| Citation: |
Danzhu Lü, Jiale Yu, Zhiliang Hong. A 10 MHz ripple-based on-time controlled buck converter with dual ripple compensation[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2013, 34(2): 025005. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/2/025005
****
D Z Lü, J L Yu, Z L Hong. A 10 MHz ripple-based on-time controlled buck converter with dual ripple compensation[J]. J. Semicond., 2013, 34(2): 025005. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/2/025005.
|
A 10 MHz ripple-based on-time controlled buck converter with dual ripple compensation
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/2/025005
More Information
-
Abstract
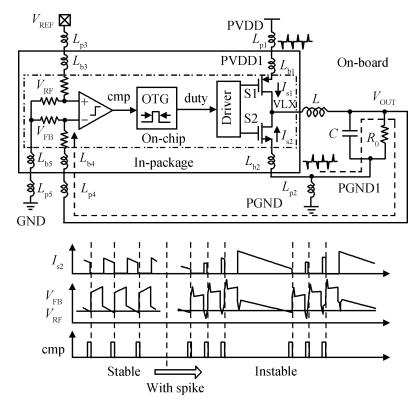
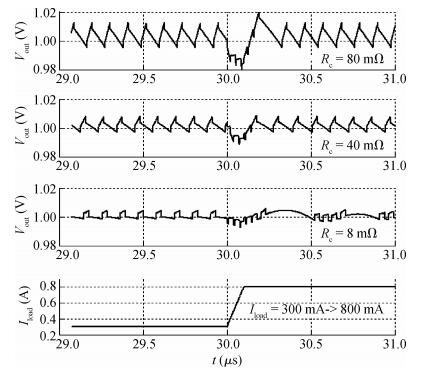
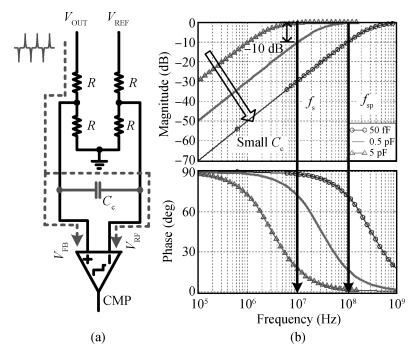
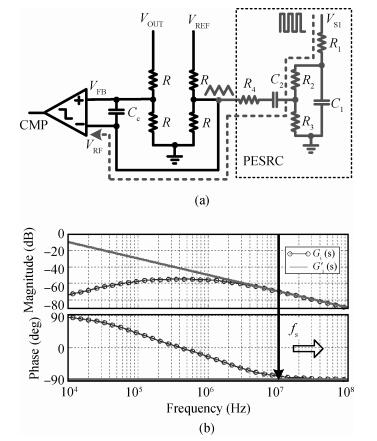
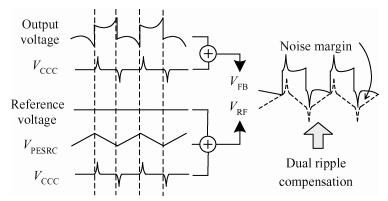
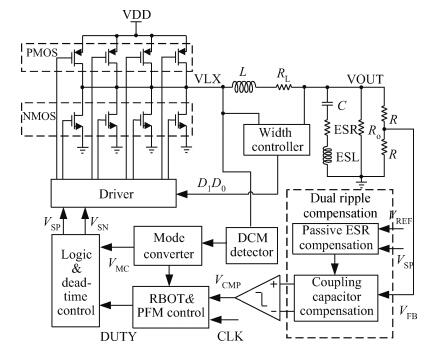
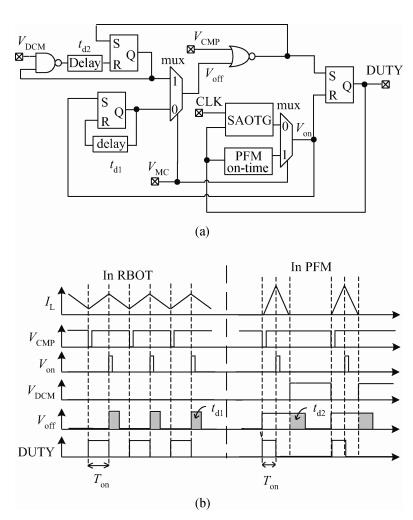
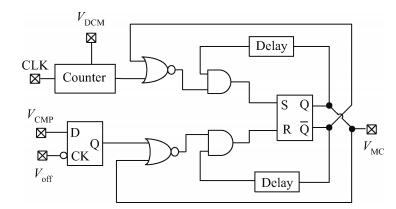
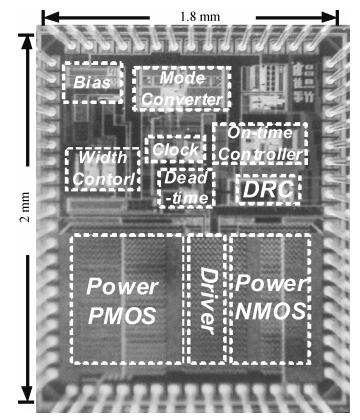
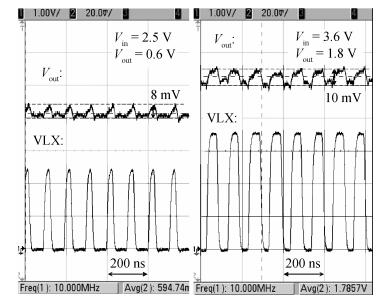
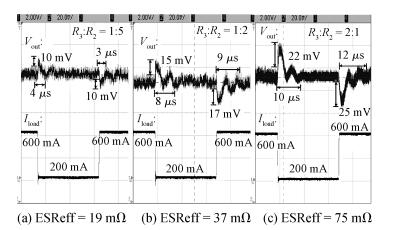
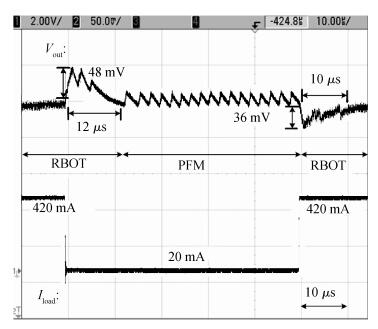
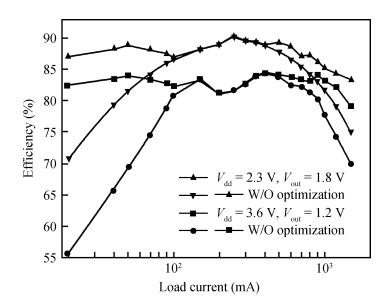
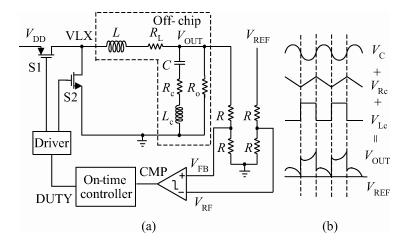
A 10 MHz ripple-based on-time controlled buck converter is presented. A novel low-cost dual ripple compensation, which consists of coupling capacitor compensation and passive equivalent series resistance compensation, is proposed to achieve a fast load transient response and robust stability simultaneously. Implemented in a 2P4M 0.35 μm CMOS process, the converter achieves fix-frequency output with a ripple of below 10 mV and an overshoot of 10 mV at 400 mA step load transient response. With width optimization of the power transistors in an ultra-heavy load and PFM control in a light load, the efficiency stays at over 83% for a load range from 20 mA to 1.5 A and the peak efficiency reaches 90.16%. -
References
[1] Du M, Lee H, Liu J. A 5-MHz 91% peak-power-efficiency buck regulator with auto-selectable peak-and valley-current control. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2011, 46(8):1928 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2011.2151470[2] Maity A, Patra A, Yamamura N, et al. Design of a 20 MHz DC-DC buck converter with 84 percent efficiency for portable applications. Proc Int Conf VLSI Design, 2011:316 doi: 10.1007/s10470-015-0589-9[3] Redl R, Sun J. Ripple-based control of switching regulators——an overview. IEEE Trans Power Electron, 2009, 24(12):2669 doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2009.2032657[4] Li J, Lee F C. Modeling of V2 current-mode control. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I, 2010, 57(9):2552 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2010.2043018[5] Lee K, Lee F C, Xu M. Novel hysteretic control method for multiphase voltage regulators. Proc IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (APEC), 2008:1508 http://www.nsfc.gov.cn/Portals/0/fj/fj20160106_01.xls[6] Zhou X, Fan J, Huang A. Monolithic DC offset self-calibration method for adaptive on-time control buck converter. Proc IEEE Energy Convers Congr Expo (ECCE), 2009:655 http://scm.nsfc.gov.cn/indexhtml/pub_maint_en_US.html[7] Chen H, Ma D. A fast-transient DVS-capable switching converter with ΔIL-emulated hysteretic control. Proc IEEE Symp VLSI Circuits, 2011:282[8] Lu D, Yu J, Hong Z, et al. A 1500 mA, 10 MHz on-time controlled buck converter with ripple compensation and efficiency optimization. Proc IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (APEC), 2012:1232[9] Rocha J, Santos M, Santos G, et al. Limiting internal supply voltage spikes in DC-DC converters. Proc IEEE Int Symp Industrial Electron (ISIE), 2009:1060[10] Sahu B, Rincon-Mora G A. An accurate, low-voltage, CMOS switching power supply with adaptive on-time pulse-frequency modulation (PFM) control. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I, 2007, 54(2):312 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2006.887472[11] Cliquennois S, Donida A, Malcovati P, et al. A 65-nm, 1-A buck converter with multi-function SAR-ADC-based CCM/PSK digital control loop. Proc IEEE ESSCIRC, 2011:427[12] Parayandeh A, Mahdavikkhah B, Ahsanuzzaman S M, et al. A 10 MHz mixed-signal CPM controlled DC-DC converter IC with novel gate swing circuit and instantaneous efficiency optimization. Proc IEEE Energy Convers Congr Expo (ECCE), 2011:1229 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: