| Citation: |
Yiqi Mao, Tongqiang Gao, Xiaodong Xu, Haigang Yang, Xinxia Cai. A fully integrated CMOS super-regenerative wake-up receiver for EEG applications[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2016, 37(9): 095001. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/37/9/095001
****
Y Q Mao, T Q Gao, X D Xu, H G Yang, X X Cai. A fully integrated CMOS super-regenerative wake-up receiver for EEG applications[J]. J. Semicond., 2016, 37(9): 095001. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/37/9/095001.
|
A fully integrated CMOS super-regenerative wake-up receiver for EEG applications
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/37/9/095001
More Information
-
Abstract
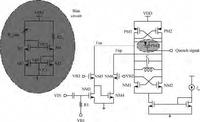
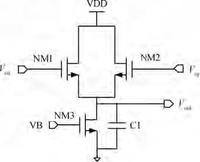
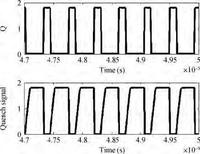
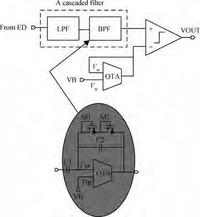
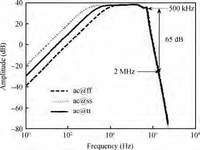
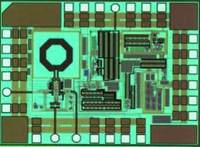
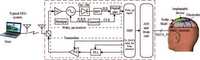
A fully integrated super-regenerative wake-up receiver for wireless body area network applications is presented. The super-regeneration receiver is designed to receive OOK-modulated data from the base station. A low power waveform generator is adopted both to provide a quench signal for VCO and to provide a clock signal for the digital module. The receiver is manufactured in 0.18 μm CMOS process and the active area is 0.67 mm2. It achieves a sensitivity of -80 dBm for 10-3 BER with a data rate of 200 kbps. The power consumption of the super-regenerative wake-up receiver is about 2.16 mW.-
Keywords:
- super-regenerative receiver,
- wake-up circuit,
- EEG,
- OOK,
- CMOS
-
References
[1] Armstrong E H. Some recent developments of regenerative circuits. Proceedings of the Institute of Radio Engineers, 1922, 10(4): 244 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2150943617&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn[2] Favre P, Joehl N, Vouilloz A, et al. A 2-V 600-μ A 1-GHz BiCMOS super-regenerative receiver for ISM application. IEEE J Solid-State Circuit, 1998, 33(12): 2186 doi: 10.1109/4.735703[3] Zahabi A, Anis M, Ortmanns M. 2.4 GHz super-regeneration amplifier with degenerative quenching technique for RF-pulse width transceiver. IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and System (ISCAS), 2012: 2147 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1967046438&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn[4] Otis B, Chee Y H, Rabaey J. A 400μ W-RX, 1.6 mW-TX super-regenerative transceiver for wireless sensor networks. Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC), 2005, 1: 396[5] Chen J Y, Flynn M P, Hayes J P. A fully integrated auto-calibrated super-regenerative receiver in 0.13-μm CMOS. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2007, 42(9): 1976 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2007.903092[6] Meyer R. Low-power monolithic RF peak detector analysis. IEEE J Solid State Circuits, 1995, 30(1): 65 doi: 10.1109/4.350192[7] Rabaey J M, Chandrakasam A, Nikolic B. Digital integrated circuits: a design perspective. 2nd ed. Electronics & VLSI, 2002 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2157024459&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn[8] Chen J Y. Design of low-power super-regenerative receivers. The University of Michigan, 2006[9] Barner R, Liu J. A 0.8 V 1.52 MHz MSVC relaxation oscillator with inverted mirror feedback reference for UHF RFID. IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference (CICC), 2006: 769[10] Harrison R R, Charles C. A low-power low-noise CMOS amplifier for neural recording applications. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2003, 38(6): 958 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2003.811979[11] Zhu Wenrui, Yang Haigang, Gao Tongqiang, et al. A baseband circuit for wake-up receivers with double-mode detection and enhanced sensitivity robustness. Journal of Semiconductors, 2013, 34(8): 085011 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/8/085011[12] Liu Y H, Lin T H. A delta-sigma pulse-width digitization technique for super-regenerative receivers. IEEE J Solid State-Circuits, 2010, 45(10): 2066 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2010.2061614 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: