| Citation: |
Nan Qi, Fan Chen, Lingwei Zhang, Xiaoman Wang, Baoyong Chi. A reconfigurable multi-mode multi-band transmitter with integrated frequency synthesizer for short-range wireless communication[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2013, 34(9): 095008. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/9/095008
****
N Qi, F Chen, L W Zhang, X M Wang, B Y Chi. A reconfigurable multi-mode multi-band transmitter with integrated frequency synthesizer for short-range wireless communication[J]. J. Semicond., 2013, 34(9): 095008. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/9/095008.
|
A reconfigurable multi-mode multi-band transmitter with integrated frequency synthesizer for short-range wireless communication
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/9/095008
More Information
-
Abstract
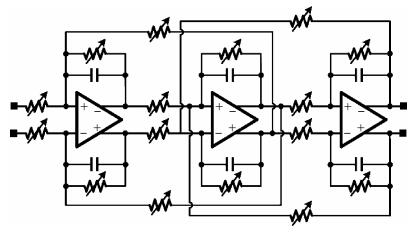
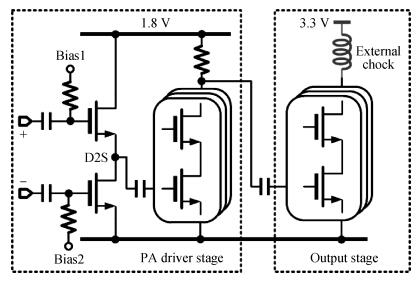
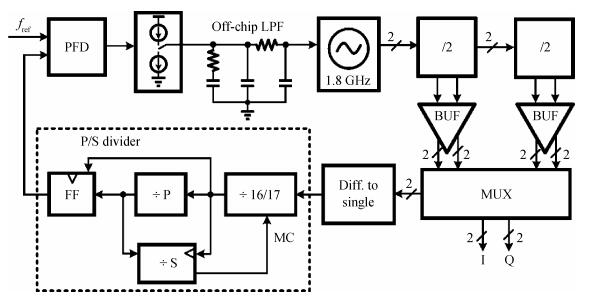
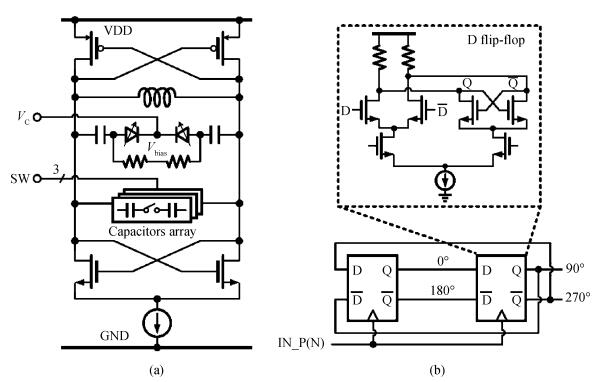
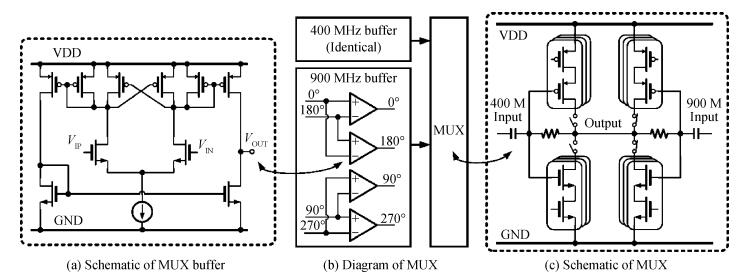
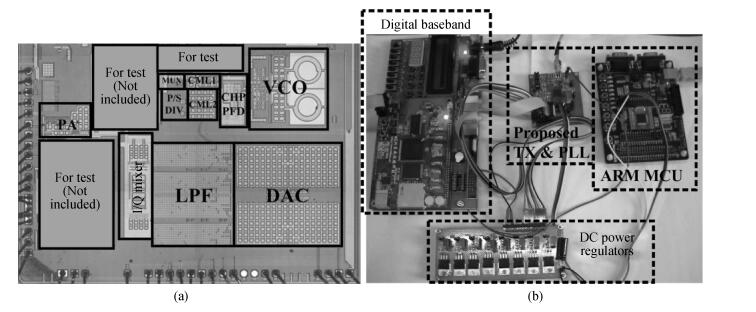
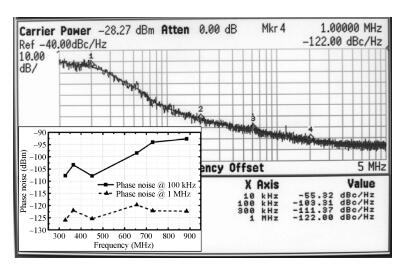
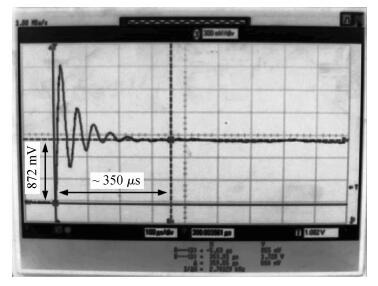
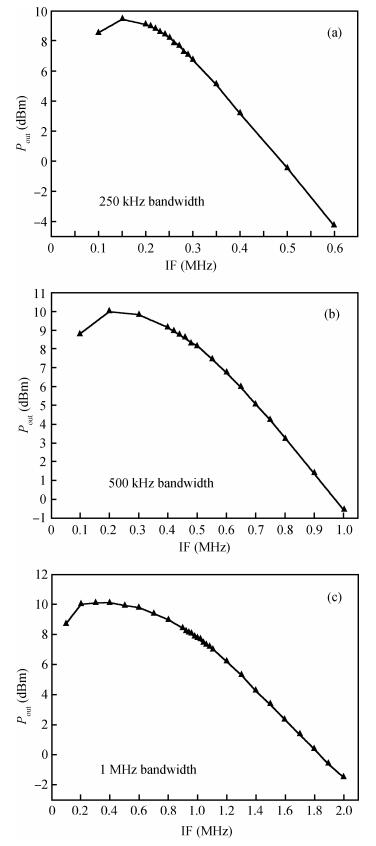
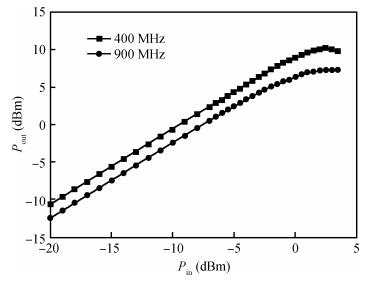
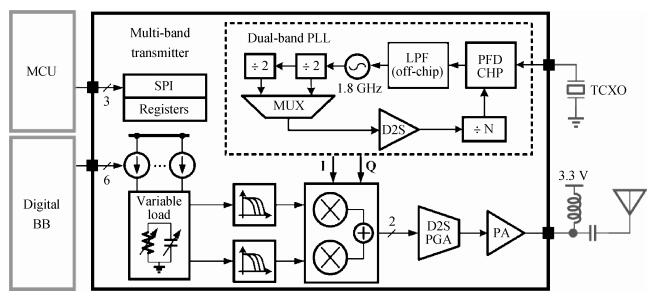
A reconfigurable multi-mode direct-conversion transmitter (TX) with integrated frequency synthesizer (FS) is presented. The TX as well as the FS is designed with a flexible architecture and frequency plan, which helps to support all the 433/868/915 MHz ISM band signals, with the reconfigurable bandwidth from 250 kHz to 2 MHz. In order to save power and chip area, only one 1.8 GHz VCO is adopted to cover the whole frequency range. All the operation modes can be regulated in real time by configuring the integrated register-bank through an SPI interface. Implemented in 180 nm CMOS, the FS achieves a frequency coverage of 320-460 MHz and 620-920 MHz. The lowest phase noise can be -107 dBc/Hz at a 100 kHz offset and -126 dBc/Hz at a 1 MHz offset. The transmitter features a +10.2 dBm peak output power with a +9.5 dBm 1-dB-compression point and 250 kHz/500 kHz/1 MHz/2 MHz reconfigurable signal bandwidth.-
Keywords:
- transmitter,
- frequency synthesizer,
- multi-mode multi-band,
- reconfigurable,
- CMOS
-
References
[1] Wong A, Kathiresan G, Chan C, et al. A 1 V wireless transceiver for an ultra-low-power SoC for biotelemetry applications. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2008, 43(7):1511 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2008.923717[2] Quinlan P, Crowley P, Chanca M, et al. A multimode 0.3-200-kb/s transceiver for the 433/868/915-MHz bands in 0.25-μm CMOS. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2004, 39(12):2297 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2004.836330[3] Zhang Qi, Kuang Xiaofei, Wu Nanjian. An ultra-low-power RF transceiver for WBANs in medical applications. Journal of Semiconductors, 2011, 32(6):065008 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/32/6/065008[4] Peiris V, Arm C, Bories S, et al. A 1 V 433/868 MHz 25 kb/s-FSK 2 kb/s-OOK RF transceiver SoC in standard digital 0.18μm CMOS. IEEE ISSCC Dige Tec Papers, 2005, 48:258[5] Zhang Lingwei, Chi Baoyong, Qi Nan, et al. A lower power reconfigurable multi-band transceiver for short-range communication. Journal of Semiconductors, 2013, 34(3):035008 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/3/035008[6] Gu Qizheng. RF system design of transceivers for wireless communications. New York:Springer, 2005:350 http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=1941742[7] Singh U, Green M M. High-frequency CML clock dividers in 0.13-μm CMOS operating up to 38 GHz. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2005, 40(8):1658 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2005.852420[8] Kim S, Lepkowski W, Wilk S, et al. A low-power CMOS BFSK transceiver for health monitoring systems. IEEE Biomedical Circ Syst Conf, 2011:157 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6107751/keywords -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: