| Citation: |
Weiru Gu, Fan Ye, Junyan Ren. An 11-bit 22-MS/s 0.6 mW SAR ADC with parasitic capacitance compensation[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2014, 35(8): 085006. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/8/085006
****
W R Gu, F Ye, J Y Ren. An 11-bit 22-MS/s 0.6 mW SAR ADC with parasitic capacitance compensation[J]. J. Semicond., 2014, 35(8): 085006. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/8/085006.
|
An 11-bit 22-MS/s 0.6 mW SAR ADC with parasitic capacitance compensation
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/8/085006
More Information
-
Abstract
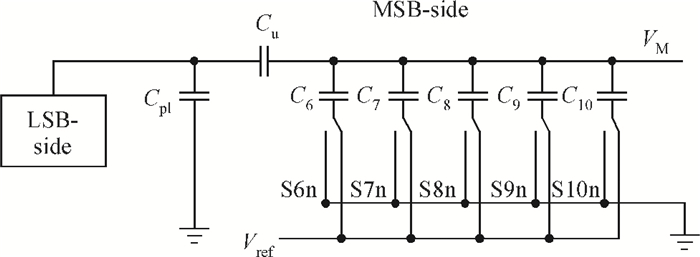
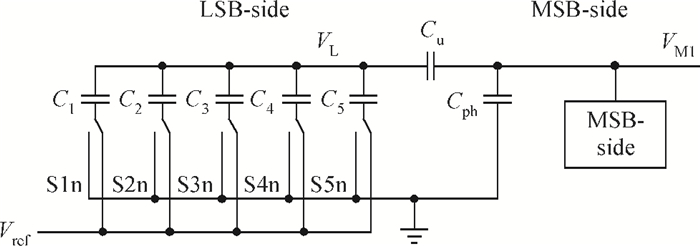
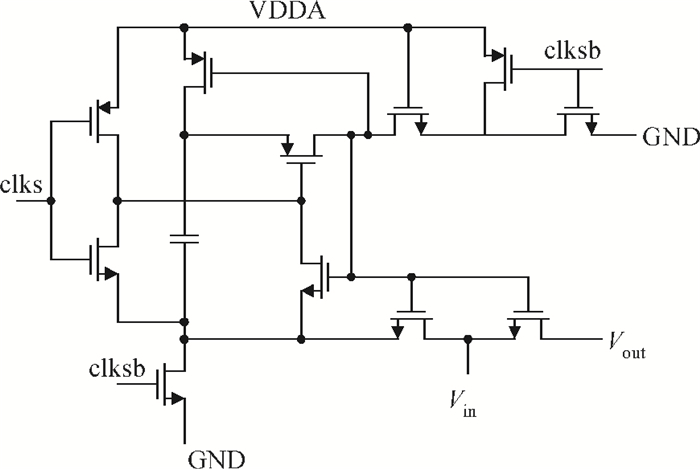
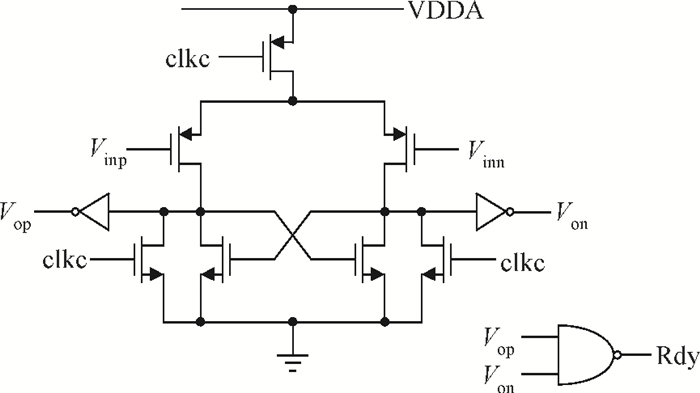
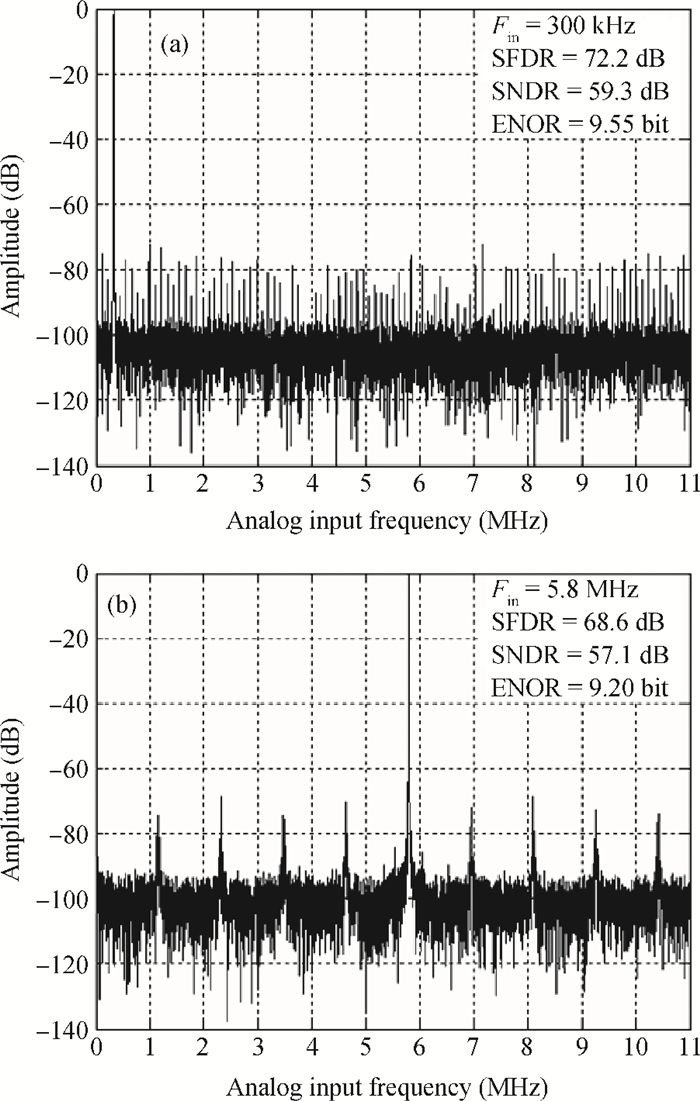
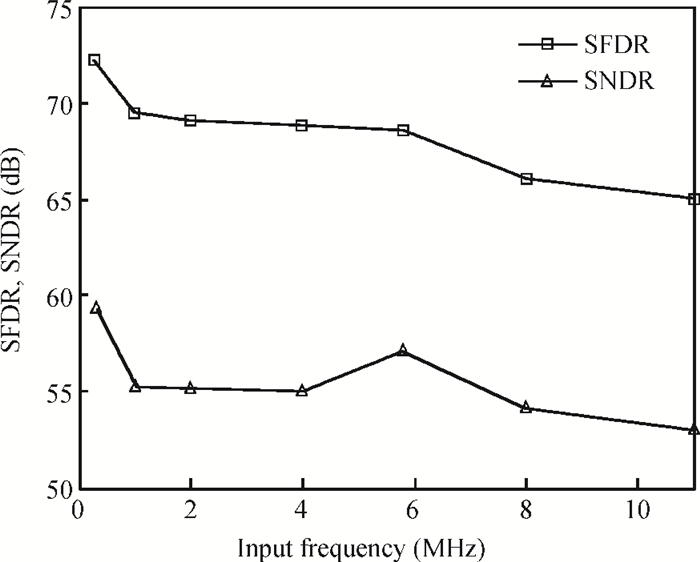
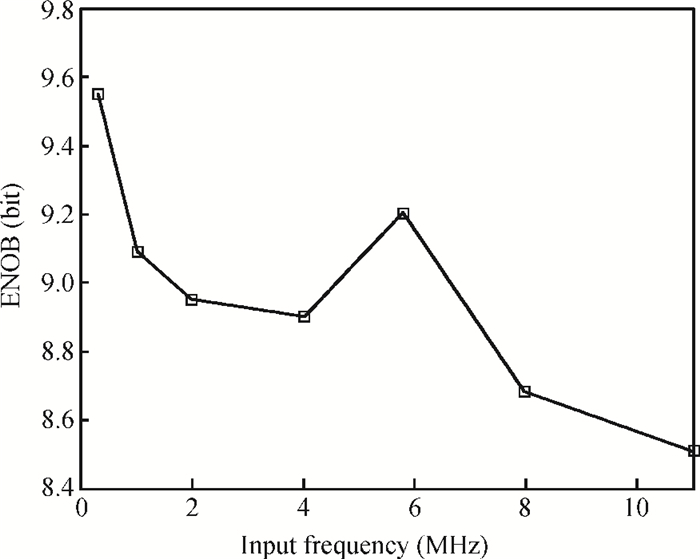
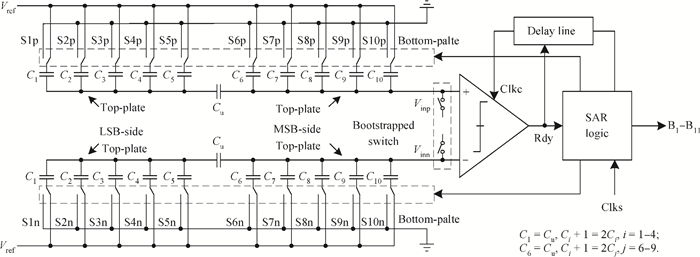
This paper presents an 11-bit 22-MS/s 0.6-mW successive approximation register (SAR) analog-to-digital converter (ADC) using SMIC 65-nm low leakage (LL) CMOS technology with a 1.2 V supply voltage. To reduce the total capacitance and core area the split capacitor architecture is adopted. But in high resolution ADCs the parasitic capacitance in the LSB-side would decrease the linearity of the ADC and it is hard to calibrate. This paper proposes a parasitic capacitance compensation technique to cancel the effect with no calibration circuits. Moreover, dynamic circuits are used to minimize the switching power of the digital logic and also can reduce the latency time. The prototype chip realized an 11-bit SAR ADC fabricated in SMIC 65-nm CMOS technology with a core area of 300×200 μm2. It shows a sampling rate of 22 MS/s and low power dissipation of 0.6 mW at a 1.2 V supply voltage. At low input frequency the signal-to-noise-and-distortion ratio (SNDR) is 59.3 dB and the spurious-free dynamic range is 72.2 dB. The peak figure-of-merit is 36.4 fJ/conversion-step. -
References
[1] Lee K H, Kim K S, Lee S H. A 12 b 50 MS/s 21.6 mW 0.18μm CMOS ADC maximally sharing capacitors and op-amps. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I, Reg Papers, 2011, 58(9):2127 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2011.2112591[2] Liu W, Huang P, Chiu Y. A 12-bit, 45-MS/s, 3-mW redundant successive-approximation-register analog-to-digital converter with digital calibration. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2011, 46(11):2661 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2011.2163556[3] Chen Y, Zhu X, Tamura H, et al. Split capacitor DAC mismatch calibration in successive approximation ADC. Proc CICC, 2009:279 doi: 10.1007/s12209-013-2015-7[4] Kuramochi Y, Matsuzawa A, Kawabata M. A 0.05-mm2 110-μW 10-b self-calibrating successive approximation ADC core in 0.18-μm CMOS. Proc ASSCC, 2007:224 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpl/abstractKeywords.jsp?reload=true&arnumber=4425771[5] Zhu Y, Chan C H, Chio U F, et al. A 10-bit 100-MS/s reference-free SAR ADC in 90 nm CMOS. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2010, 45(6):1111 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2010.2048498[6] Liu C C, Chang S J, Huang G Y, et al. A 10-bit 50-MS/s SAR ADC with a monotonic capacitor switching procedure. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2010, 45(4):731 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2010.2042254[7] Chen S W M, Brodersen R W. A 6 b 600 MS/s 5.3 mW asynchronous ADC in 0.13μm CMOS. IEEE ISSCC Dig Tech Papers, 2006:574 doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-46628-6_7[8] Abo A M, Gray P R. A 1.5-V, 10-bit, 14.3-MS/s CMOS pipeline analog-to-digital converter. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 1999, 34(5):599 doi: 10.1109/4.760369[9] Yuan J, Svensson C. High-speed CMOS circuit technique. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 1989, 24(1):62 doi: 10.1109/4.16303[10] Lin Y Z, Chang S J, Shyu Y T, et al. A 0.9-V 11-bit 25-MS/s binary-search SAR ADC in 90-nm CMOS. Proc ASSCC, 2011:69[11] Cho S H, Lee C K, Kwon J K, et al. A 550-μW 10-b 40-MS/s SAR ADC with multistep addition-only digital error correction. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2011, 46(8):1881 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2011.2151450 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: