| Citation: |
Xiaoyun Jia, Peng Feng, Shengguang Zhang, Nanjian Wu, Baiqin Zhao, Su Liu. An ultra-low-power area-efficient non-volatile memory in a 0.18 μm single-poly CMOS process for passive RFID tags[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2013, 34(8): 085004. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/8/085004
****
X Y Jia, P Feng, S G Zhang, N J Wu, B Q Zhao, S Liu. An ultra-low-power area-efficient non-volatile memory in a 0.18 μm single-poly CMOS process for passive RFID tags[J]. J. Semicond., 2013, 34(8): 085004. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/8/085004.
|
An ultra-low-power area-efficient non-volatile memory in a 0.18 μm single-poly CMOS process for passive RFID tags
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/8/085004
More Information
-
Abstract
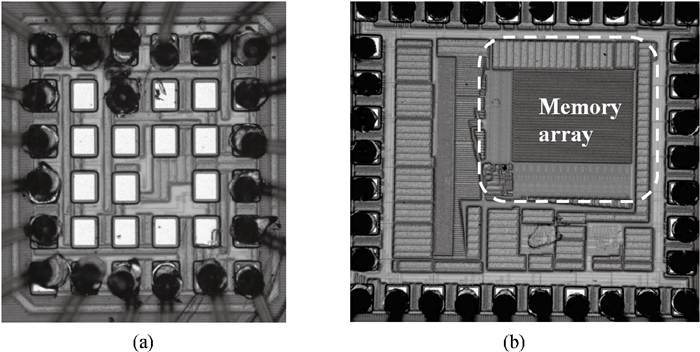
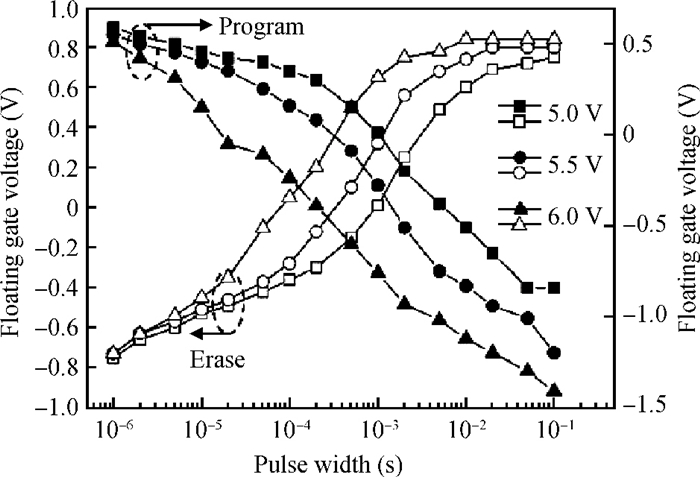
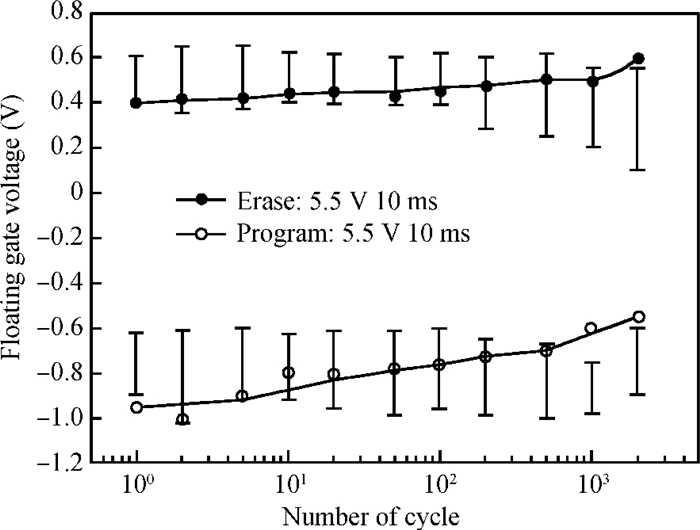
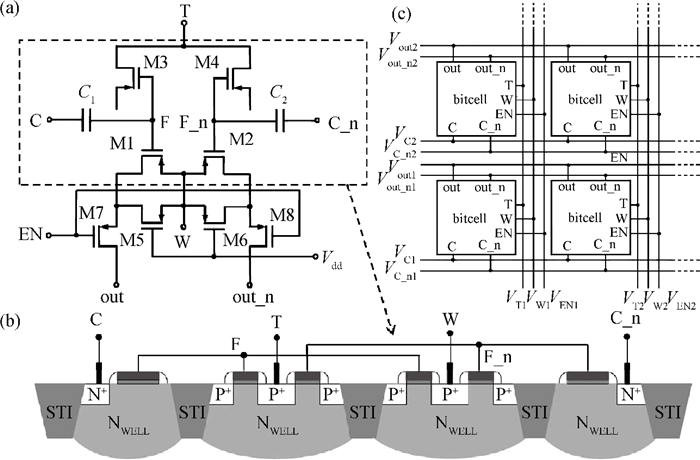
This paper presents an ultra-low-power area-efficient non-volatile memory (NVM) in a 0.18 μm single-poly standard CMOS process for passive radio frequency identification (RFID) tags. In the memory cell, a novel low-power operation method is proposed to realize bi-directional Fowler-Nordheim tunneling during write operation. Furthermore, the cell is designed with PMOS transistors and coupling capacitors to minimize its area. In order to improve its reliability, the cell consists of double floating gates to store the data, and the 1 kbit NVM was implemented in a 0.18 μm single-poly standard CMOS process. The area of the memory cell and 1 kbit memory array is 96 μm2 and 0.12 mm2, respectively. The measured results indicate that the program/erase voltage ranges from 5 to 6 V. The power consumption of the read/write operation is 0.19 μW/0.69 μW at a read/write rate of (268 kb/s)/(3.0 kb/s).-
Keywords:
- non-volatile memory,
- ultra-low-power,
- area-efficient,
- CMOS,
- RFID
-
References
[1] Finkenzeller K. RFID handbook:fundamentals and applications in contactless smart cards, radio frequency identification and near-field communication identification. United Kingdom:John Wiley & Sons, 2010 http://ci.nii.ac.jp/ncid/BB02892073[2] Feng Peng, Zhang Qi, Wu Nanjian. A passive UHF RFID tag chip with a dual-resolution temperature sensor in a 0.18μm standard CMOS process. Journal of Semiconductors, 2011, 32:115013 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/32/11/115013[3] Wang Yaowen, Guang Jun, Mao Wei, et al. Design of a passive UHF RFID tag for the ISO18000-6C protocol. Journal of Semiconductors, 2011, 32:055009 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/32/5/055009[4] Yin J, Yi J, Law M K, et al. A system-on-chip EPC Gen-2 passive UHF RFID tag with embedded temperature sensor. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2010, 45:2404 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/5593894/[5] Ohsaki K, Asamoto N, Takagaki S. A single poly EEPROM cell structure for use in standard CMOS processes. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 1994, 29:311 doi: 10.1109/4.278354[6] Raszka J, Advani M, Tiwari V, et al. Embedded flash memory for security applications in a 0.13μm CMOS logic process. IEEE ISSCC Dig Tech Papers, 2004, 1:46[7] Pan L, Luo X, Yan Y, et al. Pure logic CMOS based embedded non-volatile random access memory for low power RFID application. Custom Integrated Circuits Conference, 2008:197 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/4672057/keywords[8] Feng P, Li Y, Wu N. An ultra low power non-volatile memory in standard CMOS process for passive RFID tags. Custom Integrated Circuits Conference, 2009:713 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/5280734/[9] Zhao D, Yan N, Xu W, et al. A low power, single poly, non-volatile memory for passive RFID tags. Journal of Semiconductors, 2008, 29:1 http://www.jos.ac.cn/bdtxbcn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=07070303&flag=1[10] Pikhay E, Dayan V, Roizin Y, et al. A low-cost low-power non-volatile memory for RFID applications. IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), 2012:1827 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6271623/ -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: