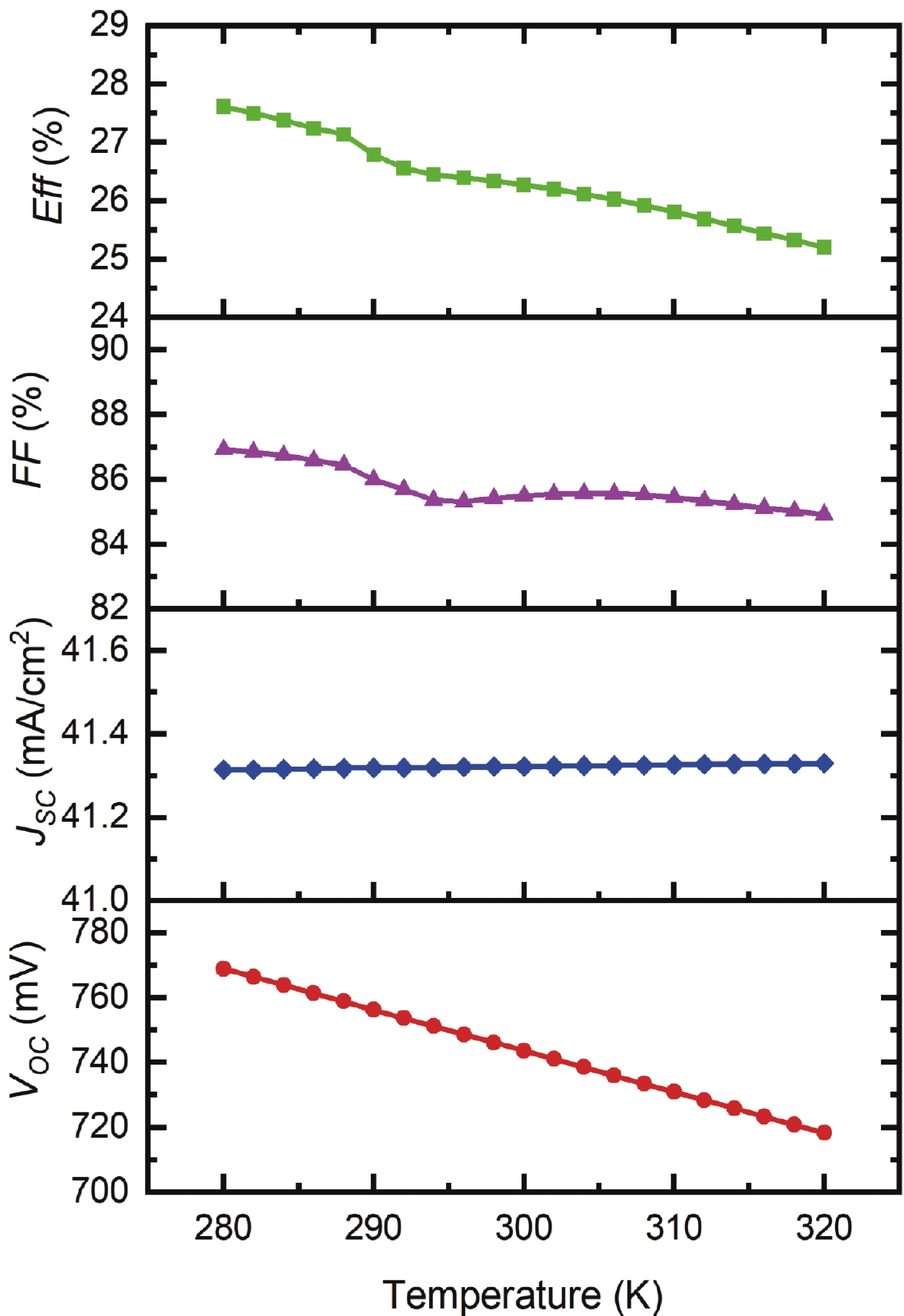
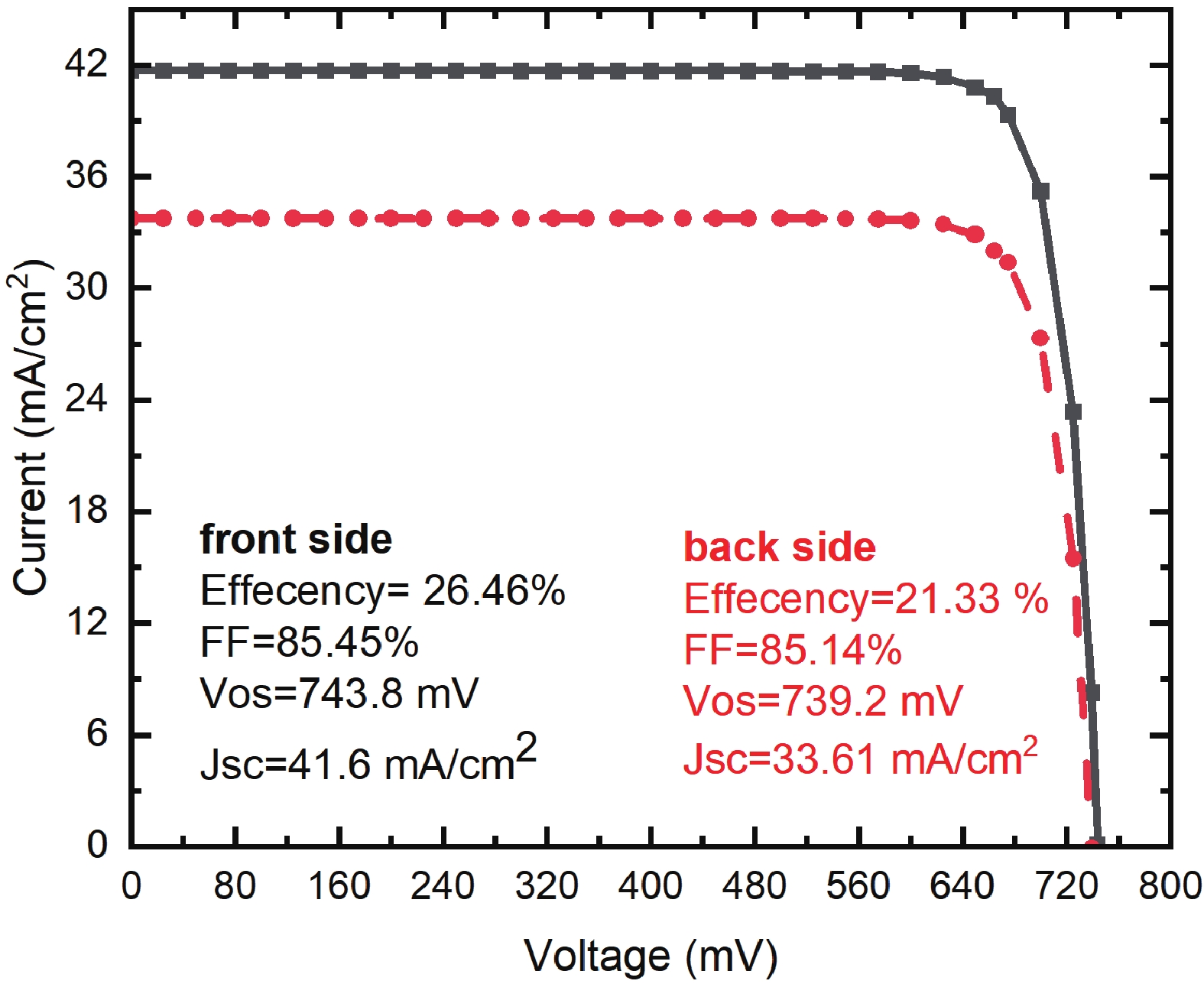
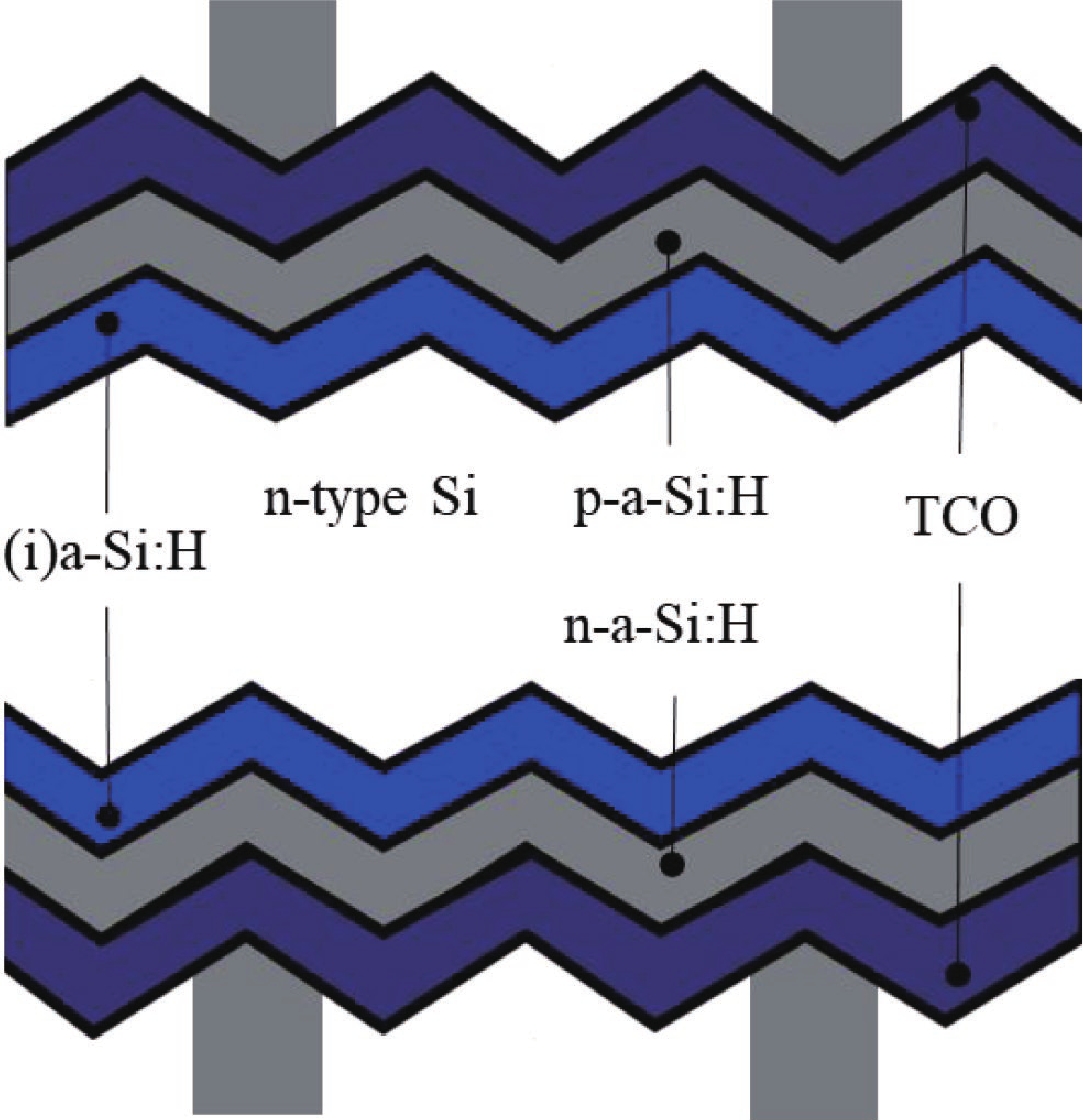
Silicon solar cells continue to dominate the market, due to the abundance of silicon and their acceptable efficiency. The heterojunction with intrinsic thin layer (HIT) structure is now the dominant technology. Increasing the efficiency of these cells could expand the development choices for HIT solar cells. We presented a detailed investigation of the emitter a-Si:H(n) layer of a p-type bifacial HIT solar cell in terms of characteristic parameters which include layer doping concentration, thickness, band gap width, electron affinity, hole mobility, and so on. Solar cell composition: (ZnO/nc-Si:H(n)/a-Si:H(i)/c-Si(p)/a-Si:H(i)/nc-Si:H(p)/ZnO). The results reveal optimal values for the investigated parameters, for which the highest computed efficiency is 26.45% when lighted from the top only and 21.21% when illuminated from the back only. -
References
[1] Wakisaka K, Taguchi M, Sawada T, et al. More than 16% solar cells with a new ‘HIT’ (doped a-Si/nondoped a-Si/crystalline Si) structure. The Conference Record of the Twenty-Second IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference, 1991, 887[2] Sawada T, Terada N, Tsuge S, et al. High-efficiency a-Si/c-Si heterojunction solar cell. Proceedings of 1994 IEEE 1st World Conference on Photovoltaic Energy Conversion, 1994, 2, 1219 doi: 10.1109/WCPEC.1994.519952[3] Mishima T, Taguchi M, Sakata H, et al. Development status of high-efficiency HIT solar cells. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells, 2011, 95, 18 doi: 10.1016/j.solmat.2010.04.030[4] Gorle D K, Chander N. A simulation approach for device structure and thickness optimization of silicon heterojunction solar cells featuring TiO2 as carrier-selective contact. Mater Today Proc, 2021, 39, 1916 doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2020.08.312[5] Champory R, Mandorlo F, Seassal C, et al. Influence of patterning the TCO layer on the series resistance of thin film HIT solar cells. EPJ Photovolt, 2017, 8, 80101 doi: 10.1051/epjpv/2016006[6] Li S, Pomaska M, Lambertz A, et al. Transparent-conductive-oxide-free front contacts for high-efficiency silicon heterojunction solar cells. Joule, 2021, 5, 1535 doi: 10.1016/j.joule.2021.04.004[7] Dwivedi N, Kumar S, Bisht A, et al. Simulation approach for optimization of device structure and thickness of HIT solar cells to achieve ~27% efficiency. Sol Energy, 2013, 88, 31 doi: 10.1016/j.solener.2012.11.008[8] Libal J, Kopecek R. Bifacial Photovoltaics: Technology, applications and economics. Institution of Engineering and Technology, 2018[9] Liang T S, Pravettoni M, Deline C, et al. A review of crystalline silicon bifacial photovoltaic performance characterisation and simulation. Energy Environ Sci, 2019, 12, 116 doi: 10.1039/C8EE02184H[10] Liu J, Huang S H, He L. Simulation of a high-efficiency silicon-based heterojunction solar cell. J Semicond, 2015, 36, 044010 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/36/4/044010[11] Oppong-Antwi L, Huang S H, Li Q N, et al. Influence of defect states and fixed charges located at the a-Si:H/c-Si interface on the performance of HIT solar cells. Sol Energy, 2017, 141, 222 doi: 10.1016/j.solener.2016.11.049[12] Varache R, Leendertz C, Gueunier-Farret M E, et al. Investigation of selective junctions using a newly developed tunnel current model for solar cell applications. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells, 2015, 141, 14 doi: 10.1016/j.solmat.2015.05.014[13] Kanneboina V. The simulated performance of c-Si/a-Si:H heterojunction solar cells with nc-Si:H, µc-Si:H, a-SiC:H, and a-SiGe:H emitter layers. J Comput Electron, 2021, 20, 344 doi: 10.1007/s10825-020-01626-y[14] Azzemou F, Rached D, Rahal W. Optimisation of emitter properties for silicon heterojunction solar cell ITO/pa-Si:H/ia-Si:H/nc-Si/BSF/Al. Optik, 2020, 217, 164802 doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2020.164802[15] Huang H B, Tian G Y, Zhou L, et al. Simulation and experimental study of a novel bifacial structure of silicon heterojunction solar cell for high efficiency and low cost. Chin Phys B, 2018, 27, 038502 doi: 10.1088/1674-1056/27/3/038502[16] Kim S, Park H, Pham D P, et al. Design of front emitter layer for improving efficiency in silicon heterojunction solar cells via numerical calculations. Optik, 2021, 235, 166580 doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2021.166580[17] Sathya P, Natarajan R. Design and optimization of amorphous based on highly efficient HIT solar cell. Appl Sol Energy, 2018, 54, 77 doi: 10.3103/S0003701X18020123[18] Yao Y, Xu X Y, Zhang X M, et al. Enhanced efficiency in bifacial HIT solar cells by gradient doping with AFORS-HET simulation. Mater Sci Semicond Process, 2018, 77, 16 doi: 10.1016/j.mssp.2018.01.009[19] Honsberg C, Bowden S. Photovoltaics education website. PV Education, 2019 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: