| Citation: |
Zhao Si, Tongbo Wei, Ning Zhang, Jun Ma, Junxi Wang, Jinmin Li. Improvement of carrier distribution in dual wavelength light-emitting diodes[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2013, 34(5): 054008. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/5/054008
****
Z Si, T B Wei, N Zhang, J Ma, J X Wang, J M Li. Improvement of carrier distribution in dual wavelength light-emitting diodes[J]. J. Semicond., 2013, 34(5): 054008. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/5/054008.
|
Improvement of carrier distribution in dual wavelength light-emitting diodes
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/5/054008
More Information
-
Abstract
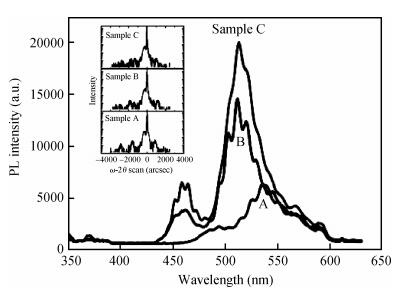
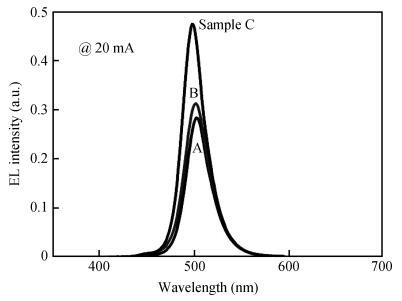
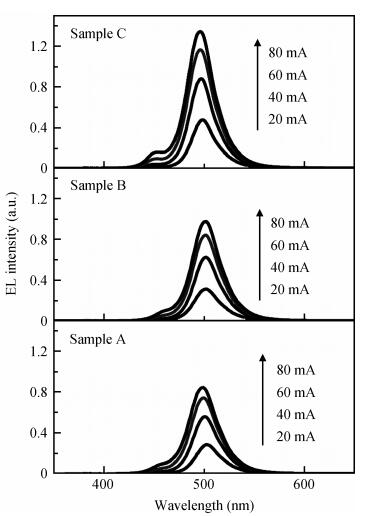
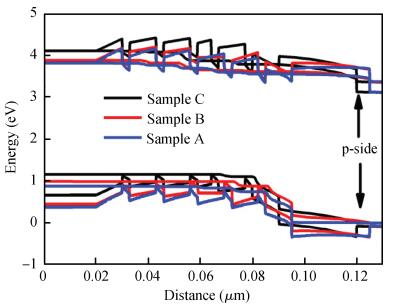
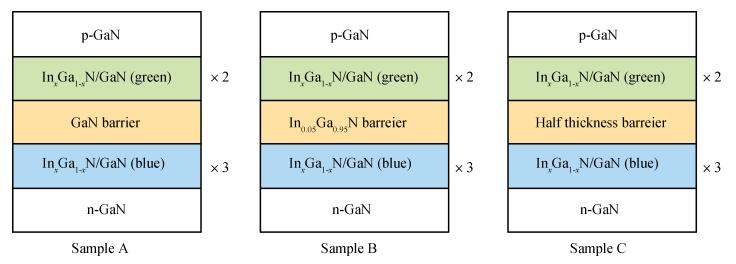
The effect of different barriers between green and blue light regions in dual wavelength light emitting diodes was studied. Compared with a traditional sample, electroluminescence and photoluminescence spectra of the newly designed samples showed peak intensity improvements and smaller blue-shifts with increasing injection current level, and the bottom quantum-wells light emitting is enhanced. All these phenomena can be ascribed to reduced barrier thickness and indium doping in the quantum-barrier influencing electric fields and more holes injecting into the bottom QWs.-
Keywords:
- LED,
- dual wavelength,
- quantum barrier,
- holes injection,
- carrier distribution
-
References
[1] Wang L S, Lu Z Q, Liu S, et al. Shallow-deep InGaN multiple-quantum-well system for dual-wavelength emission grown on semipolar (1122) facet GaN. J Electron Mater, 2011, 40:1572 doi: 10.1007/s11664-011-1652-7[2] Qi Y D, Liang H, Tang W, et al. Dual wavelength InGaN/GaN multi-quantum well LEDs grown by metalorganic vapor phase epitaxy. J Cryst Growth, 2004, 272:333 doi: 10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2004.08.097[3] Yamada M, Narukawa Y, Tamaki H, et al. A methodological study of the best solution for generating white light using nitride-based light-emitting diodes. IEICE Trans Electron, 2005, E88-C:1860 doi: 10.1093/ietele/e88-c.9.1860[4] Chen H S, Yeh D M, Lu C F, et al. Mesa-size-dependent color contrast in flip-chip blue/green two-color InGaN/GaN multi-quantum-well micro-light-emitting diodes. Appl Phys Lett, 2006, 89:093501 doi: 10.1063/1.2339034[5] Damilano B, Grandjean N, Pernot C, et al. Monolithic white light emitting diodes based on InGaN/GaN multiple-quantum wells. Jpn J Appl Phys, 2001, 40:L918 doi: 10.1143/JJAP.40.L918[6] Yamada M, Narukawa Y, Mukai T. Phosphor free high-luminous-efficiency white light-emitting diodes composed of InGaN multi-quantum well. Jpn J Appl Phys, 2002, 41:L246 doi: 10.1143/JJAP.41.L246[7] Jeon S R, Cho M S, Yu M A, et al. GaN-based light-emitting diodes using tunnel junctions. IEEE J Sel Topics Quantum Electron, 2002, 8:739 doi: 10.1109/JSTQE.2002.800847[8] Ozden I, Makarona E, Nurmikko A V, et al. A dual-wavelength indium gallium nitride quantum well light emitting diode. Appl Phys Lett, 2001, 79:2532 doi: 10.1063/1.1410345[9] Chen H S, Yeh D M, Lu C F, et al. White light generation with CdSe-ZnS nanocrystals coated on an InGaN-GaN quantum-well blue/green two-wavelength light-emitting diode. IEEE Photonics Technol Lett, 2006, 18:1430 doi: 10.1109/LPT.2006.877551[10] Wang T, Nakagawa D, Wang J, et al. Photoluminescence investigation of InGaN/GaN single quantum well and multiple quantum wells. Appl Phys Lett, 1998, 73:3571 doi: 10.1063/1.122810[11] Wang T, Bai J, Sakai S, et al. Investigation of the emission mechanism in InGaN/GaN-based light-emitting diodes. Appl Phys Lett, 2001, 78:2617 doi: 10.1063/1.1368374[12] David A, Grundmann M J, Kaeding J F, et al. Carrier distribution in (0001) InGaN/GaN multiple quantum well light-emitting diodes. Appl Phys Lett, 2008, 92:053502 doi: 10.1063/1.2839305[13] Liu J P, Ryou J H, Dupuis R D, et al. Barrier effect on hole transport and carrier distribution in InGaN/GaN multiple quantum well visible light-emitting diodes. Appl Phys Lett, 2008, 93:021102 doi: 10.1063/1.2957667[14] Lu C F, Yeh D M, Chen H S, et al. Junction temperature-controlled spectrum in a two-color InGaN-GaN quantum-well light-emitting diode. IEEE Photonics Technol Lett, 2006, 18:2671 doi: 10.1109/LPT.2006.887797 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: