| Citation: |
Quanliang Li, Liyuan Liu, Ye Han, Zhongxiang Cao, Nanjian Wu. A 12-bit compact column-parallel SAR ADC with dynamic power control technique for high-speed CMOS image sensors[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2014, 35(10): 105008. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/10/105008
****
Q L Li, L Y Liu, Y Han, Z X Cao, N J Wu. A 12-bit compact column-parallel SAR ADC with dynamic power control technique for high-speed CMOS image sensors[J]. J. Semicond., 2014, 35(10): 105008. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/10/105008.
|
A 12-bit compact column-parallel SAR ADC with dynamic power control technique for high-speed CMOS image sensors
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/10/105008
More Information
-
Abstract
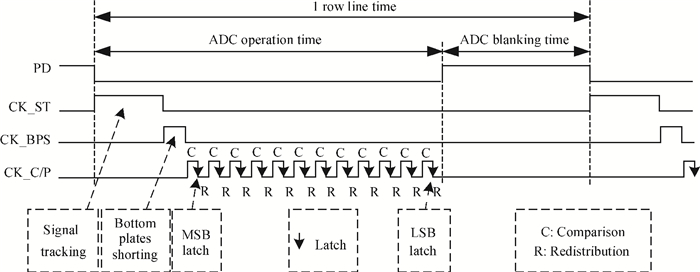
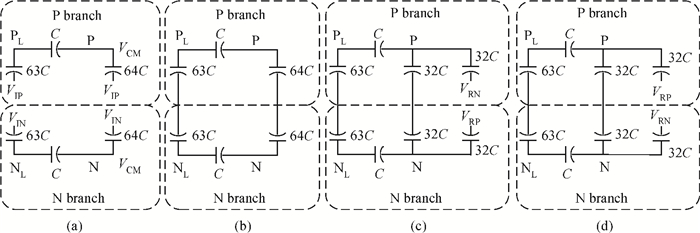
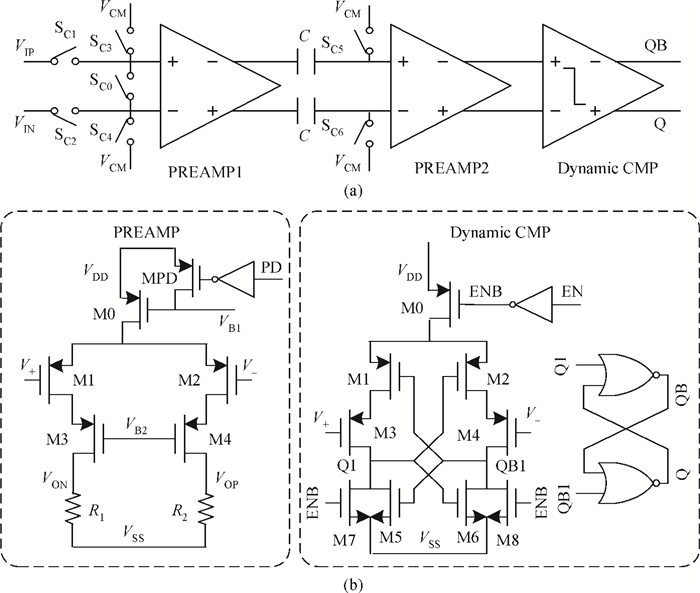
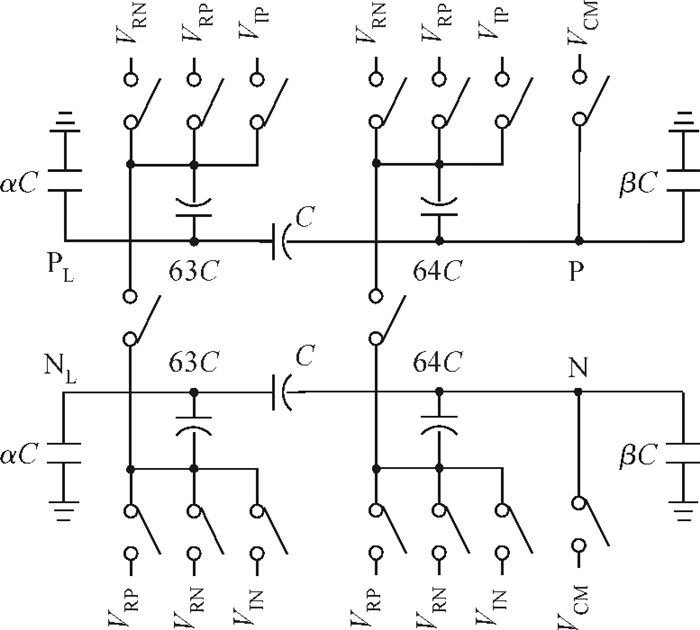
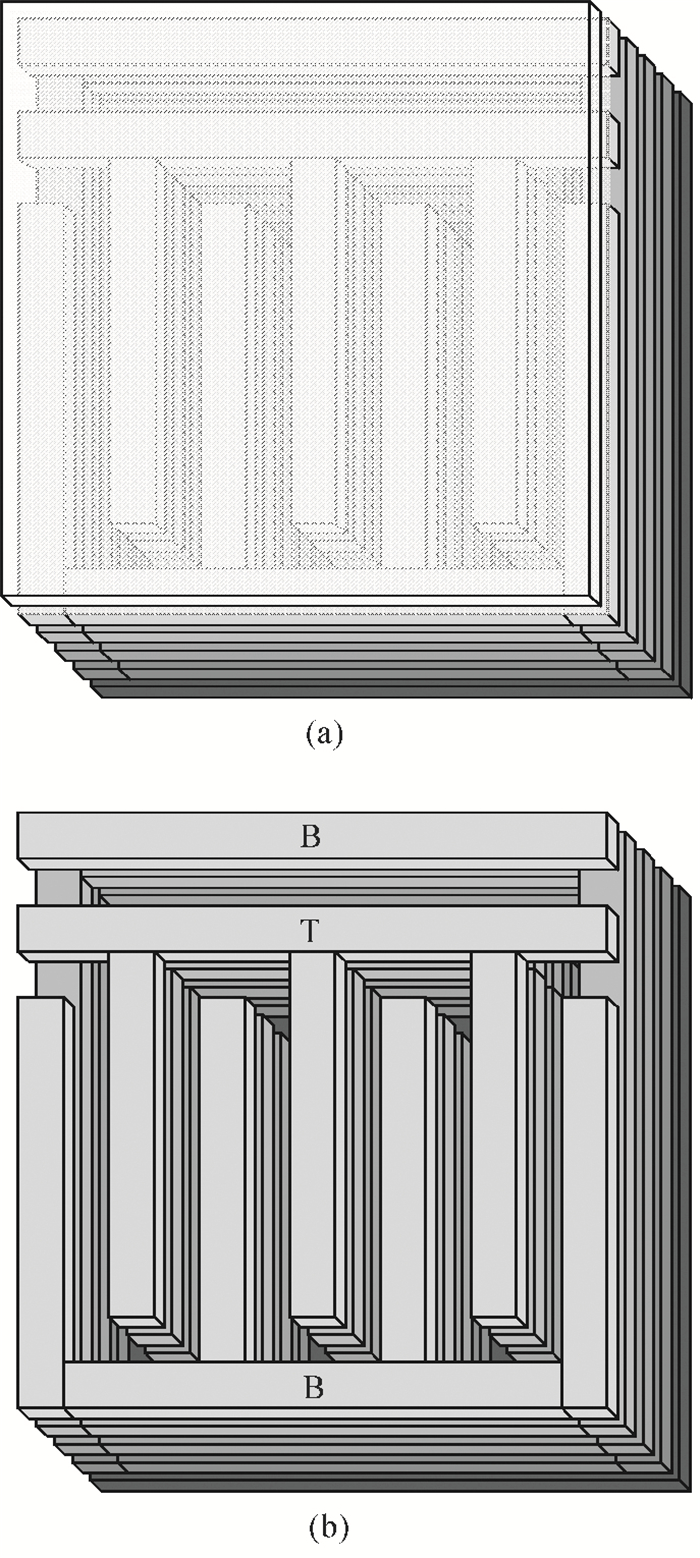
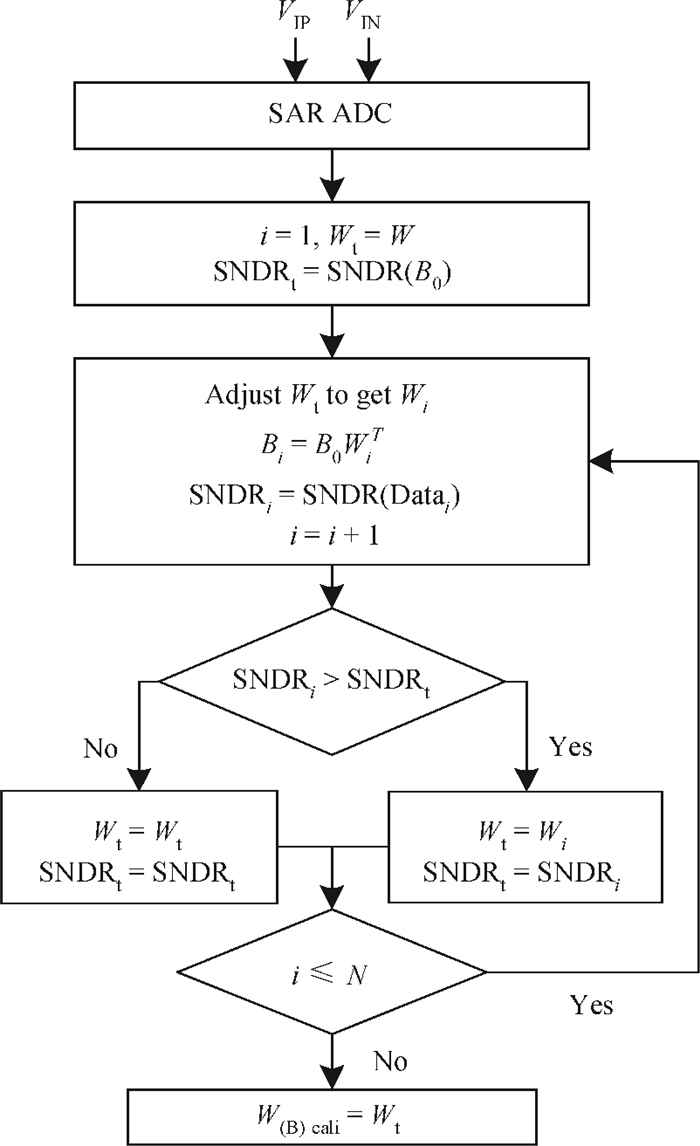
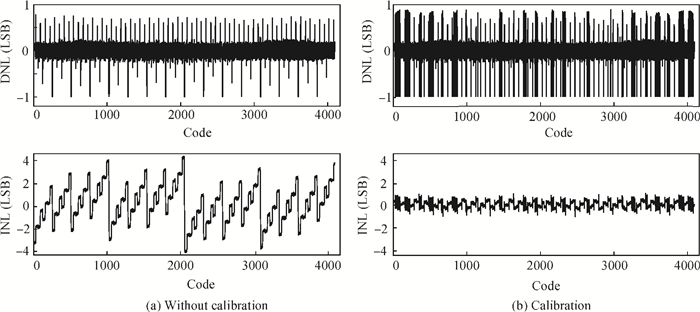
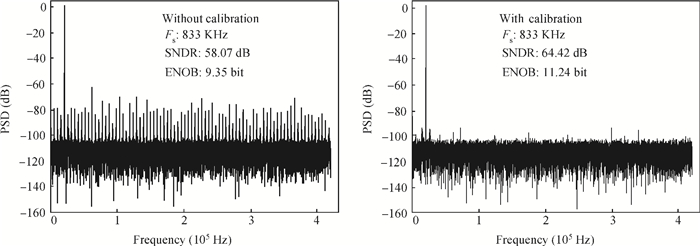
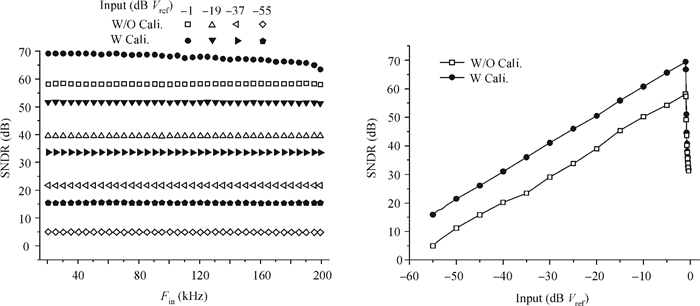
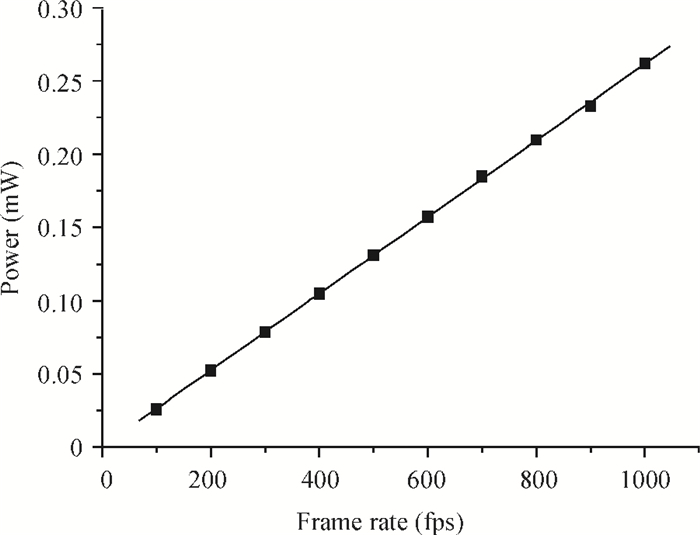
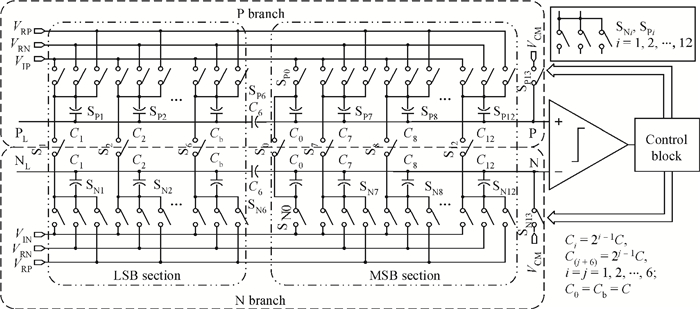
This paper presents a 12-bit column-parallel successive approximation register analog-to-digital converter (SAR ADC) for high-speed CMOS image sensors. A segmented binary-weighted switched capacitor digital-to-analog converter (CDAC) and a staggered structure MOM unit capacitor is used to reduce the ADC area and to make its layout fit double pixel pitches. An electrical field shielding layout method is proposed to eliminate the parasitic capacitance on the top plate of the unit capacitor. A dynamic power control technique is proposed to reduce the power consumption of a single channel during readout. An off-chip foreground digital calibration is adopted to compensate for the nonlinearity due to the mismatch of unit capacitors among the CDAC. The prototype SAR ADC is fabricated in a 0.18 μm 1P5M CIS process. A single SAR ADC occupies 20×2020 μm2. Sampling at 833 kS/s, the measured differential nonlinearity, integral nonlinearity and effective number of bits of SAR ADC with calibration are 0.9/-1 LSB, 1/-1.1 LSB and 11.24 bits, respectively; the power consumption is only 0.26 mW under a 1.8-V supply and decreases linearly as the frame rate decreases. -
References
[1] Bigas M, Cabruja E, Forest J, et al. Review of CMOS image sensors. Microelectron J, 2006, 37(5):433 doi: 10.1016/j.mejo.2005.07.002[2] Lee D, Cho K, Kim D, et al. Low-noise in-pixel comparing active pixel sensor using column-level single-slope ADC. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2008, 55(12):3383 doi: 10.1109/TED.2008.2006735[3] Lim S, Lee J, Kim D, et al. A high-speed CMOS image sensor with column-parallel two-step single-slope ADCs. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2009, 56(3):393 doi: 10.1109/TED.2008.2011846[4] Han Ye, Li Quanliang, Shi Cong, et al. A 10-bit column-parallel cyclic ADC for high-speed CMOS image sensors. Journal of Semiconductors, 2013, 34(8):085016 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/8/085016[5] Masanori F, Yukinari N, Toru I, et al. A high-speed, high-sensitivity digital CMOS image sensor with a global shutter and 12-bit column-parallel cyclic A/D converters. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2007, 42(4):766 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2007.891655[6] Krymski A I, Bock N E, Tu N, et al. A high-speed, 240-frames/s, 4.1-mpixel CMOS sensor. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2003, 50(1):130 doi: 10.1109/TED.2002.806961[7] Tsai S J, Chen Y C, Hsieh C C, et al. A column-parallel SA ADC with linearity calibration for CMOS imagers. IEEE Sensors, 2012: 1[8] Zhu Y, Chan C H, Seng-Pan U. A 10. 4-ENOB 120 MS/s SAR ADC with DAC linearity calibration in 90 nm CMOS. IEEE Asian Solid-State Circuits Conference, 2013: 69[9] Abusleme A, Dragone A, Haller G, et al. Mismatch of lateral field metal-oxide-metal capacitors in 180 nm CMOS process. Electron Lett, 2012, 48(5):286 doi: 10.1049/el.2011.3804[10] Aparicio R, Hajimiri A. Capacity limits and matching properties of integrated capacitors. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2002, 37(3):384 doi: 10.1109/4.987091[11] Chen Y, Zhu X, Tamura H, et al. Split capacitor DAC mismatch calibration in successive approximation ADC. IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference, 2009: 279[12] Li W, Wang T, Temes G C. Digital foreground calibration methods for SAR ADCs. IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, 2012: 1054 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: