| Citation: |
Zhenxing Yu, Jun Feng. An ultra-broadband distributed passive gate-pumped mixer in 0.18 μm CMOS[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2013, 34(8): 085005. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/8/085005
****
Z X Yu, J Feng. An ultra-broadband distributed passive gate-pumped mixer in 0.18 μm CMOS[J]. J. Semicond., 2013, 34(8): 085005. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/8/085005.
|
An ultra-broadband distributed passive gate-pumped mixer in 0.18 μm CMOS
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/8/085005
More Information
-
Abstract
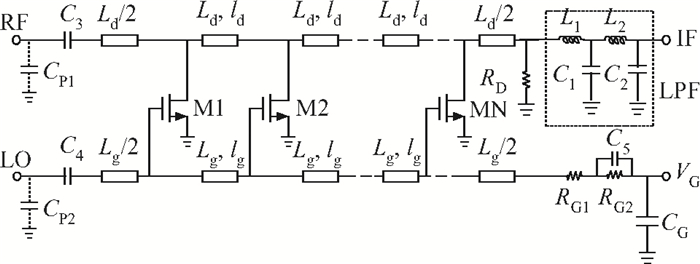
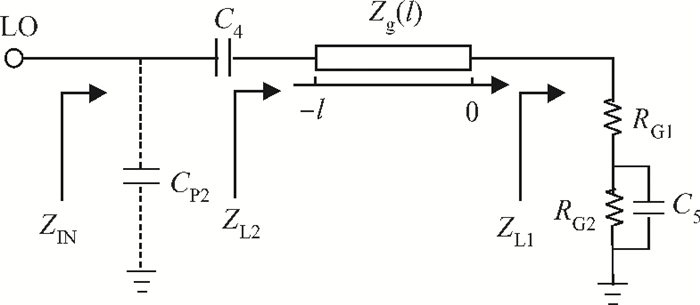
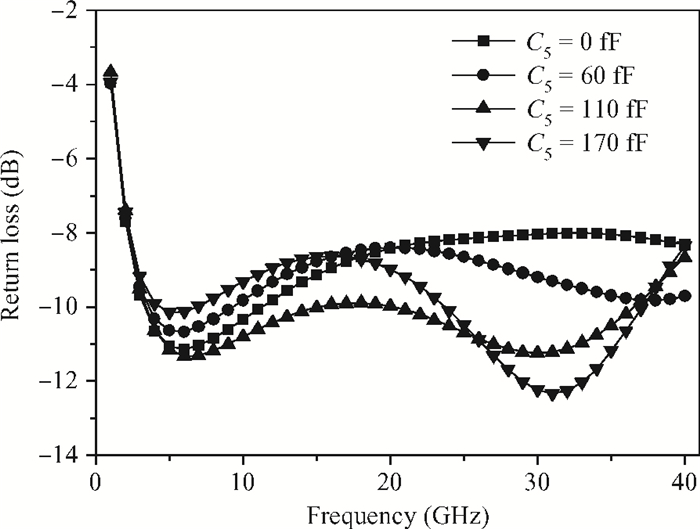
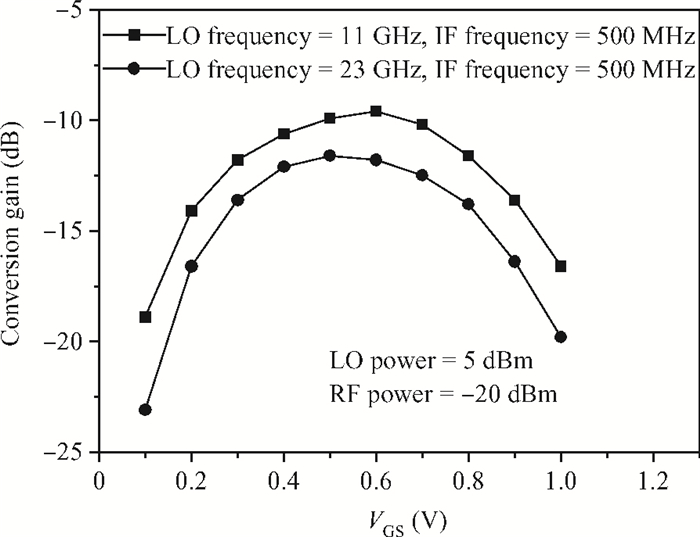
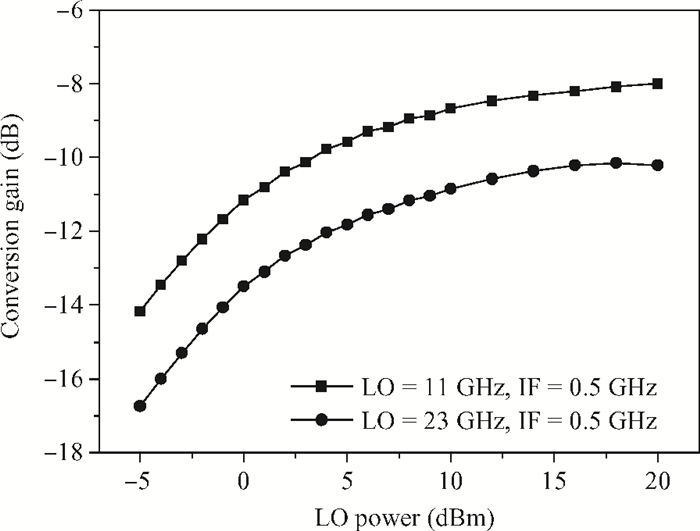
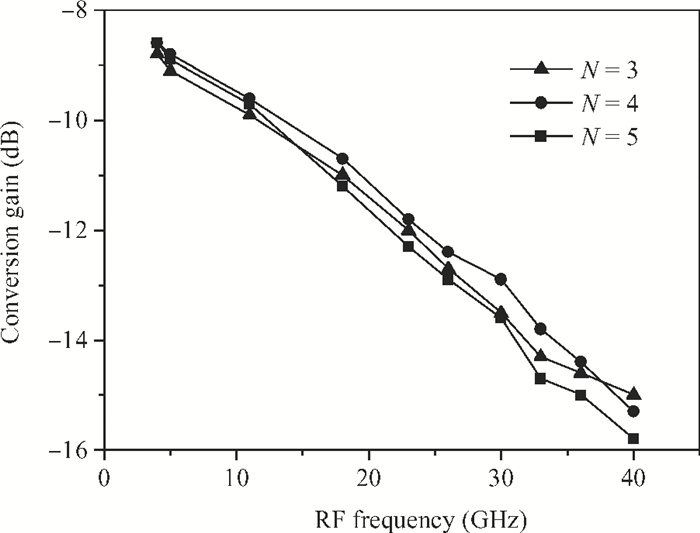
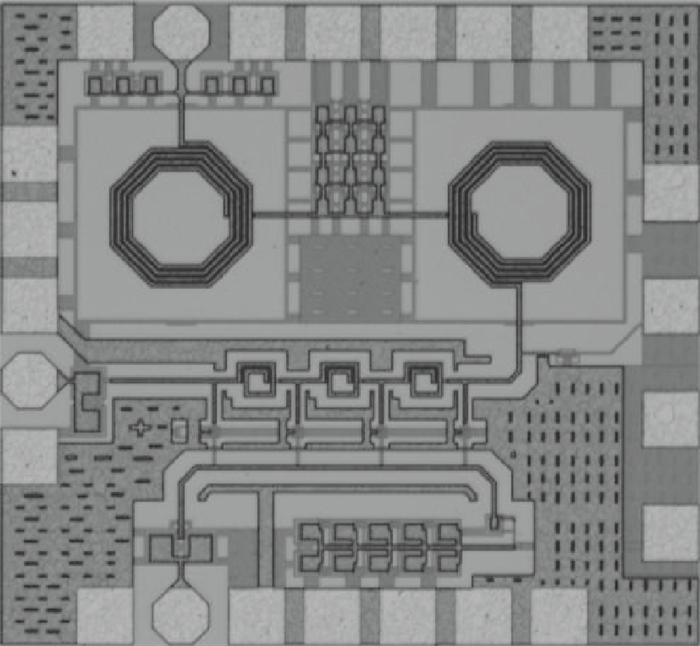
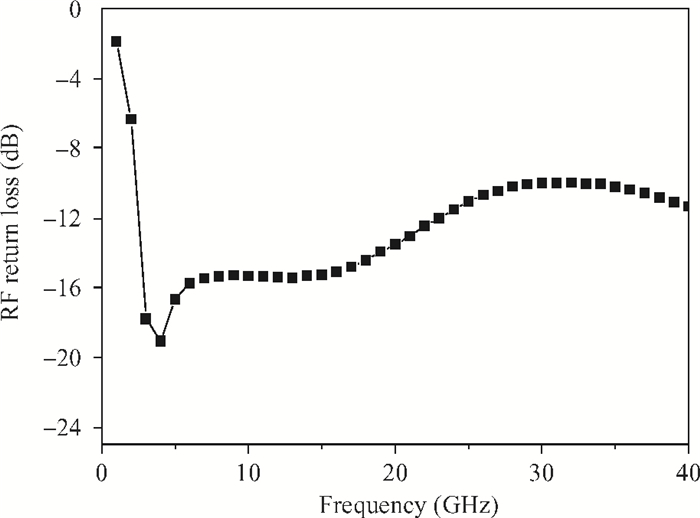
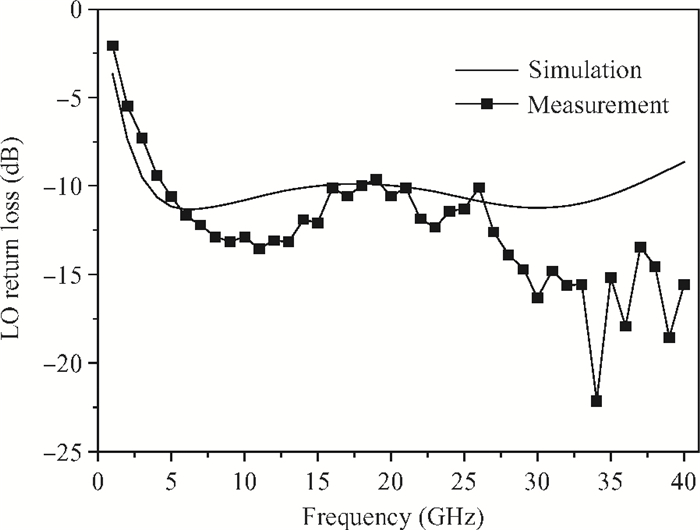
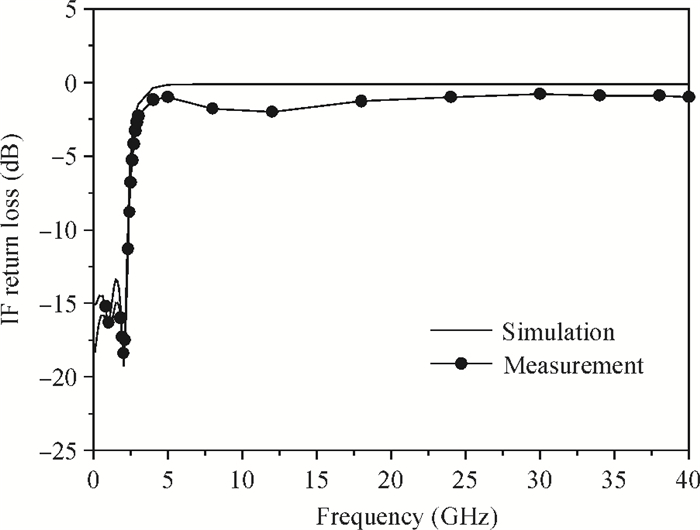
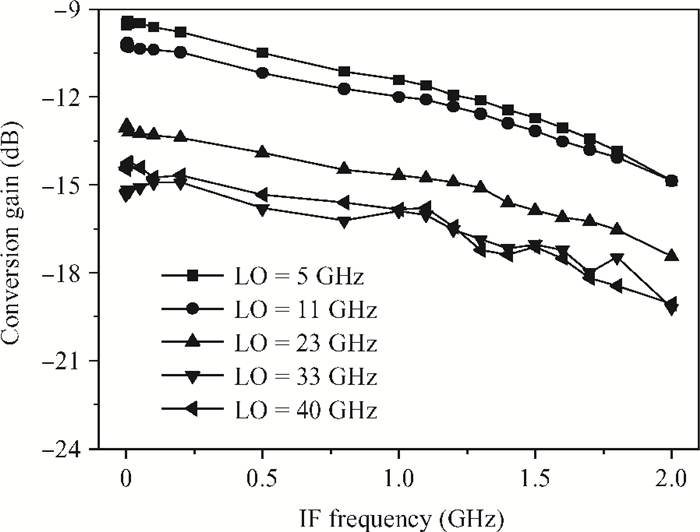
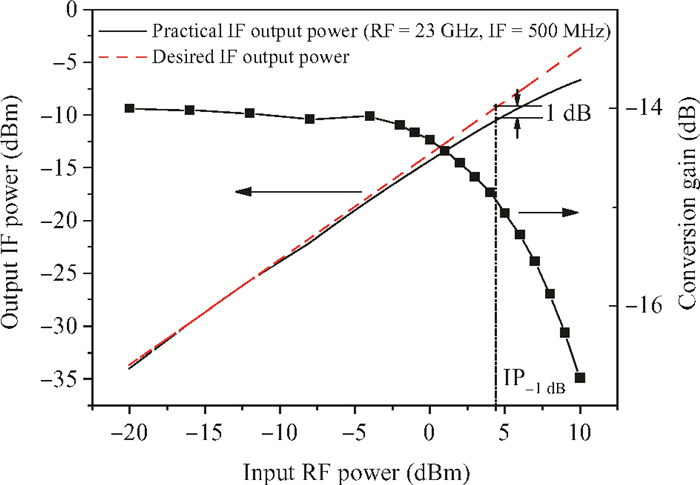
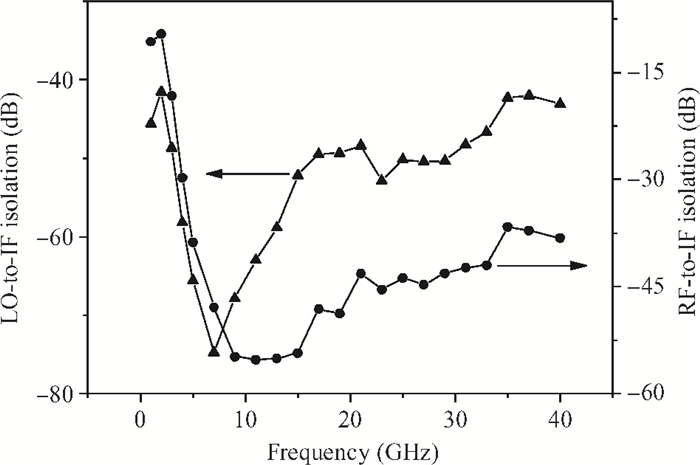
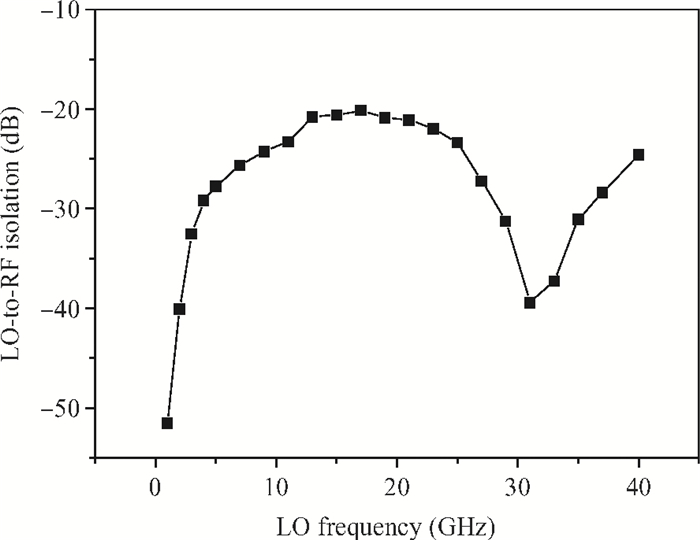
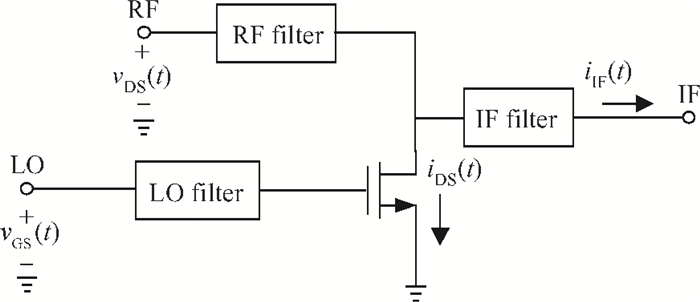
A broadband distributed passive gate-pumped mixer (DPGM) using standard 0.18 μm CMOS technology is presented. By employing distributed topology, the mixer can operate at a wide frequency range. In addition, a fourth-order low pass filter is applied to improve the port-to-port isolation. This paper also analyzes the impedance match and conversion loss of the mixer, which consumes zero dc power and exhibits a measured conversion loss of 9.4-17 dB from 3 to 40 GHz with a compact size of 0.78 mm2. The input referred 1 dB compression point is higher than 4 dBm at a fixed IF frequency of 500 MHz and RF frequency of 23 GHz, and the measured RF-to-LO, RF-to-IF and LO-to-IF isolations are better than 21, 38 and 45 dB, respectively. The mixer is suitable for WLAN, UWB, Wi-Max, automotive radar systems and other millimeter-wave radio applications. -
References
[1] Wenger J. Auto-motive radar:status and perspectives. Compound Semiconductor Integrated Circuit Symposium, 2005:21 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/1531741/?reload=true&arnumber=1531741[2] Federal Communication Commission. $§$15. 252[3] Tsai J H. Design of 40-108-GHz low-power and high-speed CMOS up/down-conversion ring mixers for multi-standard MMW radio applications. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech, 2012, 60(3):670 doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2011.2178258[4] Tai J H. Design of 1.2-V broadband high data-rate MMW CMOS I/Q modulator and demodulator using modified Gilbert-cell mixer. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech, 2011, 59(5):1350 doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2011.2116035[5] Bao M Q, Jacobsson H, Aspemyr L, et al. A 9-31GHz sub-harmonic passive mixer in 90 nm CMOS technology. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2006, 41(10):2257 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2006.881551[6] Lin S K, Kuo J L, Wang H. A 60 GHz sub-harmonic resistive FET mixer using 0.13μm CMOS technology. IEEE Microw Wireless Compon Lett, 2011, 21(10):562 doi: 10.1109/LMWC.2011.2165701[7] Tsai J H, Huang T W. 35-65 GHz CMOS broadband modulator and demodulator with sub-harmonic pumping for MMW wireless gigabit applications. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech, 2007, 55(10):2075 doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2007.905497[8] Yang H Y, Tsai J H, Wang C H, et al. Design and analysis of a 0.8-77.5 GHz ultra-broadband distributed drain mixer using 0.13μm CMOS technology. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech, 2009, 57(3):562 doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2009.2013299[9] Lin C H, Lin C M, Lai Y A, et al. A 26-38 GHz monolithic doubly balanced mixer. IEEE Microw Wireless Compon Lett, 2008, 18(9):623 doi: 10.1109/LMWC.2008.2002465[10] Lai Y A, Lin C M, Lin C H, et al. A new Ka-band doubly balanced mixer based on Lange coupler. IEEE Microw Wireless Compon Lett, 2008, 18(7):458 doi: 10.1109/LMWC.2008.925110[11] Ellinger F, Rodoni L C, Sialm G, et al. 30-40 GHz drain pumped passive down mixer MMIC fabricated on VLSI SOI CMOS technology. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech, 2004, 52(5):1382 doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2004.827004[12] Yang H Y, Tsai J H, Huang T W, et al. Analysis of a new 33-58-GHz doubly balanced drain mixer in 90-nm CMOS technology. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech, 2012, 60(4):1057 doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2012.2183609[13] Chen J H, Kuo C C, Hsin Y M, et al. A 15-50 GHz broadband resistive FET ring mixer using 0.18-μm CMOS technology. IEEE Microwave Symposium Digest, 2010:784 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: