| Citation: |
Yue Han, Shushan Qiao, Yong Hei. An all-digital synthesizable baseband for a delay-based LINC transmitter with reconfigurable resolution[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2014, 35(11): 115001. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/11/115001
****
Y Han, S S Qiao, Y Hei. An all-digital synthesizable baseband for a delay-based LINC transmitter with reconfigurable resolution[J]. J. Semicond., 2014, 35(11): 115001. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/11/115001.
|
An all-digital synthesizable baseband for a delay-based LINC transmitter with reconfigurable resolution
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/11/115001
More Information
-
Abstract
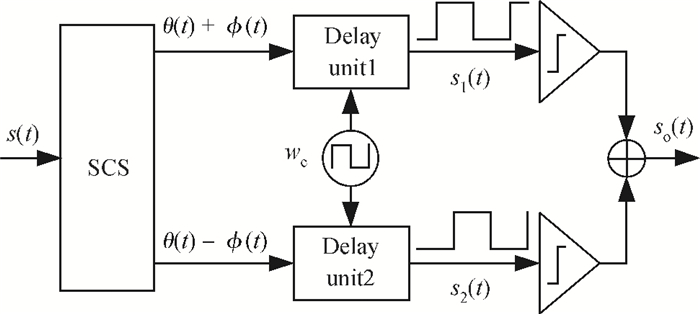
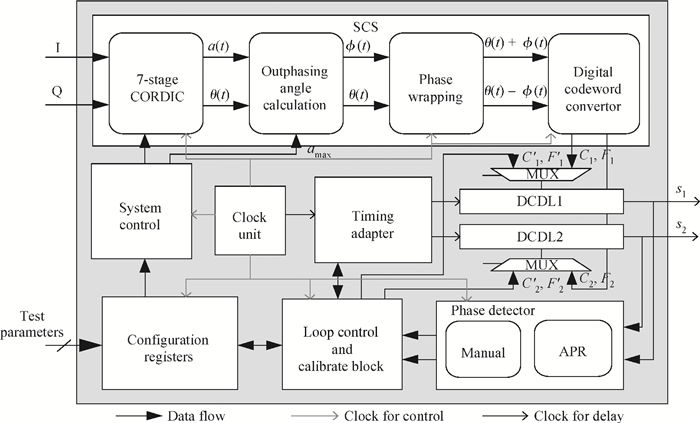
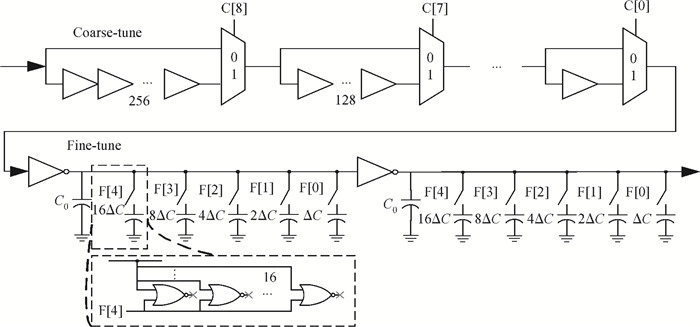
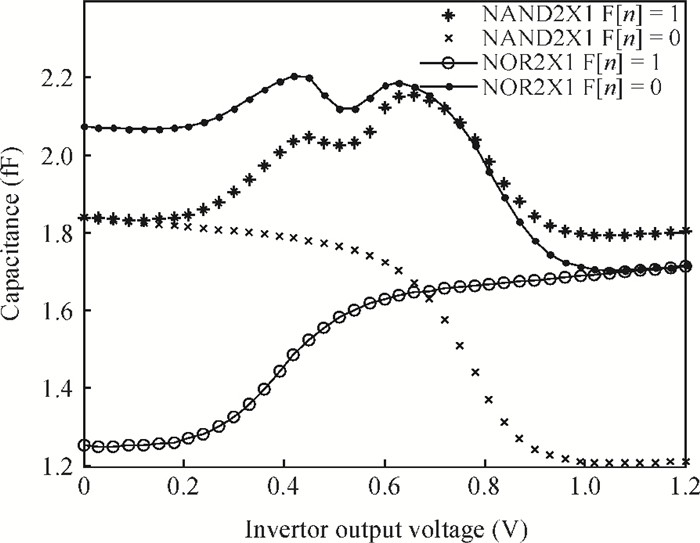
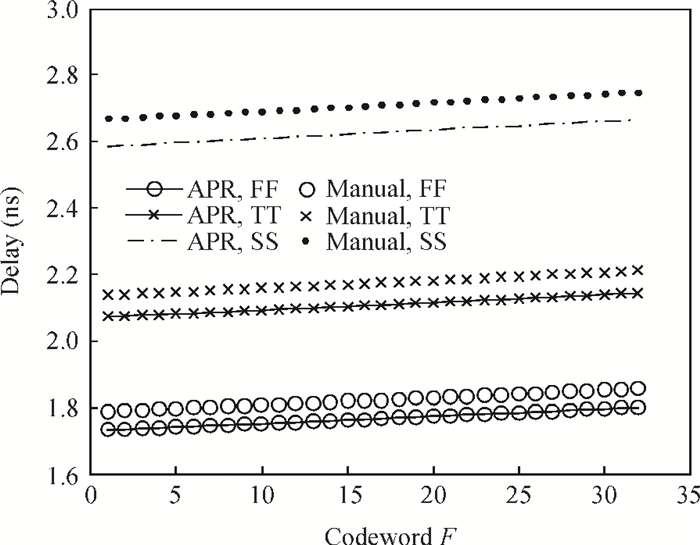
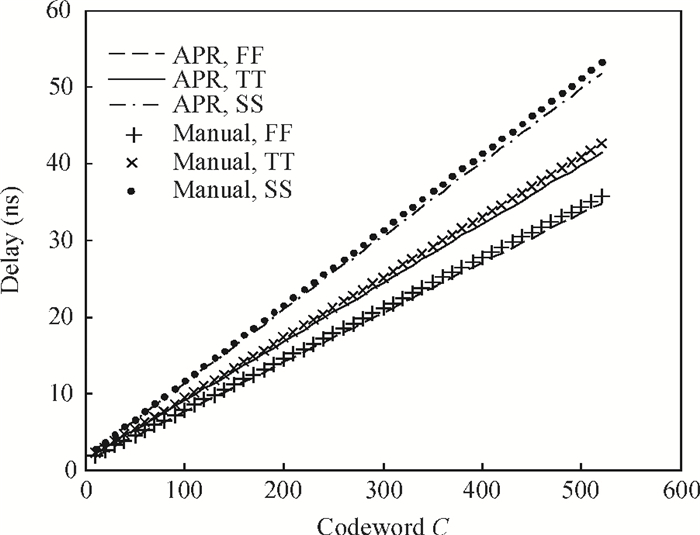
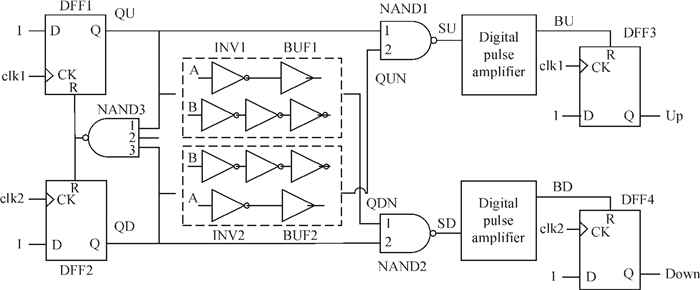
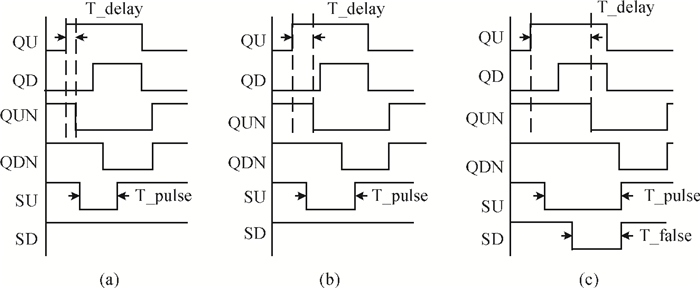
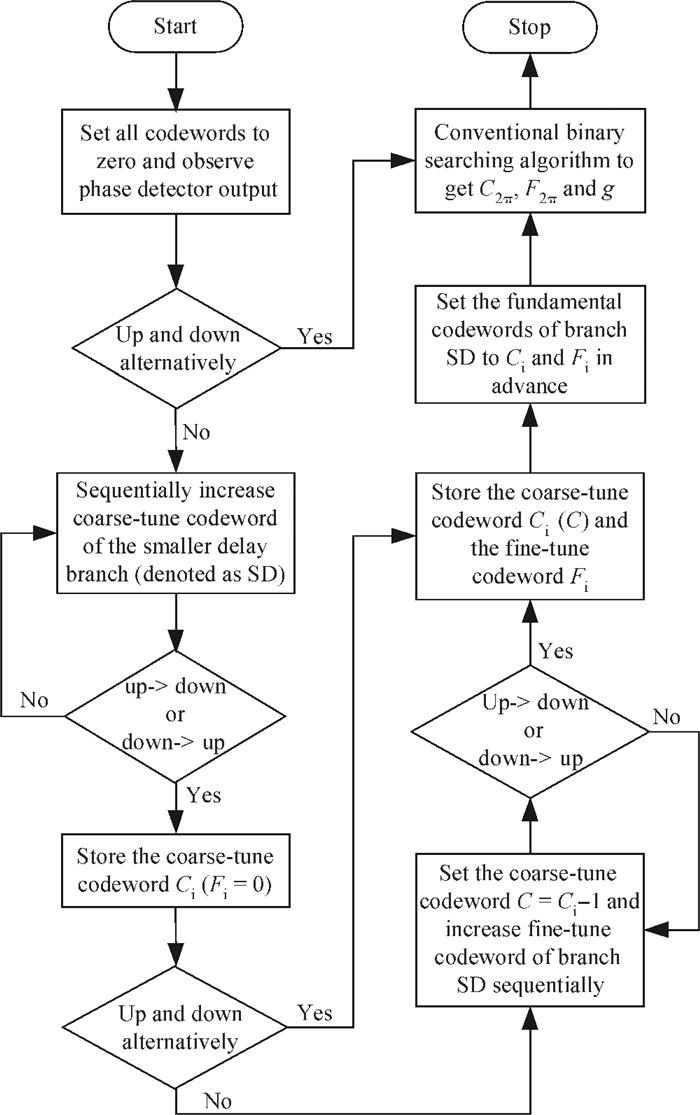
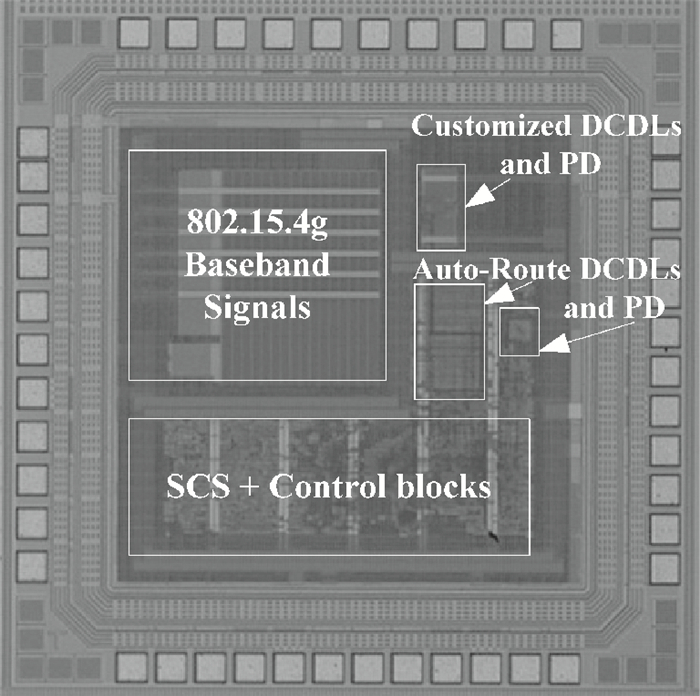
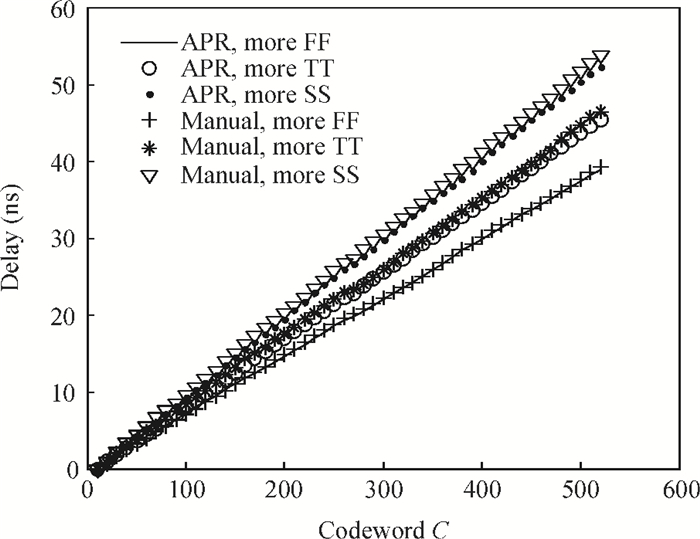
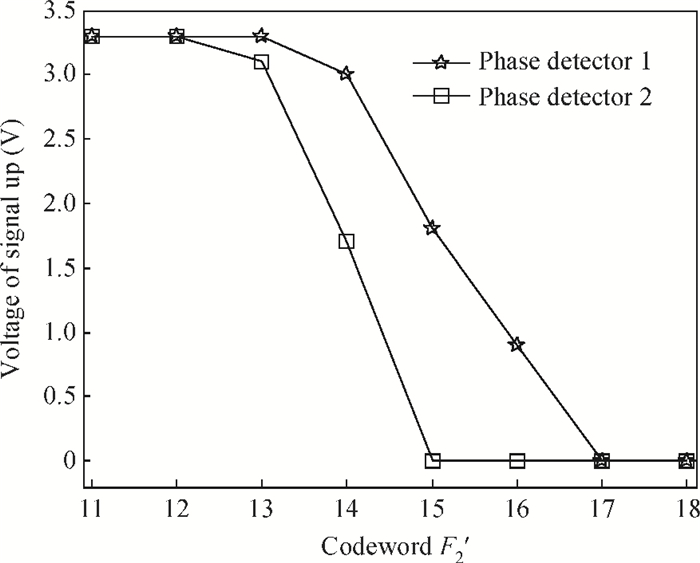
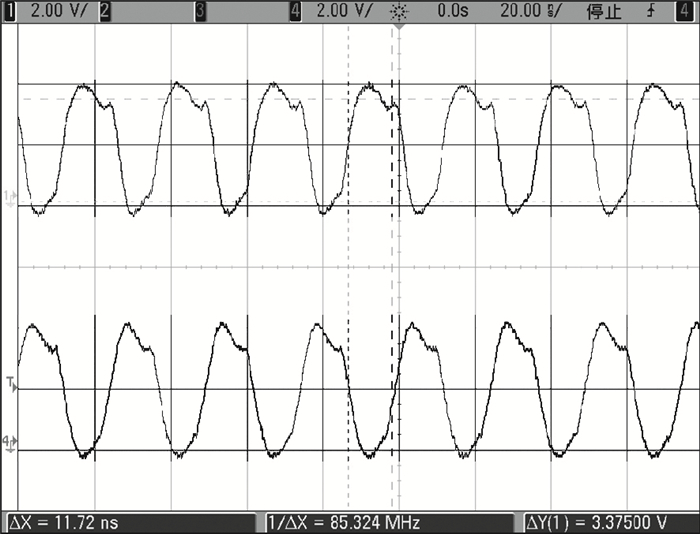
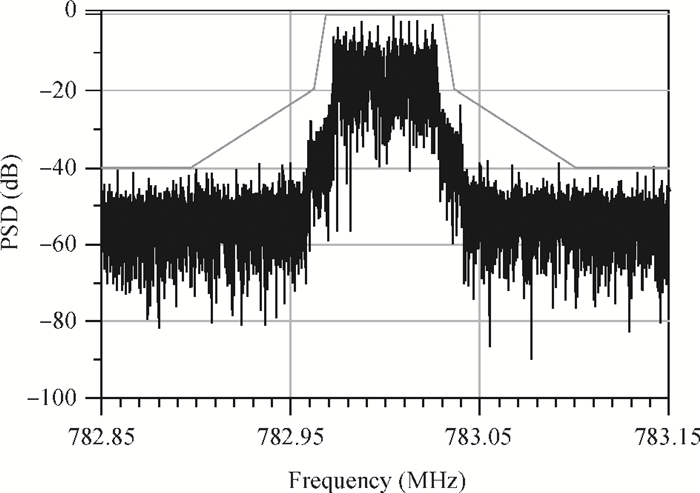
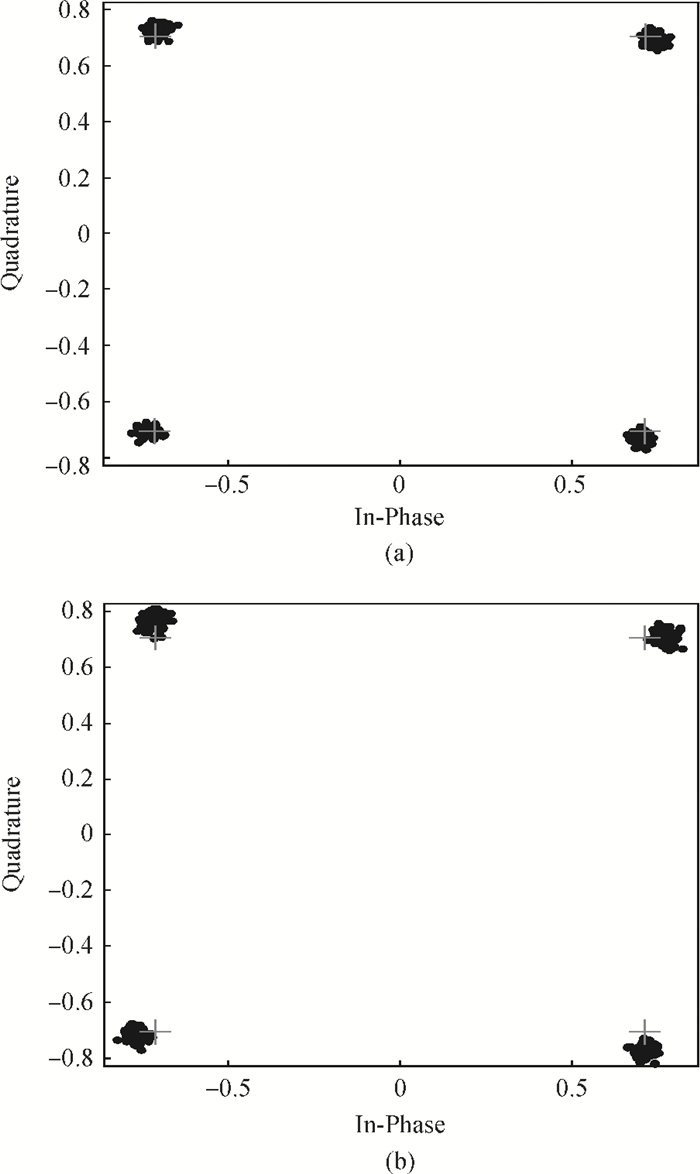
The linear amplification with nonlinear component transmitter is a promising solution to high efficiency and high linearity amplification for non-constant envelope signals. An all-digital synthesizable baseband for a delay-based LINC transmitter is implemented. This paper proposes a standard-cell based synthesizable methodology which can be applied in the ASIC process efficiently without performance degradation compared to the manual layout. A scheme to overcome the limited resolution of conventional phase detectors is proposed. It employs alternative phase detector structures to provide reconfigurability for higher resolution after fabricating, resulting in an 11 ps resolution improvement. Due to the PVT variation, an adaptive calibration scheme focusing on the inherent imbalance between two delay lines is depicted, which reveals an effective EVM enhancement of 5.37 dB. This baseband chip is implemented in 0.13 μm CMOS technology, and the transmitter with the baseband has an EVM of -28.96 dB and an ACPR of -29.51 dB, meeting the design requirement. -
References
[1] Tai W, Xu H T. Ashokeack-off power efficiency enhancement. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2012, 43(12):1646[2] Cui Jie, Chen Lei, Kang Chunlei, et al. A high-linearity InGaP/GaAs HBT power amplifier for IEEE 802.11a/n. Journal of Semiconductors, 2013, 34(6):065001 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/6/065001[3] Hur J, Kim H, Lee O, et al. Multi-level LINC transmitter with non-isolated power combiner. Electron Lett, 2013, 49(25):1624 doi: 10.1049/el.2013.3117[4] Cox D C. Linear amplification with nonlinear components. IEEE Trans Commun, 1974, COM-22(12):1942 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/abs_all.jsp?arnumber=1092141[5] Chireix H. High power outphasing modulation. Proc IRE, 1935, 23(11):1370 doi: 10.1109/JRPROC.1935.227299[6] Shi B, Sundström L. A 200-MHz IF BiCMOS signal component separator for linear LINC transmitters. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2000, 35(7):987 doi: 10.1109/4.848207[7] Shi B, Sundström L. An IF CMOS signal component separator chip for LINC transmitter. Proc IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conf, 2001, 5:49 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/icp.jsp?arnumber=929721[8] Panseri L, Romanó L, Levantino S, et al. Low-power signal component separator for a 64-QAM 802.11 LINC transmitter. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2008, 43(5):1274 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2008.920321[9] Ravi A, Madoglio P, Xu H T, et al. A 2.4 GHz 20-40-MHz channel WLAN digital outphasing transmitter utilizing a delay-based wideband phase modulator in 32-nm CMOS. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2012, 47(12):3184 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2012.2216671[10] Li Y, Li Z P, Uyar O, et al. High-throughput signal component separator for asymmetric multi-level outphasing power amplifiers. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2013, 48(2):369 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2012.2229071[11] Chen T W, Tsai P Y, Yu J Y, et al. A sub-mW all-digital signal component separator with branch mismatch compensation for OFDM LINC transmitter. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2011, 46(11):2514 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2011.2164133[12] Chung C C, Lee C Y. An all-digital phase-locked loop for high speed clock generation. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2003, 38(2):347 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2002.807398 -
Proportional views






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: