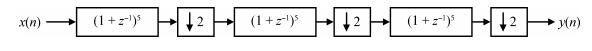| Citation: |
Jinchen Zhao, Menglian Zhao, Xiaobo Wu, Hanqing Wang. A 0.9-V switched-opamp-based delta-sigma ADC with dual cycle shift DWA[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2013, 34(6): 065004. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/6/065004
****
J C Zhao, M L Zhao, X B Wu, H Q Wang. A 0.9-V switched-opamp-based delta-sigma ADC with dual cycle shift DWA[J]. J. Semicond., 2013, 34(6): 065004. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/6/065004.
|
A 0.9-V switched-opamp-based delta-sigma ADC with dual cycle shift DWA
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/6/065004
-
Abstract
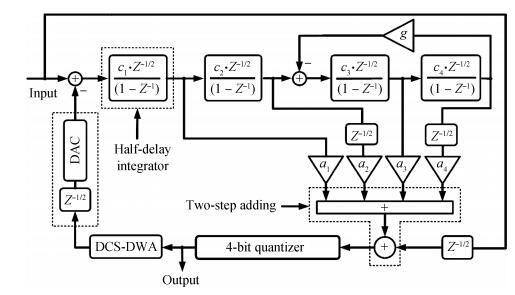
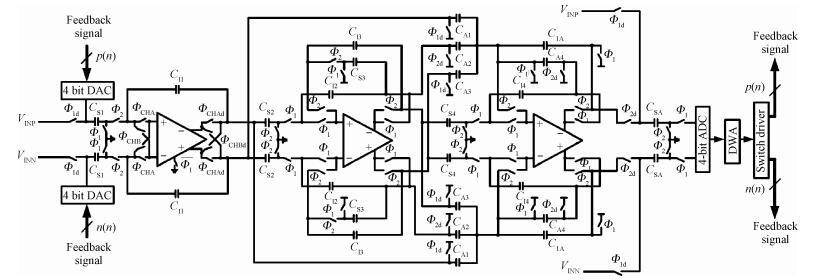
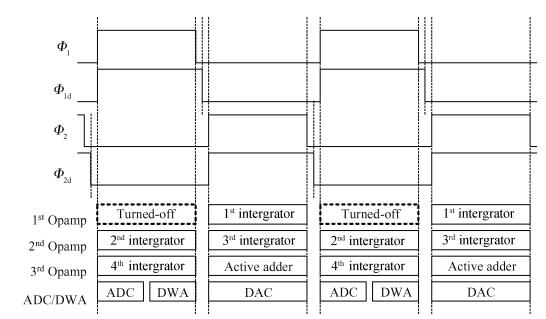
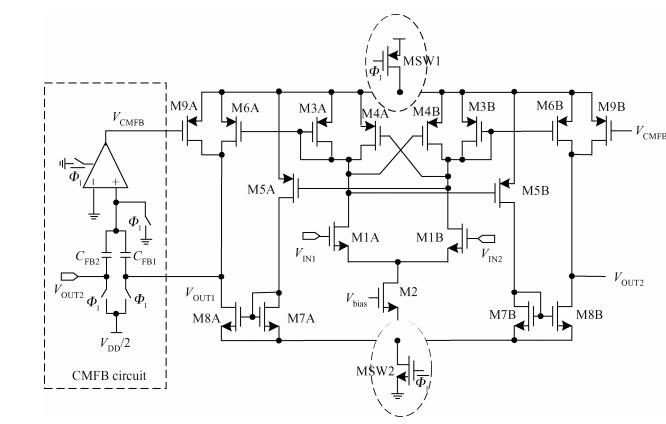
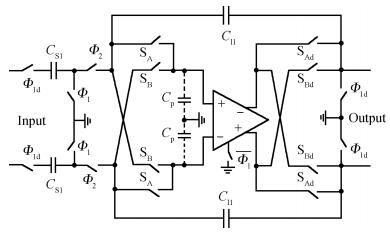
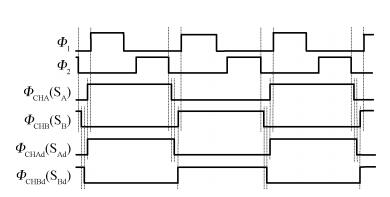
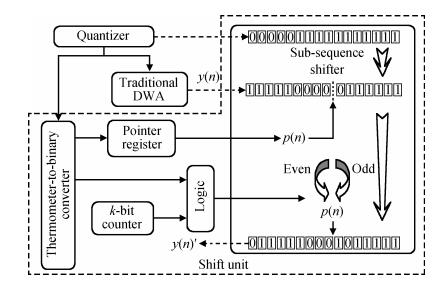
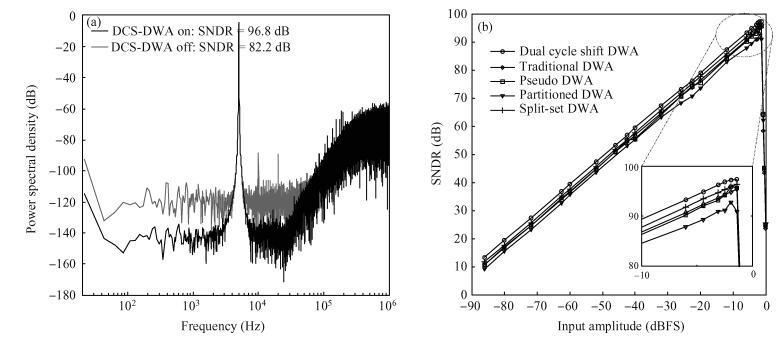
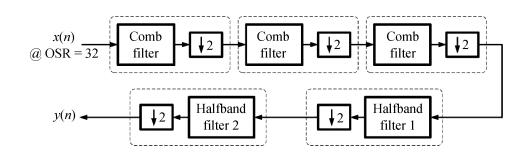
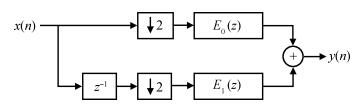
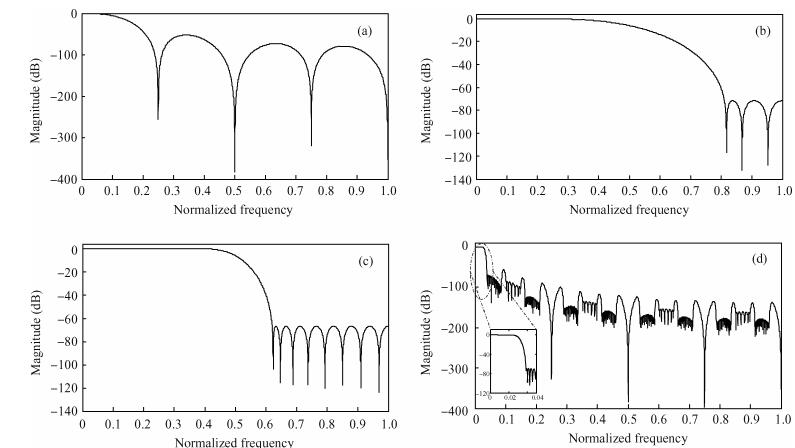
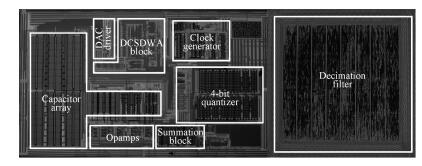
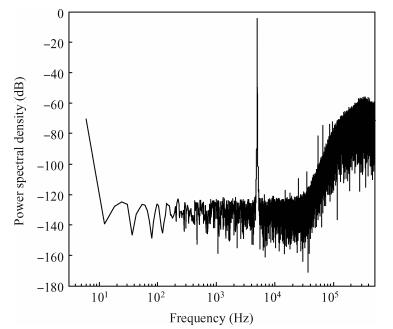
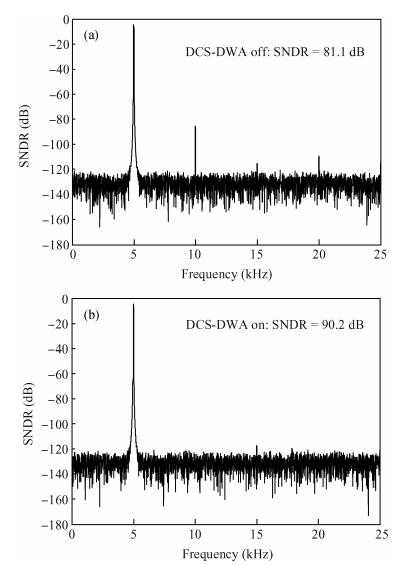
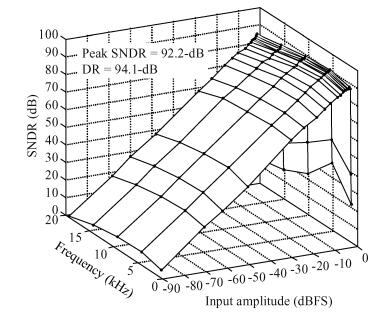
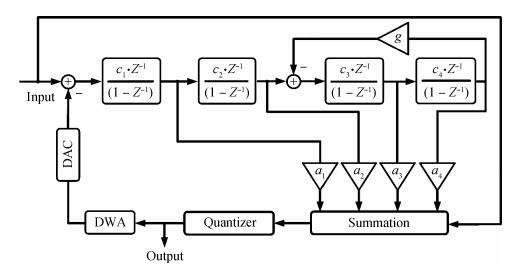
This paper presents a low-power high-precision switched-opamp (SO)-based delta-sigma (Δ Σ) analog-to-digital converter (ADC). The proposed SO design allows circuit operation at sub-1 V supply voltage, only needs to work in half of a clock cycle, and thus is suitable for low power applications. In addition, an opamp-sharing technique is applied to save on hardware overheads. Due to the use of a dual cycle shift data weighted averaging (DCS-DWA) technique, mismatch errors caused in the feedback DAC have been eliminated without introducing signal-dependent tones. The proposed ADC has been implemented in a standard 0.18 μm process and measured to have a 92.2 dB peak SNDR and 94.1 dB dynamic range with 25 kHz signal bandwidth. The power consumption is 58 μ W for the modulator at 0.9 V supply voltage and 96 μ W for the decimation filter, which translate to the figure-of-merit (FOM) of 35.4 fJ/step for the solo modulator, and 94 fJ/step for the whole system. -
References
[1] Sansen W, Steyaert M, Peluso V, et al. Toward sub-1-V analog integrated circuits in submicron standard CMOS technologies. Proceedings of IEEE International Solid-State Circuit Conference, 1998:186[2] Norsworthy S R, Schreier R, Temes G C. Delta-sigma data converters——theory, design, and simulation. New York:IEEE Press, 1997[3] Baird R T, Fiez T S. Improved Δ Σ DAC linearity using data weighted averaging. Proceedings of IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, 1995:13[4] Hamoui A A, Martin K. Linearity enhancement of multibit Δ-Σ modulators using pseudo data-weighted averaging. IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, 2002:Ⅲ-285 doi: 10.1023/A:1020769913779[5] Vleugels K, Rabii S, Wooley B A. A 2.5-V sigma-delta modulator for broadband communications applications. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2001, 36(12):1887 doi: 10.1109/4.972139[6] Wang R. A multi-bit delta sigma audio digital-to-analog converter. PhD Dissertation, EECS, Oregon State University, Cor-vallis, OR, 2006[7] Crols J, Steyaert M. Switched-opamp:an approach to realize full CMOS switched-capacitor circuits at very low power supply voltages. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 1994, 29(8):936 doi: 10.1109/4.297698[8] Ma X, Xu J, Wu X. Dual cycle shift data-weighted averaging technique for multi-bit sigma-delta modulators. IEEE International Conference of Electron Devices and Solid-State Circuits, 2009:174 http://psrcentre.org/images/extraimages/55.%200112302.pdf[9] Silva J, Moon U, Steensgaard J, et al. Wideband low-distortion delta-sigma ADC topology. IEE Electron Lett, 2001, 37(12):737 doi: 10.1049/el:20010542[10] Cheung V, Luong H. A 0.9-V 0.5-μ W CMOS single-switched-op-amp signal-conditioning system for pacemaker applications. IEEE International Solid-State Circuit Conference Digest of Technical Papers, 2003:408 doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-1371-4_6/fulltext.html[11] Yang Y, Chokhawala A, Alexander M, et al. A 114-dB 68-mW chopper-stabilized stereo multibit audio ADC in 5.62 mm. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2003, 38(12):2061 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2003.819164[12] Early A B. Chopper stabilized delta-sigma analog-to-digital converter. US Patent, No. 4939516, July 3, 1990[13] Wang H, Zhao M, Wu X, et al. 0.9 V 58μ W 92 dB SNDR audio Δ Σ modulator with high efficiency low noise switched-opamp and novel DWA technique. IEE Electron Lett, 2011, 47(4):237 doi: 10.1049/el.2010.7409[14] Gao Y, Jia L, Tenhunen H. A fifth-order comb decimation filter for multi-standard transceiver applications. IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, 2000:Ⅲ-89[15] Park H, Nam K, Su D K, et al. A 0.7-V 870-μ W digital-audio CMOS sigma-delta modulator. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2009, 44(4):1078 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2009.2014708[16] Chae Y, Lee I, Han G. Low voltage, low power, inverter-based switched-capacitor delta-sigma modulator. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2009, 44(2):458 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2008.2010973[17] Kuo C, Shi D, Chang K. A low-voltage fourth-order cascade delta-sigma modulator in 0.18-μm CMOS. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I, Regular Papers, 2010, 57(9):450 doi: 10.1007%2F978-3-642-19712-3_72.pdf[18] Zhang J, Lian Y, Yao L, et al. A 0.6 V 82 dB 28.6μW continuous time audio delta sigma modulator. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2011, 46(10):2326 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2011.2161212[19] Michel F, Steyaert M. A 250 mV 7.5μW 61 dB SNDR CMOS SC Δ Σ modulator using a near-threshold-voltage-biased CMOS inverter technique. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2012, 47(3):709 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2011.2179732 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: