| Citation: |
Xin Cheng, Haigang Yang, Tongqiang Gao, Tao Yin. A CMOS Gm-C complex filter with a reconfigurable center and cutoff frequencies in low-IF WiMAX receivers[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2013, 34(7): 075004. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/7/075004
****
X Cheng, H G Yang, T Q Gao, T Yin. A CMOS Gm-C complex filter with a reconfigurable center and cutoff frequencies in low-IF WiMAX receivers[J]. J. Semicond., 2013, 34(7): 075004. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/7/075004.
|
A CMOS Gm-C complex filter with a reconfigurable center and cutoff frequencies in low-IF WiMAX receivers
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/7/075004
More Information
-
Abstract
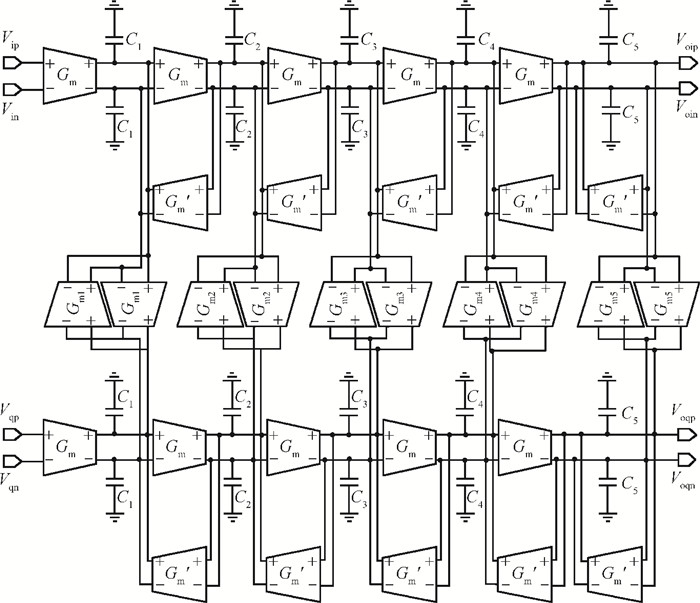
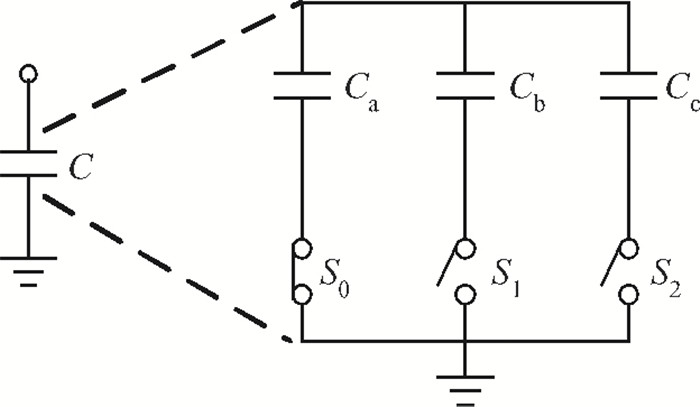
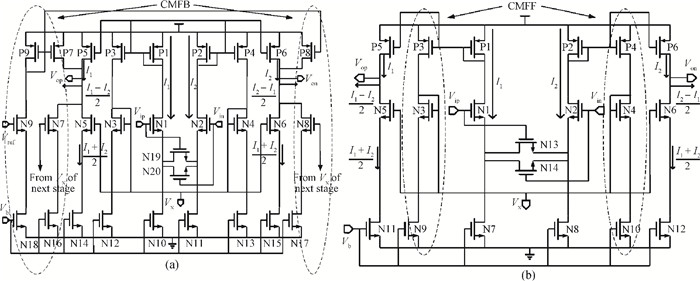
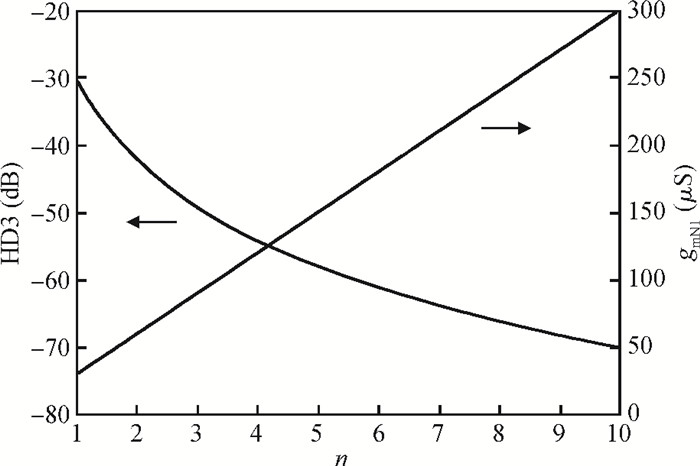
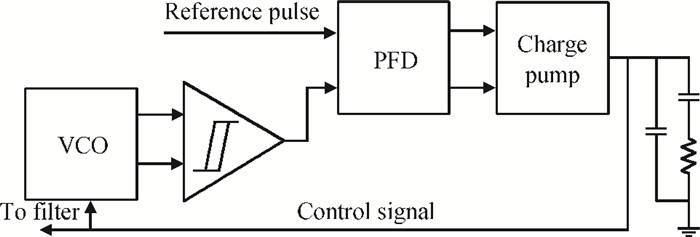
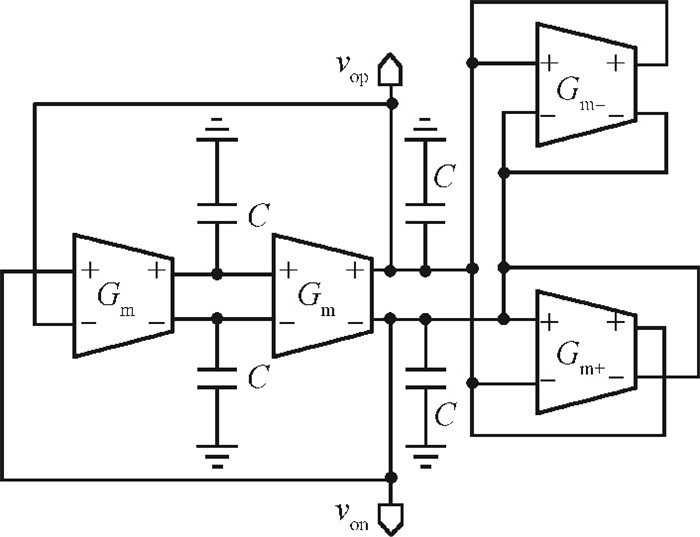
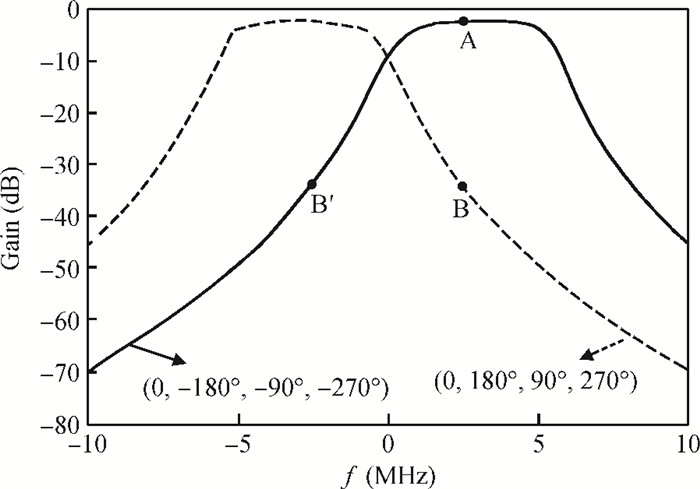
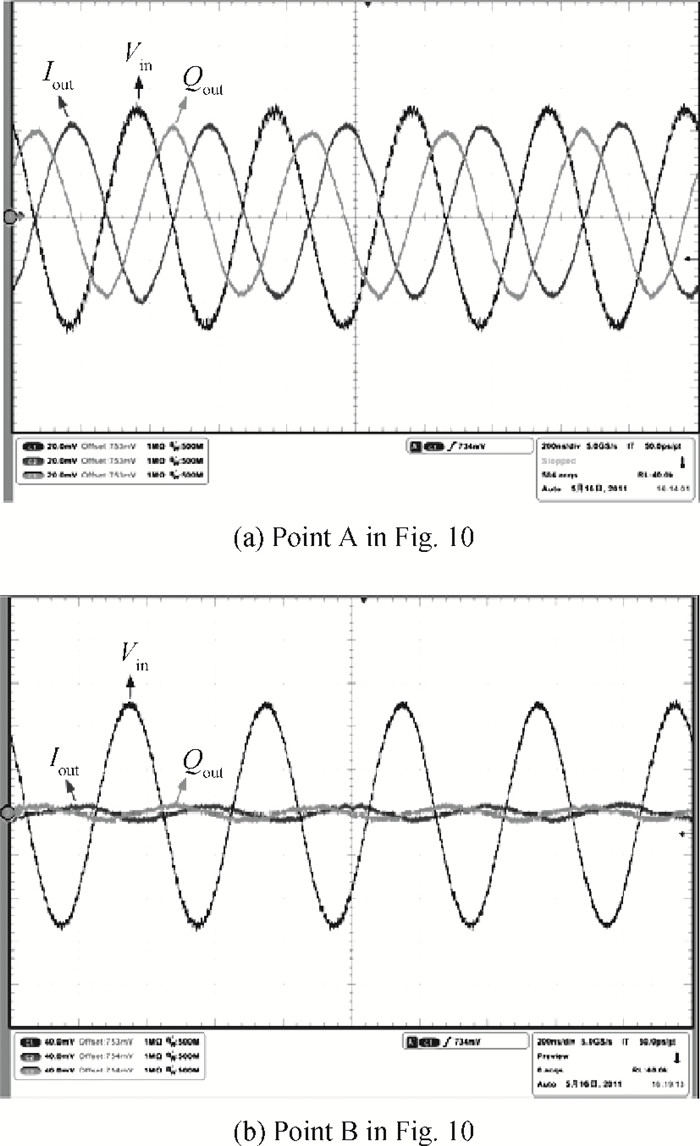
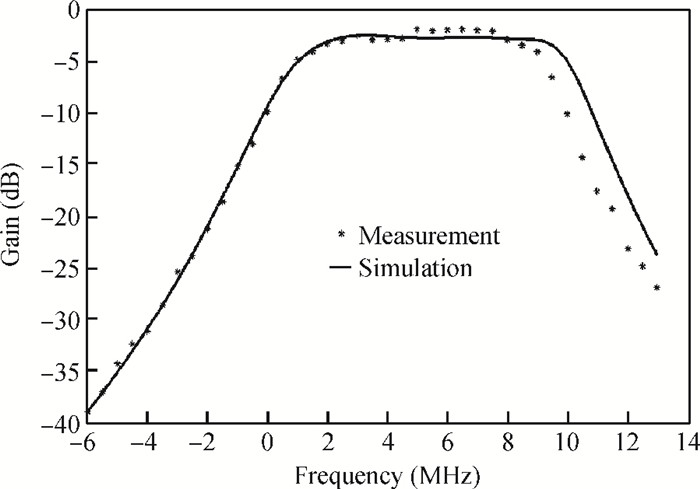
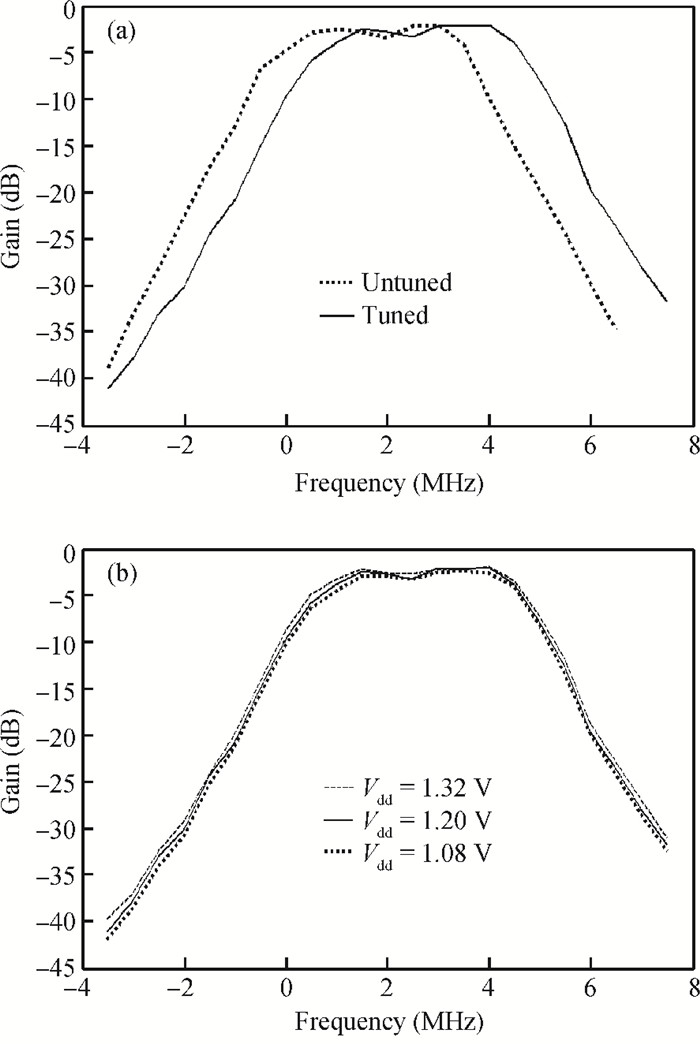
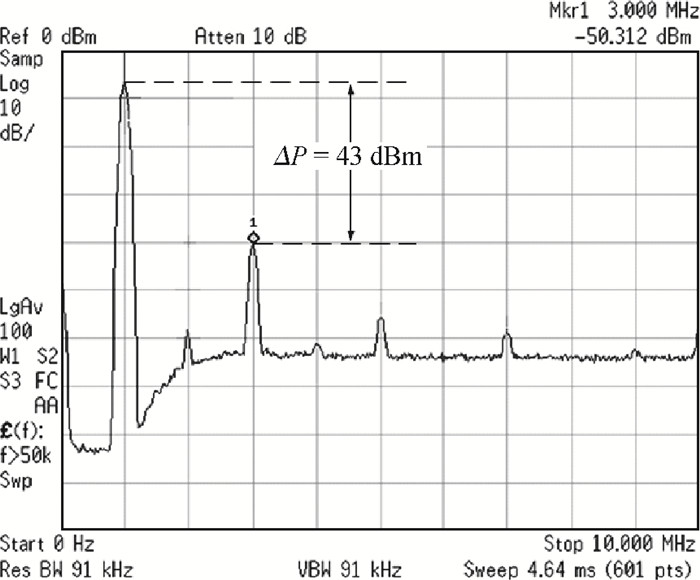
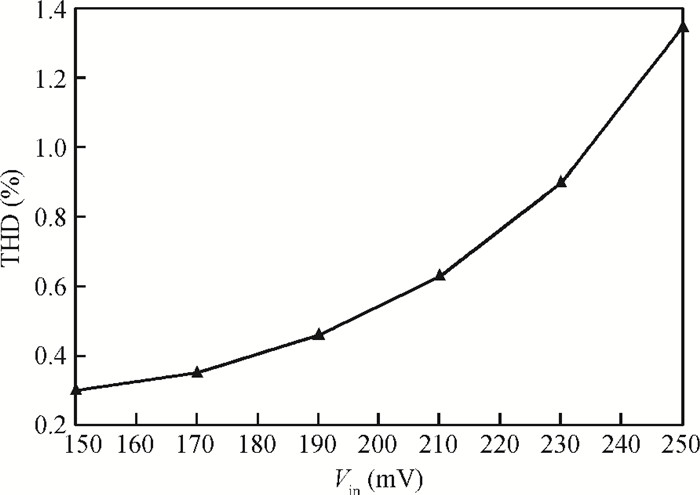
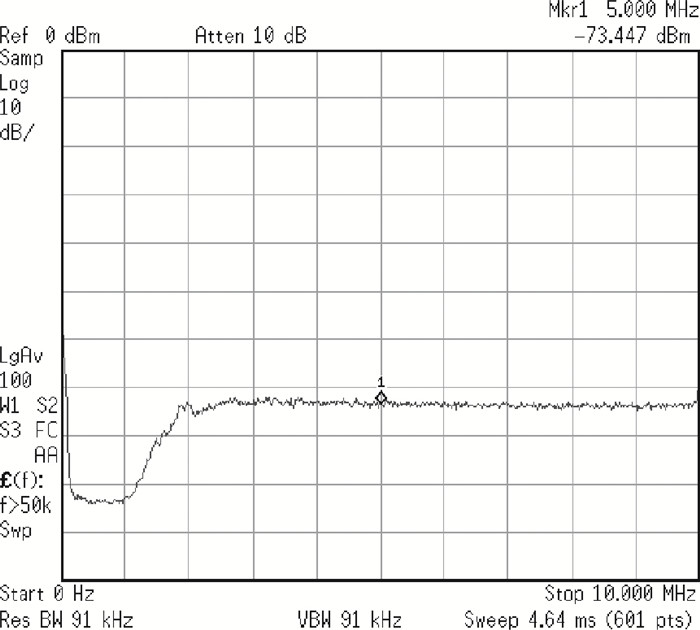
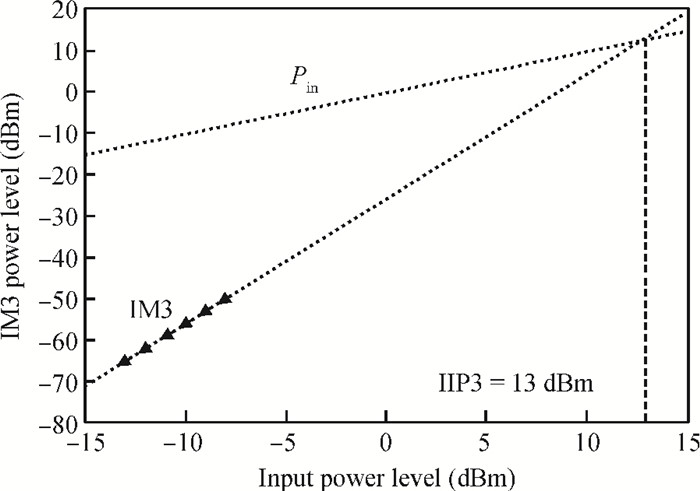
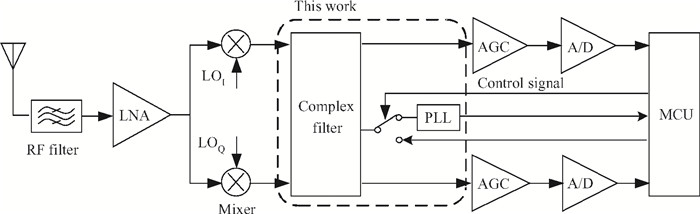
This paper presents a reconfigurable fifth-order complex Gm-C filter for different data rates in low-IF WiMAX applications. The design procedure and linearized measures to realize the complex filter are described. In order to achieve the reconfigurability of bandwidth window, the center frequency and the cutoff frequency filter are adjusted simultaneously by changing capacitor values while keeping transconductors unchanged. Also, the filter integrates an on-chip automatic frequency tuning circuit based on a PLL. Experimental results show that it has an IRR of 32 dB, a THD of-43 dB, and an input-referred noise of 21 μVrms. The chip is fabricated in 0.13 μm CMOS process, occupies 0.7×1 mm2, and consumes 4.8 mA current from a 1.2 V power supply.-
Keywords:
- complex filter,
- low-IF receiver,
- WiMAX,
- frequency tuning
-
References
[1] IEEE Computer Society. IEEE Std 802. 16TM-2004-Air Interface for Fixed Broadband Wireless Access Systems, New York, Oct. 2004[2] Jun D, Daisuke M, Yosuke O, et al. A fully integrated 2×1 dual-band direct-conversion mobile WiMAX transceiver with dual-mode fractional divider and noise-shaping transimpedance amplifier in 65 nm CMOS. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2010, 45:2774 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2010.2075295[3] Camus M, Butaye B, Garcia L, et al. A 5.4 mW/0.07 mm2 2.4 GHz front-end receiver in 90 nm CMOS for IEEE 802.15.4 WPAN standard. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2008, 43:1372 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2008.922720[4] Liu S L, Ma H P, Shi Y. A low power Gm-C filter with on-chip automatic tuning for a WLAN transceiver. Journal of Semiconductors, 2010, 31:065008 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/31/6/065008[5] Hesam A A, Erik J P, Edgar S S. A 1-V +31 dBm ⅡP3, reconfigurable, continuously tunable, power-adjustable active-RC LPF. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2009, 44:495 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2008.2011037[6] Pan W G, Ma C Y, Gan Y B, et al. A reconfigurable OTA-C baseband filter with wide digital tuning for GSNN receivers. Journal of Semiconductors, 2010, 31:095006 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/31/9/095006[7] D'Amico S, Giannini V, Baschirotto A. A 4th-order active-Gm-RC reconfigurable (UMTS/WLAN) filter. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2006, 41:1630 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2006.873676[8] Cheng X, Zhong L G, Yang H G, et al. A pseudo differential Gm-C complex filter with frequency tuning for IEEE802.15.4 applications. Journal of Semiconductors, 2011, 32:075005 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/32/7/075005[9] Tajali A, Leblebici Y. Low-power and widely tunable linearized biquadratic low-pass transconductor-C filter. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Ⅱ:Express Briefs, 2011, 58:159 doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2011.2111530[10] Xu Y, Chi B Y, Yu X B, et al. Power-scalable, complex bandpass/low-pass filter with I/Q imbalance calibration for a multimode GSNN receiver. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Ⅱ:Express Briefs, 2012, 59:30 doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2011.2177700 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: