| Citation: |
Lidan Wang, Zhiqun Li. A 0.5 V divider-by-2 design with optimization methods for wireless sensor networks[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2013, 34(5): 055004. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/5/055004
****
L D Wang, Z Q Li. A 0.5 V divider-by-2 design with optimization methods for wireless sensor networks[J]. J. Semicond., 2013, 34(5): 055004. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/5/055004.
|
A 0.5 V divider-by-2 design with optimization methods for wireless sensor networks
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/5/055004
More Information
-
Abstract
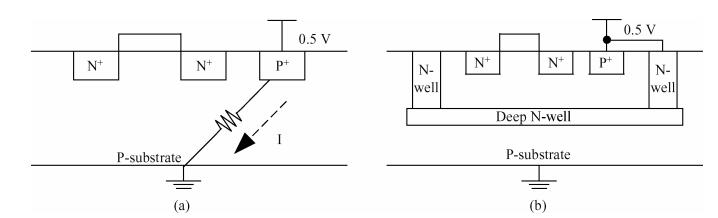
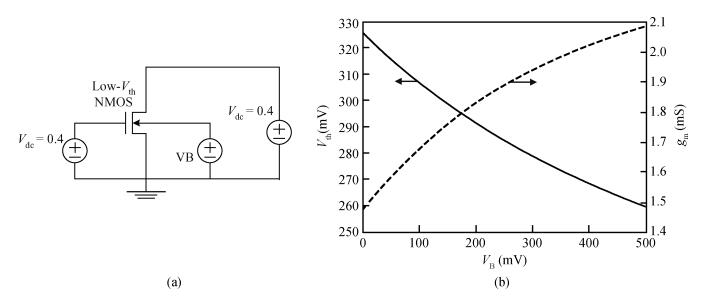
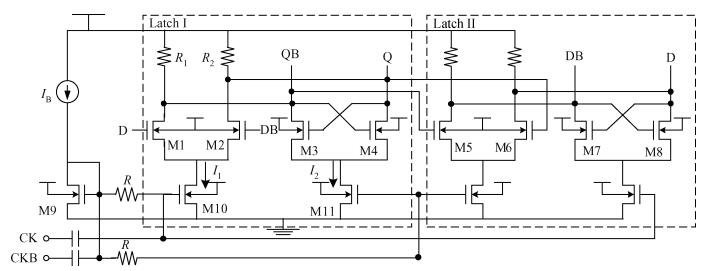
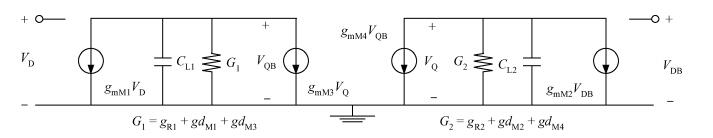
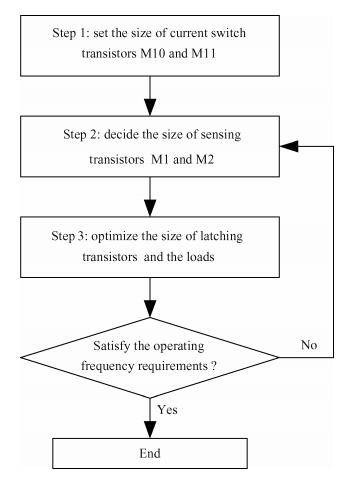
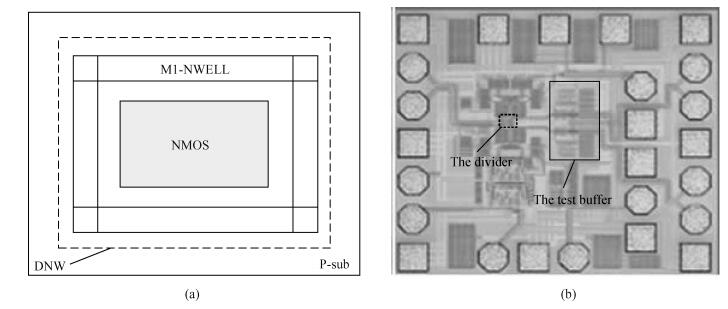
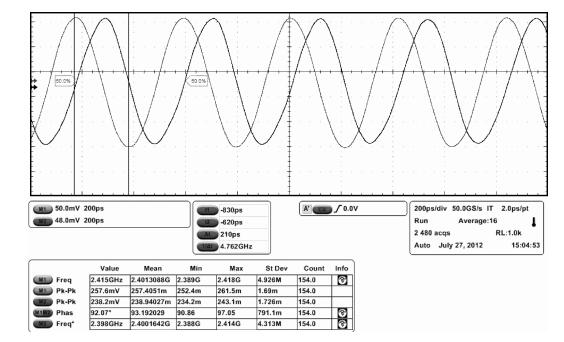
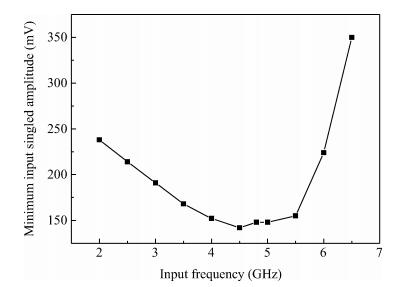
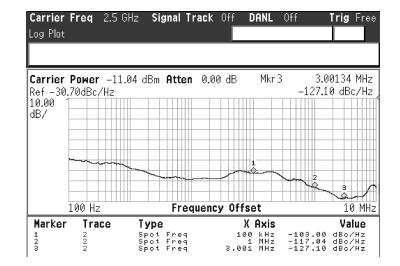
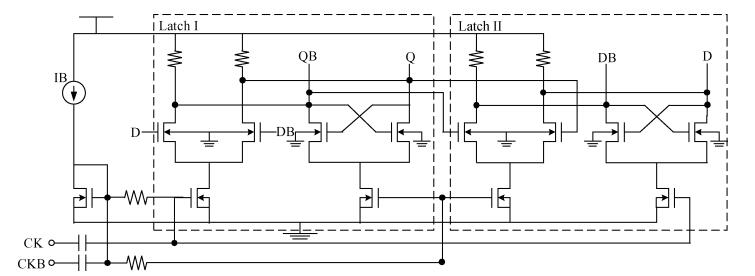
A 0.5 V static master-slave D flip-flop (DFF) divider-by-2 is implemented with a 0.13 μm 1P8M RF-mixed signal CMOS process. Low-threshold transistors in a deep-N well with forward-body bias technology are used in the circuit. Each of the D-latch with source coupled logic consists of sensing and latching circuits. To increase the maximum operating frequency and decrease power consumption, the latching current is one half of the sensing current. The circuit optimization methods are described in this paper. The measured maximum operating frequency is 6.5 GHz and the minimum input singled-signal amplitude is 0.15 V.-
Keywords:
- low-threshold transistors,
- deep-N well,
- forward-body bias,
- low voltage
-
References
[1] Lin T H, Kaiser W J, Pottie G J. Integrated low-power communication system design for wireless sensor networks. IEEE Commun Mag, 2004, 12:142 http://www.eeweb.ee.ucla.edu/publications/journalGregoryPottiekaiser_ieeecomm-mag_dec04.pdf[2] Van der Tang J, van de Ven P, van Roermund A. Analysis and design of an optimally coupled 5-GHz quadrature LC oscillator. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2005, 37(5):657 http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/summary?doi=10.1.1.667.6961[3] Gierkink S L J, Levantino S, Frye R C, et al. A low-phase-noise 5 GHz quadrature CMOS VCO using common-mode inductive coupling. Proceedings of the 28th European Solid-State Circuits Conference, 2002:539 doi: 10.1007/s10470-011-9729-z[4] Singh U, Green M. Dynamics of high-frequency CMOS dividers. IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, 2002, 5:421 doi: 10.1109/ISCAS.2002.1010730[5] Wong L S Y, Rigby G A. A 1 V CMOS digital circuit with double-gate-driven MOSFET. IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, 1997, 17:292 doi: 10.1007%2Fs10825-011-0359-6.pdf[6] Mutoh S, Douseki T, Matsuya Y, et al. 1-V power supply high-speed digital circuit technology with multithreshold-voltage CMOS. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 1995, 30(8):847 doi: 10.1109/4.400426[7] Von Arnim K, Borinski E, Seegebrecht P, et al. Efficiency of body biasing in 90-nm CMOS for low-power digital circuits. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2005, 40(7):1549 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2005.847517[8] Chen W H, Loke W F, Jung B. A 0.5-V, 440-μ W frequency synthesizer for implantable medical devices. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2012, 47(8):1896 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2012.2196315[9] Ding Y, Kenneth K O. A 21-GHz 8-modulus prescaler and a 20-GHz phase-locked loop fabricated in 130-nm CMOS. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2007, 42(6):1240 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2007.897140[10] Luong H C, Leung G C T. Low-voltage CMOS RF frequency synthesizers. New York:Cambridge University Press, 2004:44 http://www.worldcat.org/title/low-voltage-cmos-rf-frequency-synthesizers/oclc/54529293[11] Wong J M C, Cheung V S L, Luong H C. A 1-V 2.5-mW 5.2-GHz frequency divider in a 0.35-μ m CMOS process. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2003, 38(10):1643 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2003.817261[12] Cao C, Kenneth K O. A power efficient 26-GHz 32:1 static frequency divider in 130-nm bulk CMOS. IEEE Microw Wireless Compon Lett, 2005, 15(11):721 doi: 10.1109/LMWC.2005.858998[13] Otsuji T, Yoneyama M, Murata K, et al. A super-dynamic flip-flop circuit for broad-band applications up to 24 Gb/s utilizing production-level 0.2-μ m GaAs MESFETs. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 1997, 32(9):1357 doi: 10.1109/4.628739[14] Murata K, Ohhata M, Togashi M, et al. 20 Gbit/s GaAs MESFET multiplexer IC using a novel T-type flip-flop circuit. Electron Lett, 1992, 28(22):2092 https://www.toshiba.co.jp/tech/review/1996/08/f02/bunken1.htm[15] Gu Z, Thiede A. 18 GHz low-power CMOS static frequency divider. Electron Lett, 2003, 39(20):1433 doi: 10.1049/el:20030932[16] Hung C M, Floyd B A, Park N, et al. Fully integrated 5.35-GHz CMOS VCOs and prescalers. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech, 2001, 49(1):17 doi: 10.1109/22.899957[17] Leung G C T, Luong H C. A 1-V 5.2-GHz CMOS synthesizer for WLAN applications. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2004, 39(11):1873 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2004.835830[18] Razavi B, Lee K F, Yan R H. Design of high-speed, low-power frequency dividers and phase-locked loops in deep submicron CMOS. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 1995, 30(2):101 doi: 10.1109/4.341736 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: