| Citation: |
Bo Gan, Tingcun Wei, Wu Gao, Yongcai Hu. Design and performances of a low-noise and radiation-hardened readout ASIC for CdZnTe detectors[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2016, 37(6): 065007. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/37/6/065007
****
B Gan, T C Wei, W Gao, Y C Hu. Design and performances of a low-noise and radiation-hardened readout ASIC for CdZnTe detectors[J]. J. Semicond., 2016, 37(6): 065007. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/37/6/065007.
|
Design and performances of a low-noise and radiation-hardened readout ASIC for CdZnTe detectors
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/37/6/065007
More Information
-
Abstract
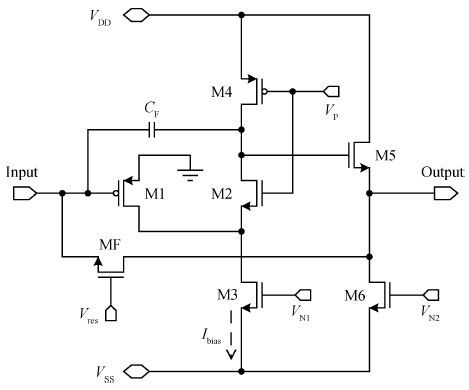
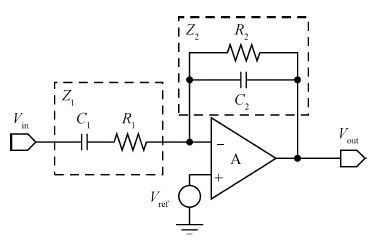
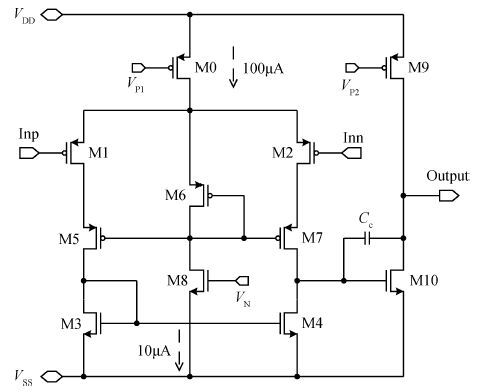
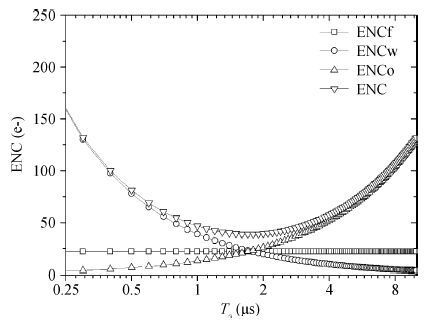
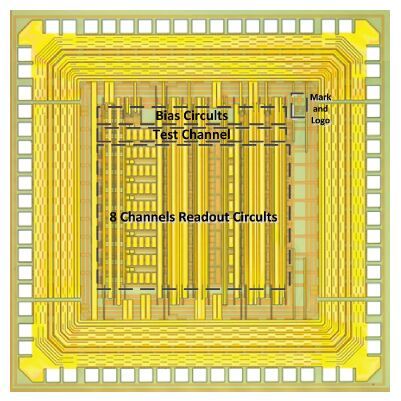
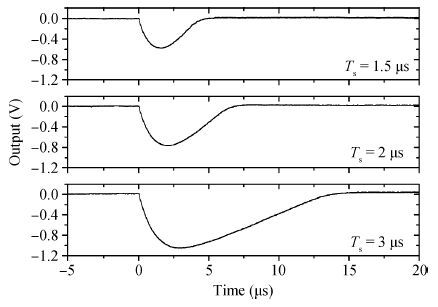
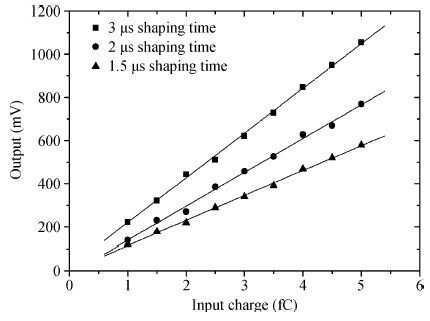
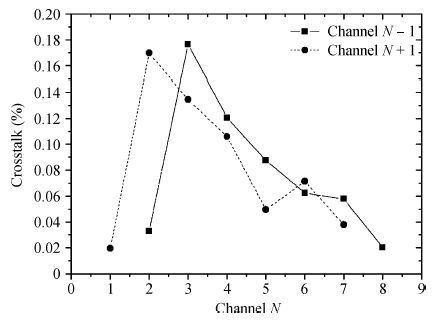
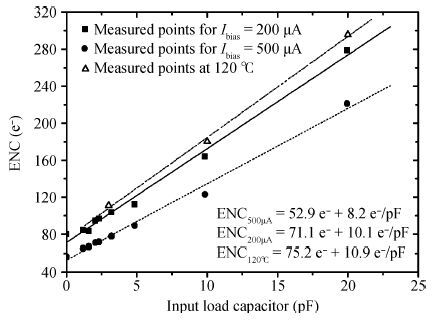
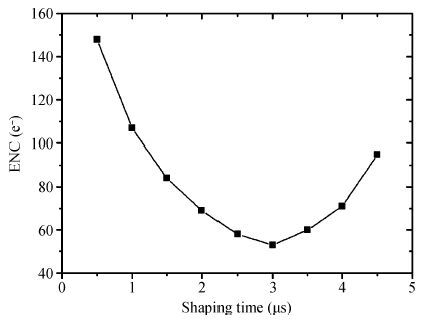
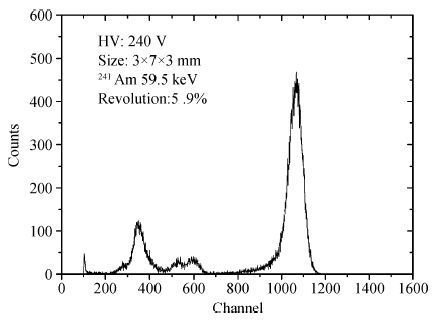
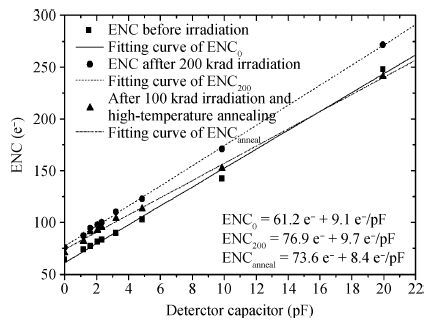
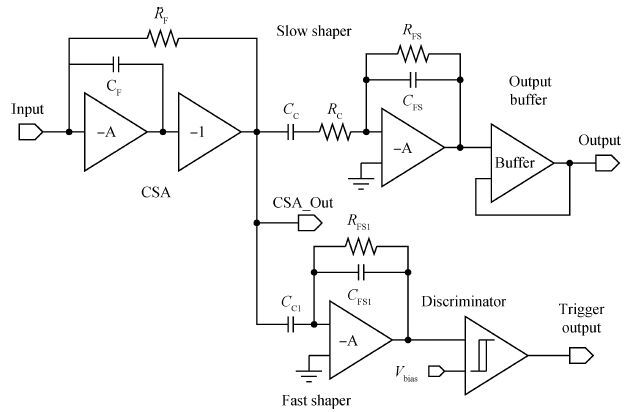
In this paper, we present the design and performances of a low-noise and radiation-hardened front-end readout application specific integrated circuit (ASIC) dedicated to CdZnTe detectors for a hard X-ray imager in space applications. The readout channel is comprised of a charge sensitive amplifier, a CR-RC shaping amplifier, an analog output buffer, a fast shaper, and a discriminator. An 8-channel prototype ASIC is designed and fabricated in TSMC 0.35-μm mixed-signal CMOS technology, the die size of the prototype chip is 2.2×2.2 mm2. The input energy range is from 5 to 350 keV. For this 8-channel prototype ASIC, the measured electrical characteristics are as follows:the overall gain of the readout channel is 210 V/pC, the linearity error is less than 2%, the crosstalk is less than 0.36%, The equivalent noise charge of a typical channel is 52.9 e- at zero farad plus 8.2 e- per picofarad, and the power consumption is less than 2.4 mW/channel. Through the measurement together with a CdZnTe detector, the energy resolution is 5.9% at the 59.5-keV line under the irradiation of the radioactive source 241Am. The radiation effect experiments show that the proposed ASIC can resist the total ionization dose (TID) irradiation of higher than 200 krad(Si).-
Keywords:
- CdZnTe detector,
- low-noise,
- front-end readout,
- ASIC,
- X-ray,
- radiation-hardened
-
References
[1] Butcher J, Hamade M, Petryk M, et al. Drift time variations in CdZnTe detectors measured with alpha particles and gamma rays:their correlation with detector response. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci, 2013, 60(2):1189[2] Overdick M, Baumer C, Engel K J, et al. Status of direct conversion detectors for medical imaging with X-rays. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci, 2009, 56(4):1800[3] Yao C, Zhou M, Luo Y, et al. Millimeter wave broadband high sensitivity detectors with zero-bias Schottky diodes. Journal of Semiconductors, 2015, 36(6):065002[4] Amman M, Lee J S, Luke P N, et al. Evaluation of THM-grown CdZnTe material for large-volume gamma-ray detector applications. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci, 2009, 56(3):795[5] Jones L, Seller P, Wilson M, et al. HEXITEC ASIC-A pixellated readout chip for CZT detectors. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physical Research Section A, 2009, 604(s 1-2):34[6] Lazzari O, Jacques S, Sochi T, et al. Reconstructive color X-ray diffraction imaging-A novel TEDDI imaging method. RSC Analyst, 2009, 134(9):1802[7] Allen B, Hong J, Grindlay J, et al. Development of the ProtoEXIST2 advanced CZT detector plane. IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference, 2011:4470[8] Gao W, Gan B, Li X, et al. Development of a compact radiationhardened low-noise front-end readout ASIC for CZT-based hard X-ray imager. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 2015, 780:15[9] Clajus M, Snyder S, Tumer E, et al. A low-power 2-D ASIC for high-resolution gamma-ray spectroscopy. IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference, 2011:4701[10] Voelker M, Carrascal J, Soriano-Asensi A. Design and preliminary performance of a readout ASIC for CZT based high resolution PET. IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference, 2011:4593[11] Meier D, Gheorghe C, Johansen T M, et al. Interpolation in a pixellated CZT-radiation detector. IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference, 2011:4550[12] Gevin O, Lemaire O, Lugiez F, et al. Imaging X-ray detector front-end with high dynamic range:IDeF-X HD. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 2012, 695(6):415[13] Gan B, Wei T, Gao W, et al. Design of a multi-channel low-noise readout ASIC for CdZnTe-based X-ray and-ray spectrum analyzer. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci, 2015, 62(5):1995[14] Hu Y, Dulinski W, Turchetta R, et al. Design of a low noise, selftriggered, monolithic preamplifier dedicated to silicon trackers and X-βimaging. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physical Research Section A, 1995, 361(3):568[15] Fang X C, Ch H G, Ollivier-Henry N, et al. Design of a multichannel front-end readout ASIC with low noise and large dynamic input range for APD-based PET imaging. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci, 2009, 56(4):2351[16] Sansen W, Chang Z. Limits of low noise performance of detector readout front ends in CMOS technology. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst, 1990, 37(11):1375[17] Gao W, Gao D, Ch H G, et al. Design and characteristics of an integrated multichannel ramp ADC using digital DLL techniques for small animal PET imaging. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci, 2011, 58(5):2161[18] Gevin O, Baron P, Coppolani X, et al. IDeF-X ECLAIRs:a CMOS ASIC for the readout of CdTe and CdZnTe detectors for high resolution spectroscopy. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci, 2009, 56(4):2351[19] Michalowska A, Gevin O, Lemaire O, et al. IDeF-X HD:a low power multi-gain CMOS ASIC for the readout of Cd(Zn)Te detectors. IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference, 2010:1556[20] Kishishita T, Sato G, Ikeda H, et al. Low-noise analog ASIC for silicon and CdTe sensors. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci, 2010, 57(5):2971[21] Luo J, Deng Z, Wang G, et al. Development of a low noise readout ASIC for CZT detectors for gamma-ray spectroscopy applications. Journal of Instrumentation, 2012, 7(8):P08030[22] Liu W, Wei T, Li B, et al. A 12-bit 1 MS/s SAR-ADC for multichannel CdZnTe detectors. Journal of Semiconductors, 2015, 36(4):045007 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: