| Citation: |
Jingzhi Fang, Huading Song, Bo Li, Ziqi Zhou, Juehan Yang, Benchuan Lin, Zhimin Liao, Zhongming Wei. Large unsaturated magnetoresistance of 2D magnetic semiconductor Fe-SnS2 homojunction[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2022, 43(9): 092501. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/43/9/092501
****
J Z Fang, H D Song, B Li, Z Q Zhou, J H Yang, B C Lin, Z M Liao, Z M Wei. Large unsaturated magnetoresistance of 2D magnetic semiconductor Fe-SnS2 homojunction[J]. J. Semicond, 2022, 43(9): 092501. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/43/9/092501
|
Large unsaturated magnetoresistance of 2D magnetic semiconductor Fe-SnS2 homojunction
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/43/9/092501
More Information
-
Abstract
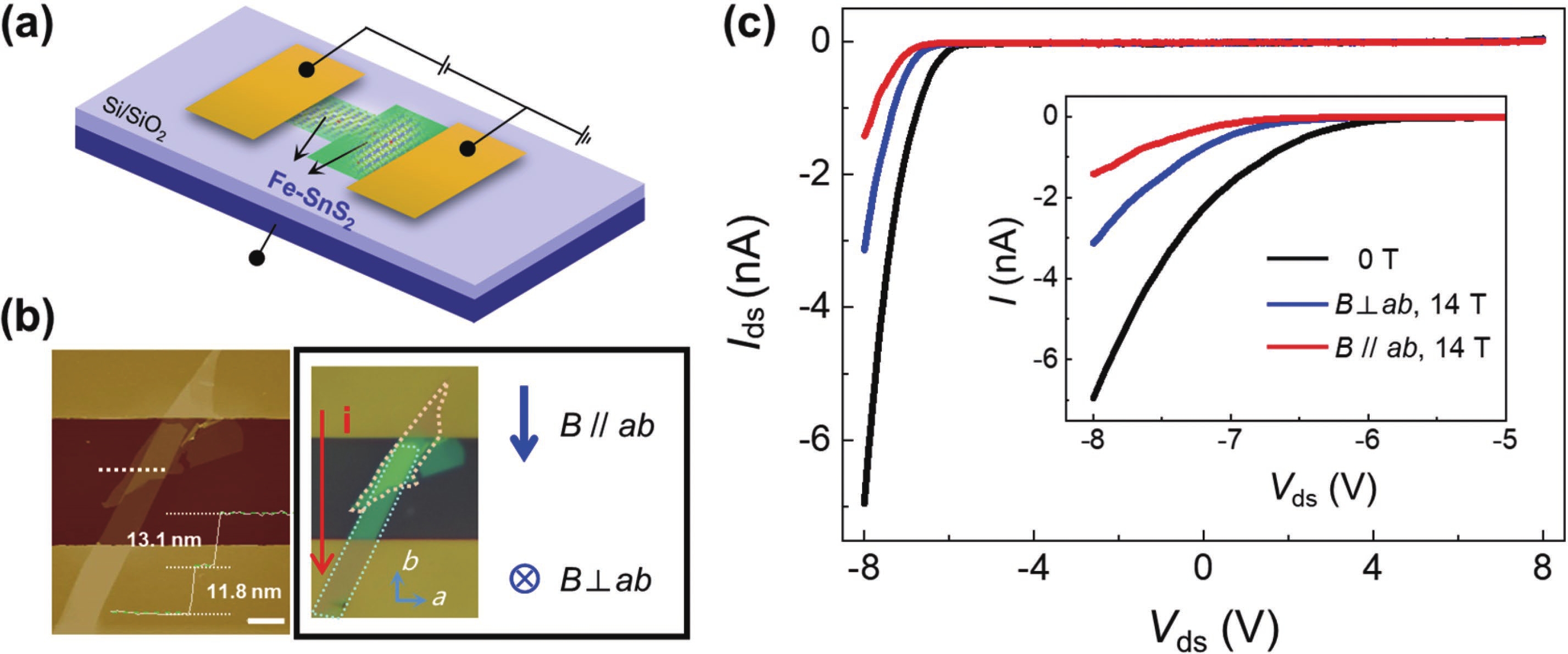
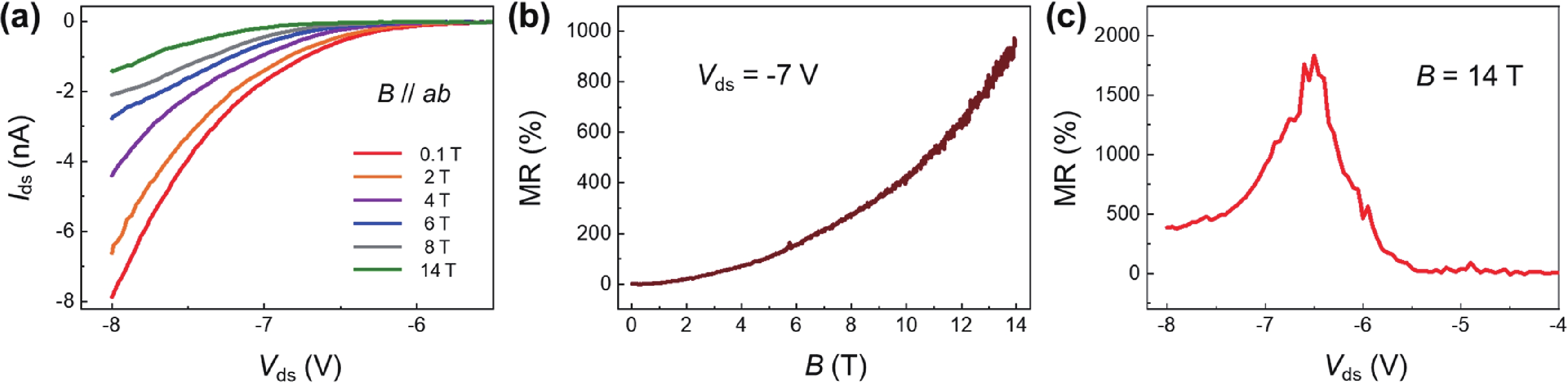
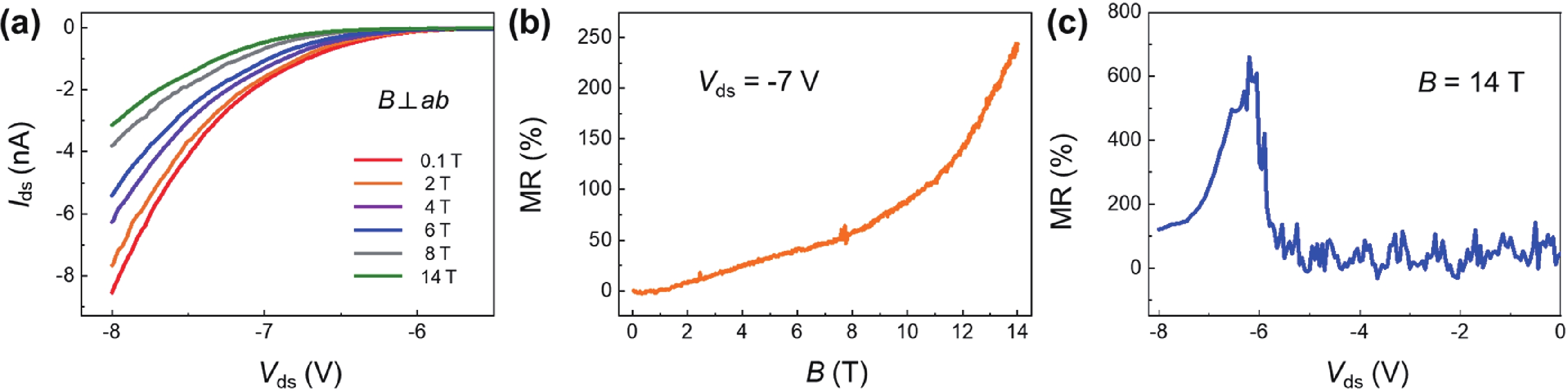
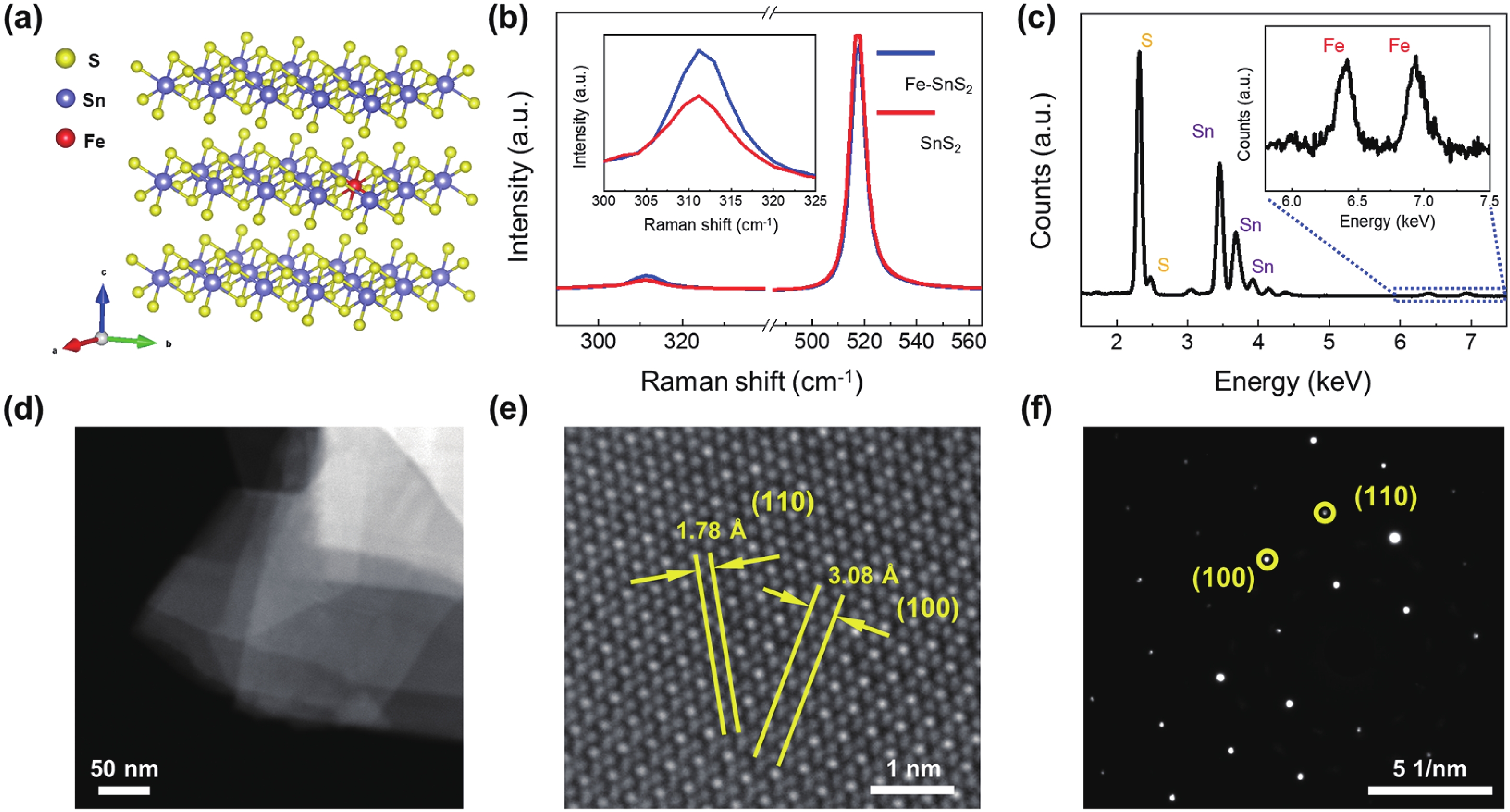
A magnetic semiconductor whose electronic charge and spin can be regulated together will be an important component of future spintronic devices. Here, we construct a two-dimensional (2D) Fe doped SnS2 (Fe-SnS2) homogeneous junction and investigate its electromagnetic transport feature. The Fe-SnS2 homojunction device showed large positive and unsaturated magnetoresistance (MR) of 1800% in the parallel magnetic field and 600% in the vertical magnetic field, indicating an obvious anisotropic MR feature. In contrast, The MR of Fe-SnS2 homojunction is much larger than the pure diamagnetic SnS2 and most 2D materials. The application of a gate voltage can regulate the MR effect of Fe-SnS2 homojunction devices. Moreover, the stability of Fe-SnS2 in air has great application potential. Our Fe-SnS2 homojunction has a significant potential in future magnetic memory applications. -
References
[1] Gong C, Zhang X. Two-dimensional magnetic crystals and emergent heterostructure devices. Science, 2019, 363, 706 doi: 10.1126/science.aav4450[2] Song T, Cai X, Tu M W, et al. Giant tunneling magnetoresistance in spin-filter van der Waals heterostructures. Science, 2018, 360, 1214 doi: 10.1126/science.aar4851[3] Bhatti S, Sbiaa R, Hirohata A, et al. Spintronics based random access memory: a review. Mater Today, 2017, 20, 530 doi: 10.1016/j.mattod.2017.07.007[4] Wang Z, Gutierrez-Lezama I, Ubrig N, et al. Very large tunneling magnetoresistance in layered magnetic semiconductor CrI3. Nat Commun, 2018, 9, 2516 doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04953-8[5] Ikeda S, Hayakawa J, Ashizawa Y, et al. Tunnel magnetoresistance of 604% at 300 K by suppression of Ta diffusion in CoFeB/MgO/CoFeB pseudo-spin-valves annealed at high temperature. Appl Phys Lett, 2008, 93, 082508 doi: 10.1063/1.2976435[6] Ikeda S, Miura K, Yamamoto H, et al. A perpendicular-anisotropy CoFeB-MgO magnetic tunnel junction. Nat Mater, 2010, 9, 721 doi: 10.1038/nmat2804[7] Niu R, Zhu W. Materials and possible mechanisms of extremely large magnetoresistance: a review. J Phys: Condens Matter, 2022, 34, 113001 doi: 10.1088/1361-648X/ac3b24[8] Ali M, Xiong J, Flynn S, et al. Large, non-saturating magnetoresistance in WTe2. Nature, 2014, 514, 205 doi: 10.1038/nature13763[9] Dietl T, Ohno H. Dilute ferromagnetic semiconductors: Physics and spintronic structures. Rev Mod Phys, 2014, 86, 187 doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.86.187[10] Dietl T. A ten-year perspective on dilute magnetic semiconductors and oxides. Nat Mater, 2010, 9, 965 doi: 10.1038/nmat2898[11] Ramasubramaniam A, Naveh D. Mn-doped monolayer MoS2: An atomically thin dilute magnetic semiconductor. Phys Rev B, 2013, 87, 195201 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.87.195201[12] Loh L, Zhang Z, Bosman M, et al. Substitutional doping in 2D transition metal dichalcogenides. Nano Res, 2021, 14, 1668 doi: 10.1007/s12274-020-3013-4[13] Tedstone A A, Lewis D J, O’Brien P. Synthesis, properties, and applications of transition metal-doped layered transition metal dichalcogenides. Chem Mater, 2016, 28, 1965 doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.6b00430[14] Fang J Z, Zhou Z Z, Xiao M Q, et al. Recent advances in low-dimensional semiconductor nanomaterials and their applications in high-performance photodetectors. InfoMat, 2019, 2, 291 doi: 10.1002/inf2.12067[15] Hossain M, Qin B, Li B, et al. Synthesis, characterization, properties and applications of two-dimensional magnetic materials. Nano Today, 2022, 42, 101338 doi: 10.1016/j.nantod.2021.101338[16] Kochat V, Apte A, Hachtel J A, et al. Re Doping in 2D transition metal dichalcogenides as a new route to tailor structural phases and induced magnetism. Adv Mater, 2017, 29, 1703754 doi: 10.1002/adma.201703754[17] Li B, Xing T, Zhong M Z, et al. A two-dimensional Fe-doped SnS2 magnetic semiconductor. Nat Commun, 2017, 8, 1958 doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-02077-z[18] Bouzid H, Sahoo R, Yun S J, et al. Multiple magnetic phases in van der Waals Mn-doped SnS2 semiconductor. Adv Func Mater, 2021, 31, 2102560 doi: 10.1002/adfm.202102560[19] Li B. Huang L, Zhong M Z, et al. Synthesis and transport properties of large-scale alloy Co0.16Mo0.84S2 bilayer nanosheets. ACS Nano, 2015, 9, 1257 doi: 10.1021/nn505048y[20] Zhou J, Lin J, Sims H, et al. Synthesis of Co-doped MoS2 monolayers with enhanced valley splitting. Adv Mater, 2020, 32, 1906536 doi: 10.1002/adma.201906536[21] Coelho P M, Komsa H, Lasek K, et al. Room-temperature ferromagnetism in MoTe2 by post-growth incorporation of vanadium impurities. Adv Elec Mater, 2019, 5, 1900044 doi: 10.1002/aelm.201900044[22] Fu S, Kang K, Shayan K, et al. Enabling room temperature ferromagnetism in monolayer MoS2 via in situ iron-doping. Nat Commun, 2020, 11, 2034 doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-15877-7[23] Pham Y T H, Liu M, Jimenez V O, et al. Tunable ferromagnetism and thermally induced spin flip in vanadium-doped tungsten diselenide monolayers at room temperature. Adv Mater, 2020, 32, 2003607 doi: 10.1002/adma.202003607[24] Yang L, Wu H, Zhang W, et al. Ta doping enhanced room-temperature ferromagnetism in 2D semiconducting MoTe2 nanosheets. Adv Electrin Mater, 2019, 5, 1900552 doi: 10.1002/aelm.201900552[25] Yun S J, Duong D L, Ha D M, et al. Ferromagnetic order at room temperature in monolayer WSe2 semiconductor via vanadium dopant. Adv Sci, 2020, 7, 1903076 doi: 10.1002/advs.201903076[26] Zhang F, Zheng B, Sebastian A, et al. Monolayer vanadium-doped tungsten disulfide: A room-temperature dilute magnetic semiconductor. Adv Sci, 2020, 7, 2001174 doi: 10.1002/advs.202001174[27] Huang B, Clark G, Klein D, et al. Electrical control of 2D magnetism in bilayer CrI3. Nat Nanotech, 2018, 13, 544 doi: 10.1038/s41565-018-0121-3[28] Jiang S, Li L, Wang Z, et al. Controlling magnetism in 2D CrI3 by electrostatic doping. Nat Nanotech, 2018, 13, 549 doi: 10.1038/s41565-018-0135-x[29] Jiang S, Shan J, Mak K F. Electric-field switching of two-dimensional van der Waals magnets. Nat Mater, 2018, 17, 406 doi: 10.1038/s41563-018-0040-6[30] Huang B, Clark G, Navarro-Moratalla E, et al. Layer-dependent ferromagnetism in a van der Waals crystal down to the monolayer limit. Nature, 2017, 546, 270 doi: 10.1038/nature22391[31] Lee J U, Lee S, Ryoo J H, et al. Ising-type magnetic ordering in atomically thin FePS3. Nano Lett, 2016, 16, 7433 doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.6b03052[32] Gong C, Li L, Li Z, et al. Discovery of intrinsic ferromagnetism in two-dimensional van der Waals crystals. Nature, 2017, 546, 265 doi: 10.1038/nature22060[33] Xing W, Chen Y, Odenthal P M, et al. Electric field effect in multilayer Cr2Ge2Te6: a ferromagnetic 2D material. 2D Mater, 2017, 4, 2053 doi: 10.1088/2053-1583/aa7034[34] Wang Z, Zhang T, Ding M, et al. Electric-field control of magnetism in a few-layered van der Waals ferromagnetic semiconductor. Nat Nanotech, 2018, 13, 554 doi: 10.1038/s41565-018-0186-z[35] Mogi M, Tsukazaki A, Kaneko Y, et al. Ferromagnetic insulator Cr2Ge2Te6 thin films with perpendicular remanence. APL Mater, 2018, 6, 091104 doi: 10.1063/1.5046166[36] Deng Y J, Yu Y J, Song Y C, et al. Gate-tunable room-temperature ferromagnetism in two-dimensional Fe3GeTe2. Nature, 2018, 563, 94 doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0626-9[37] Fei Z, Huang B, Malinowski P, et al. Two-dimensional itinerant ferromagnetism in atomically thin Fe3GeTe2. Nat Mater, 2018, 17, 778 doi: 10.1038/s41563-018-0149-7[38] Bonilla M, Kolekar S, Ma Y, et al. Strong room-temperature ferromagnetism in VSe2 monolayers on van der Waals substrates. Nat Nanotech, 2018, 13, 289 doi: 10.1038/s41565-018-0063-9[39] Li X, Lu J T, Zhang J, et al. Spin-dependent transport in van der Waals magnetic tunnel junctions with Fe3GeTe2 electrodes. Nano Lett, 2019, 19, 5133 doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.9b01506[40] Miao G, Müller M, Moodera J S, et al. Magnetoresistance in double spin filter tunnel junctions with nonmagnetic electrodes and its unconventional bias dependence. Phys Rev Lett, 2009, 102, 076601 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.102.076601[41] Song H D, Zhu P F, Fang J Z, et al. Anomalous Hall effect in graphene coupled to a layered magnetic semiconductor. Phys Rev B, 2021, 103, 125304 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.103.125304[42] Chen Y, Dumcenco D, Zhu Y, et al. Composition-dependent Raman modes of Mo1–xWxS2 monolayer alloys. Nanoscale, 2014, 6, 2833 doi: 10.1039/C3NR05630A -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: