| Citation: |
Zhan Gao, Dan Ren, Shuai Yan, Xiaoyu Xu, Zhuoxiang Ren. Computation of sensitivities of IC interconnect parasitic capacitances to the process variation with dual discrete geometric methods[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2016, 37(8): 085003. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/37/8/085003
****
Z Gao, D Ren, S Yan, X Y Xu, Z X Ren. Computation of sensitivities of IC interconnect parasitic capacitances to the process variation with dual discrete geometric methods[J]. J. Semicond., 2016, 37(8): 085003. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/37/8/085003.
|
Computation of sensitivities of IC interconnect parasitic capacitances to the process variation with dual discrete geometric methods
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/37/8/085003
More Information
-
Abstract
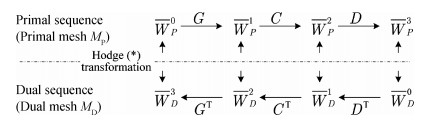
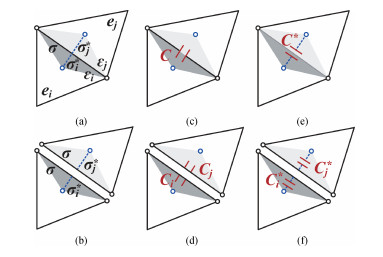
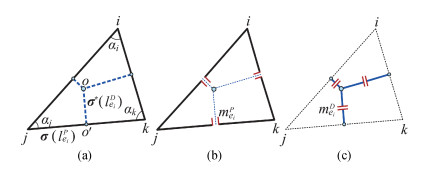
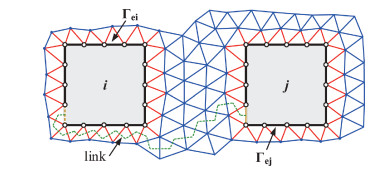
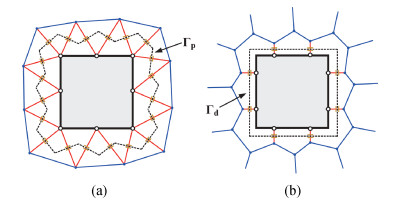
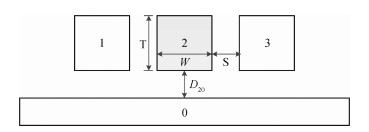
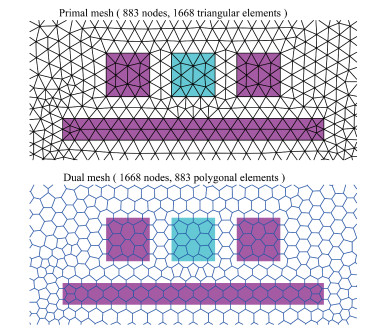
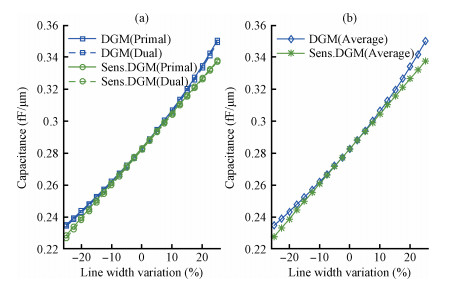
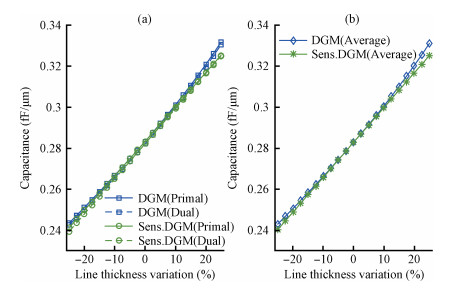
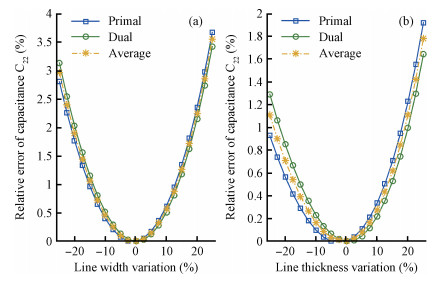
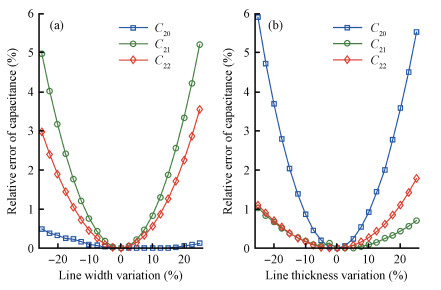
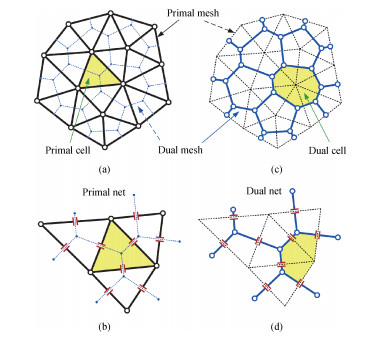
Sensitivity analysis methods help to deal with the challenges of process variation in extraction of parasitic capacitances in an integrated circuit. The dual discrete geometric methods (DGMs), which have been recently utilized to extract parasitic capacitances, are reviewed. The computation method based on the dual DGMs for sensitivities of capacitances with respect to the given process parameters is presented. As the dual DGMs utilize scalar electric potential is unknown, the capacitances are obtained effectively, and then the sensitivities are calculated conveniently. -
References
[1] International technology roadmap for semiconductors (ITRS) reports 2013. http://www.itrs.net, 2014[2] Gu Weiru, Ye Fan, Ren Junyan. An 11-bit 22-MS/s 0.6 mW SAR ADC with parasitic capacitance compensation. Journal of Semiconductors, 2014, 35(8): 085006 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/8/085006[3] Ren X, Pang C, Qin Z, et al. Design, analysis and test of high-frequency interconnections in 2.5D package with silicon interposer. Journal of Semiconductors, 2016, 37(4): 045003 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/37/4/045003[4] Yu W, Zhuang H, Zhang C, et al. RWCap: a floating random walk solver for 3-D capacitance extraction of VLSI interconnects. IEEE Trans Comput-Aided Design, 2013, 32(3): 353 doi: 10.1109/TCAD.2012.2224346[5] Nabors K, White J. FastCap: a multipole accelerated 3-D capacitance extraction program. IEEE Trans Comput-Aided Des Integr Circuits Syst, 1991, 10(11): 1447 doi: 10.1109/43.97624[6] Zhu Z, White J, Demir A. A stochastic integral equation method for modeling the rough surface effect on interconnect capacitance. IEEE/ACM International Conference on Computer Aided Design, ICCAD-2004: 887[7] Hou J, Wang Z, Hong X. The hierarchical h-adaptive 3D boundary element computation of VLSI interconnect capacitance. Proceeding of the Asia South Pacific Design Automation Conference (ASP-DAC), 1999: 93 http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/summary?doi=10.1.1.494.9270[8] Shi W, Yu F. A divide-and-conquer algorithm for 3-D capacitance extraction. IEEE Trans Comput-Aided Des of Integr Circuits Syst, 2004, 23(8): 1157 doi: 10.1109/TCAD.2004.831595[9] Chen G, Zhu H, Cui T, et al. ParAFEMCap: a parallel adaptive finite-element method for 3-D VLSI interconnect capacitance extraction. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech, 2012, 60(2): 218 doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2011.2176137[10] Specogna R. Extraction of VLSI multiconductor transmission line parameters by complementarity. IEEE Trans Very Large Scale Integr Syst, 2014, 22(1): 146 doi: 10.1109/TVLSI.2012.2232320[11] Bossavit A. Computational electromagnetism, variational formulations, complementarity, edge elements. New York: Academic Press, 1997[12] Ren Z, Xu X. Dual discrete geometric methods in terms of scalar potential on unstructured mesh in electrostatics. IEEE Trans Magnet, 2014, 50(2): 37 doi: 10.1109/TMAG.2013.2280452[13] Ren Dan, Xu Xiaoyu, Qu Hui, et al. Two-dimensional parasitic capacitance extraction for integrated circuit with dual discrete geometric methods. Journal of Semiconductors, 2015, 36(4): 045008 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/36/4/045008[14] Hirani A N. Discrete exterior calculus. PhD thesis, California Institute of Technology, 2003 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2120103450&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn[15] Specogna R. Complementary geometric formulations for electrostatics. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 2011, 86(8): 1041 doi: 10.1002/nme.v86.8[16] Ren Z. A 3-D vector potential formulation using edge element for electrostatic field computation. IEEE Trans Magnet, 1995, 31: 1520 doi: 10.1109/20.376319[17] Xu X, Ren Z, Qu H, Ren D. 3-D IC interconnect capacitance extraction using dual discrete geometric methods with prism elements. IEEE Trans Very Large Scale Integr Syst, 2016, 24(4): 1524 doi: 10.1109/TVLSI.2015.2459043[18] El-Moselhy A T, Elfadel I M, Daniel L. A capacitance solver for incremental variation-aware extraction. IEEE/ACM International Conference on Date of Conference Computer-Aided Design, ICCAD 2008: 662 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1903428531&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn[19] Yu B, Kolk K J, Meijs N P. Sensitivity computation using domain-decomposition for boundary element method based capacitance extractors. IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference CICC, 2009: 423 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2138889479&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn[20] Qu H, Kong L, Xu Y, et al. Finite-element computation of sensitivities of interconnect parasitic capacitances to the process variation in VLSI. IEEE Trans Magnet, 2008, 44(8): 1386 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2096056818&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn[21] Bossavit A. How weak is the "weak solution" in finite element methods. IEEE Trans Magnet, 1998, 34(5): 2429 doi: 10.1109/20.717558[22] Ren Z, Xu X. Computation of second order capacitance sensitivity using adjoint method in finite element modeling. IEEE Trans Magnet, 2012, 48(2): 231 doi: 10.1109/TMAG.2011.2172194 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: