| Citation: |
Qing Hua, Zehong Li, Bo Zhang, Xiangjun Huang, Dekai Cheng. Analysis of the dV/dt effect on an IGBT gate circuit in IPM[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2013, 34(4): 045001. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/4/045001
****
Q Hua, Z H Li, B Zhang, X J Huang, D K Cheng. Analysis of the dV/dt effect on an IGBT gate circuit in IPM[J]. J. Semicond., 2013, 34(4): 045001. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/4/045001.
|
Analysis of the dV/dt effect on an IGBT gate circuit in IPM
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/4/045001
More Information
-
Abstract
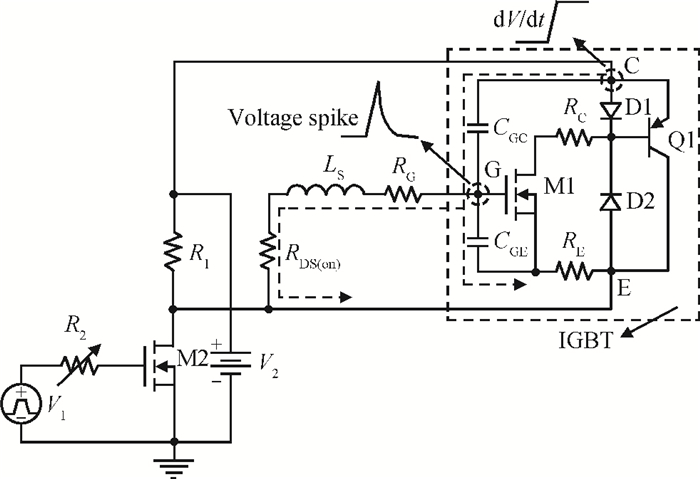
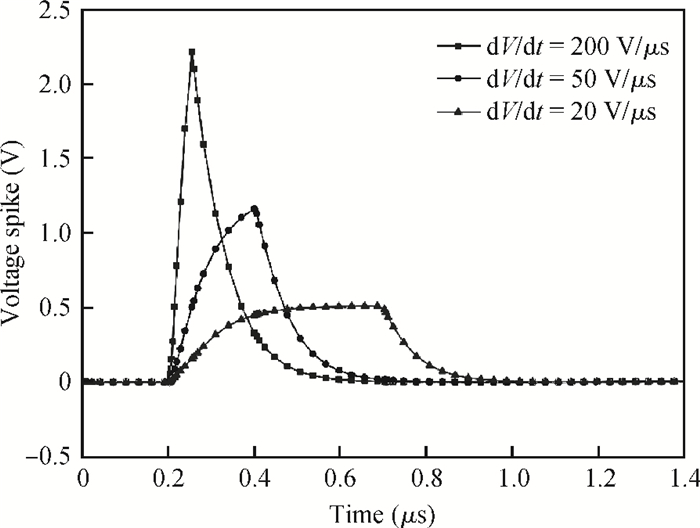
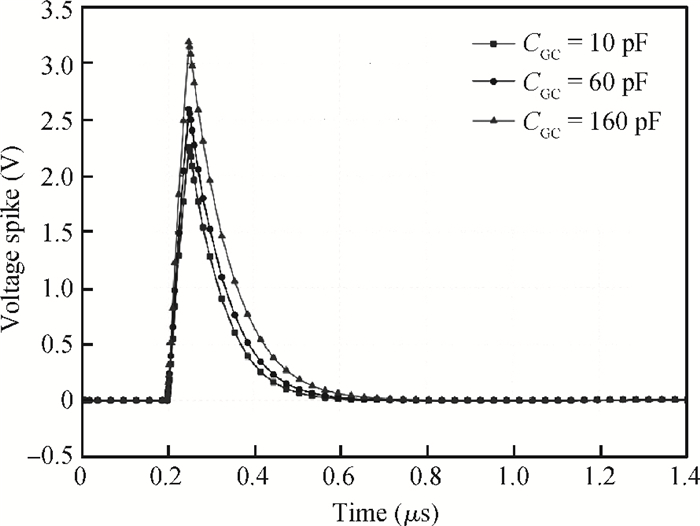
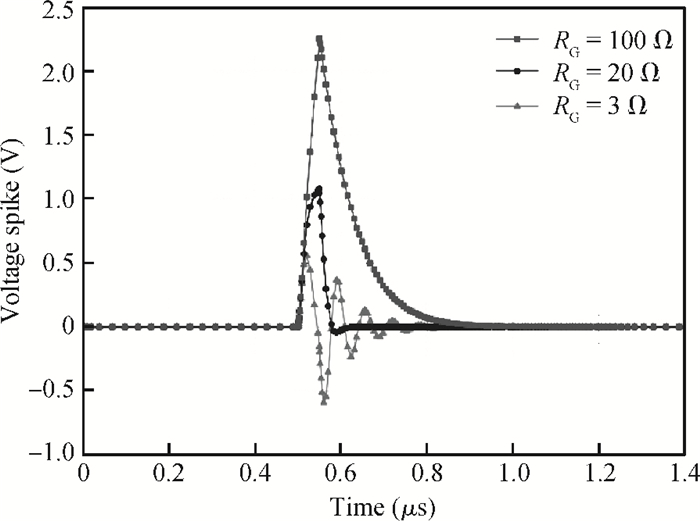
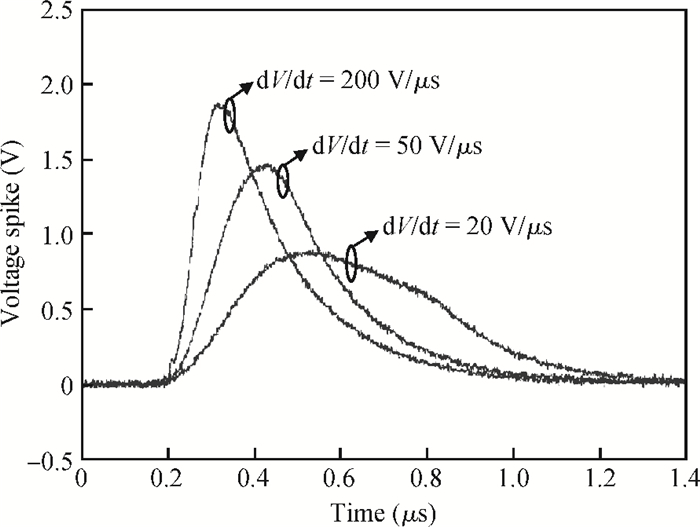
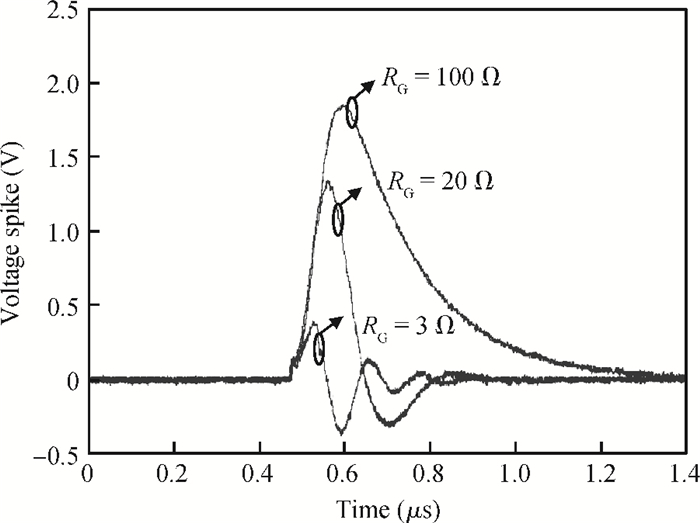
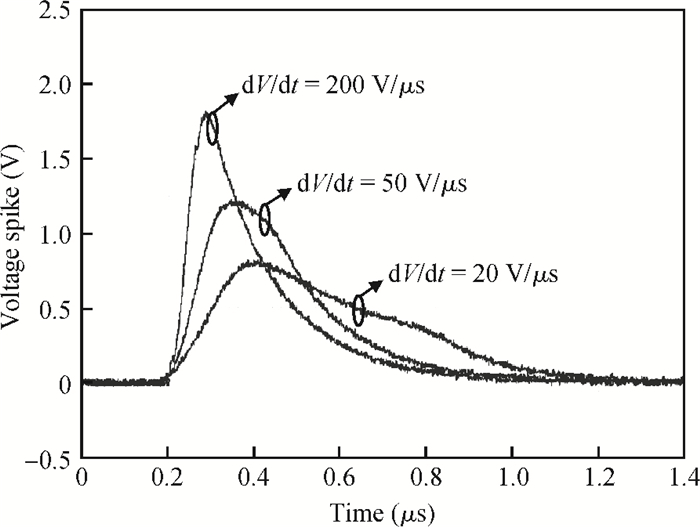
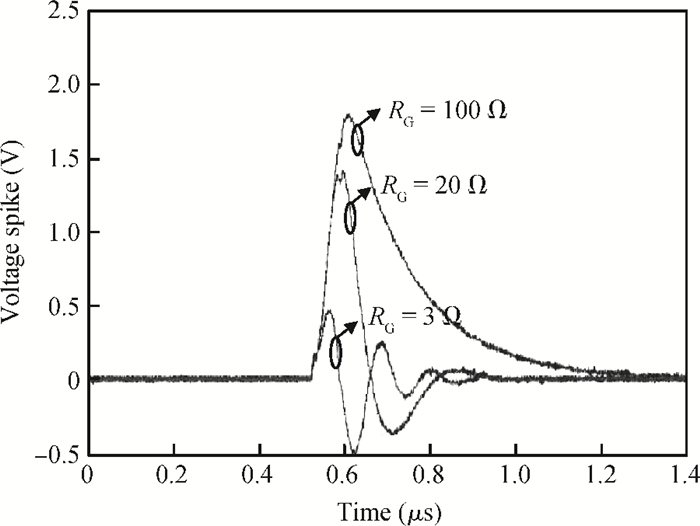
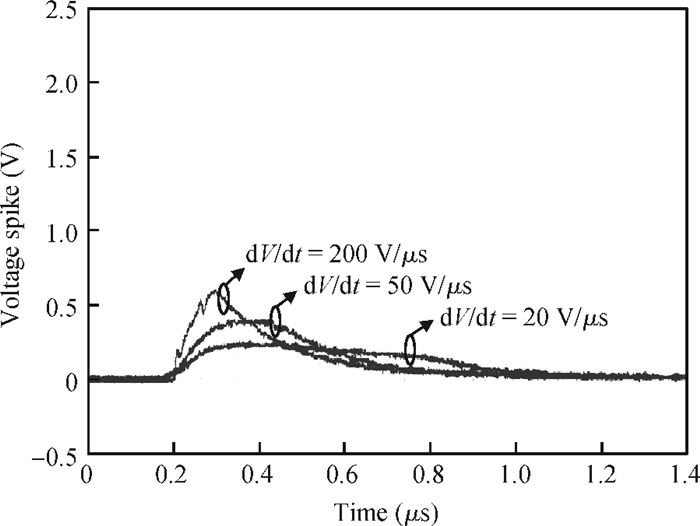
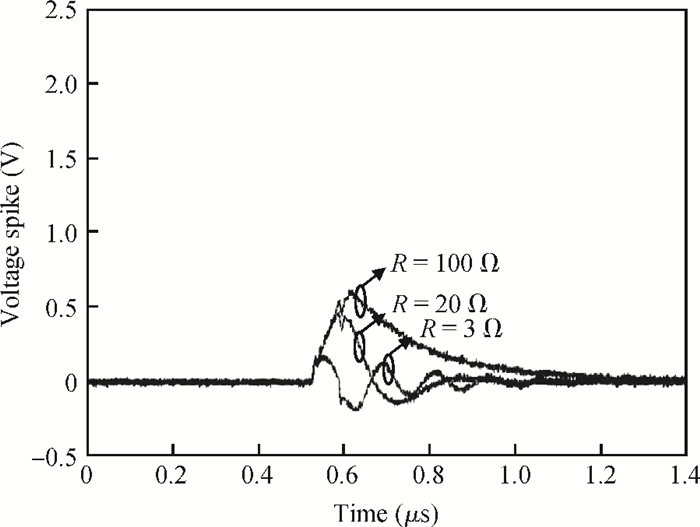
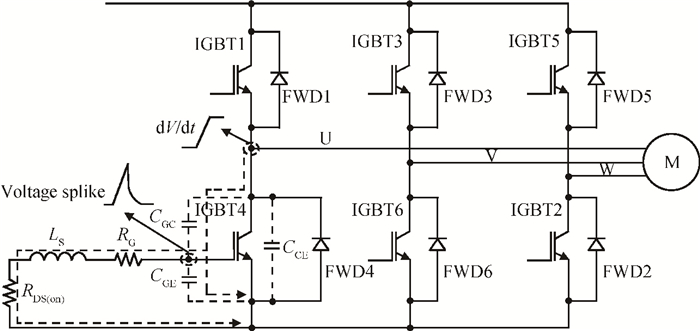
The effect of dV/dt on the IGBT gate circuit in IPM is analyzed both by simulation and experiment. It is shown that a voltage slope applied across the collector-emitter terminals of the IGBT can induce a gate voltage spike through the feedback action of the parasitic capacitances of the IGBT. The dV/dt rate, gate-collector capacitance, gate-emitter capacitance and gate resistance have a direct influence on this voltage spike. The device with a higher dV/dt rate, gate-collector capacitance, gate resistance and lower gate-emitter capacitance is more prone to dV/dt induced self turn-on. By optimizing these parameters, the dV/dt induced voltage spike can be effectively controlled.-
Keywords:
- IGBT,
- dV/dt,
- voltage spike,
- IPM
-
References
[1] Ranstad P, Nee H P. On dynamic effects influencing IGBT losses in soft-switching converters. IEEE Trans Power Electron, 2011, 26(1):260 doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2010.2055581[2] Letor R, Aniceto G C. Short circuit behavior of IGBT's correlated to the intrinsic device structure and on the application circuit. IEEE Trans Industry Applications, 1995, 31(2):234 doi: 10.1109/28.370268[3] Park S, Jahns T M. Flexible dv/dt and di/dt control method for insulated gate power switches. IEEE Trans Industry Applications, 2003, 39(3):657 doi: 10.1109/TIA.2003.810654[4] Takizawa S, Igarashi S, Kuroki K. A new di/dt control gate drive circuit for IGBTs to reduce EMI noise and switching losses. IEEE PESC, 1998, 2:1443[5] Igarashi S, Takizawa S, Tabata M, et al. An active control gate drive circuit for IGBT's to realize low-noise and snubberless system. Proc ISPSD, 1997:69[6] Bryant A, Yang S, Mawby P, et al. Investigation into IGBT dV/dt during turn-off and its temperature dependence. IEEE Trans Power Electron, 2011, 26(10):3019 doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2011.2125803[7] Idir N, Bausiere R, Franchaud J J. Active gate voltage control of turn-on di/dt and turn-off dv/dt in insulated gate transistors. IEEE Trans Power Electron, 2006, 21(4):849 doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2007.876895[8] Wu W, Held M, Umbricht N, et al. dv/dt induced latching failure in 1200 V/400 A halfbridge IGBT modules. IEEE IRPS, 1994:420 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/307804/?reload=true&arnumber=307804&filter%3DAND(p_IS_Number:7501)[9] Murata K, Harada, K. Analysis of a self turn-on phenomenon on the synchronous rectifier in a DC-DC converter. INTELEC, 2004:199 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/1252113/[10] Yedinak J, Gladish J, Brockway B, et al. A 600 V quick punch through (QPT) IGBT design concept for reducing EMI. Proc ISPSD, 2003:67[11] Musumeci S, Pagano R, Raciti A, et al. A novel protection technique devoted to the improvement of the short circuit ruggedness of IGBTs. IECON, 2003, 2:1733 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/1280319/?arnumber=1280319 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: