| Citation: |
Qiang Huang, Tao Fan, Xiangming Dai, Guoshun Yuan. A low-power DCO using inverter interlaced cascaded delay cell[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2014, 35(11): 115004. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/11/115004
****
Q Huang, T Fan, X M Dai, G S Yuan. A low-power DCO using inverter interlaced cascaded delay cell[J]. J. Semicond., 2014, 35(11): 115004. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/11/115004.
|
A low-power DCO using inverter interlaced cascaded delay cell
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/11/115004
More Information
-
Abstract
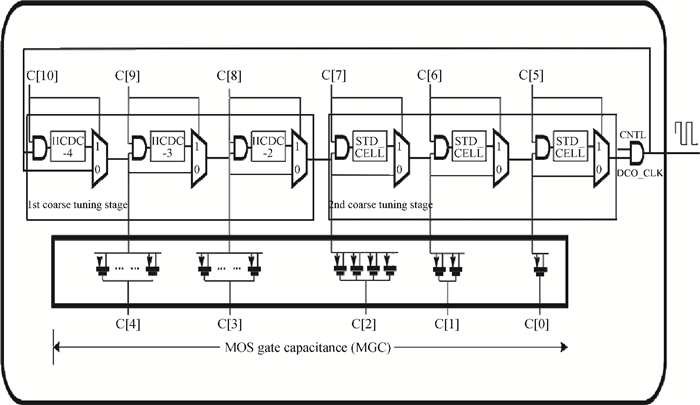
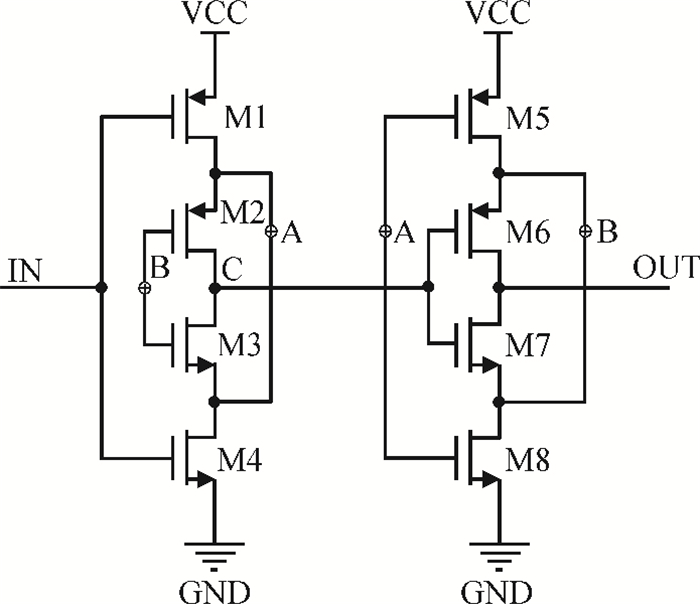
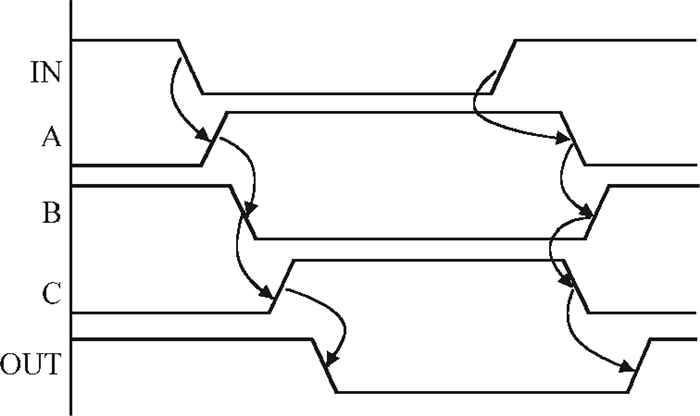
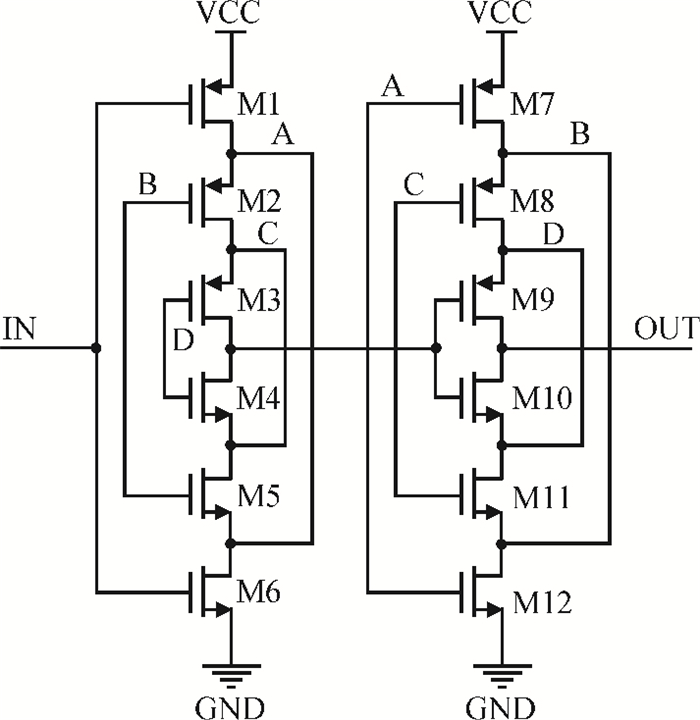
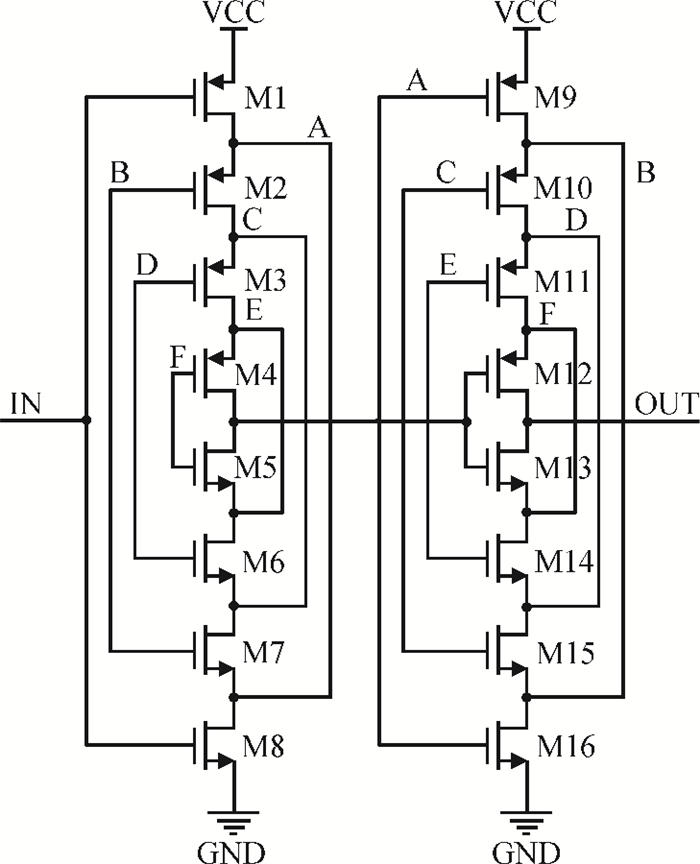
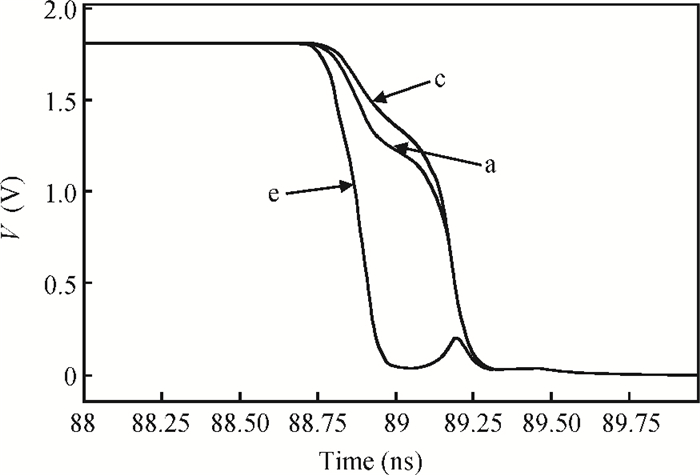
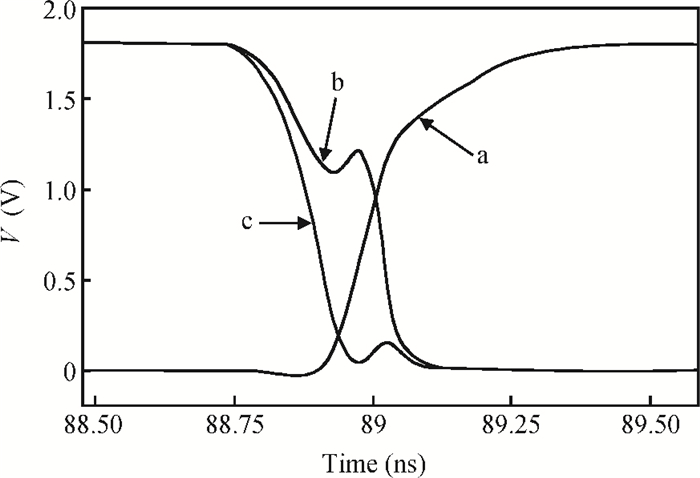
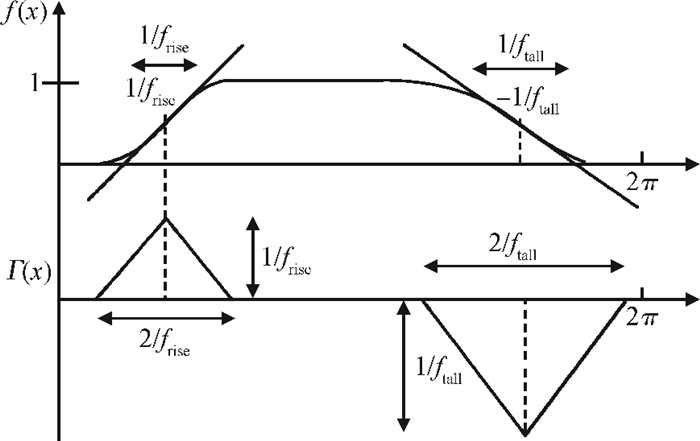
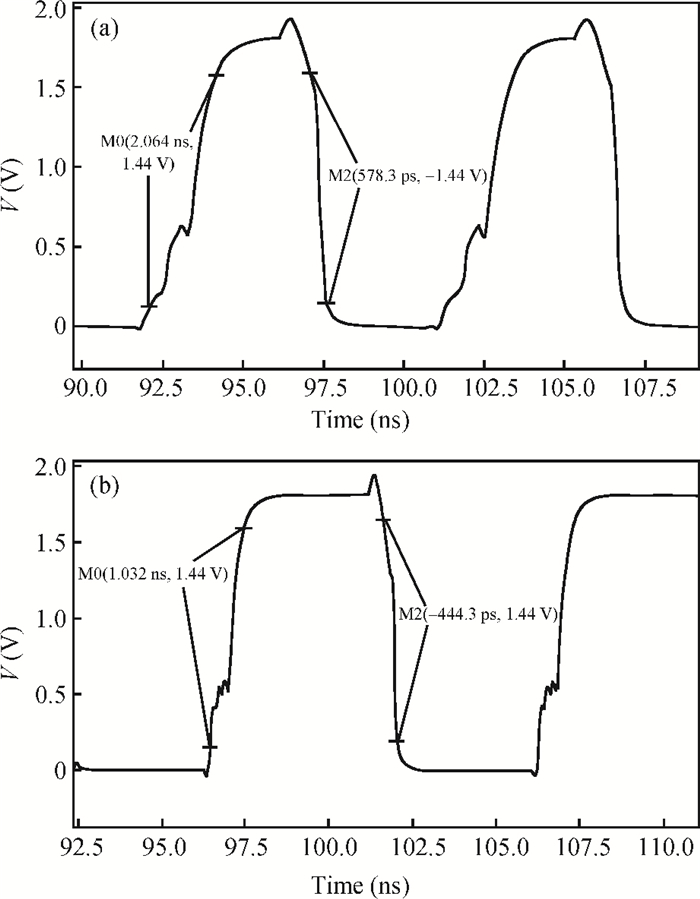
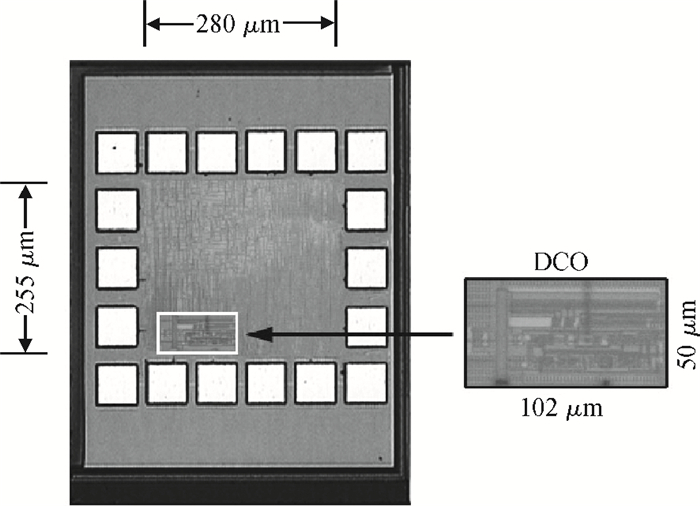
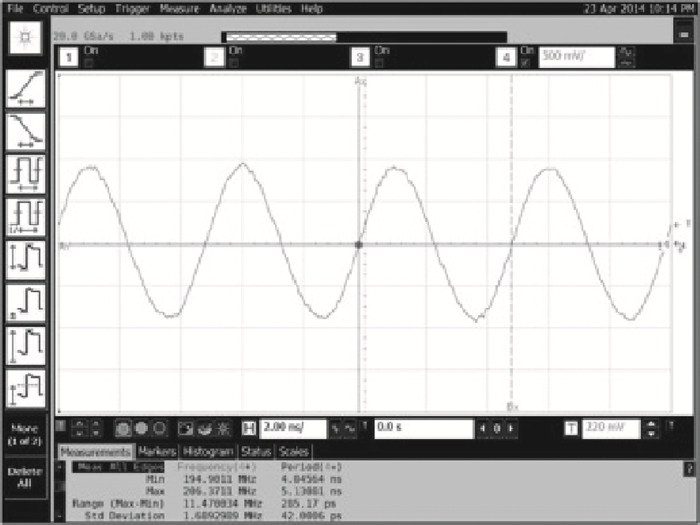
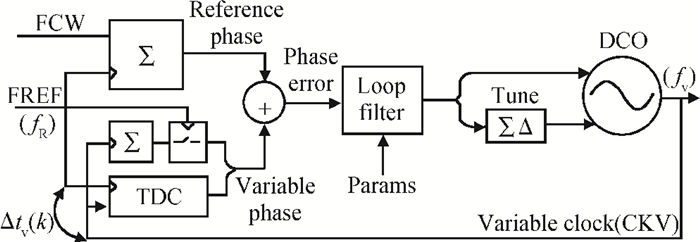
This paper presents a low-power small-area digitally controlled oscillator (DCO) using an inverters interlaced cascaded delay cell (IICDC). It uses a coarse-fine architecture with binary-weighted delay stages for the delay range and resolution. The coarse-tuning stage of the DCO uses IICDC, which is power and area efficient with low phase noise, as compared with conventional delay cells. The ADPLL with a DCO is fabricated in the UMC 180-nm CMOS process with an active area of 0.071 mm2. The output frequency range is 140-600 MHz at the power supply of 1.8 V. The power consumption is 2.34 mW@a 200 MHz output. -
References
[1] Zhuang J, Staszewski R B. A low-power all-digital PLL architecture based on phase prediction. IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Circuits and Systems, 2012:797 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/icp.jsp?arnumber=6463539[2] Staszewski R B. State-of-the-art and future directions of high performance all-digital frequency synthesis in nanometer CMOS. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Ⅰ, Reg Papers, 2011, 58(7):1497 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2011.2150890[3] Tian Huanhuan, Li Zhiqiang, Chen Pufeng, et al. A low-power and low-phase-noise LC digitally controlled oscillator featuring a novel capacitor bank. Journal of Semiconductors, 2010, 31(12):125003 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/31/12/125003[4] Chung C C, Lee C Y. An all-digital phase-locked loop for high speed clock generation. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2003, 38(2):347 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2002.807398[5] Choi K H, Shin J B, Sim J Y, et al. An interpolating digitally controlled oscillator for a wide-range all-digital PLL. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Ⅰ, Reg Papers, 2009, 56(9):2055 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2008.2011577[6] Hsu H J, Huang S Y. A low-jitter ADPLL via a suppressive digital filter and an interpolation-based locking scheme. IEEE Trans Very Large Scale Integr (VLSI) Syst, 2011, 19(1):165 doi: 10.1109/TVLSI.2009.2030410[7] Chung C C, Ko C Y. A fast phase tracking ADPLL for video pixel clock generation in 65 nm CMOS technology. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2011, 46(10):2300 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2011.2160789[8] Hsu S Y, Yu J Y, Lee C Y. A sub-10μW DCO based on HDC topologies for WBAN applications. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Ⅱ, Exp Briefs, 2010, 57(12):951 doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2010.2087991[9] Sheng D, Chung C C, Lee C Y. An ultra-low-power and portable digitally controlled oscillator for SoC applications. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Ⅱ, Exp Briefs, 2007, 54(11):954 doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2007.903782[10] Yu C, Chung C, Yu C, et al. A low-power DCO using interlaced hysteresis delay cells. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Ⅱ:Express Briefs, 2012, 59(10):673 doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2012.2213357[11] Chenguang W. Research on key techniques of all-digital clock cells in low-power high-integration transceivers. Institute of Microelectronics of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2013[12] Hajimiri A, Limotyrakis S, Lee T H. Jitter and phase noise in ring oscillators. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 1999, 34(6):790 doi: 10.1109/4.766813[13] Lee T H, Yu Z P, Zhou R D. The design of CMOS radio frequency integrated circuits. 2nd ed. Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2006:525[14] Liu W, Li W, Ren P, et al. A PVT tolerant 10 to 500 MHz all-digital phase-locked loop with coupled TDC and DCO. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2010, 45(2):314 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2009.2038127[15] Wu C T, Shen W C, Wang W, et al. A two-cycle lock-in time ADPLL design based o n a frequency estimation algorithm. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Ⅱ, Exp Briefs, 2010, 57(6):430 doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2010.2048358 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: