| Citation: |
Hongyang Zhang, Xinlin Geng, Zonglin Ye, Kailei Wang, Qian Xie, Zheng Wang. A frequency servo SoC with output power stabilization loop technology for miniaturized atomic clocks[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2024, 45(6): 062202. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/23120056
****
H Y Zhang, X L Geng, Z L Ye, K L Wang, Q Xie, and Z Wang, A frequency servo SoC with output power stabilization loop technology for miniaturized atomic clocks[J]. J. Semicond., 2024, 45(6), 062202 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/23120056
|
A frequency servo SoC with output power stabilization loop technology for miniaturized atomic clocks
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/23120056
More Information
-
Abstract
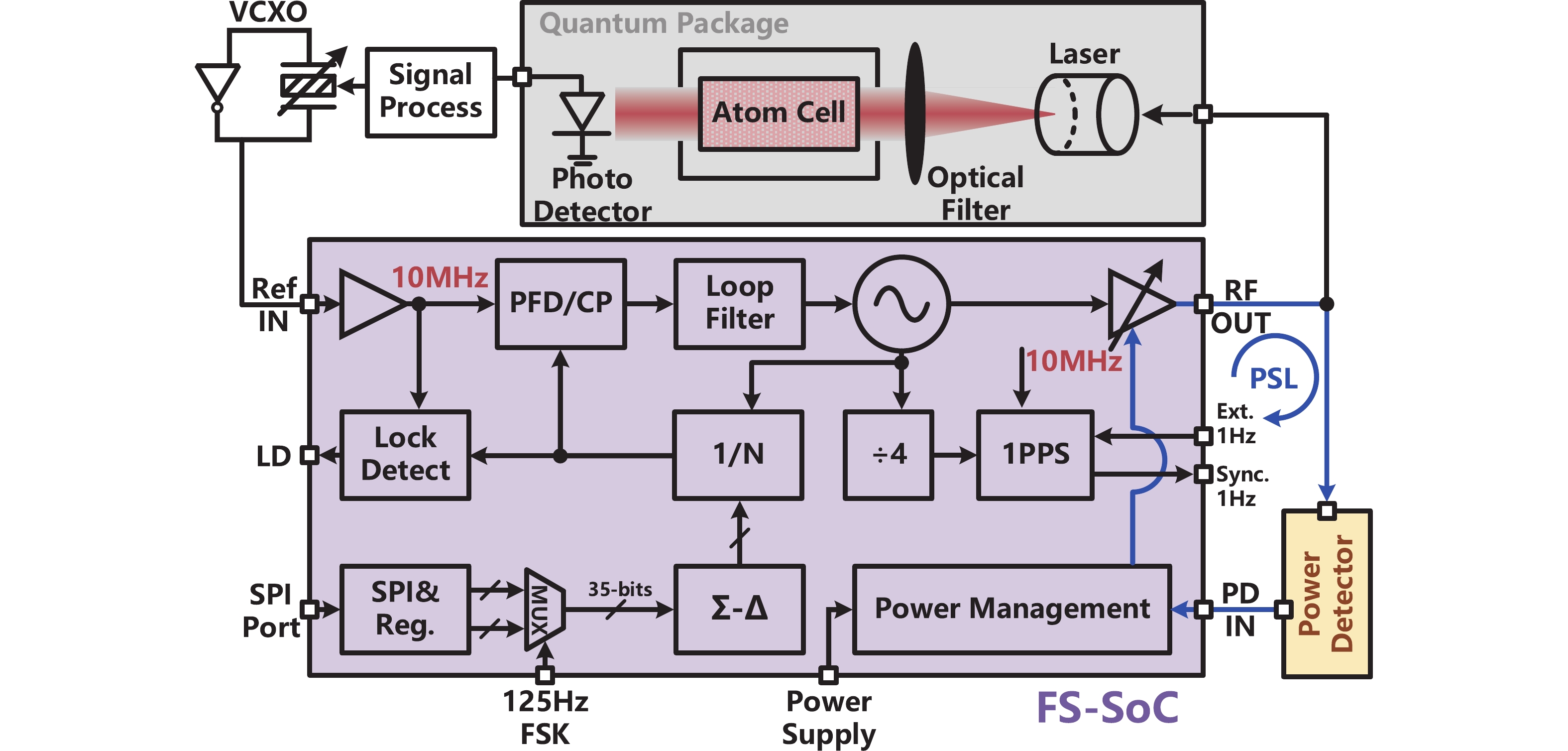
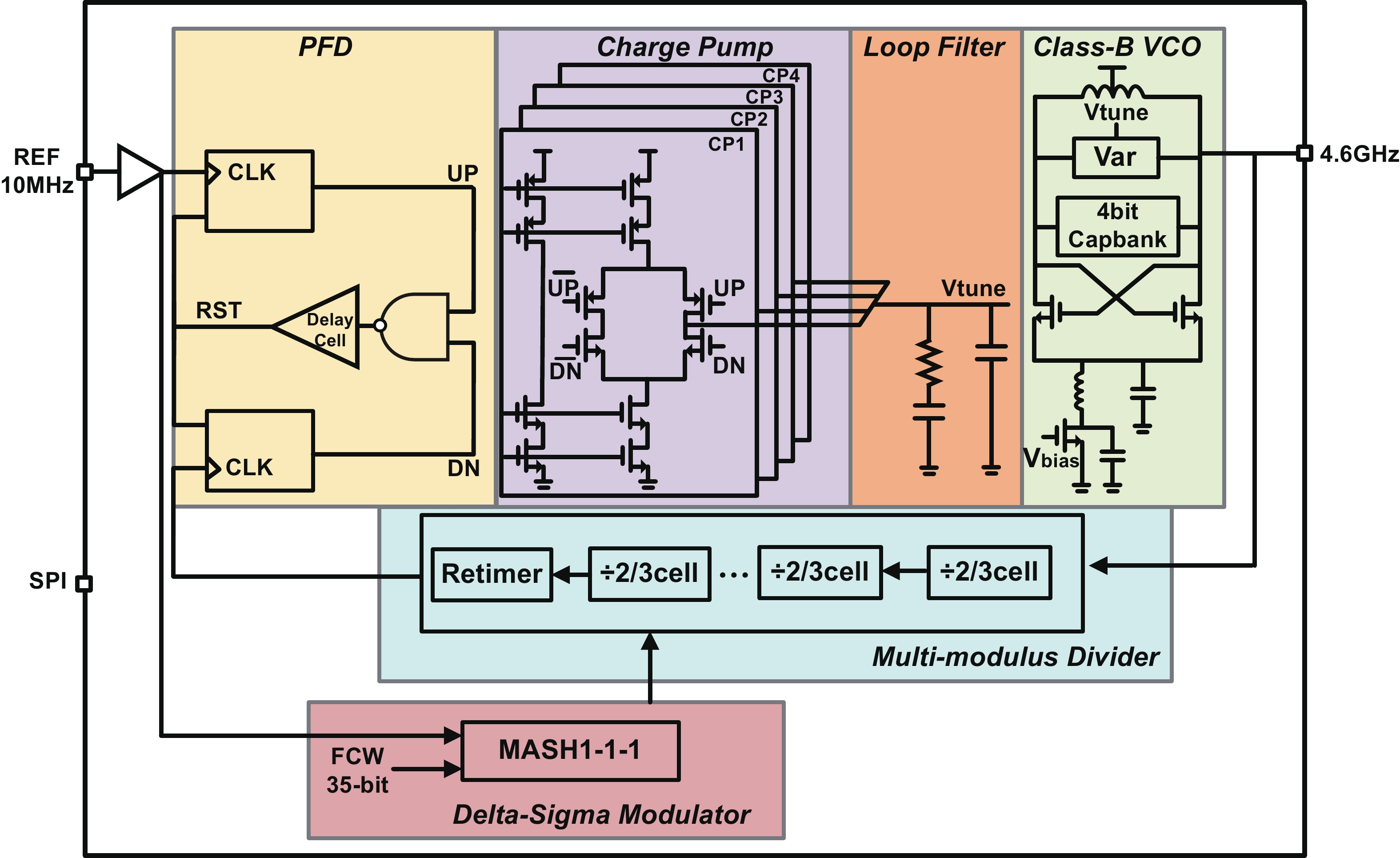
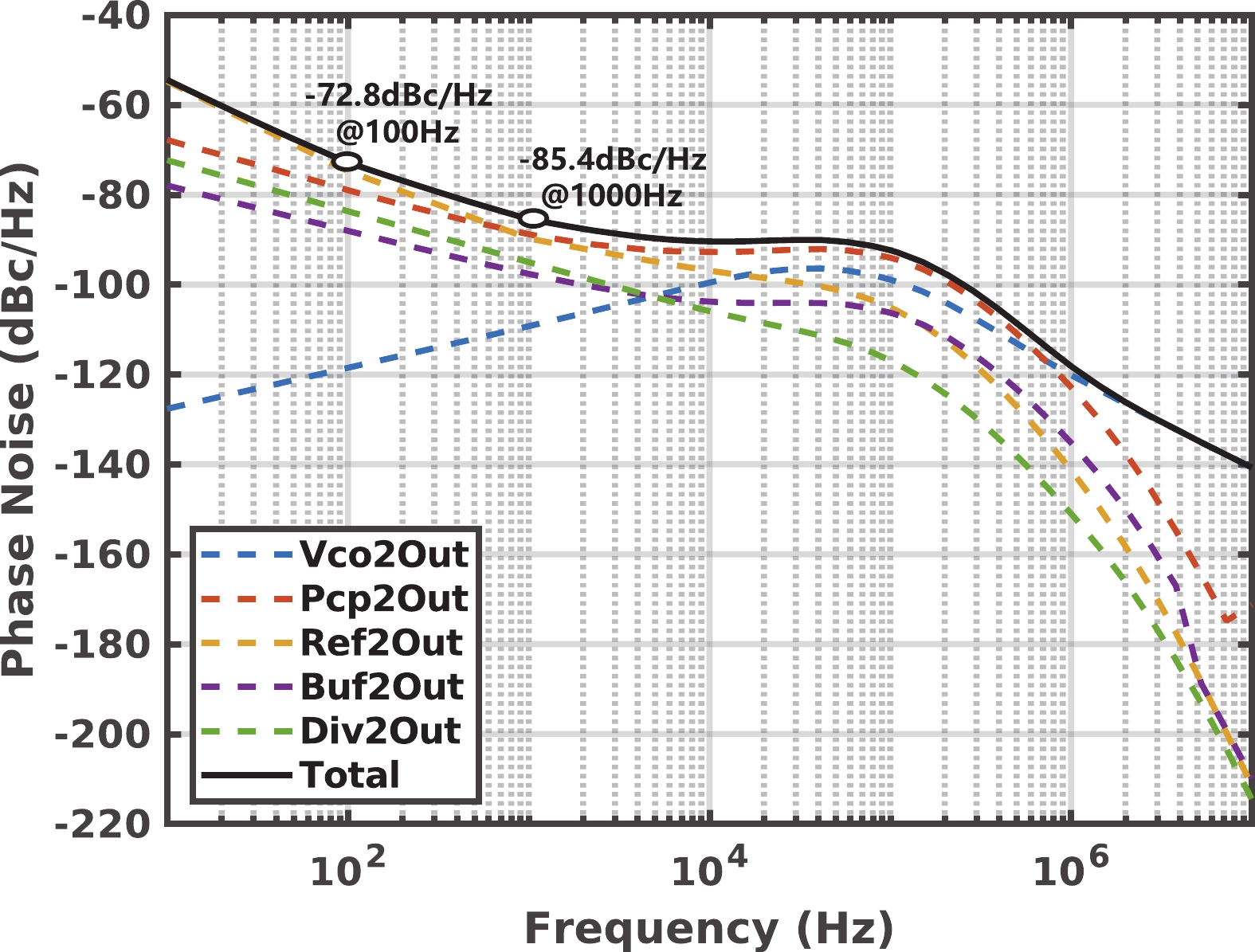
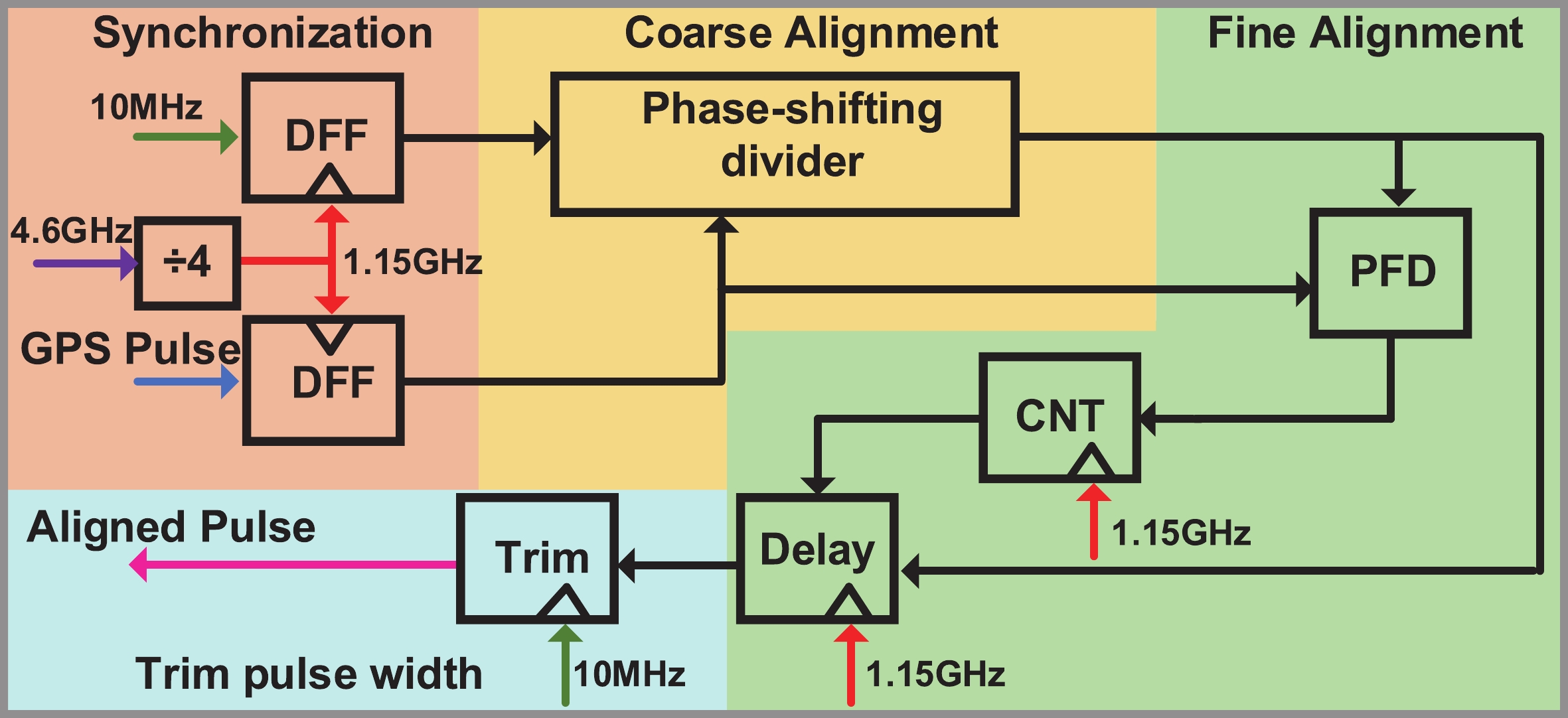
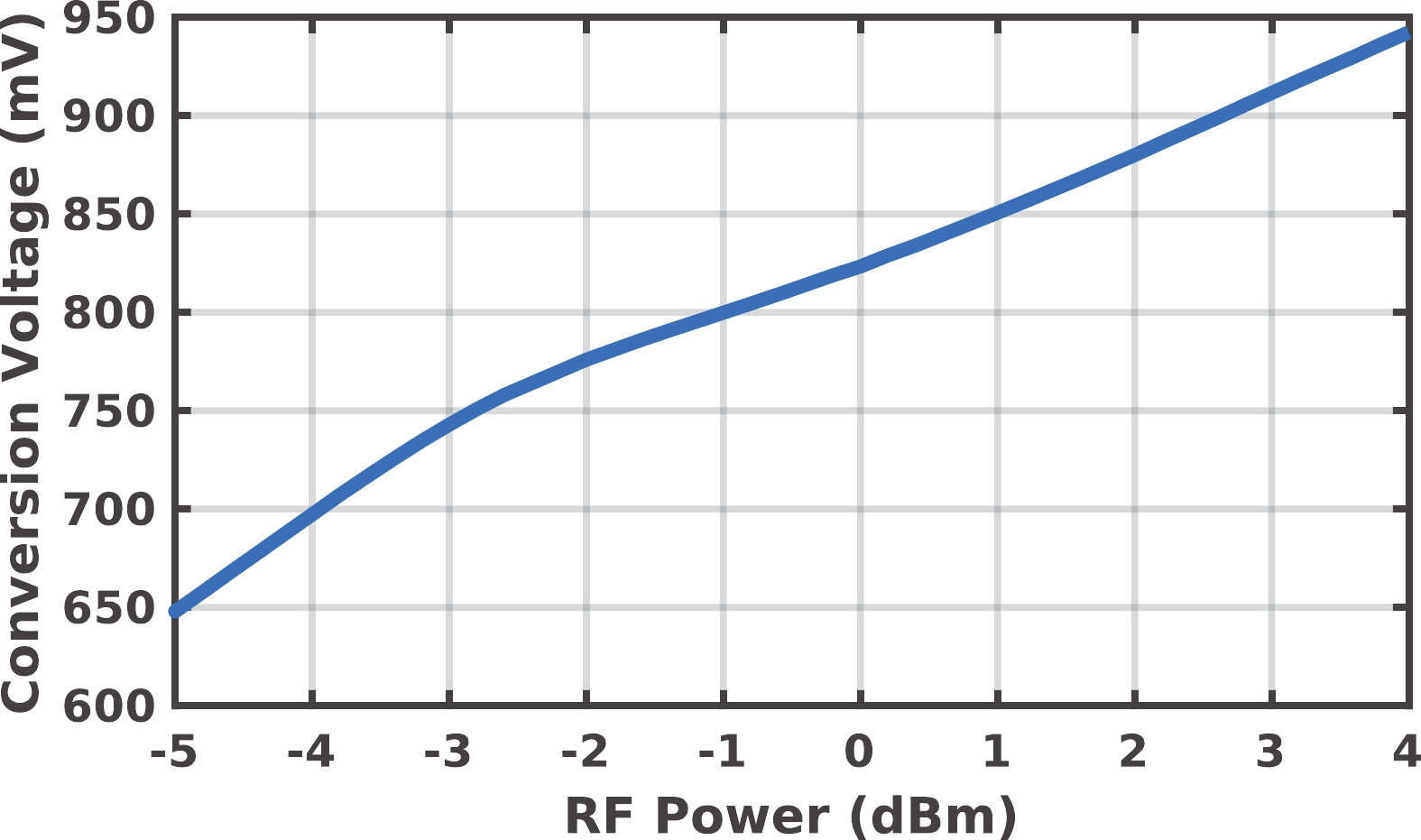
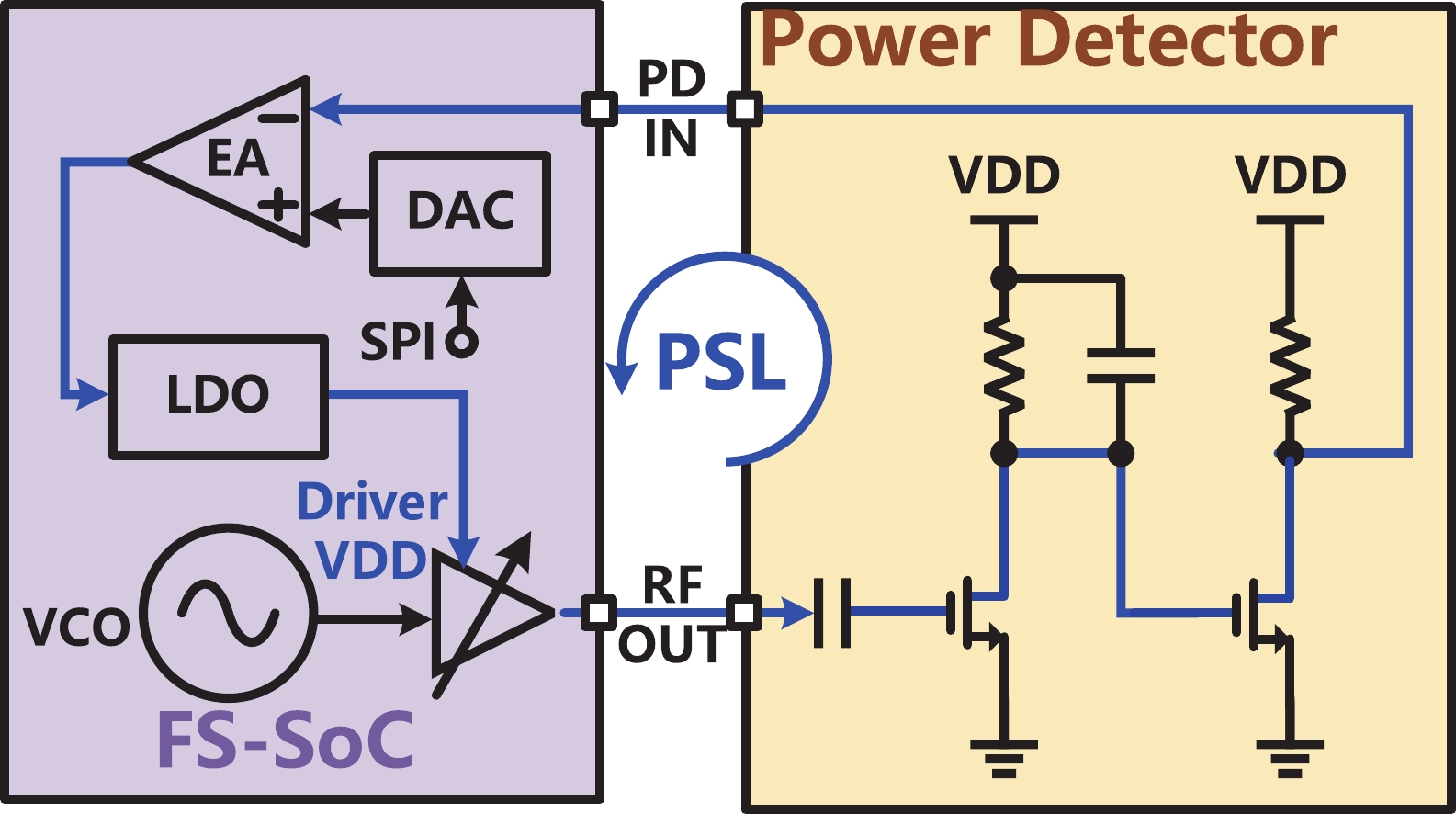
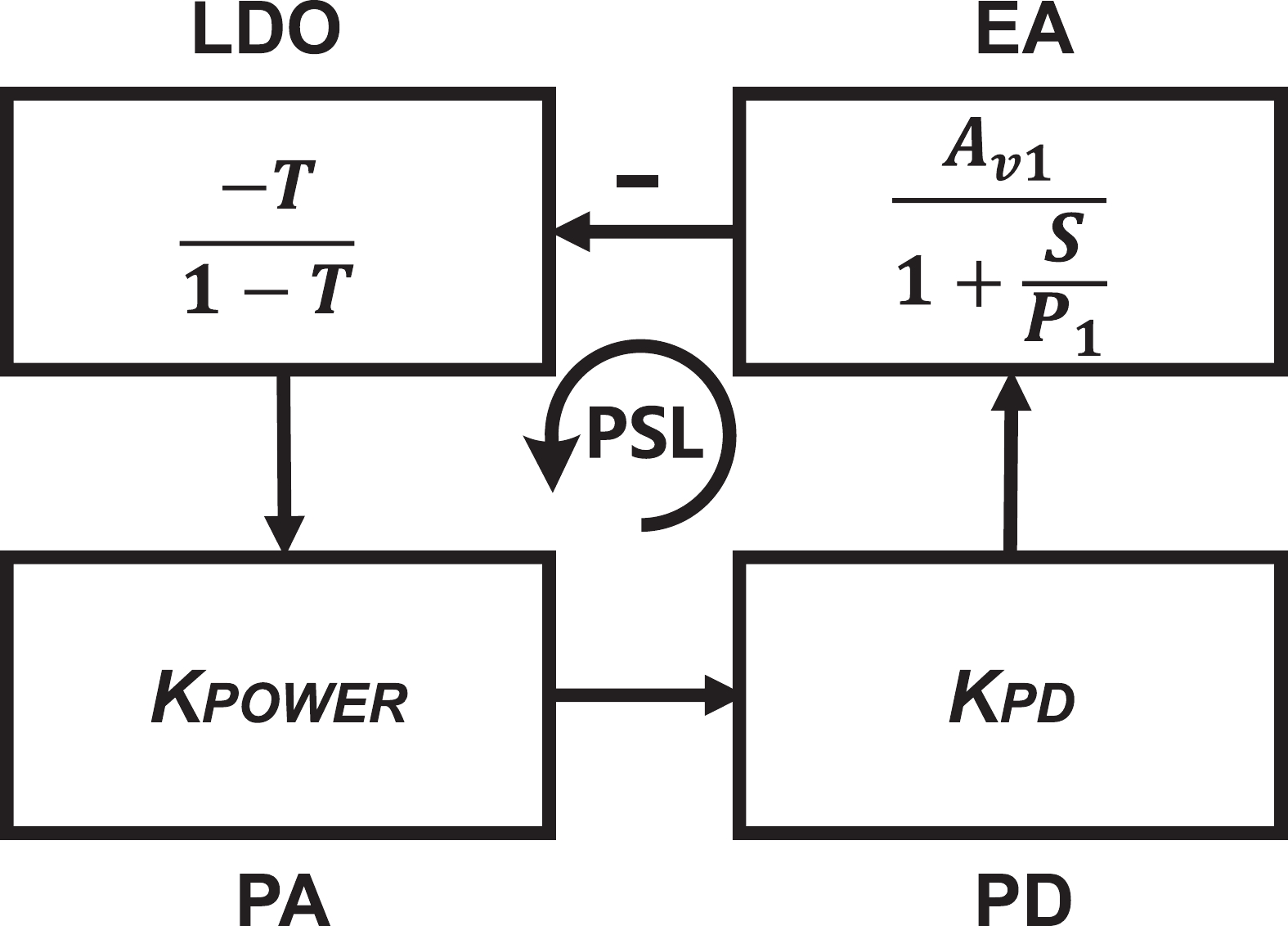
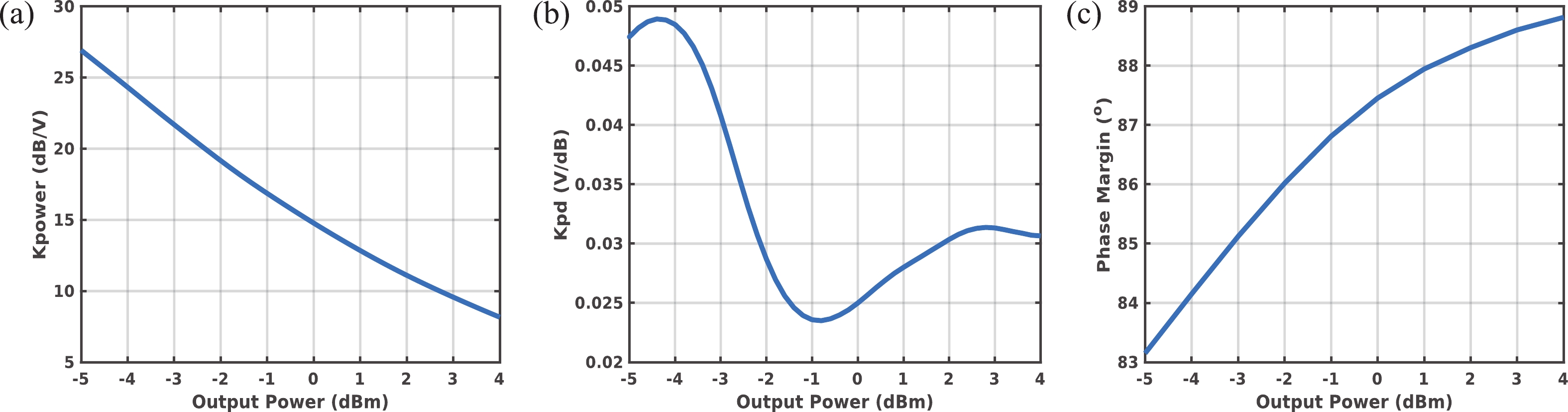
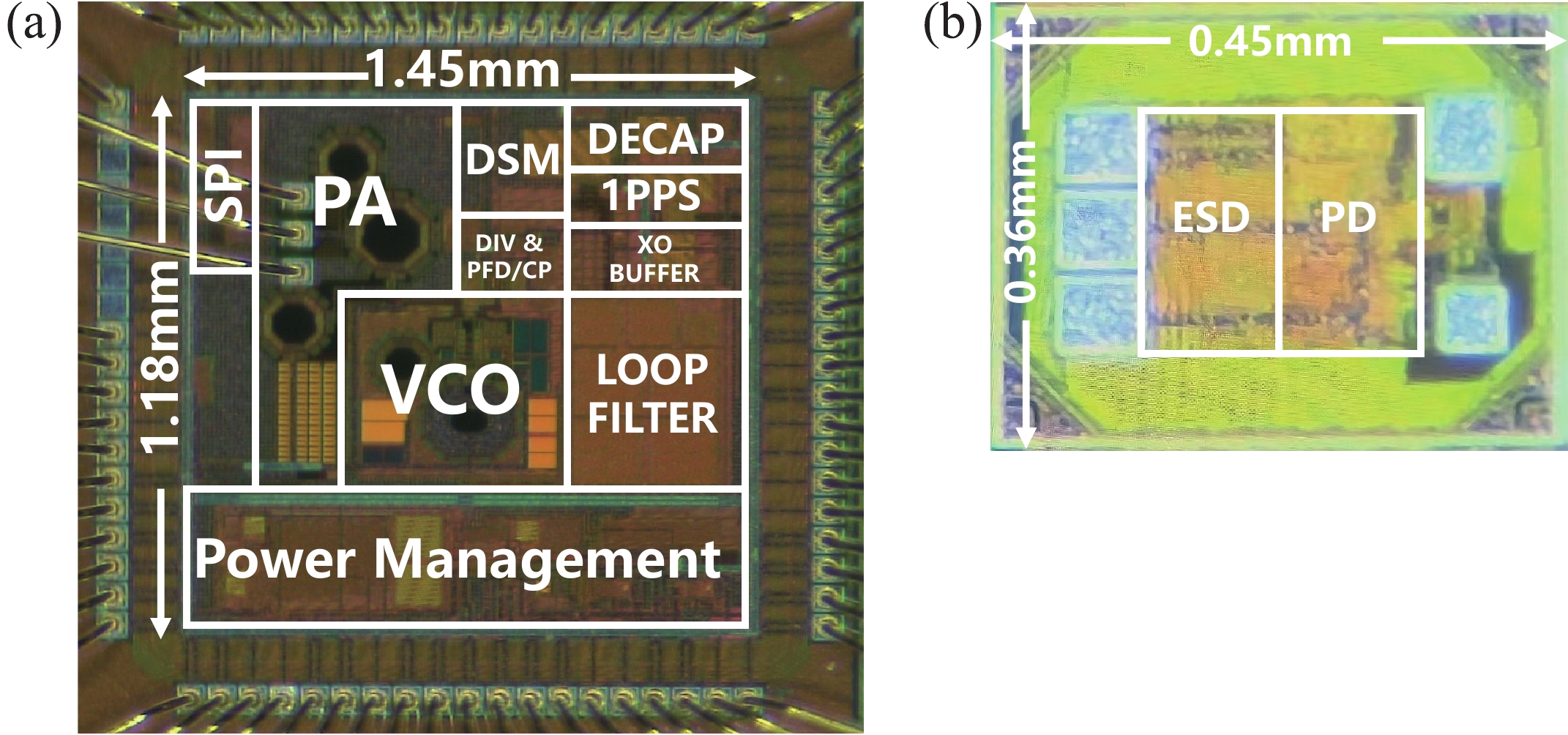
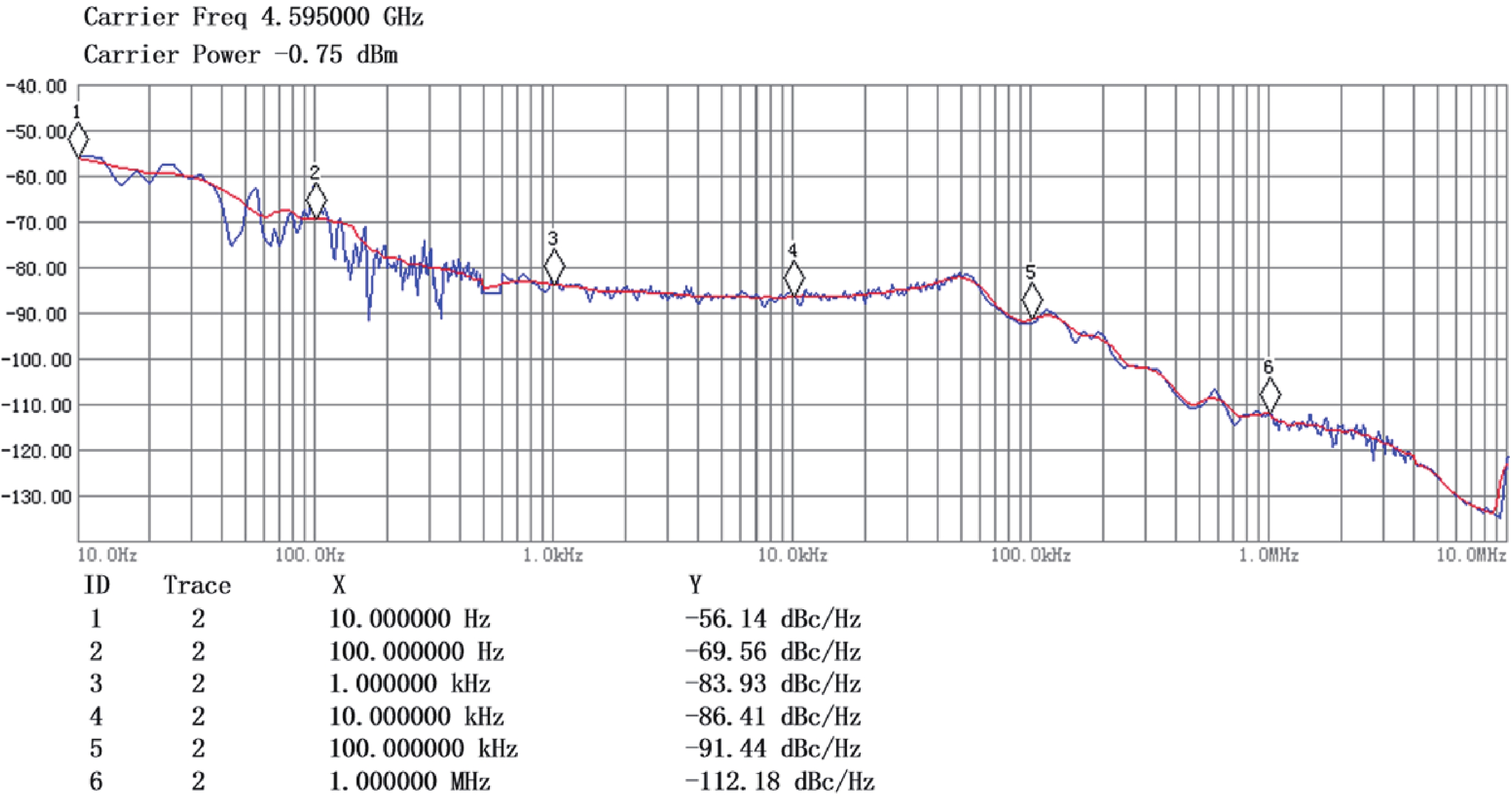
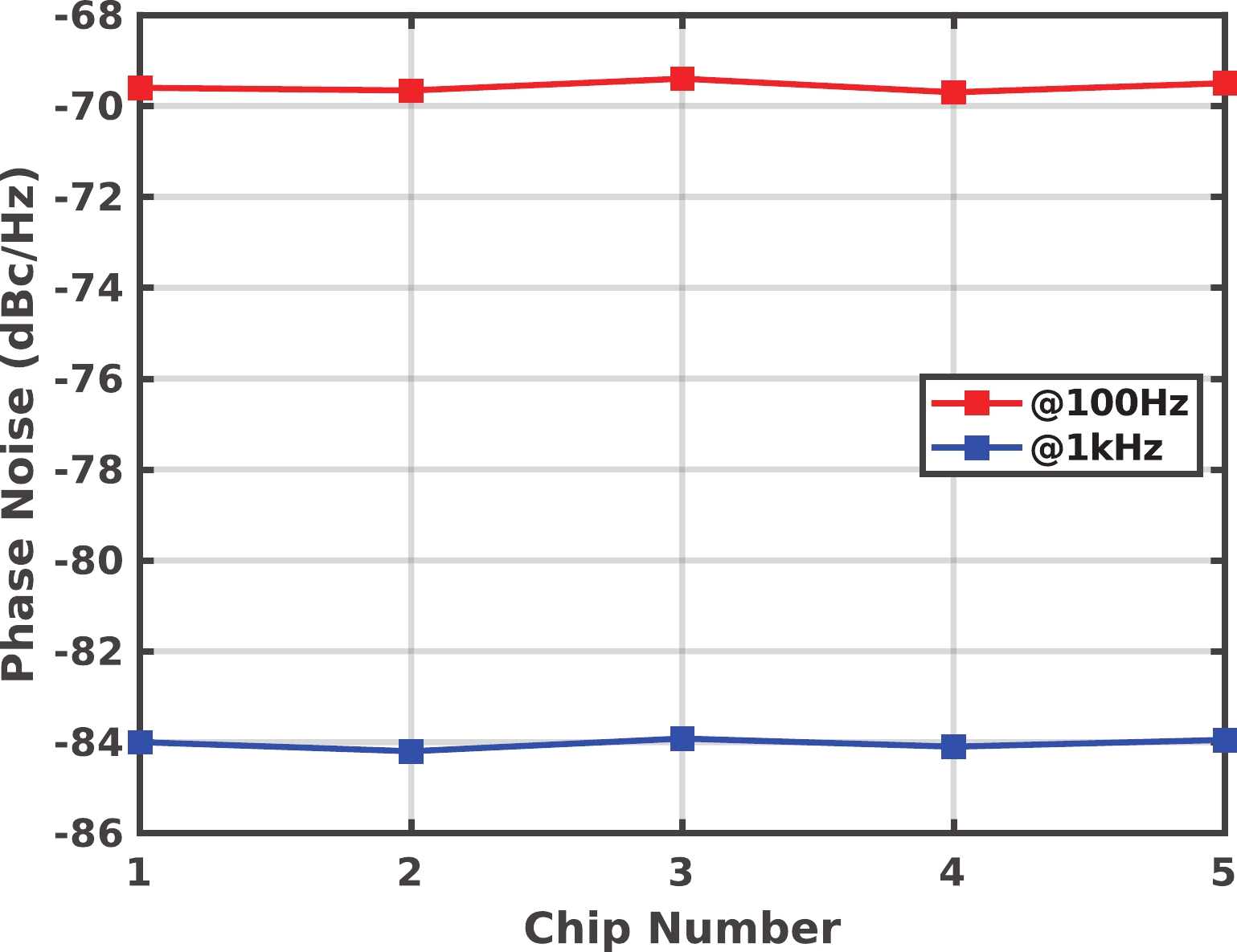
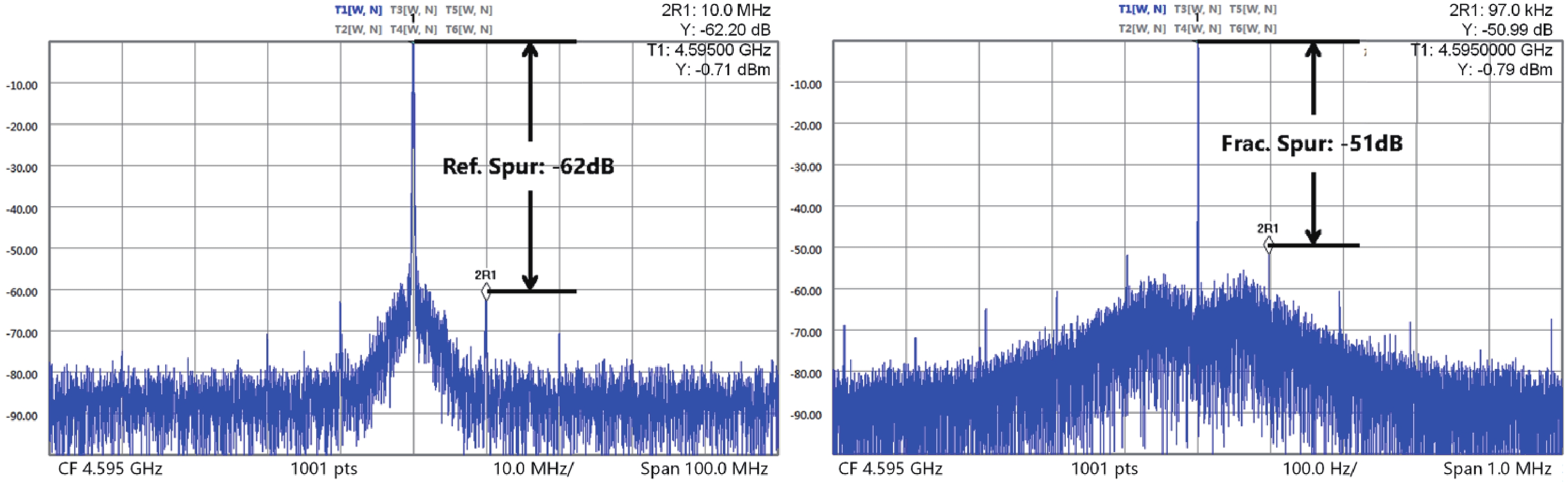
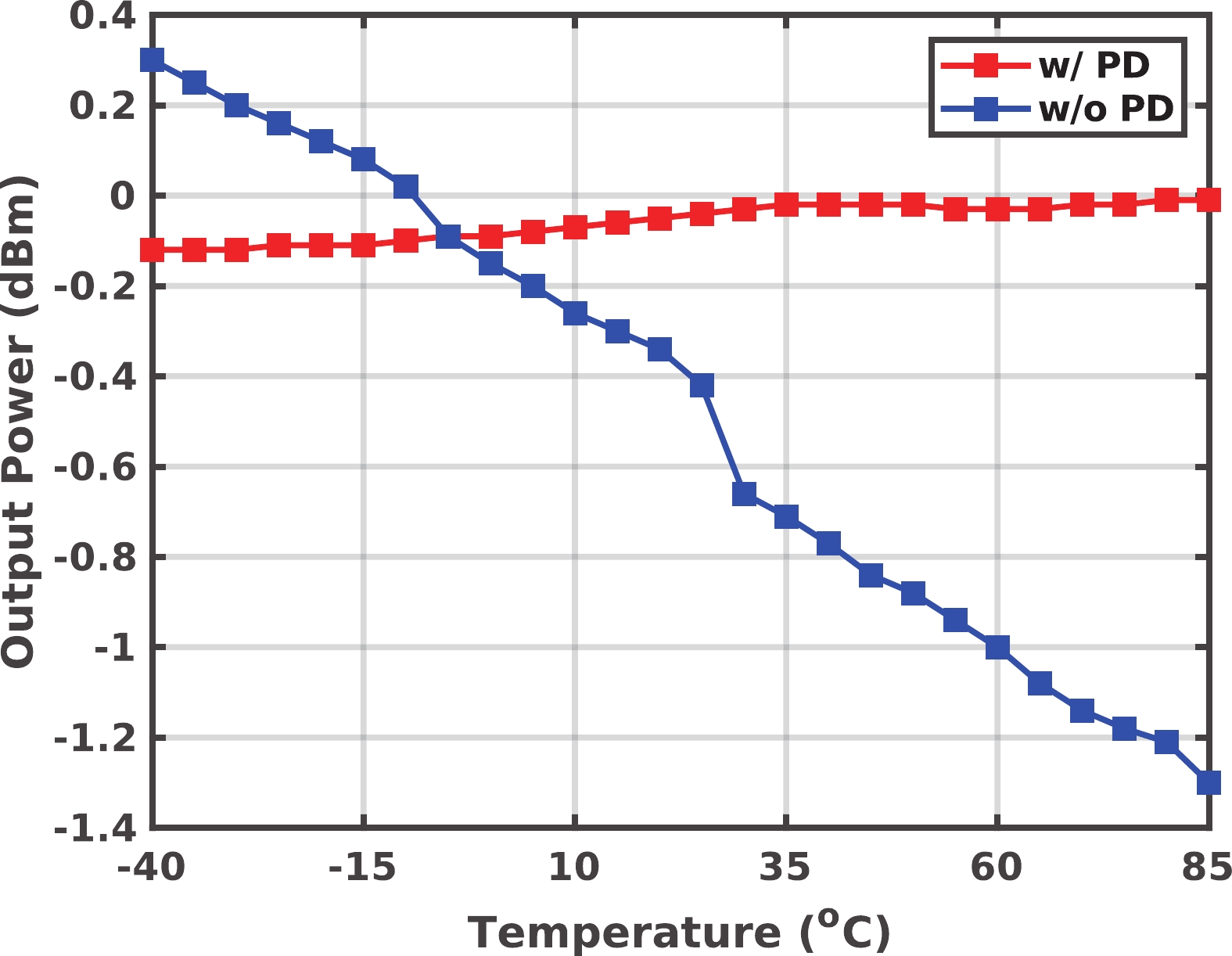
A frequency servo system-on-chip (FS-SoC) featuring output power stabilization technology is introduced in this study for high-precision and miniaturized cesium (Cs) atomic clocks. The proposed power stabilization loop (PSL) technique, incorporating an off-chip power detector (PD), ensures that the output power of the FS-SoC remains stable, mitigating the impact of power fluctuations on the atomic clock's stability. Additionally, a one-pulse-per-second (1PPS) is employed to synchronize the clock with GPS. Fabricated using 65 nm CMOS technology, the measured phase noise of the FS-SoC stands at −69.5 dBc/Hz@100 Hz offset and −83.9 dBc/Hz@1 kHz offset, accompanied by a power dissipation of 19.7 mW. The Cs atomic clock employing the proposed FS-SoC and PSL obtains an Allan deviation of 1.7 × 10−11 with 1-s averaging time. -
References
[1] Allan D, Ashby N, Hodge C C . The science of timekeeping. Palo Alto, CA, USA: Hewlett-Packard, 1997. http://www.leapsecond.com/hpan/an1289.pdf[2] Reid T G R, Neish A M, Walter TF, et al. Leveraging commercial broadband LEO constellations for navigation. The 29th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS), 2016, 2300 doi: 10.33012/2016.14729[3] Alvarez J, Walls B. Constellations, clusters, and communication technology: Expanding small satellite access to space. 2016 IEEE Aerospace Conference. Big Sky, MT, USA. IEEE, 2016, 1 doi: 10.1109/AERO.2016.7500896[4] Saroufim J, Hayek S W, Kassas Z M. Simultaneous LEO satellite tracking and differential LEO-aided IMU navigation. 2023 IEEE/ ION Position, Location and Navigation Symposium (PLANS). Monterey, CA, USA. IEEE, 2023, 179 doi: 10.1109/PLANS53410.2023.10140087[5] Lutwak R, Emmons D, English T, et al. The chip-scale atomic clock - recent development progress. 2004 doi: 10.1109/FREQ.2009.5168247[6] Lutwak R. The SA. 45s chip-scale atomic clock–early production statistics. Annual Precise Time and Time Interval (PTTI) Systems and Applications Meeting, 2011, 207[7] Cash P, Kosvin I, Park H, et al. Low phase noise low power atomic clocks. 2022 Joint Conference of the European Frequency and Time Forum and IEEE International Frequency Control Symposium (EFTF/IFCS). Paris, France. IEEE, 2022, 1 doi: 10.1109/EFTF/IFCS54560.2022.9850528[8] Cash P, Krzewick W, Machado P, et al. Microsemi Chip Scale Atomic Clock (CSAC) technical status, applications, and future plans. 2018 European Frequency and Time Forum (EFTF). Turin, Italy. IEEE, 2018, 65 doi: 10.1109/EFTF.2018.8408999[9] Kitching J, Hollberg L, Knappe S, et al. Compact atomic clock based on coherent population trapping. Electron Lett, 2001, 37, 1449 doi: 10.1049/el:20010959[10] Microchip Technology. SA. 45s CSAC and RoHS CSAC options 001and 003 chip-scale atomic clock. DS00002985A Datasheet, Microchip Technology, Chandler, AZ, USA, 2019[11] Park J, Hong H G, Kwon T Y, et al. Flexible hybrid approach for a 3D integrated physics package of chip-scale atomic clocks. IEEE Sens J, 2021, 21, 6839 doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.3042703[12] Vanier J. Atomic clocks based on coherent population trapping: A review. Appl Phys B, 2005, 81, 421 doi: 10.1007/s00340-005-1905-3[13] Zhang H S, Okada K, Herdian H, et al. ULPAC: A miniaturized ultralow-power atomic clock. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2019, 54, 3135 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2019.2941004[14] Zhao Y Z, Tanner S, Farine P A, et al. A 15 mW, 4.6 GHz frequency synthesizer ASIC with −85 dBc/Hz at 2 kHz for miniature atomic clocks. 2013 Joint European Frequency and Time Forum & International Frequency Control Symposium (EFTF/IFC). Prague, Czech Republic. IEEE, 2013, 715 doi: 10.1109/EFTF-IFC.2013.6702186[15] Calosso C E, Gozzelino M, Godone A, et al. Intensity detection noise in pulsed vapor-cell frequency standards. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Contr, 2020, 67, 1074 doi: 10.1109/TUFFC.2019.2957418[16] Danet J M, Lours M, Guérandel S, et al. Dick effect in a pulsed atomic clock using coherent population trapping. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Contr, 2014, 61, 567 doi: 10.1109/TUFFC.2014.2945[17] Pollock J W, Yudin V I, Shuker M, et al. Ac Stark shifts of dark resonances probed with Ramsey spectroscopy. Phys Rev A, 2018, 98, 053424 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.98.053424[18] Kozlova O, Danet J M, Guérandel S, et al. Limitations of long-term stability in a coherent population trapping Cs clock. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas, 2014, 63, 1863 doi: 10.1109/TIM.2014.2298672[19] Gasparini L, Zadedyurina O, Fontana G, et al. A digital circuit for jitter reduction of GPS-disciplined 1-pps synchronization signals. 2007 IEEE International Workshop on Advanced Methods for Uncertainty Estimation in Measurement. Sardinia, Italy. IEEE, 2007, 84 doi: 10.1109/AMUEM.2007.4362576[20] Rabus D, Goavec-Merou G, Cabodevila G, et al. Generating A timing information (1-PPS) from a software defined radio decoding of GPS signals. 2021 Joint Conference of the European Frequency and Time Forum and IEEE International Frequency Control Symposium (EFTF/IFCS). Gainesville, FL, USA. IEEE, 2021, 1 doi: 10.1109/EFTF/IFCS52194.2021.9604249[21] Zhao J Y, Guo P, Dan L, et al. Advances of chip-scale atomic clock in Peking university in 2020. 2021 Joint Conference of the European Frequency and Time Forum and IEEE International Frequency Control Symposium (EFTF/IFCS). Gainesville, FL, USA. IEEE, 2021, 1 doi: 10.1109/EFTF/IFCS52194.2021.9604289[22] Vyskocil P, Sebesta J. Relative timing characteristics of GPS timing modules for time synchronization application. 2009 International Workshop on Satellite and Space Communications. Siena, Italy. IEEE, 2009, 230 doi: 10.1109/IWSSC.2009.5286378[23] Arceo-Miquel L, Shmaliy Y S, Ibarra-Manzano O. Optimal synchronization of local clocks by GPS 1PPS signals using predictive FIR filters. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas, 2009, 58, 1833 doi: 10.1109/TIM.2009.2013654[24] Wynands R, Nagel A. Precision spectroscopy with coherent dark states. Appl Phys B, 1999, 68, 1 doi: 10.1007/s003400050581[25] Geng X L, Tian Y B, Xiao Y, et al. A 25.8GHz integer-N PLL with time-amplifying phase-frequency detector achieving 60fsrms jitter, -252.8dB FoMJ, and robust lock acquisition performance. 2022 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC). San Francisco, CA, USA. IEEE, 2022, 388 doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2023.3269572[26] Yu Y F, Yue J L, Xiao S M, et al. A low-power CMOS frequency synthesizer for GPS receivers. J Semicond, 2010, 31, 065012 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/31/6/065012[27] Chu X J, Lin M, Shi Y, et al. A fully integrated frequency synthesizer for a dual-mode GPS and Compass receiver. J Semicond, 2012, 33, 035004 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/33/3/035004[28] Geng Z Q, Yan X Z, Lou W F, et al. A low power fast-settling frequency-presetting PLL frequency synthesizer. J Semicond, 2010, 31, 085002 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/31/8/085002[29] Chen P F, Li Z Q, Wang X S, et al. A 6–9 GHz 5-band CMOS synthesizer for MB-OFDM UWB. J Semicond, 2010, 31, 075001 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/31/7/075001[30] Zheng Y Z, Xia L L, Li W N, et al. A fast-hopping 3-band CMOS frequency synthesizer for MB-OFDM UWB system. J Semicond, 2009, 30, 095006 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/30/9/095006[31] Zhang H S, Herdian H, Narayanan A T, et al. A −194 dBc/hz FoM VCO with low-supply sensitivity for ultra-low-power atomic clock. 2018 Asia-Pacific Microwave Conference (APMC). Kyoto, Japan. IEEE, 2018, 788 doi: 10.23919/APMC.2018.8617628[32] Geng X L, Ye Z L, Xiao Y, et al. A 26GHz fractional-N charge-pump PLL based on A dual-DTC-assisted time-amplifying-phase-frequency detector achieving 37.1fs and 45.6fs rms jitter for integer-N and fractional-N channels. 2023 IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference (CICC). San Antonio, TX, USA. IEEE, 2023, 1 doi: 10.1109/CICC57935.2023.10121261[33] Zhou C Y, Li G L, Zhang C, et al. A fractional-Nfrequency synthesizer for WCDMA/Bluetooth/ZigBee applications. J Semicond, 2009, 30, 075008 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/30/7/075008[34] Al-Shyoukh M, Lee H, Perez R. A transient-enhanced low-quiescent current low-dropout regulator with buffer impedance attenuation. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2007, 42, 1732 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2007.900281[35] Bouvier A, Calosso C, Yun P, et al. Studies on the mid-term effects of the double-modulation cpt clock. International Conference on Space Optics (ICSO), 2021, 1185, 247 -
Proportional views




 Hongyang Zhang was born in Dandong, Liaoning, China, in 1999. He received the B.E. degrees in microelectronic science and technology from the University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu, China, in 2022, where he is currently pursuing the M.S. degree in integrated circuit science and engineering. His current research interests include frequency synthesizer techniques and power management design.
Hongyang Zhang was born in Dandong, Liaoning, China, in 1999. He received the B.E. degrees in microelectronic science and technology from the University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu, China, in 2022, where he is currently pursuing the M.S. degree in integrated circuit science and engineering. His current research interests include frequency synthesizer techniques and power management design. Xinlin Geng was born in Chengdu, Sichuan, China, in April 1996. He received the B.E. degree in microelectronic science and technology from the University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu, in 2018, where he is currently pursuing the Ph.D. degree. His research interests include the design of RF, millimeter-wave integrated circuits and systems, and especially for high-performance frequency synthesizers.
Xinlin Geng was born in Chengdu, Sichuan, China, in April 1996. He received the B.E. degree in microelectronic science and technology from the University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu, in 2018, where he is currently pursuing the Ph.D. degree. His research interests include the design of RF, millimeter-wave integrated circuits and systems, and especially for high-performance frequency synthesizers. Zonglin Ye was born in Suzhou, Jiangsu, China, in 2000. He received the B.E. degree in microelectronics from the University of Electronic Science and Technology of China (UESTC), Chengdu, China, in 2022, where he is currently pursuing the Ph.D. degree. His research interests include fractional-N, frequency synthesizer and high-performance oscillator.
Zonglin Ye was born in Suzhou, Jiangsu, China, in 2000. He received the B.E. degree in microelectronics from the University of Electronic Science and Technology of China (UESTC), Chengdu, China, in 2022, where he is currently pursuing the Ph.D. degree. His research interests include fractional-N, frequency synthesizer and high-performance oscillator. Kailei Wang was born in Zhoukou, China. He received the B.Eng. degree in microelectronics science and engineering from the University of Electronic Science and Technology of China (UESTC), Chengdu, China, in 2022, where he is currently pursuing the Master degree in electronic science and technology with the Smart Integrated Circuits and System Laboratory (SICS). His research interests include RF circuit techniques and computer-aided design of integrated circuits and system.
Kailei Wang was born in Zhoukou, China. He received the B.Eng. degree in microelectronics science and engineering from the University of Electronic Science and Technology of China (UESTC), Chengdu, China, in 2022, where he is currently pursuing the Master degree in electronic science and technology with the Smart Integrated Circuits and System Laboratory (SICS). His research interests include RF circuit techniques and computer-aided design of integrated circuits and system. Qian Xie received the B.S. degree from the University of Electronic Science and Technology of China (UESTC), Chengdu, China, in 2007, and the Ph.D. degree in microelectronics from Tsinghua University, Beijing, China, in 2013. She is currently an Associate Professor with UESTC. Her research interests include silicon-based device modeling and circuit design.
Qian Xie received the B.S. degree from the University of Electronic Science and Technology of China (UESTC), Chengdu, China, in 2007, and the Ph.D. degree in microelectronics from Tsinghua University, Beijing, China, in 2013. She is currently an Associate Professor with UESTC. Her research interests include silicon-based device modeling and circuit design. Zheng Wang received the B.S. and M.S. degrees from Tsinghua University, Beijing, China, in 2007 and 2010, respectively, and the Ph.D. degree in electrical engineering from the University of California-Irvine, CA, USA, in 2014. From 2014 to 2017, he was with Qualcomm Inc., San Diego, USA, working on RFIC design for cellular application. In 2017, he joined the University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu, China, as a Professor. His research interests include the design of novel radio frequency, millimeter-wave, and terahertz silicon-based integrated circuits for the next-generation 10-Gb wireless communications as well as imaging systems.
Zheng Wang received the B.S. and M.S. degrees from Tsinghua University, Beijing, China, in 2007 and 2010, respectively, and the Ph.D. degree in electrical engineering from the University of California-Irvine, CA, USA, in 2014. From 2014 to 2017, he was with Qualcomm Inc., San Diego, USA, working on RFIC design for cellular application. In 2017, he joined the University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu, China, as a Professor. His research interests include the design of novel radio frequency, millimeter-wave, and terahertz silicon-based integrated circuits for the next-generation 10-Gb wireless communications as well as imaging systems.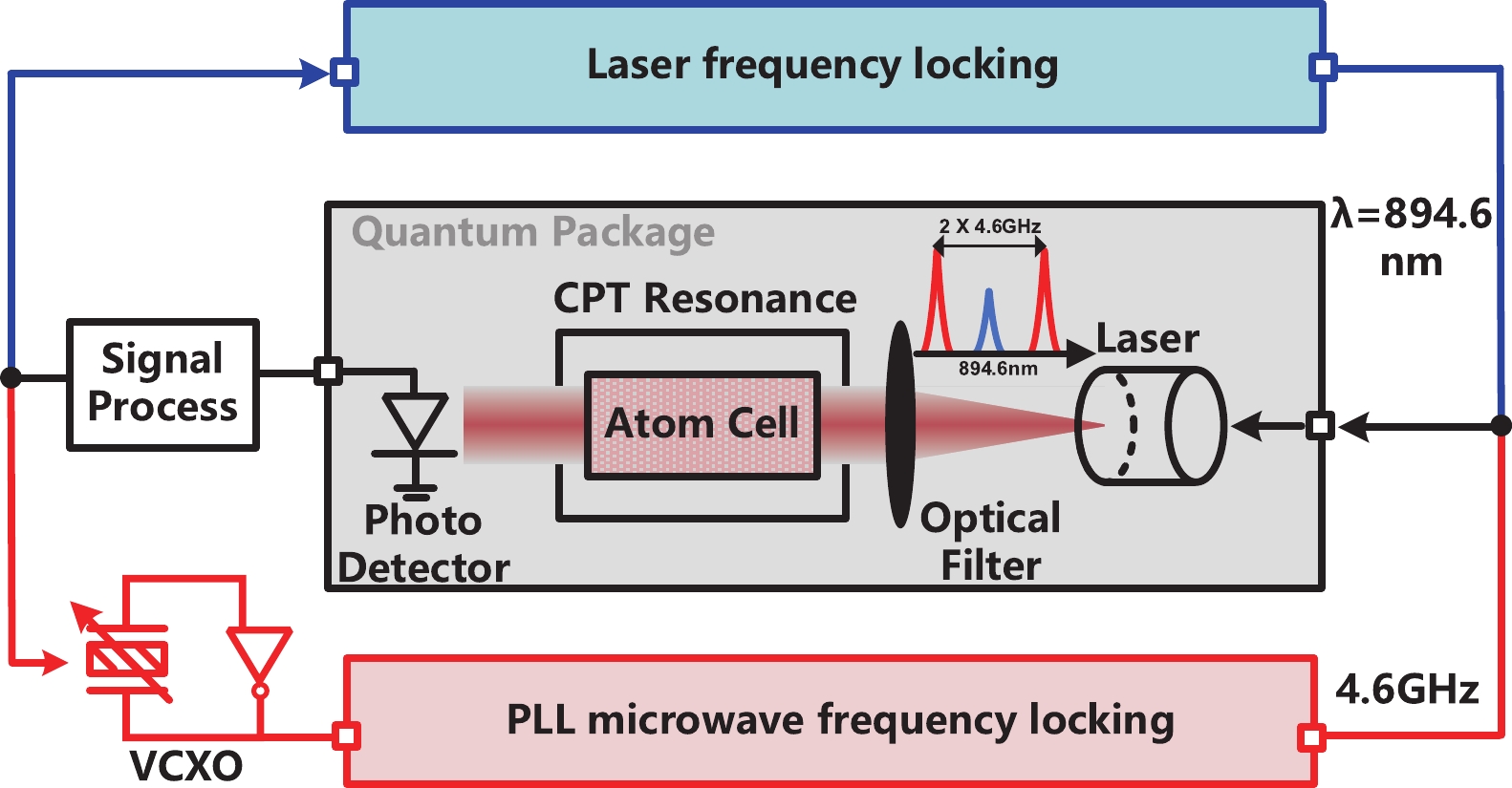
 DownLoad:
DownLoad: