| Citation: |
Gang Jin, Yiqi Zhuang, Yue Yin, Miao Cui. A digitally controlled AGC loop circuitry for GNSS receiver chip with a binary weighted accurate dB-linear PGA[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2015, 36(3): 035004. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/36/3/035004
****
G Jin, Y Q Zhuang, Y Yin, M Cui. A digitally controlled AGC loop circuitry for GNSS receiver chip with a binary weighted accurate dB-linear PGA[J]. J. Semicond., 2015, 36(3): 035004. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/36/3/035004.
|
A digitally controlled AGC loop circuitry for GNSS receiver chip with a binary weighted accurate dB-linear PGA
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/36/3/035004
More Information
-
Abstract
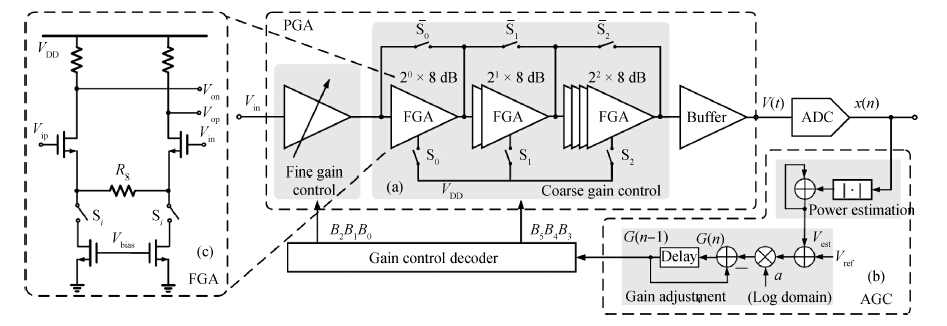
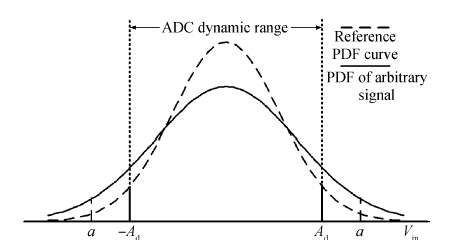
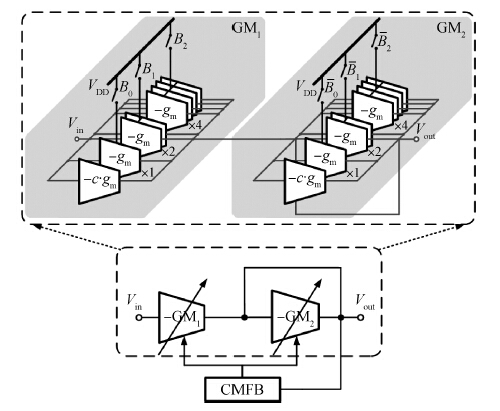
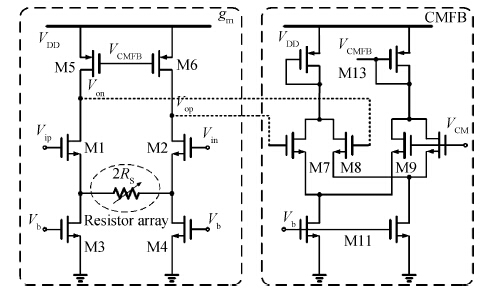
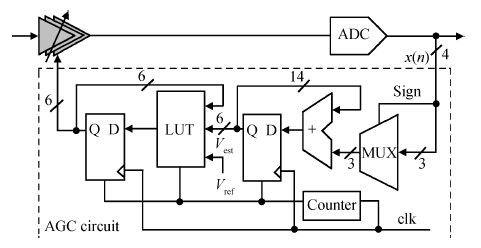
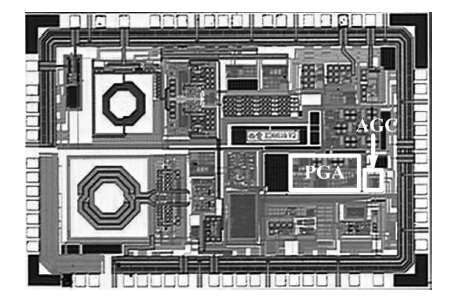
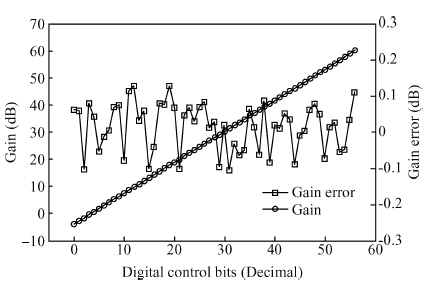
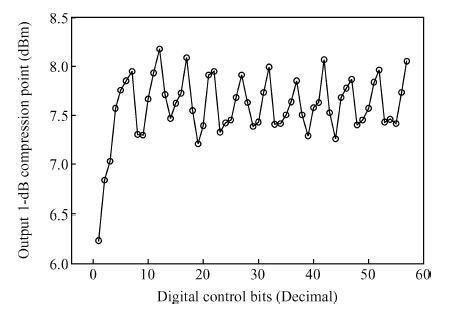
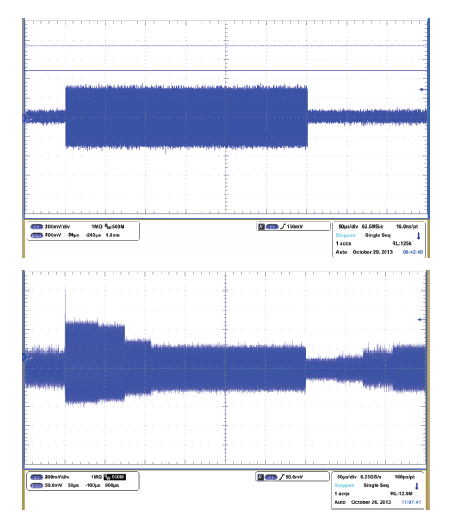
A novel digitally controlled automatic gain control (AGC) loop circuitry for the global navigation satellite system (GNSS) receiver chip is presented. The entire AGC loop contains a programmable gain amplifier (PGA), an AGC circuit and an analog-to-digital converter (ADC), which is implemented in a 0.18 μm complementary metal—oxide—semiconductor (CMOS) process and measured. A binary-weighted approach is proposed in the PGA to achieve wide dB-linear gain control with small gain error. With binary-weighted cascaded amplifiers for coarse gain control, and parallel binary-weighted trans-conductance amplifier array for fine gain control, the PGA can provide a 64 dB dynamic range from -4 to 60 dB in 1.14 dB gain steps with a less than 0.15 dB gain error. Based on the Gaussian noise statistic characteristic of the GNSS signal, a digital AGC circuit is also proposed with low area and fast settling. The feed-backward AGC loop occupies an area of 0.27 mm2 and settles within less than 165 μs while consuming an average current of 1.92 mA at 1.8 V.-
Keywords:
- PGA,
- binary-weighted,
- AGC loop,
- GNSS,
- Gaussian noise
-
References
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] [10] [11] [12] [13] [14] [15] [16] [17] [18] -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: