| Citation: |
Yongle Lou, Yuming Zhang, Daqing Xu, Hui Guo, Yimen Zhang, Yuchen Li. Influence of oxygen content on the crystallinity of MgO layers in magnetic tunnel junctions[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2014, 35(8): 083005. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/8/083005
****
Y L Lou, Y M Zhang, D Q Xu, H Guo, Y M Zhang, Y C Li. Influence of oxygen content on the crystallinity of MgO layers in magnetic tunnel junctions[J]. J. Semicond., 2014, 35(8): 083005. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/8/083005.
|
Influence of oxygen content on the crystallinity of MgO layers in magnetic tunnel junctions
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/8/083005
More Information
-
Abstract
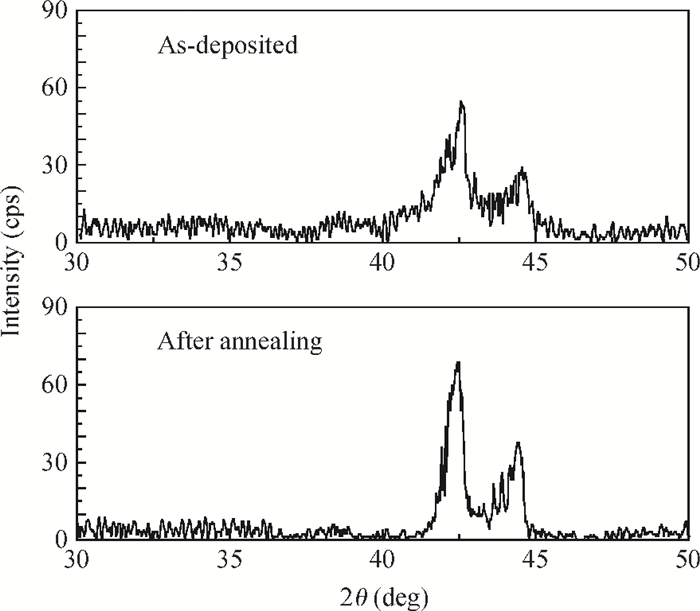
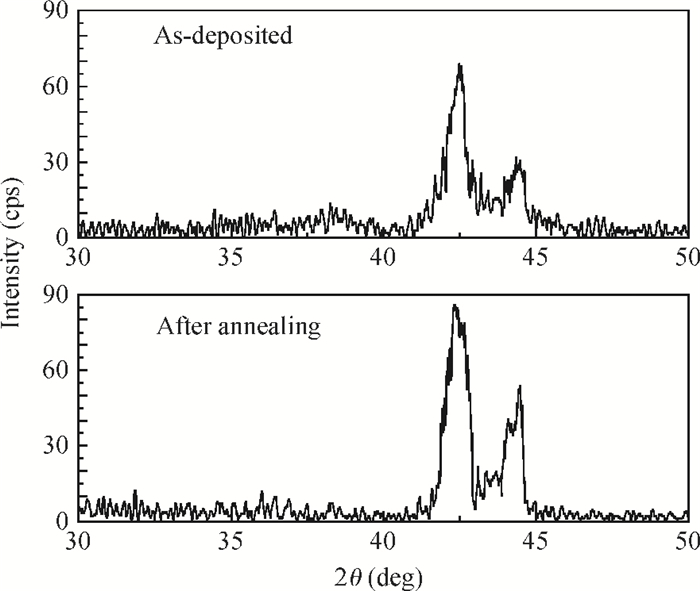
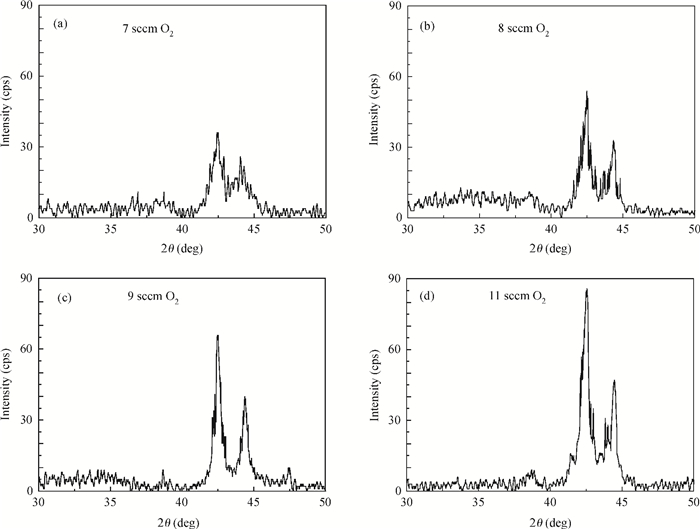
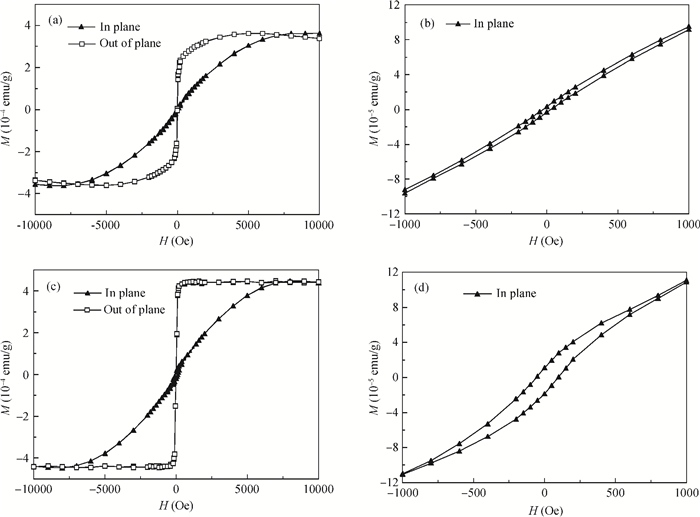
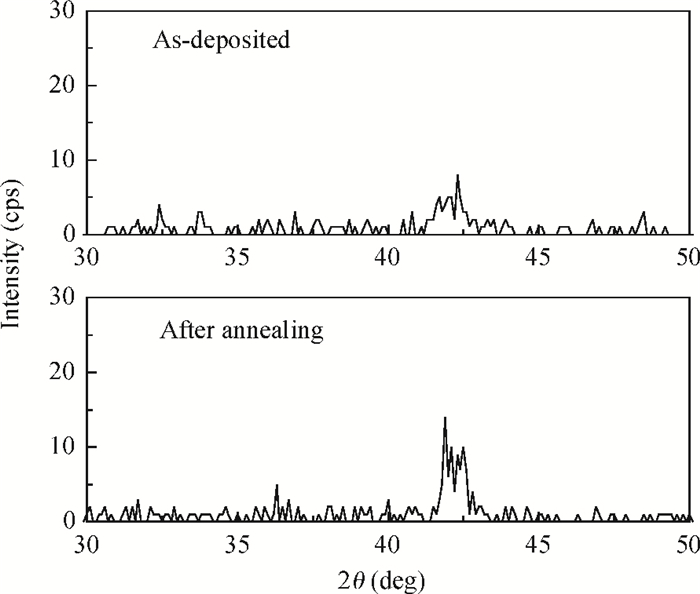
With RF sputtering process, Si/SiO2/Ta/Ru/Ta/CoFeB/MgO/CoFeB/Ta/Ru structure has been grown on Si (100) substrate. Attempting different targets and adjusting the oxygen dose, the crystallization quality of the MgO layer is studied. The X-ray diffraction measurements demonstrate that crystal structure and crystallization quality of MgO layers are related to the type of target and concentration of oxygen in sputtering process. With the method sputtering Mg in an ambient flow of oxygen, not only the crystallization quality of a normal MgO layer with lattice constant of 0.421 nm is improved, but also a new MgO crystal with lattice constant of 0.812 nm is formed and the perpendicular magnetic anisotropy of CoFeB is enhanced. Also it is found that crystallization quality for both the normal MgO and new MgO is more improved with MgO target and same oxygen dose, which means that this new method is helpful to form a new structure of MgO with lattice constant of 0.812 nm. All of the samples were annealed at 400℃ in vacuum. -
References
[1] Wang H, Kou X L, Wang S, et al. Magnetic properties and thermal stability of CoFeB/MgO films. Physics Procedia, 2011, 18:267 doi: 10.1016/j.phpro.2011.06.093[2] Alfonso J E, Cardenas M, Marco J F. Influence of fabrication parameters on crystallization, microstructure, surface composition, and optical behavior of MgO thin films deposited by RF magnetron sputtering. Journal of Superconductivity and Novel Magnetism, 2013, 26:2463 doi: 10.1007/s10948-012-1460-1[3] Butler W H, Zhang X G, Schulthess T C, et al. Influence of oxygen monolayer at Fe/MgO interface on transport properties in Fe/MgO/Fe (001) magnetic tunnel junctions. Phys Rev B, 2001, 63:054416 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.63.054416[4] Mathon J, Umerski A. Theory of tunneling magnetoresistance of an epitaxial Fe/MgO/Fe (001) junction. Phys Rev B, 2001, 63:220403 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.63.220403[5] Yuasa S, Djayaprawira D D. Giant tunnel magnetoresistance in magnetic tunnel junctions with a crystalline MgO (001) barrier. J Phys D, 2007, 40:R337 doi: 10.1088/0022-3727/40/21/R01[6] Parkin S S P, Kaiser C, Panchula A, et al. Giant tunnelling magneto-resistance at room temperature with MgO (100) tunnel barriers. Nature Mater, 2004, 3:862 doi: 10.1038/nmat1256[7] Sankha S, Mukherjee, Bai F M, et al. Crystallization and grain growth behavior of CoFeB and MgO layers in multilayer magnetic tunnel junctions. J Appl Phys, 2009, 106:033906 doi: 10.1063/1.3176501[8] Wang W G, Jordan-sweet J, Miao G X, et al. In-situ characterization of rapid crystallization of amorphous CoFeB electrodes in CoFeB/MgO/CoFeB junctions during thermal annealing. Appl Phys Lett, 2009, 95:242501 doi: 10.1063/1.3273397[9] Chung H C, Lee S R. Texture development and magnetoresistance properties of CoFeB/MgO/CoFeB-based magnetic tunnel junction depending on capping layer crystallinity. J Appl Phys, 2008, 103:07A914 doi: 10.1063/1.2837477[10] Li J, Jiang Y, Li Y, et al. Origin of room temperature ferromagnetism in MgO films. Appl Phys Lett, 2013, 102:072406 doi: 10.1063/1.4793308[11] JCPDS-ICDD 1998 PDF#300794[12] Lu Y, Deranlot C, Vaurés A, et al. Effects of a thin Mg layer on the structural and magnetoresistance properties of CoFeB/MgO/CoFeB magnetic tunnel junctions. Appl Phys Lett, 2007, 91:222504 doi: 10.1063/1.2819530[13] Kubota H, Ishibashi S, Saruy T, et al. Enhancement of perpendicular magnetic anisotropy in FeB free layers using a thin MgO cap layer. J Appl Phys, 2012, 111:07C723 doi: 10.1063/1.3679393 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: