| Citation: |
Wenyu Yuan, Jingping Xu, Lu Liu, Yong Huang, Zhixiang Cheng. Improved interfacial and electrical properties of Ge MOS devices with ZrON/GeON dual passivation layer[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2016, 37(5): 054004. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/37/5/054004
****
W Y Yuan, J P Xu, L Liu, Y Huang, Z X Cheng. Improved interfacial and electrical properties of Ge MOS devices with ZrON/GeON dual passivation layer[J]. J. Semicond., 2016, 37(5): 054004. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/37/5/054004.
|
Improved interfacial and electrical properties of Ge MOS devices with ZrON/GeON dual passivation layer
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/37/5/054004
More Information
-
Abstract
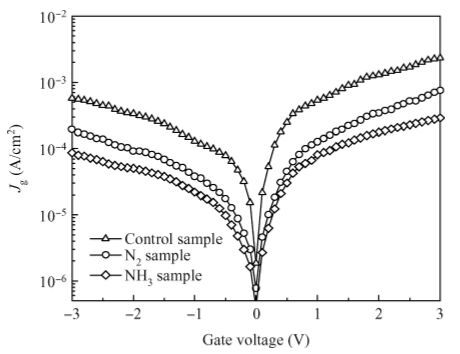
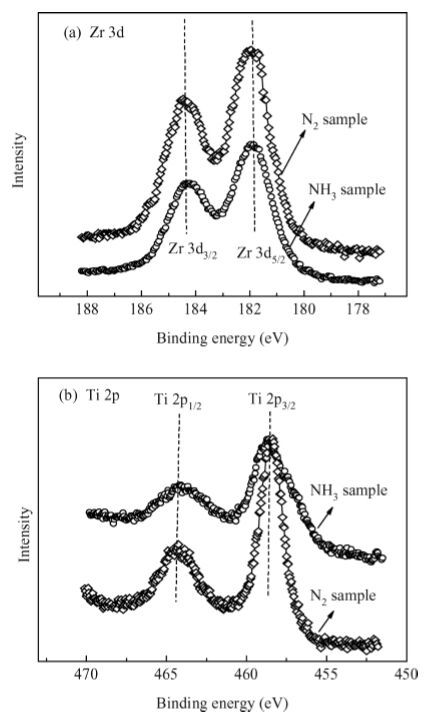
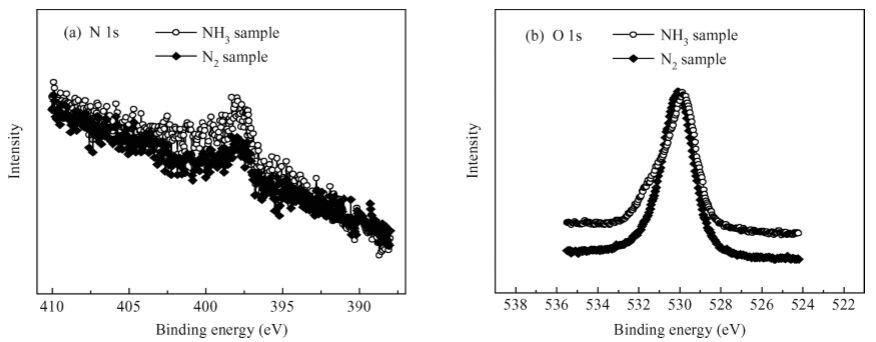
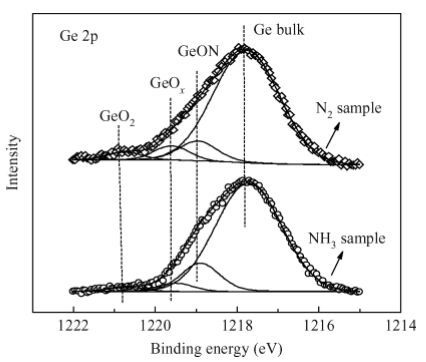
The interfacial and electrical characteristics of Ge metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) devices with a dual passivation layer of ZrON/GeON formed by NH3- or N2-plasma treatment are investigated. The experimental results show that the NH3-plasma treated sample exhibits significantly improved interfacial and electrical properties as compared to the samples with N2-plasma treatment and no treatment: a lower interface-state density at the midgap (1.64 × 1011 cm-2·eV-1) and gate leakage current (9.32 × 10-5 A/cm2 at Vfb+ 1 V), a small capacitance equivalent thickness (1.11 nm) and a high k value (32). X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy is used to analyze the involved mechanisms. It is indicated that more GeON and less GeOx (x <2) are formed on the Ge surface during NH3-plasma treatment than the N2-plasma treatment, resulting in a high-quality high-k/Ge interface, because H atoms and NH radicals in NH3-plasma can enhance volatilization of the unstable low-k GeOx, creating high-quality GeON passivation layer. Moreover, more nitrogen incorporation in ZrON/GeON induced by NH3-plasma treatment can build a stronger N barrier and thus more effectively inhibit in-diffusion of O and Ti from high-k gate dielectric and out-diffusion of Ge. -
References
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] [10] [11] [12] [13] [14] [15] [16] [17] [18] [19] [20] [21] -
Proportional views






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: