| Citation: |
Hongqi Jing, Cong Xiong, Zhen Dong, Nan Lin, Qiong Qi, Li Zhong, Suping Liu, Xiaoyu Ma. An exploration of slab-coupled semiconductor lasers[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2014, 35(5): 054007. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/5/054007
****
H Q Jing, C Xiong, Z Dong, N Lin, Q Qi, L Zhong, S P Liu, X Y Ma. An exploration of slab-coupled semiconductor lasers[J]. J. Semicond., 2014, 35(5): 054007. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/5/054007.
|
An exploration of slab-coupled semiconductor lasers
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/5/054007
More Information
-
Abstract
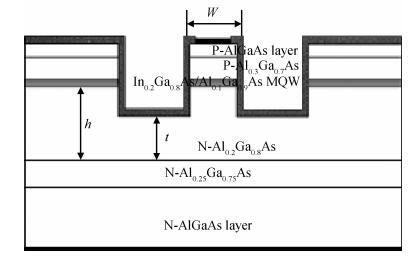
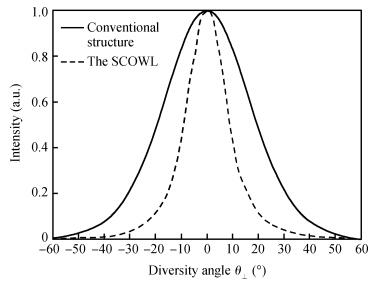
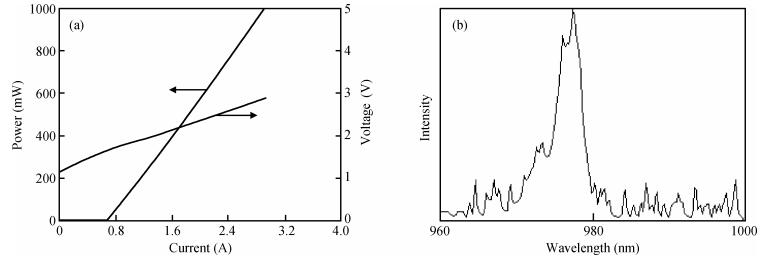
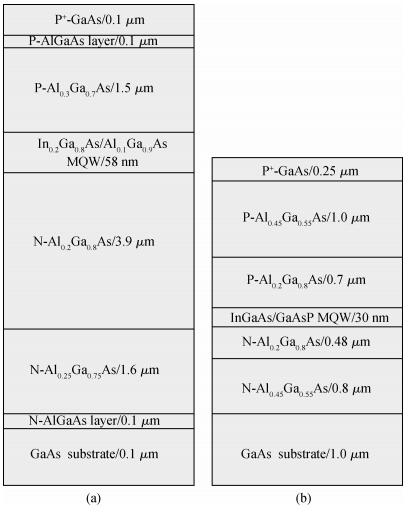
To obtain a high-power and efficient single-mode laser, a new laser called the slab coupled optical waveguide laser (SCOWL) has been developed. We have simulated its structure and grown the chip with this structure by low-pressure metal organic chemical vapor deposition. We have also produced the broad-area SCOWL and compared it with the traditional structure laser in terms of some performances. This work lays the foundation for further research of ridged lasers with the same structure.-
Keywords:
- SCOWL,
- traditional laser,
- broad-area laser
-
References
[1] Walpole J N, Kintzer E S, Chinn S R, et al. High-power, strained-layer InGaAS/AlGaAs tapered traveling wave amplifier. Appl Phys Lett, 1992, 61:740 doi: 10.1063/1.107783[2] O'Brien S, Schoenfelder A, Lang R J. 5-W CW diffraction-limited InGaAs broad-area flared amplifier at 970 nm. IEEE Photonics Technol Lett, 1997, 9:1217 doi: 10.1109/68.618483[3] Walpole J N, Donnelly J P, Missaggia L J, et al. Gaussian patterned contacts for improved beam stability of 1.55-m tapered lasers. IEEE Photonics Technol Lett, 2000, 12:257 doi: 10.1109/68.826906[4] Lang R J, Dzurko K, Hardy A A, et al. Theory of grating-confined broad area lasers. IEEE J Quantum Electron, 1998, 34:2196 doi: 10.1109/3.726614[5] Pezeshki B, Hagberg M, Zelinski M, et al. 400-mW single-frequency 660-nm semiconductor laser. IEEE Photonics Technol Lett, 1999, 11:791 doi: 10.1109/68.769709[6] Bewley W W, Vurgaftman I, Bartolo R E, et al. Limitations to beam quality of mid-infrared angled-grating distributed-feedback lasers. IEEE J Sel Topics Quantum Electron, 2001, 7:96 doi: 10.1109/2944.954116[7] Garbuzov D Z, Xu L, Forrest S R, et al. 1.5-μm wavelength SCH_MQW broadened-waveguide laser diodes with low internal loss and high output power. Electron Lett, 1996, 32:1717 doi: 10.1049/el:19961098[8] Kunetzsov M, Hakimi F, Sprague R, et al. High-power (> 0.5-W CW) diode-pumped vertical-external-cavity surface-emitting lasers with circular TEM00 beams. IEEE Photonics Technol Lett, 1997, 9:1063 doi: 10.1109/68.605500[9] Walpole J N, Donnelly J P, Taylor P J, et al. Slab-coupled 1.3-μm semiconductor laser with single-spatial large-diameter mode. IEEE Photonics Technol Lett, 2002, 14:756 doi: 10.1109/LPT.2002.1003083[10] Donnelly J P, Huang R K, Walpole J N, et al. AlGaAs-InGaAs slab-coupled optical waveguide lasers. IEEE J Quantum Electron, 2003, 9:289[11] Huang R K, Donnelly J P, Missaggia L J, et al. High-power nearly diffraction-limited AlGaAs-InGaAs semiconductor slab-coupled optical waveguide laser. IEEE Photonics Technol Lett, 2003, 15: 900[12] Marcatili E A. Slab-coupled waveguides. Bell System Tech J, 1974, 53:645 doi: 10.1002/bltj.1974.53.issue-4[13] Hu Like, Qi Qing, Xiong Cong, et al. High-power 980 nm quantum-well laser diode with a small vertical divergence angle. Semicond Optoelectron, 2010, 31(5):677 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: