| Citation: |
Xiaoyu Chen, Youwen Zhao, Zhiyuan Dong, Guiying Shen, Yongbiao Bai, Jingming Liu, Hui Xie, Jiangbian He. Performance improvement of c-Si solar cell by a combination of SiNx/SiOx passivation and double P-diffusion gettering treatment[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2017, 38(11): 114004. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/38/11/114004
****
X Y Chen, Y W Zhao, Z Y Dong, G Y Shen, Y B Bai, J M Liu, H Xie, J B He. Performance improvement of c-Si solar cell by a combination of SiNx/SiOx passivation and double P-diffusion gettering treatment[J]. J. Semicond., 2017, 38(11): 114004. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/38/11/114004.
|
Performance improvement of c-Si solar cell by a combination of SiNx/SiOx passivation and double P-diffusion gettering treatment
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/38/11/114004
More Information
-
Abstract
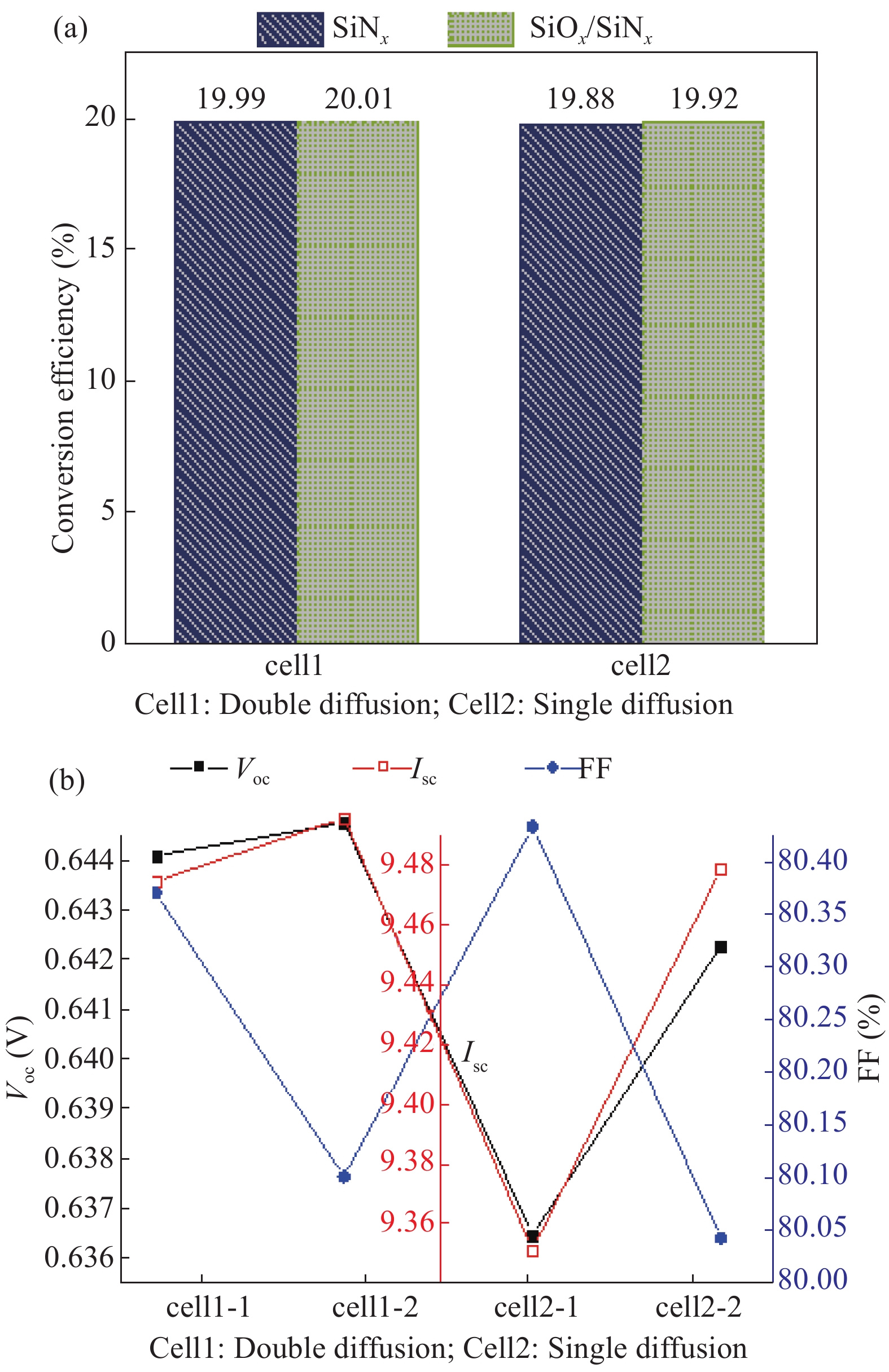
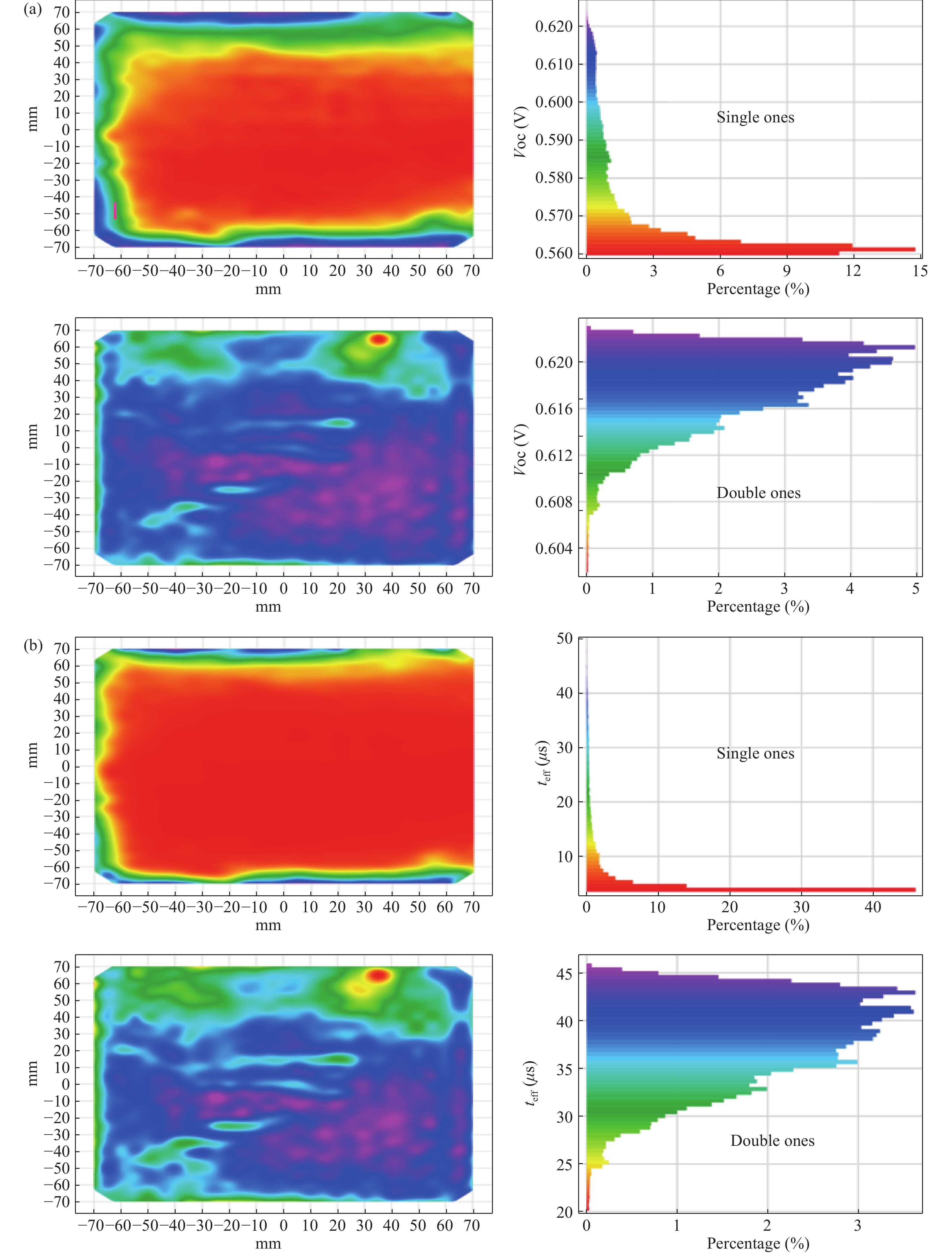
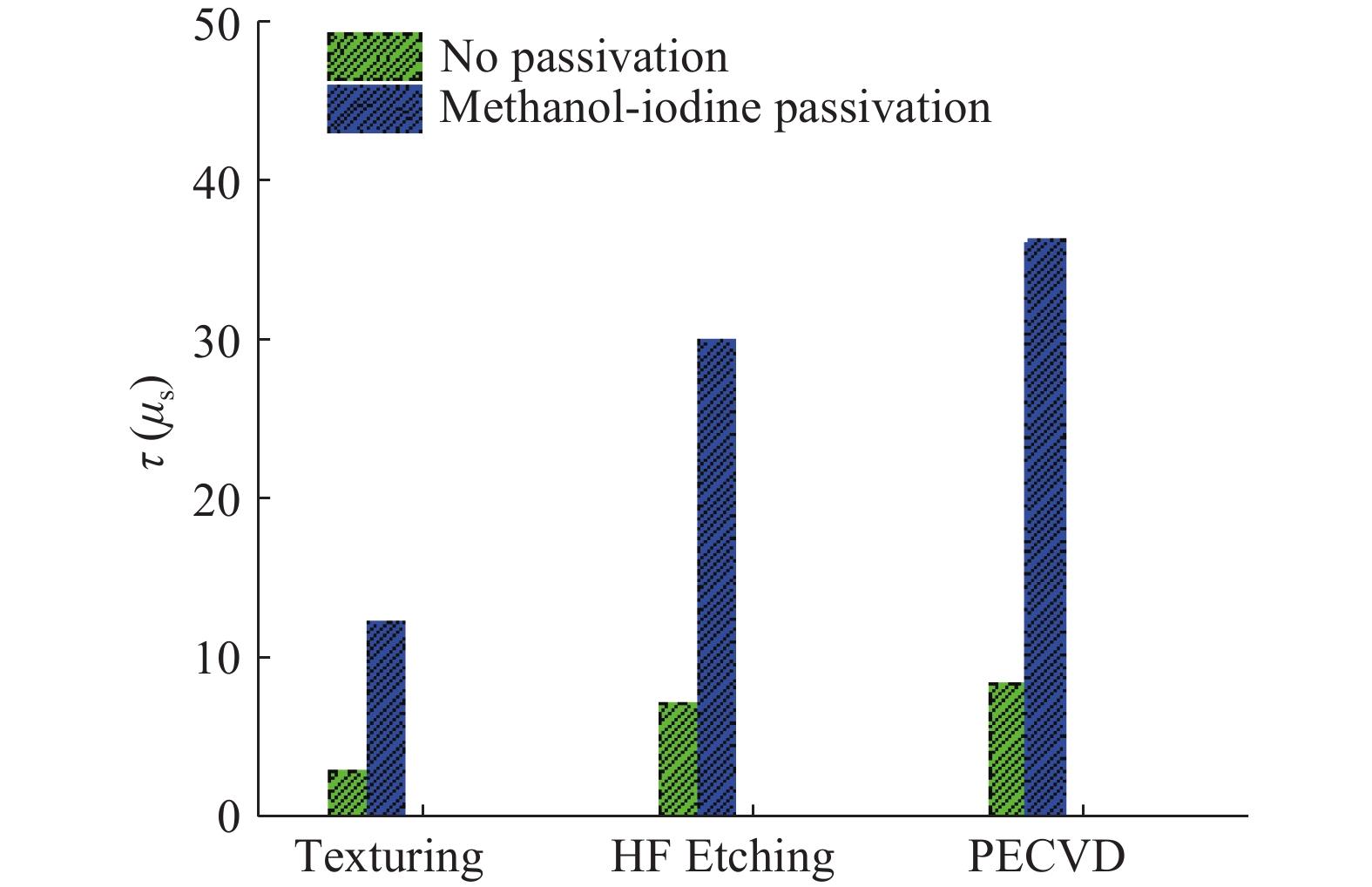
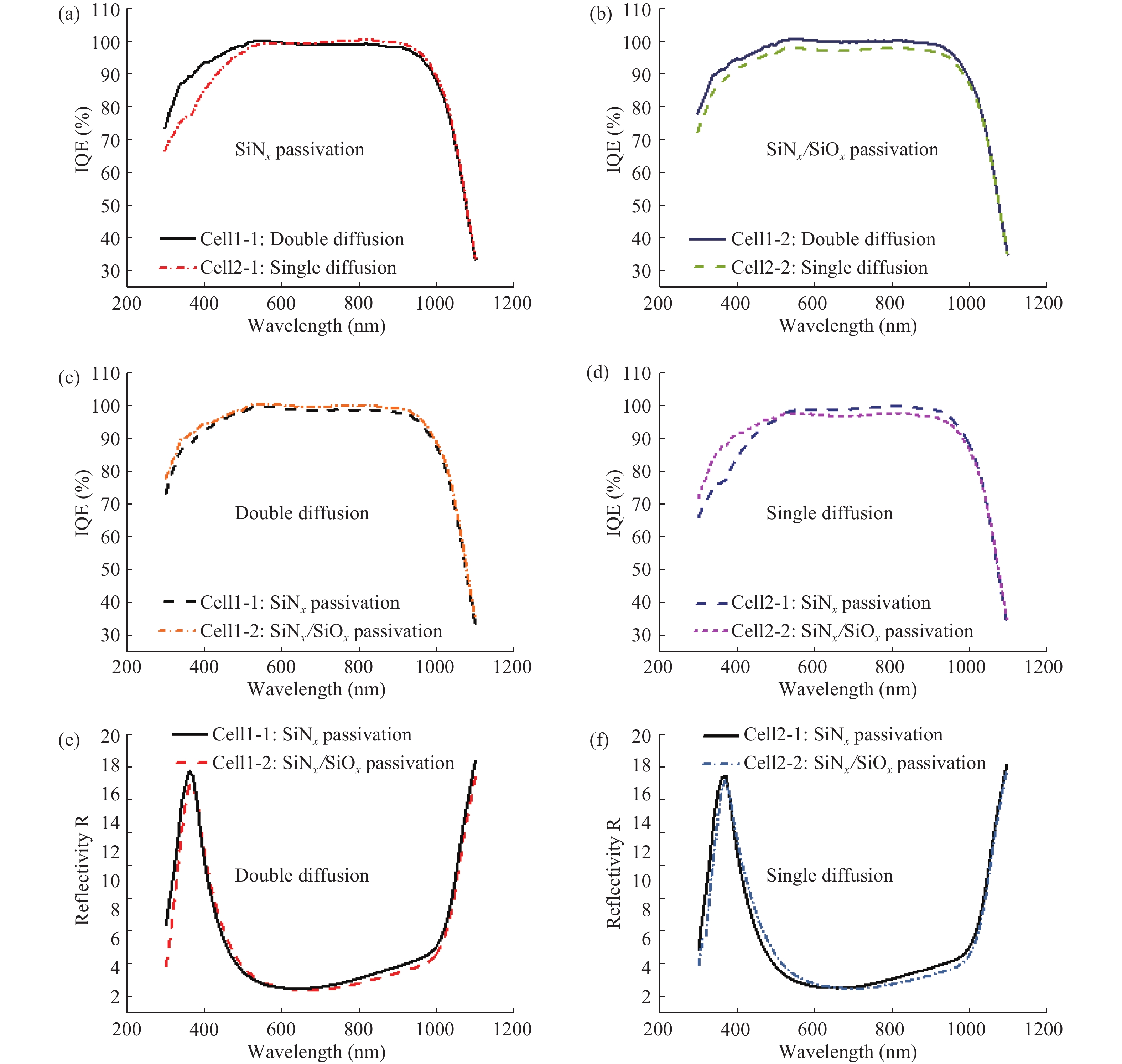
SiNx/SiOx passivation and double side P-diffusion gettering treatment have been used for the fabrication of c-Si solar cells. The solar cells fabricated have high open circuit voltage and short circuit current after the double P-diffusion treatment. In addition to better surface passivation effect, SiNx/SiOx layer has lower reflectivity in long wavelength range than conventional SiNx film. As a consequence, such solar cells exhibit higher conversion efficiency and better internal quantum efficiency, compared with conventional c-Si solar cells.-
Keywords:
- c-Si solar cell,
- double diffusion,
- SiNx/SiOx passivation
-
References
[1] Schindler F, Michl B, Schön J, et al. Solar cell efficiency losses due to impurities from the Crucible in multicrystalline silicon. IEEE J Photovolt, 2014, 4(1): 124[2] Breitenstein L, Schon J, Schubert M C, et al. Impact of iron surface contamination on the lifetime degradation of samples passivated by sired AlO/SiN stacks. IEEE J Photovolt, 2013, 3(3): 960[3] Macdonald D, Geerligs L J. Recombination activity of interstitial iron and other transition Metal point defects in p- and n-type crystalline silicon. Appl Phys Lett, 2004, 85(18): 4061 doi: 10.1063/1.1812833[4] Hofstetter J, Lelièvre J F, Fenning D P, et al. Towards the tailoring of P diffusion gettering to as-grown silicon material properties. Solid State Phenom, 2011, 178(179): 160[5] Davis J R, Rohatgi A, Hopkins R H, et al. Impurities in silicon solar cells. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 1980, 27(4): 1127[6] Cho E, Ok Y W, Dahal L D, et al. Comparison of POCl3 diffusion and phosphorus ion-implantation induced gettering in crystalline Si solar cells. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells, 2016, 157: 245 doi: 10.1016/j.solmat.2016.05.057[7] Hu Y, Meng Y Y, Wang J Q, et al. The effect of SiO2 Film on Electrical Property of Solar Cell. Journal of Shang Hai Jiao Tong University, 2009, 43(11): 1828[8] Macdonald D H, Geerligs L J, Azzizi A. Iron detection in crystalline silicon by carrier lifetime measurements for arbitrary injection and doping. J Appl Phys, 2004, 95(3): 1021 doi: 10.1063/1.1637136[9] Pickett M D, Buonassisi T. Iron point defect reduction in multicrystalline silicon solar cells. Appl Phys Lett, 2008, 92(12): 122103 doi: 10.1063/1.2898204[10] Fenning D P, Hofstetter J, Bertoni M I, et al. Iron distribution in silicon after solar cell processing: synchrotron analysis and predictive modeling. Appl Phys Lett, 2011, 98(16): 162103 doi: 10.1063/1.3575583[11] Kang J S, Schroder D K. Gettering in silicon. J Appl Phys, 1989, 65(8): 2974 doi: 10.1063/1.342714[12] Seibt M, Sattler A, Rudolf C, et al. Gettering in silicon photovoltaics: current state and future perspectives. Phys Status Solidi, 2006, 203(4): 697[13] Myers S M, Seibt M, Schröter W. Mechanisms of transition-metal gettering in silicon. J Appl Phys, 2000, 88(77): 3795[14] Shabani M B, Yamashita T, Morita E. Study of Gettering Mechanisms in Silicon: Competitive Gettering between Phosphorus Diffusion Gettering and Other Gettering Sites. Solid State Phenom, 2008, 131(133): 401[15] Khedher N, Hajji M, Hassen M, et al. Gettering impurities from crystalline silicon by phosphorus diffusion using a porous silicon layer. Sol Energy Mater Sol, 2005, 87(1-4): 605 doi: 10.1016/j.solmat.2004.09.017[16] Seibt M, Sattler A, Rudolf C. Gettering in silicon photovoltaics: current state and future perspectives, Gettering in silicon. Phys Stat Sol, 2006, 203(4): 698[17] Myers S M, Seibt M, Schröter W, Mechanisms of transition-metal gettering in silicon. J Appl Phys 2000, 88(7): 3795 doi: 10.1063/1.1289273[18] Shabani M B, Yamashita T, Morita E. Study of Gettering Mechanisms in Silicon: Competitive Gettering between Phosphorus Diffusion Gettering and Other Gettering Sites. Solid State Phenom, 2007, 131--133: 399[19] Khedher N, Hajji M, Hassen M, et al. Gettering impurities from crystalline silicon by phosphorus diffusion using a porous silicon layer. Physica Status Solidi, 2005, 87(1-4): 605[20] Hyvärinen J, Karila J. New analysis method for crystalline silicon cells. Proceedings of the 3rd World Conference on Photovoltaic Energy Conversion, 2003, 2(2): 1521[21] Vähänissi V, Haarahiltunen A, Talvitie H, et al. Impact of phosphorus gettering parameters and initial iron level on silicon solar cell properties. Prog Photovolt: Res Appl, 2013, 21(5): 1127[22] Chen J W, Zhao L, Diao H W, et al. The use of iodine passivation measuring minority carrier lifetime of crystalline silicon. CPVC12, 2013: R98[23] Zerihun L, Lindquist S E. Donor–acceptor interaction between non-aqueous solvents and I2 to generate I−3, and its implication in dye sensitized solar cells. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells, 1999, 57(3): 260[24] Dupuis J, Lelièvre J F, Fourmond E. Sioxny/sinx double antireflection layer for multicrystalline silicon solar cells. Proc 24th European PVSEC, 2009, 2: 1633[25] Murakami K, Tsujimura M, Shirakawa R, et al. Electronic states of P donors in Si Nanocrystals Embedded in amorphous SiO2 layer studied by electron spin resonance: hydrogen passivation effects. Jpn J Appl Phys, 2009, 48(8): 2 -
Proportional views






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: