| Citation: |
S Chakraborty, A Dasgupta, R Das, M Kar, A Kundu, C K Sarkar. Device and circuit analysis of a sub 20 nm double gate MOSFET with gate stack using a look-up-table-based approach[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2017, 38(12): 124001. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/38/12/124001
****
S Chakraborty, A Dasgupta, R Das, M Kar, A Kundu, C K Sarkar. Device and circuit analysis of a sub 20 nm double gate MOSFET with gate stack using a look-up-table-based approach[J]. J. Semicond., 2017, 38(12): 124001. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/38/12/124001.
|
Device and circuit analysis of a sub 20 nm double gate MOSFET with gate stack using a look-up-table-based approach
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/38/12/124001
More Information
-
Abstract
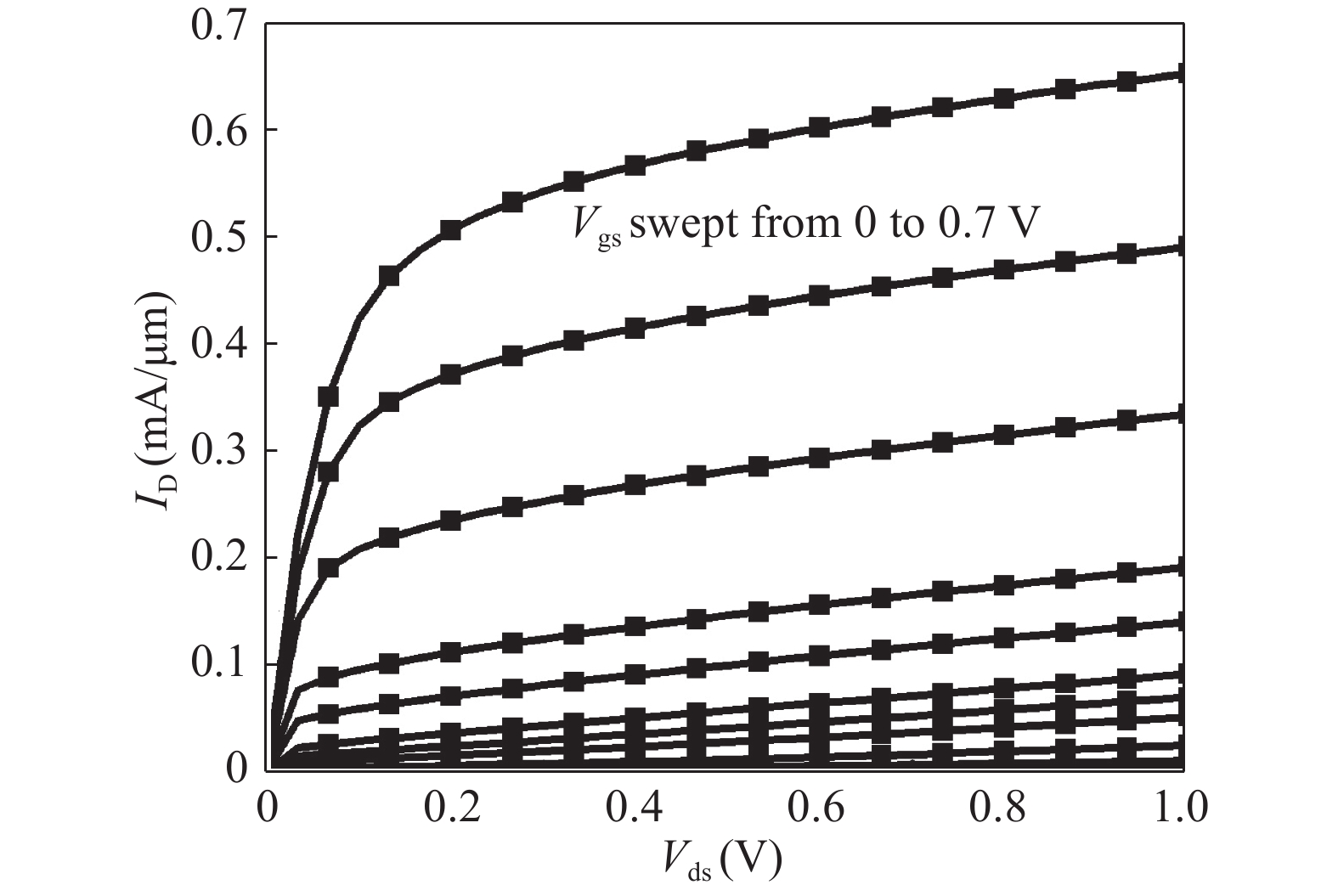
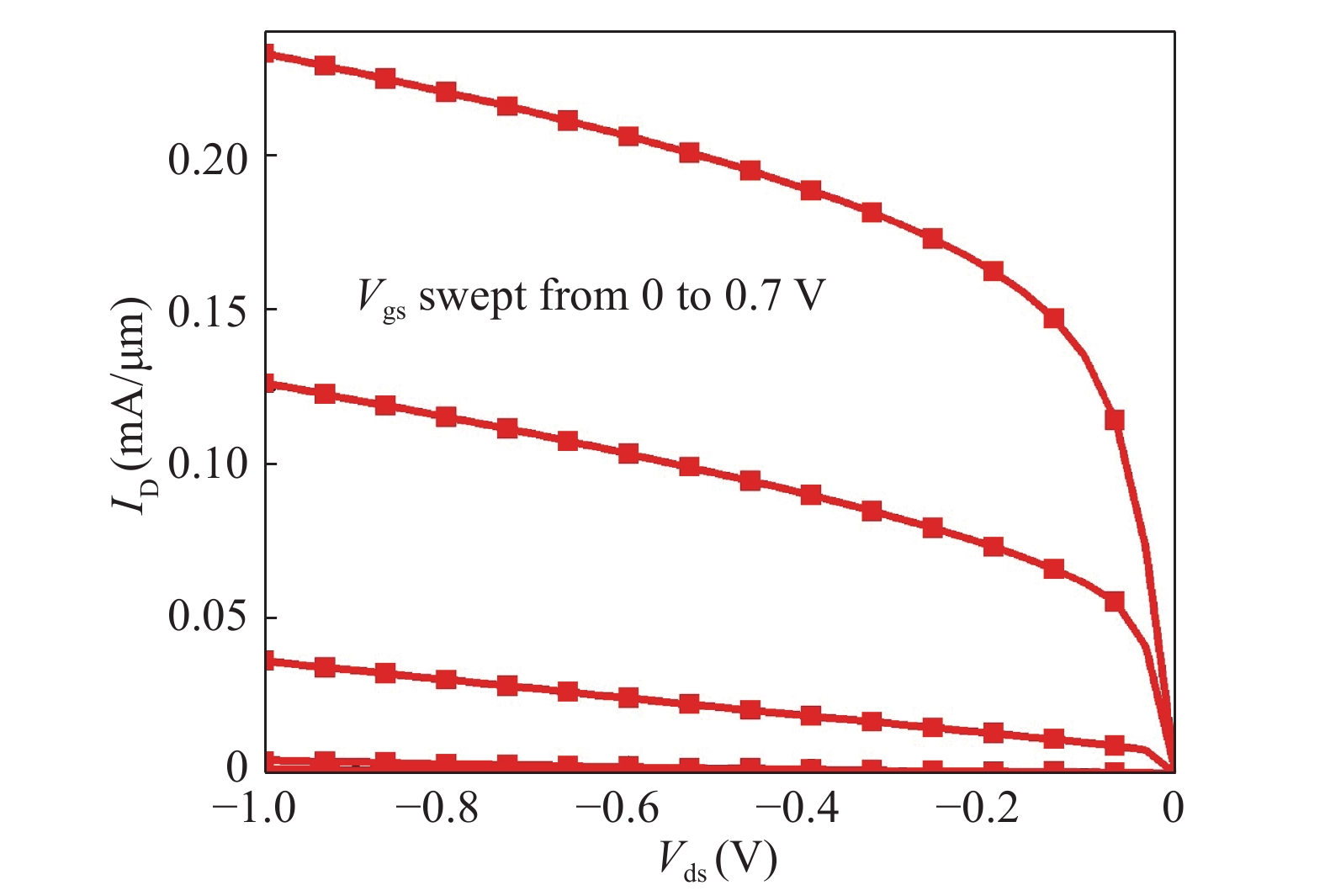
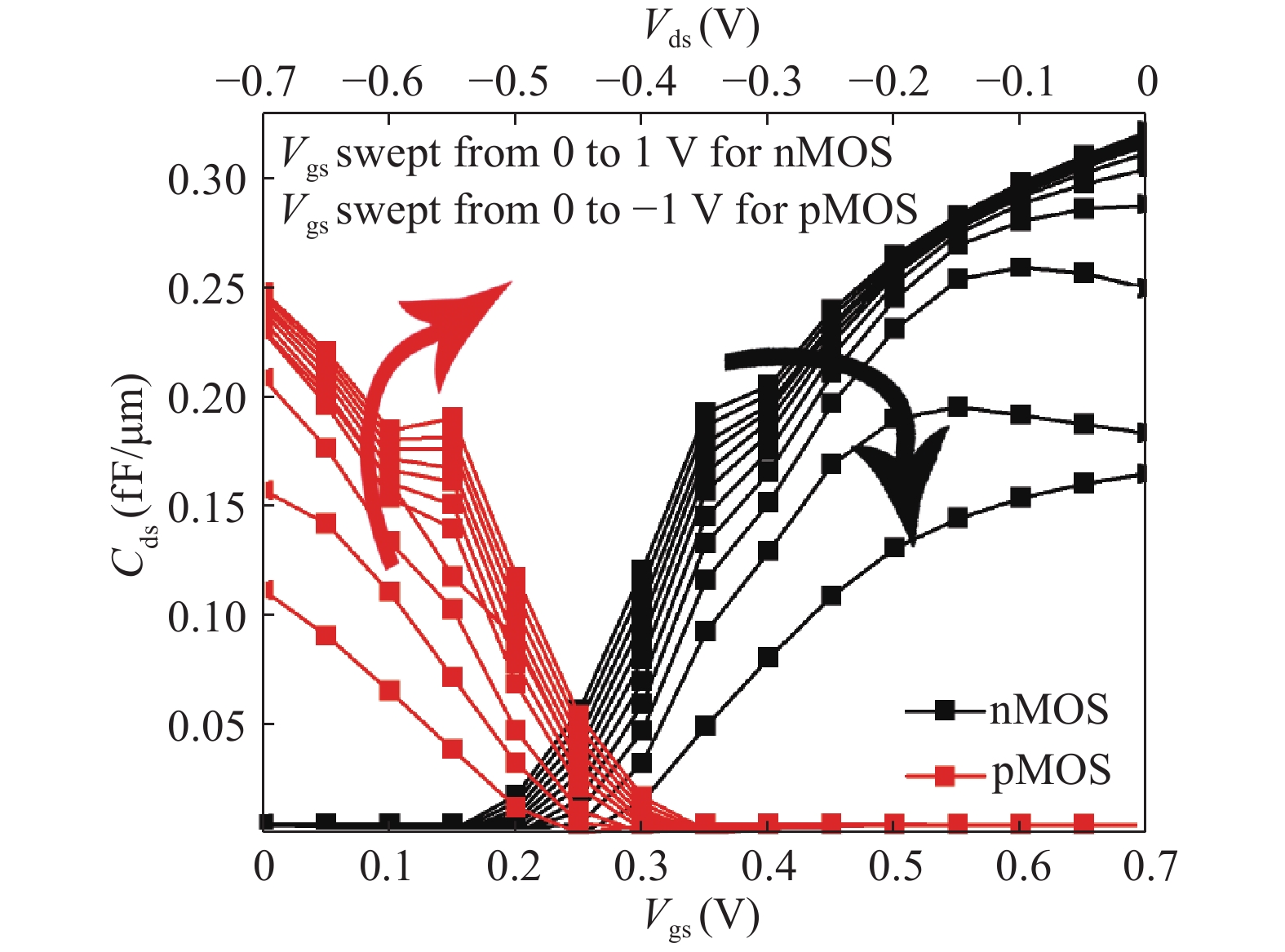
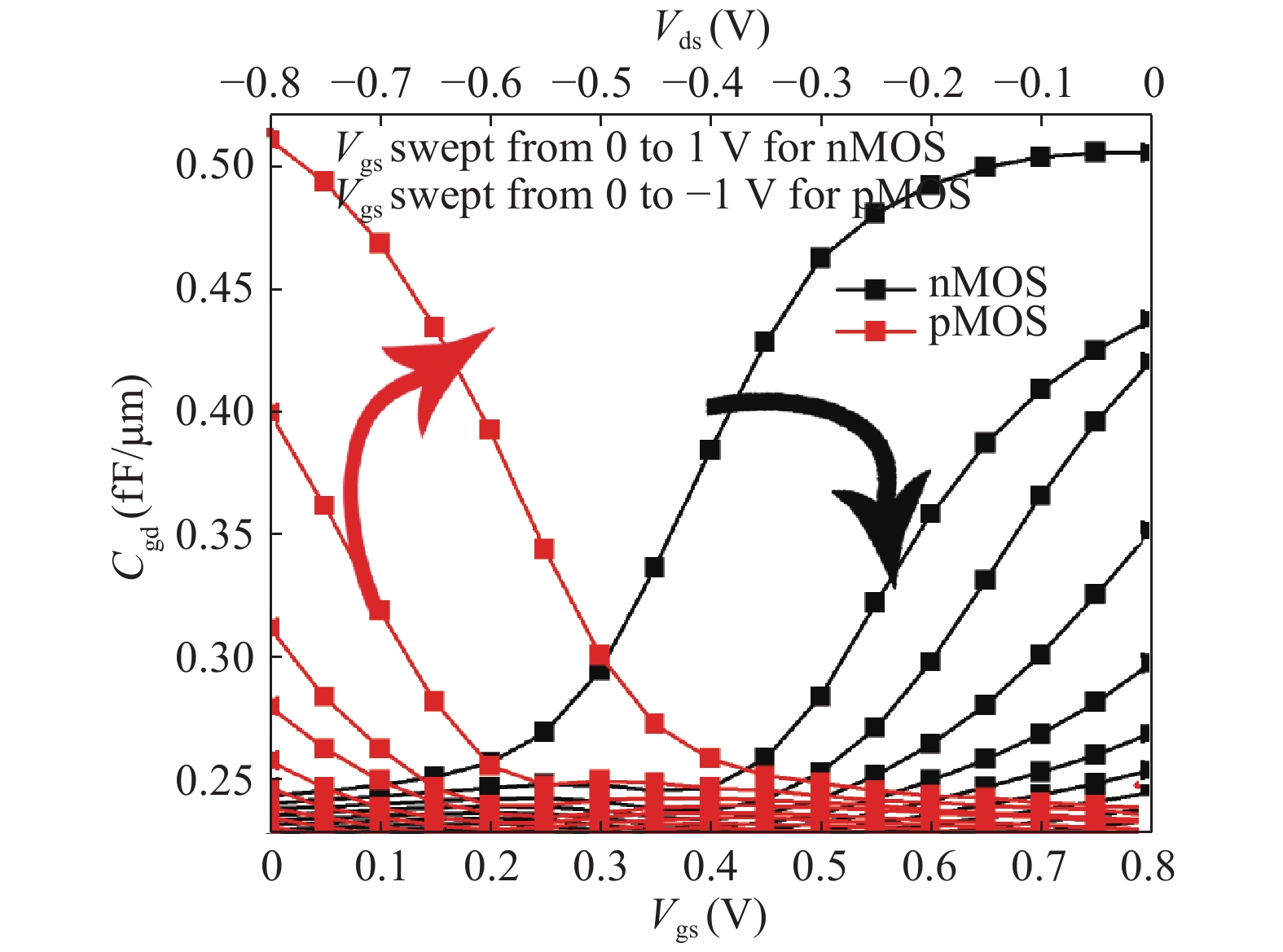
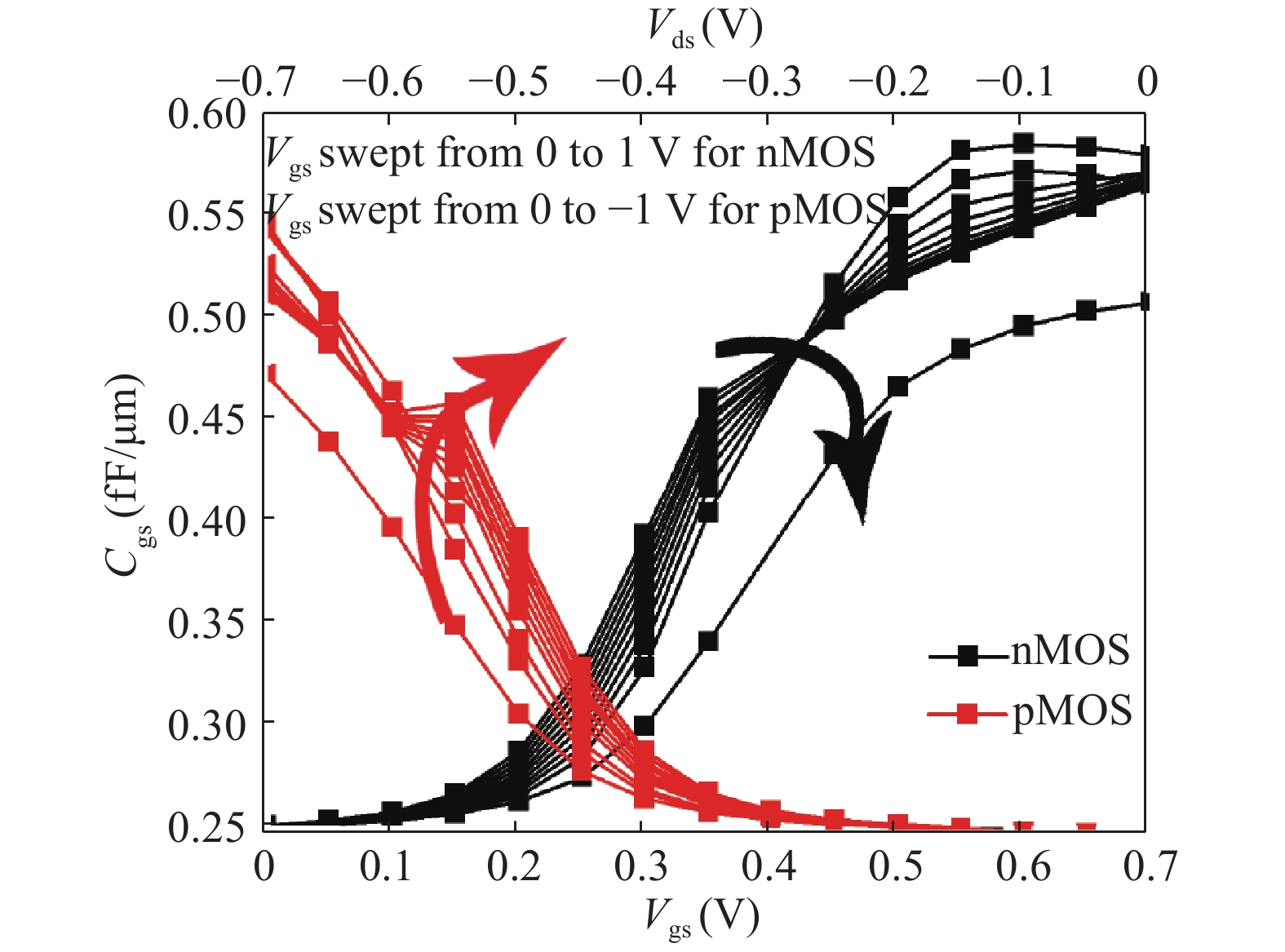
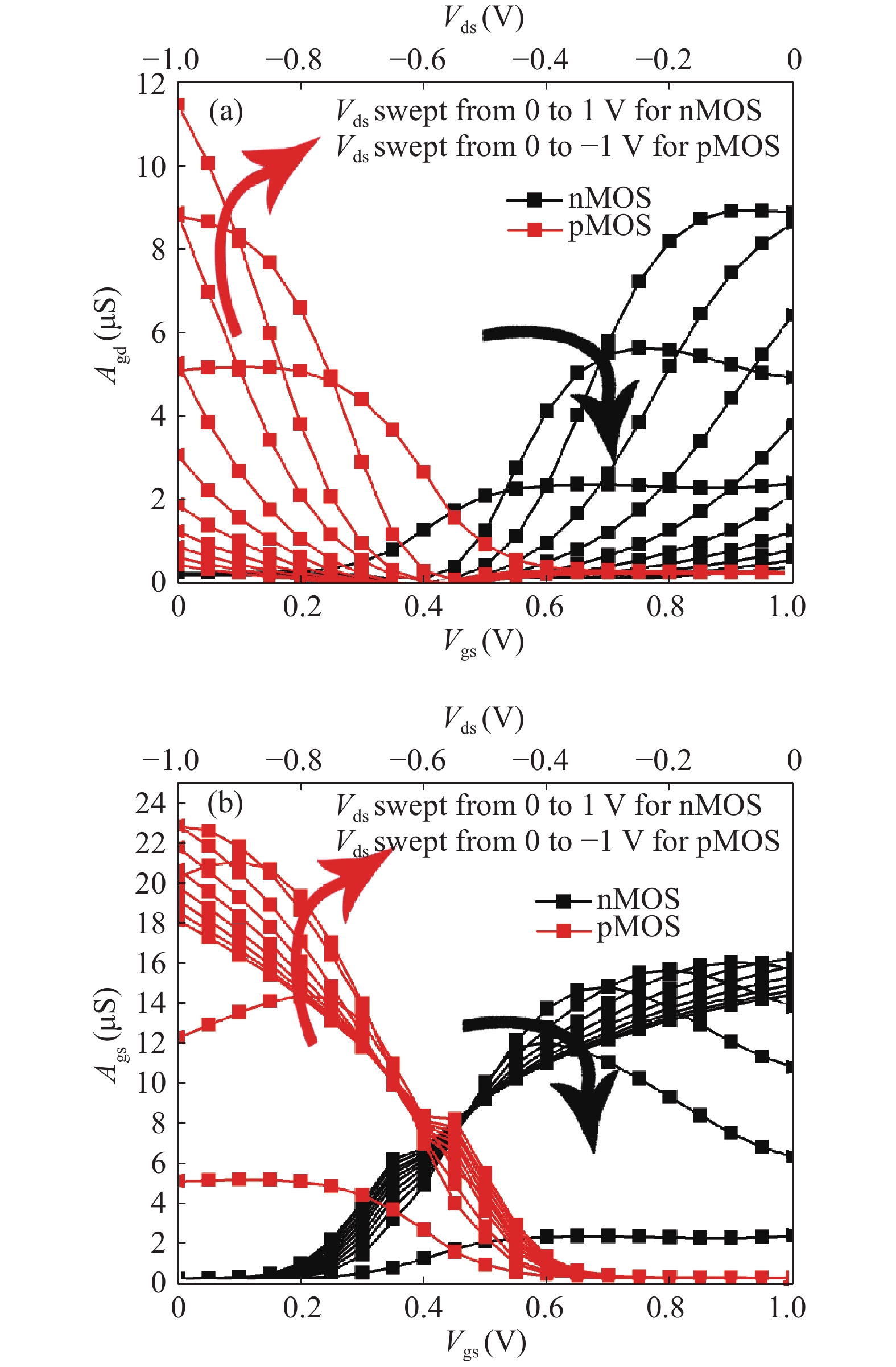
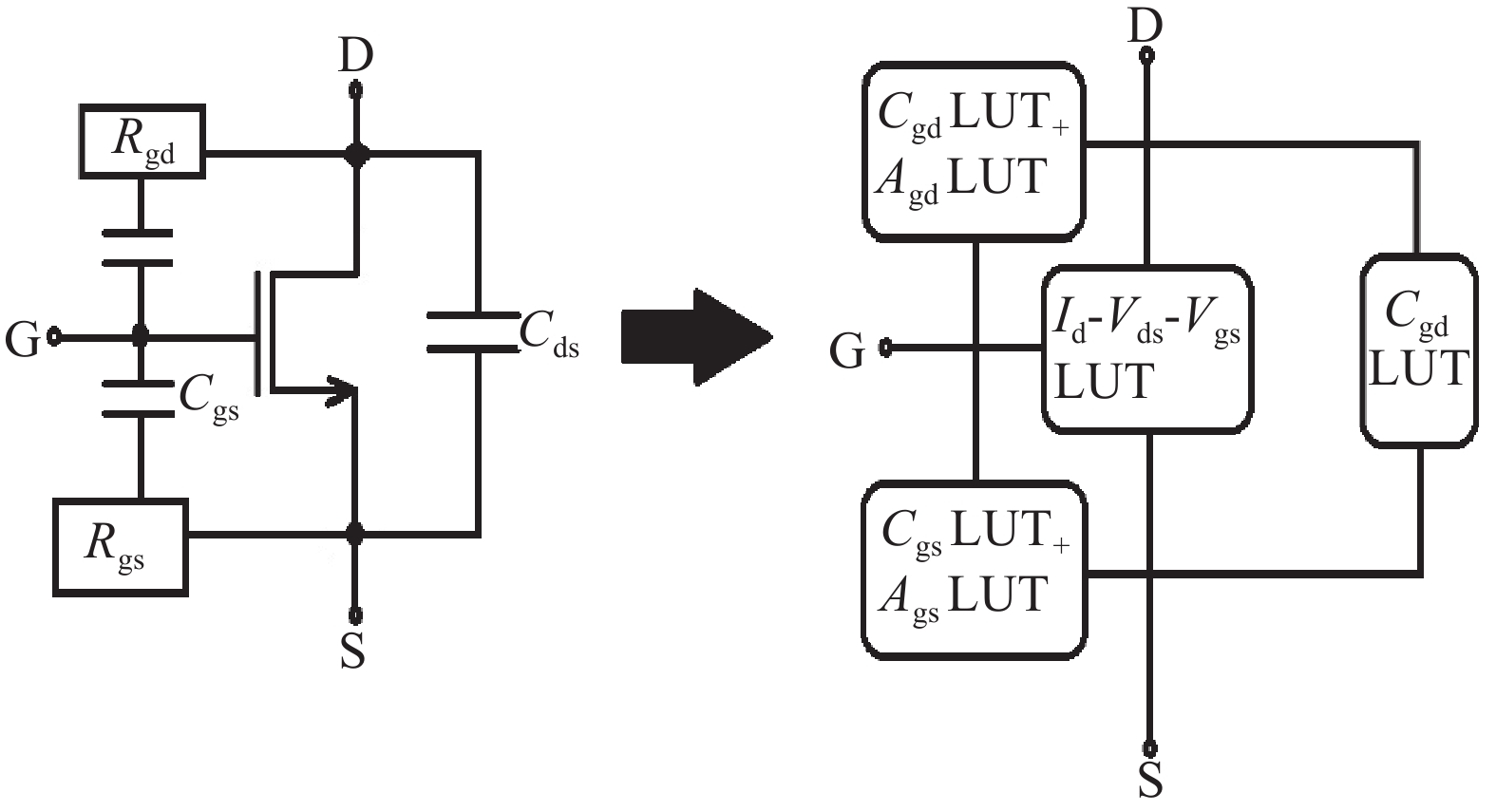
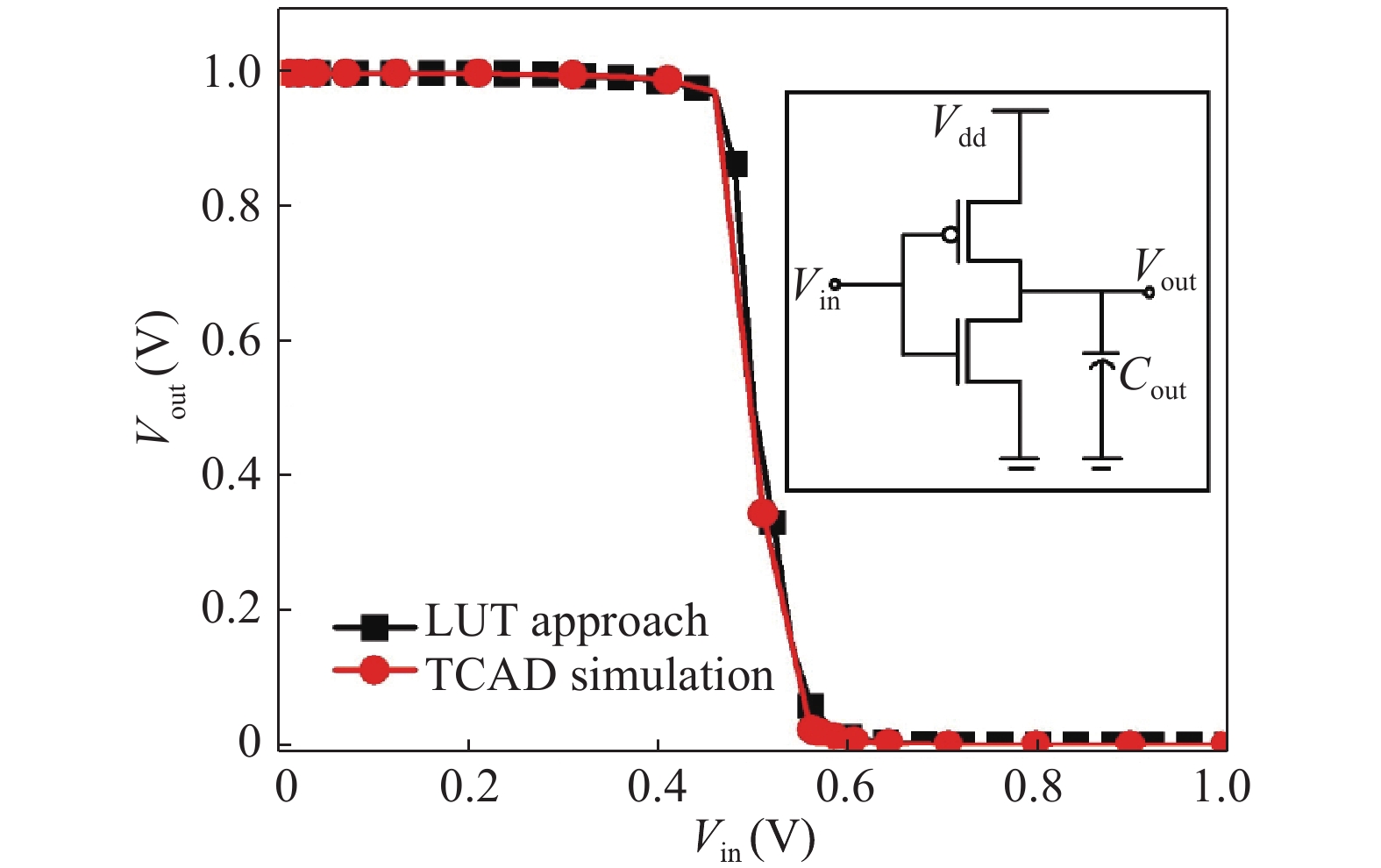
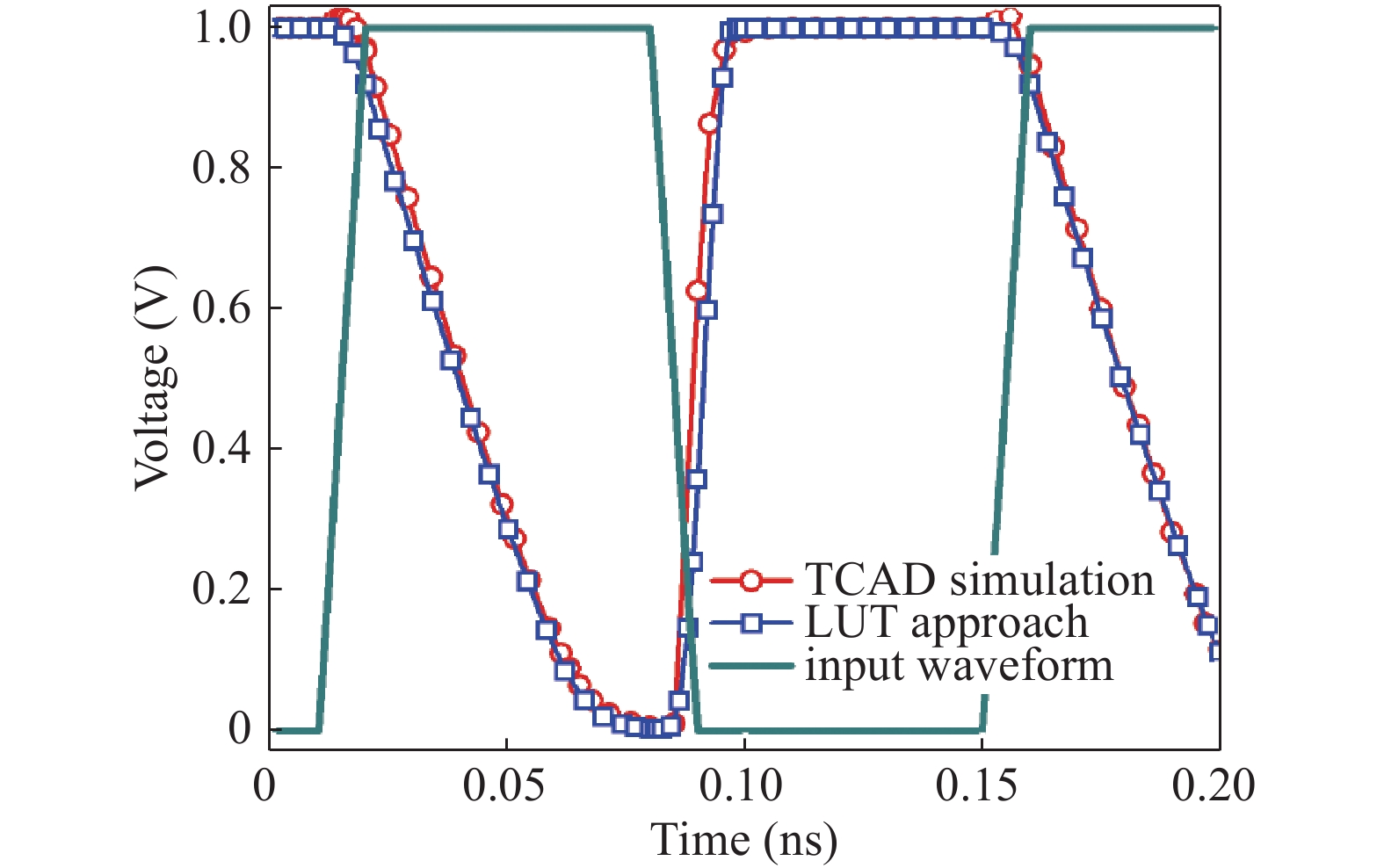
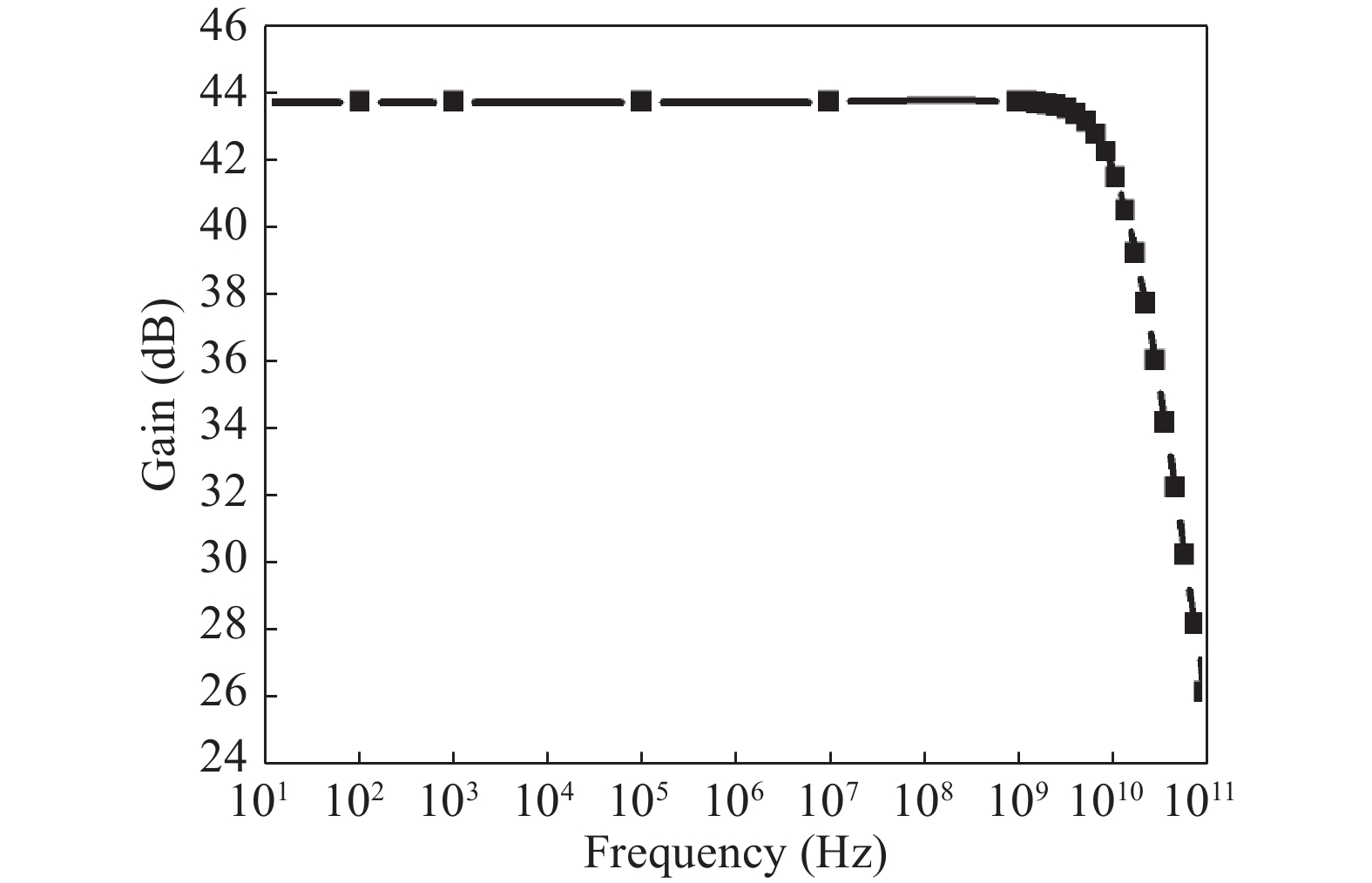
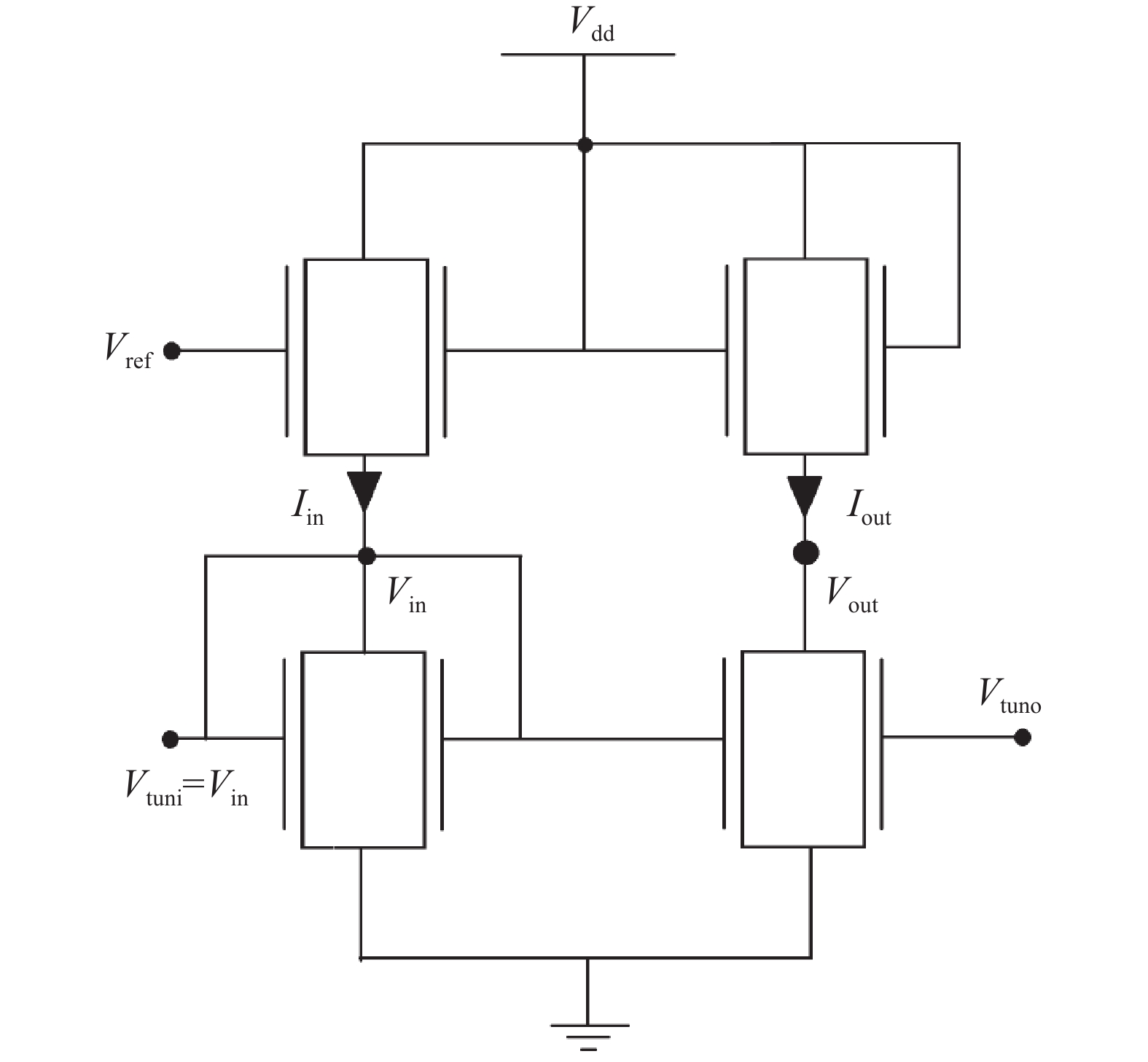
In this paper, we explore the possibility of mapping devices designed in TCAD environment to its modeled version developed in cadence virtuoso environment using a look-up table (LUT) approach. Circuit simulation of newly designed devices in TCAD environment is a very slow and tedious process involving complex scripting. Hence, the LUT based modeling approach has been proposed as a faster and easier alternative in cadence environment. The LUTs are prepared by extracting data from the device characteristics obtained from device simulation in TCAD. A comparative study is shown between the TCAD simulation and the LUT-based alternative to showcase the accuracy of modeled devices. Finally the look-up table approach is used to evaluate the performance of circuits implemented using 14 nm nMOSFET.-
Keywords:
- 14 nm,
- double gate MOSFET,
- look-up table,
- VerilogA
-
References
[1] Xie Q, Xu J, Taur Y. Review and critique of analytic models of MOSFET short-channel effects in subthreshold IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2012, 59: 1569 doi: 10.1109/TED.2012.2191556[2] Taur Y, Ning T H. Fundamentals of modern VLSI devices. Cambridge University Press, 2009[3] Fossum J G, Chowdhury M M, Trivedi V P, et al. Physical insights on design and modeling of nanoscale FinFETs. IEDM Tech Dig, 2003: 29.1.1[4] Kilchytska V, Nève A, Vancaillie L, et al. Influence of device engineering on the analog and RF performance of SOI MOSFETs. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2003, 50(3): 577 doi: 10.1109/TED.2003.810471[5] Trivedi V P, Fossum J G. Nanoscale FinFETs with gate-source/drain underlap. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2005, 52(1): 56 doi: 10.1109/TED.2004.841333[6] Deen M J, Marinov O. Effect of forward and reverse substrate biasing on lowfrequency noise in silicon PMOSFETs. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2002, 49(3): 409 doi: 10.1109/16.987110[7] Liang X, Taur Y. A 2-D analytical solution for SCEs in DG MOSFETs. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2004, 51: 1385 doi: 10.1109/TED.2004.832707[8] Sachid A B, Manoj C R, Sharma D K, et al. Gate fringe-induced barrier lowering in underlap FinFET structures and its optimization. IEEE Electron Device Lett, 2008: 29(1): 128 doi: 10.1109/LED.2007.911974[9] . Bansal A, Paul B C, Roy K. Modeling and optimization of fringe capacitance of nanoscale DGMOS devices. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2005, 52(2): 256 doi: 10.1109/TED.2004.842713[10] Paul B C, Bansal A, Roy K. Underlap DGMOS for digital-subthreshold operation. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2006, 53: 910 doi: 10.1109/TED.2006.870271[11] Magnone P, Crupi F, Giusi G, et al. 1/f Noise in Drain and Gate Current of MOSFETs With High-k Gate Stacks. IEEE Trans Device Maters Reliab, 2009, 9: 180 doi: 10.1109/TDMR.2009.2020406[12] Houssa M, Pantisano L, Ragnarsson L Å, et al. Electrical properties of high-k gate dielectrics: Challenges, current issues, and possible solutions. Mater Sci Eng, 2006, 51: 37 doi: 10.1016/j.mser.2006.04.001[13] Manoj C R, RamgopalRao V. Impact of High-k Gate Dielectrics on the Device and Circuit Performance of Nanoscale FinFETs. IEEE Electron Device Lett, 2007, 28: 295 doi: 10.1109/LED.2007.892365[14] Zhu W, Han J, Ma T P. Mobility Measurement and Degradation Mechanisms of MOSFETs Made With Ultrathin High-k Dielectrics. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2004, 51: 98 doi: 10.1109/TED.2003.821384[15] Kundu A, Dasgupta A, Das R, et al. Influence of underlap on gate stack DG-MOSFET for analytical study of Aanalog/RF performance. Superlattices Microstruct, 2016, 94: 60 doi: 10.1016/j.spmi.2016.04.013[16] International Technology Roadmap for Semiconductor, 2012[17] Sentaurus TCAD Manuals, Synopsys Inc., Mountain View, CA 94043, USA. Release C-2009.06[18] Esseni D, Mastrapasqua M, Celler G K, et al. Low field mobility of ultra-thin SOI N- and P-MOSFETs: measurements and implications on the performance of ultra short MOSFETs. IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting, Technical Digest, 2000: 671[19] Hamed H F, Kaya S, Starzyk J. Compact tunable current-mode analog circuits using DGMOSFETs. IEEE International SOI Conferencee Proceedings, 2006: 69 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: