| Citation: |
Fuxue Wang, Xiaolong Cai, Dawei Yan, Zhaomin Zhu, Xiaofeng Gu. Luminescence properties of tetrapod ZnO nanostructures[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2014, 35(6): 063004. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/6/063004
****
F X Wang, X L Cai, D W Yan, Z M Zhu, X F Gu. Luminescence properties of tetrapod ZnO nanostructures[J]. J. Semicond., 2014, 35(6): 063004. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/6/063004.
|
Luminescence properties of tetrapod ZnO nanostructures
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/6/063004
More Information
-
Abstract
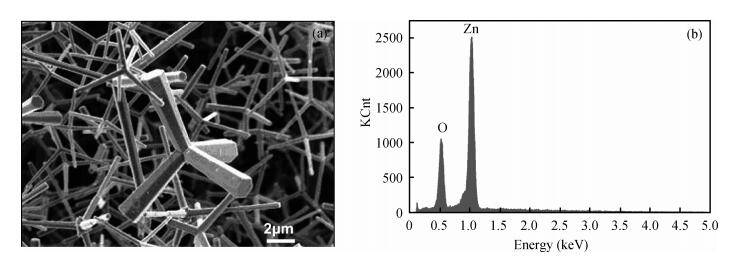
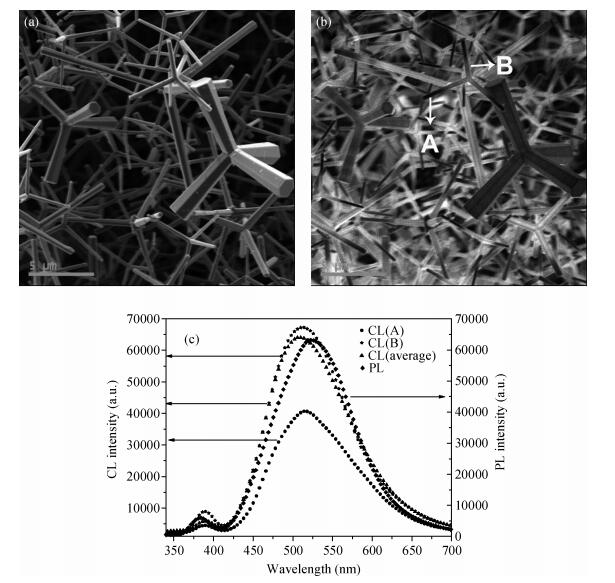
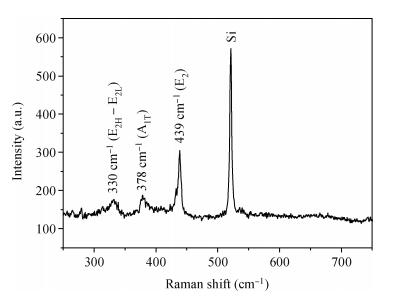
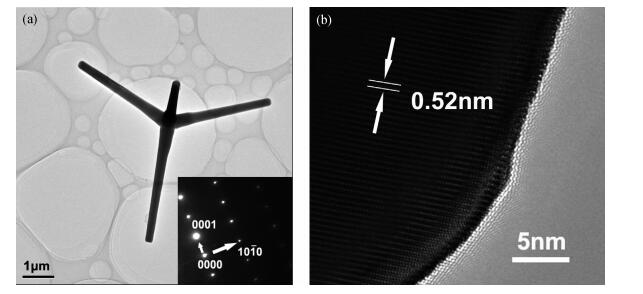
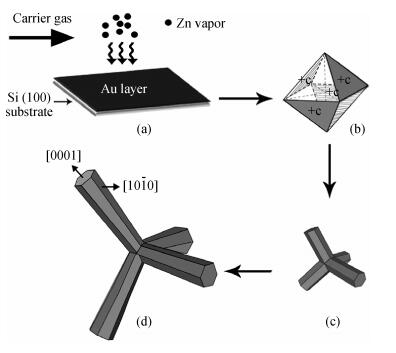
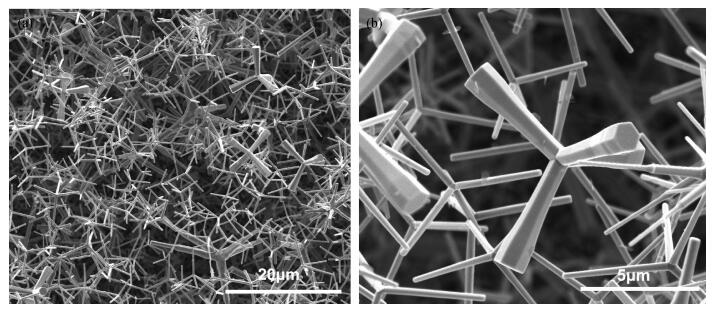
The tetrapod ZnO nanostructures are synthesized on the Si (100) substrates using the chemical vapor deposition (CVD) method at 1000℃. Each nanostructure has four arms which are about 3-10 μm in length and 0.2-1.5 μm in diameter. Further analyses on structure demonstrate that the tetrapod ZnO nanostructures have single crystalline wurtzite hexagonal structure preferentially oriented in c-axis. The photoluminescence (PL) measurements of the tetrapod ZnO nanostructures revealed a UV peak at 382 nm corresponding to the free exciton emission, and a green peak at 523 nm arising from deep level emission. For comparative analysis, cathodoluminescence (CL) spectra obtained from different regions of an individual tetrapod are investigated. Moreover, a possible growth mechanism of the tetrapod ZnO nanostructures is also discussed based on the experimental results.-
Keywords:
- ZnO,
- tetrapod,
- nanostructures,
- cathodoluminescence,
- photoluminescence,
- optical properties
-
References
[1] Rensmo H, Keis K, Lindström H, et al. High light-to-energy conversion efficiencies for solar cells based on nanostructured ZnO electrodes. J Phys Chem B, 1997, 101:2598 doi: 10.1021/jp962918b[2] Huang M H, Mao S, Feick H, et al. Room-temperature ultraviolet nanowire nanolasers. Science, 2001, 292:1897 doi: 10.1126/science.1060367[3] Sapkal R, Shinde S, Rajpure K, et al. Photoelectrocatrocatalytic hydrolysis of starch by using sprayed ZnO thin films. Journal of Semiconductors, 2013, 34(5):053001 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/5/053001[4] Cheng Zhiming, Zhou Sumei, Chen Tongyun, et al. Acetic acid gas sensors based on Ni2+ doped ZnO nanorods prepared by using the solvothermal method. Journal of Semiconductors, 2012, 33(11):112003 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/33/11/112003[5] Zhang H, Shen L, Guo S. Insight into the structures and properties of morphology-controlled legs of tetrapod-like ZnO nanostructures. J Phys Chem C, 2007, 111:12939 doi: 10.1021/jp074086v[6] Zhu Yao, Apostoluk A, Liu Shibin, et al. ZnO nanoparticles as a luminescent down-shifting layer for photosensitive devices. Journal of Semiconductors, 2013, 34(5):053005 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/5/053005[7] Liu Li, Wang Lianyuan, Han Yu, et al. Highly sensitive and selective ethanol sensors based on flower-like ZnO nanorods. Journal of Semiconductors, 2011, 32(9):092005 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/32/9/092005[8] Su Shichen, Yang Xiaodong, Hu Candong. Fabrication of ZnO nanowall-network ultraviolet photodetector on Si substrates. Journal of Semiconductors, 2011, 32(7):074008 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/32/7/074008[9] Chen Z, Shan Z, Cao M, et al. Zinc oxide nanotetrapods. Nanotechnology, 2004, 15:365 doi: 10.1088/0957-4484/15/3/023[10] Roy V, Djurisic A, Chan W, et al. Luminescent and structural properties of ZnO nanorods prepared under different conditions. Appl Phys Lett, 2003, 83:141 doi: 10.1063/1.1589184[11] Newton M C, Warburton P A. ZnO tetrapod nanocrystals. Mater Today, 2007, 10:50[12] Hong K, Song R, Liu L, et al. Synthesis and cathode luminescence properties of ZnO multipod nanoneedles. Mater Lett, 2012, 67:202 doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2011.09.063[13] Kong Y, Yu D, Zhang B, et al. Ultraviolet-emitting ZnO nanowires synthesized by a physical vapor deposition approach. Appl Phys Lett, 2001, 78:407 doi: 10.1063/1.1342050[14] Vanheusden K, Seager C, Warren W, et al. Correlation between photoluminescence and oxygen vacancies in ZnO phosphors. Appl Phys Lett, 1996, 68:403 doi: 10.1063/1.116699[15] Yan H L, Zhong X L, Wang J B, et al. Cathodoluminescence and room temperature ferromagnetism of Mn-doped ZnO nanorod arrays grown by chemical vapor deposition. Appl Phys Lett, 2007, 90:082503 doi: 10.1063/1.2460297[16] Wu X, Siu G, Fu C, et al. Photoluminescence and cathodoluminescence studies of stoichiometric and oxygen-deficient ZnO films. Appl Phys Lett, 2001, 78:2285 doi: 10.1063/1.1361288[17] Yang Y, Zhu H, Yang G. Growth, structure, and cathodoluminescence of Dy-doped ZnO nanowires. Appl Phys A, 2011, 103:73 doi: 10.1007/s00339-011-6328-x[18] Xing Y, Xi Z, Xue Z, et al. Optical properties of the ZnO nanotubes synthesized via vapor phase growth. Appl Phys Lett, 2003, 83:1689 doi: 10.1063/1.1605808[19] Yao B, Chan Y, Wang N. Formation of ZnO nanostructures by a simple way of thermal evaporation. Appl Phys Lett, 2002, 81(4):757 doi: 10.1063/1.1495878[20] Gu S, Zhang R, Sun J, et al. Role of interfacial compound formation associated with the use of ZnO buffers layers in the hydride vapor phase epitaxy of GaN. Appl Phys Lett, 2000, 76(23):3454 doi: 10.1063/1.126675[21] Li Y, Duan R, Shi P, et al. Synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles on Si substrates using a ZnS source. J Crystal Growth, 2004, 260(3):309[22] Zhao D, Andreazza C, Andreazza P, et al. Buffer layer effect on ZnO nanorods growth alignment. Chem Phys Lett, 2005, 408(4):335[23] Takeuchi S, Iwanaga H, Fujii M. Octahedral multiple-twin model of tetrapod ZnO crystals. Philos Mag A, 1994, 69(6):1125 doi: 10.1080/01418619408242243[24] Yu W, Li X, Gao X. Synthesis and structural characteristics of high-quality tetrapodlike ZnO nanocrystals on ZnO and NiO nanocrystal substrates. J Crystal Growth, 2004, 270(1):92[25] Ronning C, Shang N, Gerhards I, et al. Nucleation mechanism of the seed of tetrapod ZnO nanostructures. J Appl Phys, 2005, 98(3):034307 doi: 10.1063/1.1997290[26] Fang Z B, Gong H X, Liu X Q, et al. Effects of annealing on the structure and photoluminescence of ZnO films. Acta Physica Sinica, 2003, 52(7):1748[27] Spanhel L, Anderson M A. Semiconductor clusters in the sol-gel process:quantized aggregation, gelation, and crystal growth in concentrated zinc oxide colloids. J Am Chem Soc, 1991, 113(8):2826 doi: 10.1021/ja00008a004[28] Studenikin S, Golego N, Cocivera M. Fabrication of green and orange photoluminescent, undoped ZnO films using spray pyrolysis. J Appl Phys, 1998, 84(4):2287 doi: 10.1063/1.368295 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: