| Citation: |
Liangbo Xie, Jiaxin Liu, Yao Wang, Guangjun Wen. A low-power CMOS smart temperature sensor for RFID application[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2014, 35(11): 115002. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/11/115002
****
L B Xie, J X Liu, Y Wang, G J Wen. A low-power CMOS smart temperature sensor for RFID application[J]. J. Semicond., 2014, 35(11): 115002. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/11/115002.
|
A low-power CMOS smart temperature sensor for RFID application
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/11/115002
More Information
-
Abstract
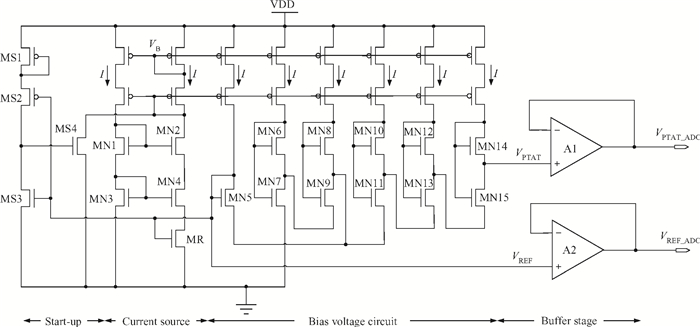
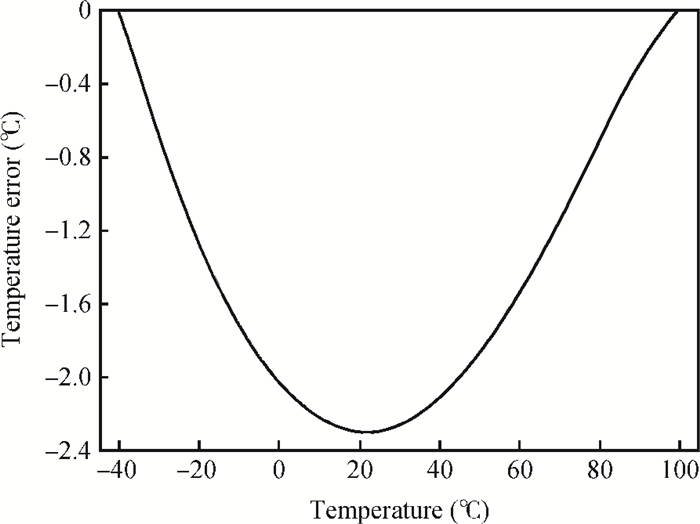
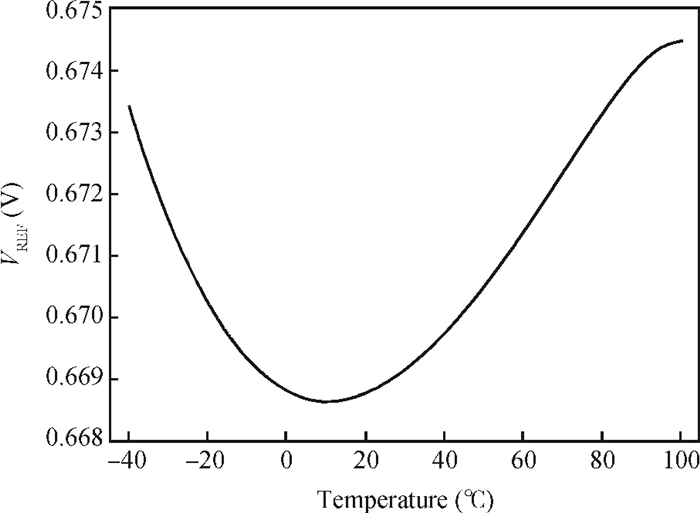
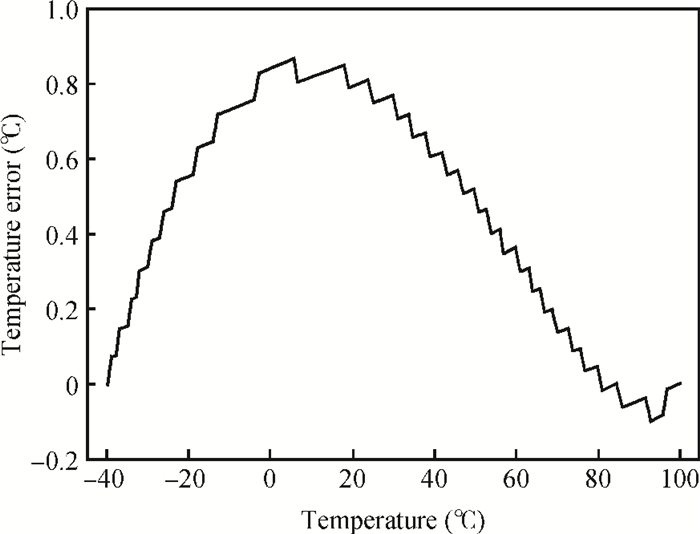
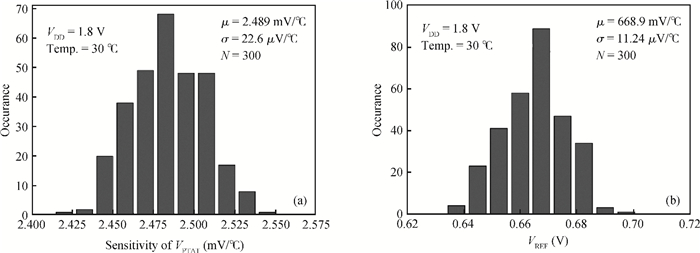
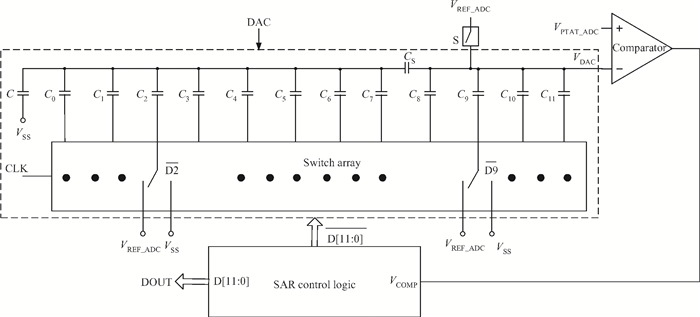
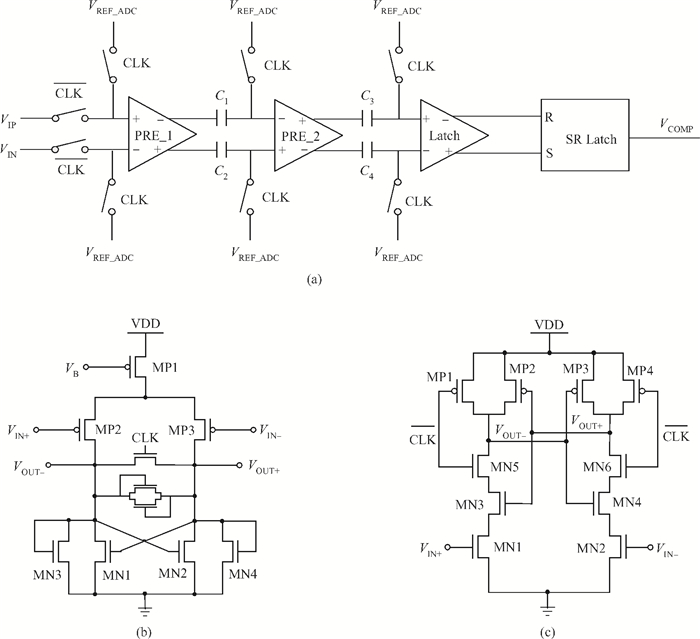
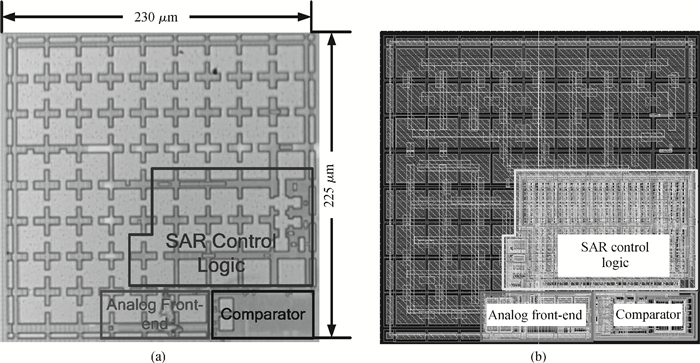
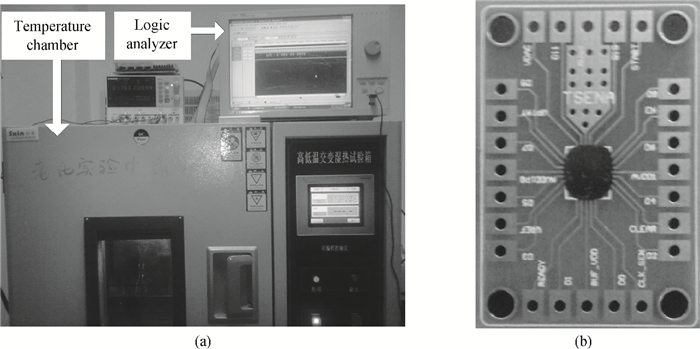
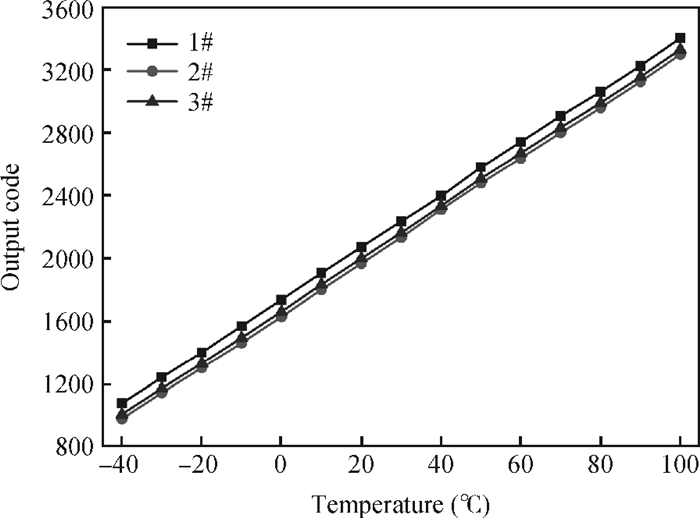
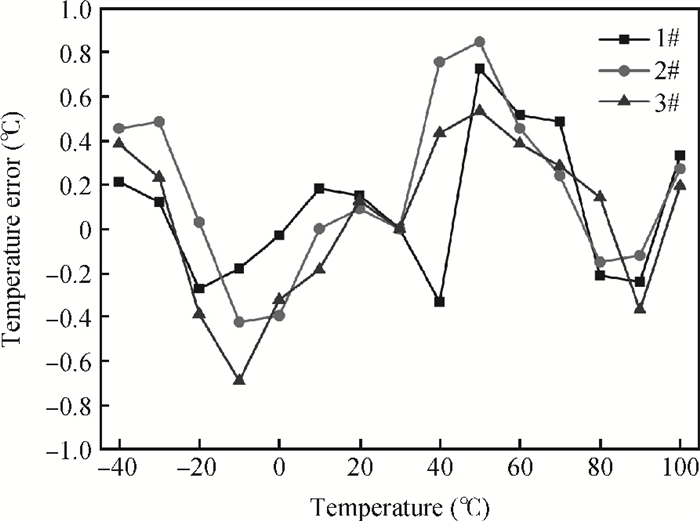
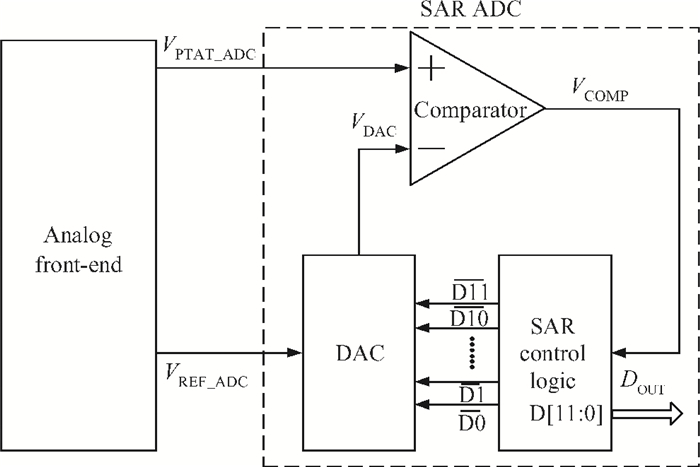
This paper presents the design and implement of a CMOS smart temperature sensor, which consists of a low power analog front-end and a 12-bit low-power successive approximation register (SAR) analog-to-digital converter (ADC). The analog front-end generates a proportional-to-absolute-temperature (PTAT) voltage with MOSFET circuits operating in the sub-threshold region. A reference voltage is also generated and optimized in order to minimize the temperature error and the 12-bit SAR ADC is used to digitize the PTAT voltage. Using 0.18 μm CMOS technology, measurement results show that the temperature error is -0.69/+0.85℃ after one-point calibration over a temperature range of -40 to 100℃. Under a conversion speed of 1K samples/s, the power consumption is only 2.02 μW while the chip area is 230×225 μm2, and it is suitable for RFID application.-
Keywords:
- CMOS,
- low power,
- temperature sensor,
- sub-threshold,
- SAR ADC
-
References
[1] Yin J, Yi J, Law M K, et al. A system-on-chip EPC Gen-2 passive UHF RFID tag with embedded temperature sensor. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2010, 45(11):2404 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/5593894/[2] Law M K, Bermak A, Luong H C. A sub-W embedded CMOS temperature sensor for RFID food monitoring application. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2010, 45(6):1246 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2010.2047456[3] Pertijs M A P, Niederkorn A, Ma X, et al. A CMOS smart temperature sensor with a 3σ inaccuracy of ±0.5℃ from -50℃ to 120℃. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2005, 40(2):454 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2004.841013[4] Sebastiano F, Breems L J, Makinwa K A A, et al. A 1.2-V 10-W NPN-based temperature sensor in 65-nm CMOS with an inaccuracy of 0.2℃ (3σ) from -70℃ to 125℃. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2010, 45(12):2591 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2010.2076610[5] Souri K, Chae Y, Makinwa K A A. A CMOS temperature sensor with a voltage-calibrated inaccuracy of 0.15℃ (3σ) from 55℃ to 125℃. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2013, 48(1):292 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2012.2214831[6] Feng Peng, Zhang Qi, Wu Nanjian. A passive UHF RFID tag chip with a dual-resolution temperature sensor in a 0.18μm standard CMOS process. Journal of Semiconductors, 2011, 32(11):115013 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/32/11/115013[7] Chen P, Chen C C, Tsai C C, et al. A time-to-digital-converter-based CMOS smart temperature sensor. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2005, 40(8):1642 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2005.852041[8] Chen P, Chen C C, Chen T K, et al. A time domain mixed-mode temperature sensor with digital set-point programming. IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference, 2006:821 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/icp.jsp?arnumber=4115079[9] Chen P, Chen C C, Peng Y H, et al. A time-domain SAR smart temperature sensor with curvature compensation and a 3σ inaccuracy of -0.4℃ +0.6℃ over a 0℃ to 90℃ range. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2010, 45(3):600 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2010.2040658[10] Sahafi A, Sobhi J, Koozehkanani Z D. Nano watt CMOS temperature sensor. Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing, 2013, 75(3):343 doi: 10.1007/s10470-013-0046-6[11] Ueno K, Hirose T, Asai T. A 300 nW, 15 ppm/℃, 20 ppm/V CMOS voltage reference circuit consisting of subthreshold MOSFETs. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2009, 44(7):2047 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2009.2021922 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: