| Citation: |
Zheng Gong, Xueqing Hu, Jun Yan, Yin Shi. A 1.2 V dual-channel 10 bit pipeline ADC in 55 nm CMOS for WLAN receivers[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2013, 34(9): 095004. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/9/095004
****
Z Gong, X Q Hu, J Yan, Y Shi. A 1.2 V dual-channel 10 bit pipeline ADC in 55 nm CMOS for WLAN receivers[J]. J. Semicond., 2013, 34(9): 095004. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/9/095004.
|
A 1.2 V dual-channel 10 bit pipeline ADC in 55 nm CMOS for WLAN receivers
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/9/095004
More Information
-
Abstract
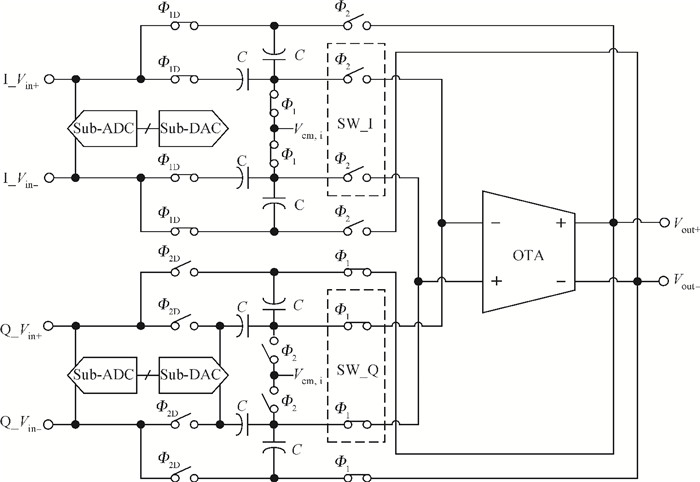
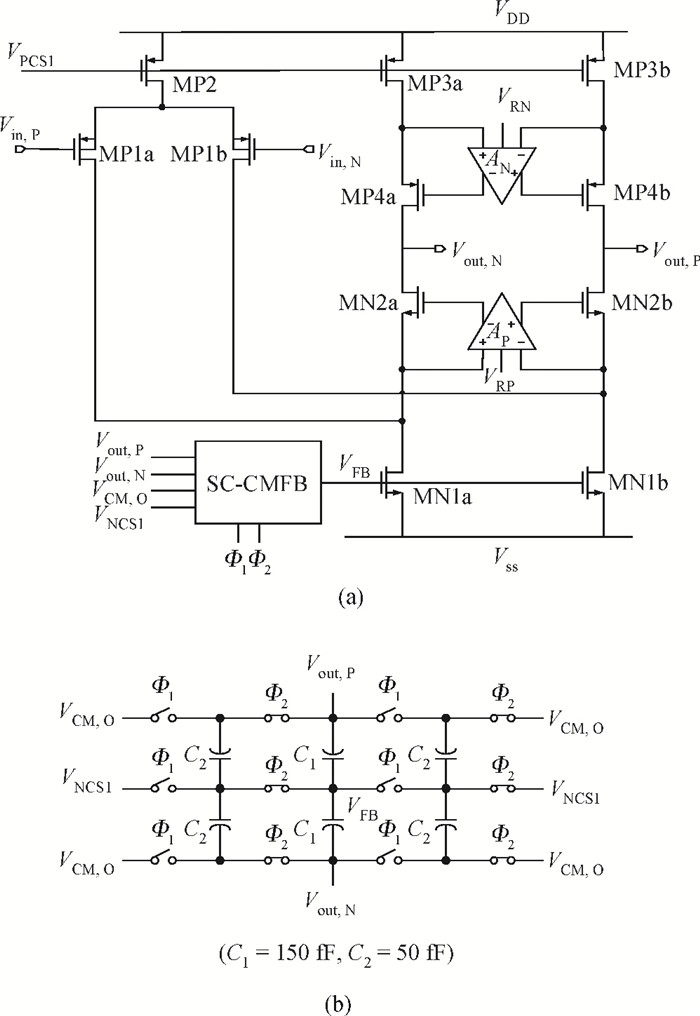
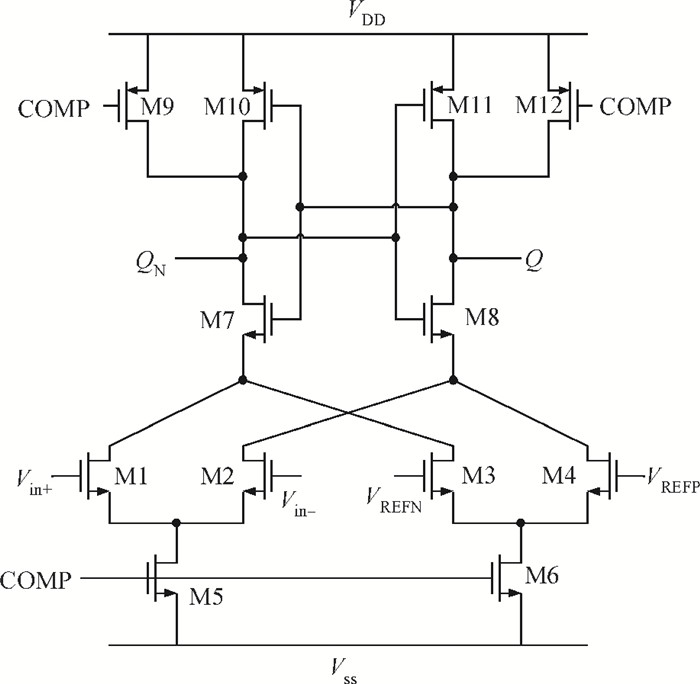
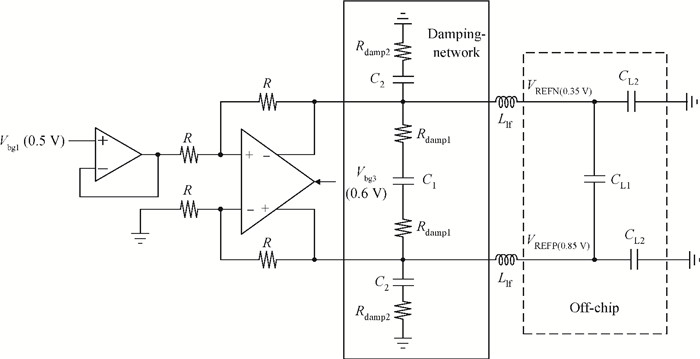
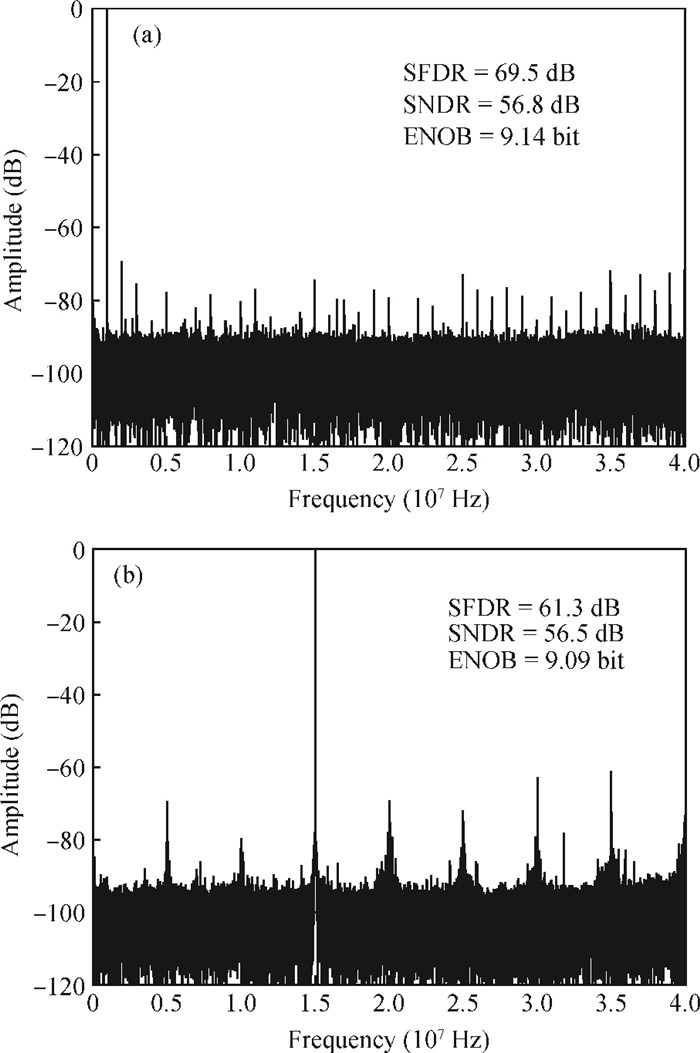
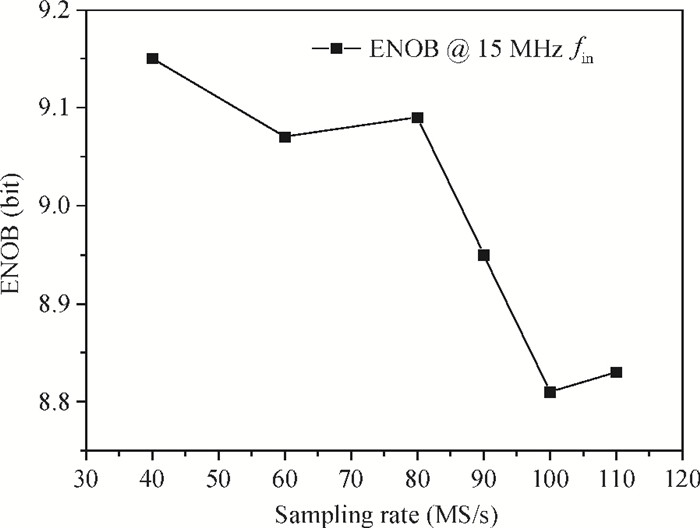
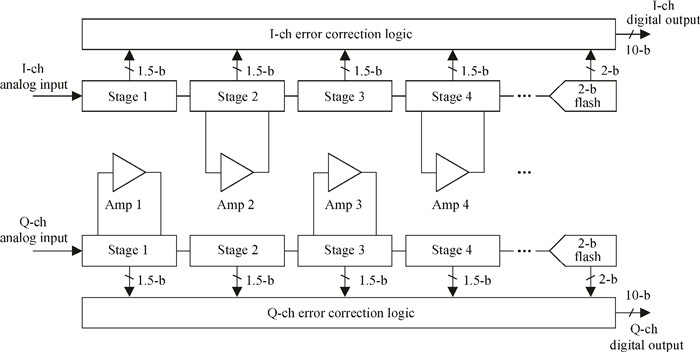
A power-efficient technique for pipeline analog-to-digital converters (ADCs) is proposed. By sharing amplifiers between I/Q channels, the power dissipation of the ADCs is reduced by almost one-half compared to conventional topologies, which makes this technique suitable for low-power direct-conversion WLAN receivers. A dual-channel ADC test chip is fabricated in 55 nm CMOS technology. The 10 bit ADC with on-chip reference generators dissipates 19.2 mW per channel from a 1.2 V supply. At an 80 MS/s sample rate, the measured spurious-free dynamic range, signal-to-noise and distortion ratio, and corresponding effective number of bits are 69.5 dB, 56.8 dB and 9.14 bits with a 1 MHz input frequency (fin), and 61.3 dB, 56.5 dB and 9.09 bits with a 15 MHz fin, respectively. The active area is 1.01×0.77 mm2.-
Keywords:
- ADC,
- amplifier sharing,
- I/Q amplifier sharing,
- WLAN receiver,
- reference buffer
-
References
[1] Bult K, Geelen G J G M. A fast-settling CMOS opamp for SC circuits with 90-dB DC gain. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 1990, 25(6):1379 doi: 10.1109/4.62165[2] Sumanen L, Waltari M, Halonen K. A mismatch insensitive CMOS dynamic comparator for pipeline A/D converters. The 7th IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Circuits and Systems, 2000, 1(12):32 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/911478/?arnumber=911478&contentType=Conference%20Publications[3] Cline D, Gray P. A power optimized 13-b 5-Msamples/s pipelined analog-digital converter in 1.2μm CMOS. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 1996, 31(3):294 doi: 10.1109/4.494191[4] Min B M, Kim P, Bowman F W, et al. A 69-mW 10-bit 80-MSample/s pipelined CMOS ADC. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2003, 38(12):2031 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2003.819166[5] Kurose D, Ito T, Ueno T, et al. 55-mW 200-MSPS 10-bit pipeline ADCs for wireless receivers. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2006, 41(7):1589 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2006.873888[6] Chen Zhenhai, Huang Songren, Zhang Hong, et al. A 27-mW 10-bit 125-MSPS charge domain pipelined ADC with a PVT insensitive boosted charge transfer circuit. Journal of Semiconductors, 2013, 34(3):035009 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/3/035009[7] Ye Mao, Zhou Yumei, Wu Bin, et al. An optimized analog to digital converter for WLAN analog front end. Journal of Semiconductors, 2012, 33(4):045008 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/33/4/045008[8] Miyazaki D, Kawahito S, Furata M. 10-b 30-MS/s low-power pipelined CMOS A/D converter using a pseudodifferential architecture. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2003, 38(2):269[9] Murmann B, Boser B E. A 12 b 75 MS/s pipelined ADC using open-loop residue amplification. IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, 2003:328 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/1234320/ -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: